|
|
|
| Elements enrichment and dilution characteristics and deep metallogenic prognosis in the Haiyu gold deposit, Jiaodong Peninsula |
ZHANG Liang-Liang1,2( ), ZHU Li-Xin3, MA Sheng-Ming1( ), ZHU Li-Xin3, MA Sheng-Ming1( ), LIN Shao-Yi2, DAI Chang-Guo2, ZHOU Ming-Ling2, HUO Guang2, XU Zhong-Hua2, XI Ming-Jie1, ZHANG Tao2 ), LIN Shao-Yi2, DAI Chang-Guo2, ZHOU Ming-Ling2, HUO Guang2, XU Zhong-Hua2, XI Ming-Jie1, ZHANG Tao2 |
1. Institute of Geophysics and Geochemical Exploration, Chinese Academy of Geological Sciences, Langfang 065000, China
2. No. 6 Institute of Geology and Mineral Resources, Weihai 264200,China
3. China Geological Survey, Beijing 100037, China |
|
|
|
|
Abstract The Haiyu gold deposit, as a superlarge gold deposit with gold reserves of 470 t and average grade of 4.30×10-6, is a typical Jiaojia-type gold deposit. The authors carried out the rock geochemical survey by the samples from drillholes, and detected the enrichment of Au, Cu, Pb, Zn, Ag, As, Sb, Cd, Bi, S and Fe2O3 and the depletion of Na2O, Ba and Sr in the ore-hosting tectonic alteration zone. The authors systematically summarized the geochemical marks used for exploration. The enrichment of S and Au, or called the positive S and Au anomalies, is the typical geochemical mark of the source rock. The enrichment of S, Au, Ag and Bi and the depletion of Na2O and CaO are typical geochemical marks of the tectonic alteration zone. Based on the above elements and their anomalies, the authors constructed the ore-induced anomaly model of the Haiyu gold deposit, which provides a useful reference for the exploration of the peripheral and deep-seated gold deposits. It is proposed that the main gold orebodies of the ore-forming zone of the sea field may be along ZK2403, ZK3008, and ZK3814 boreholes spread in NEE direction.
|
|
Received: 29 February 2020
Published: 20 August 2021
|
|
|
|
Corresponding Authors:
MA Sheng-Ming
E-mail: 15634333042@163.com;msmigge@163.com
|
|
|
|
20])
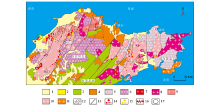
1—Quaternary; 2—Neogene,Paleogene; 3—Cretaceous; 4. Paleo-Neoproterozoic; 5—Neoproterozoic granitic gneiss containing eclogite; 6—Archean granite-greenstone belt; 7—Cretaceous Laoshan granite; 8—Cretaceous Weideshan granite; 9—Cretaceous Guojialing granodiorite; 10—Jurassic granite; 11—Triassic granite; 12—Conformity/unconformity geological boundary; 13—fault; 14—the location of the shallow gold deposits proven in the past (the diameters from large to small indicate super-large gold deposits with resource reserves ≥100 t, large-scale gold deposits with resource reserves of 20~100 t, medium-sized gold deposits with resource reserves of 5~20 t and small-scale gold deposits with reserves <5 t); 15—the location of the newly discovered deep gold deposit (the diameter has the same meaning as in legend 14); 16—altered-rock type gold deposits/quartz-vein type gold deposits/other types of gold deposits; 17—the location of north Sanshan island water gold deposit
">
|
Regional geological map of the Jiaodong Peninsula,showing distribution of gold deposits (modified from Song M C,et al[20])
1—Quaternary; 2—Neogene,Paleogene; 3—Cretaceous; 4. Paleo-Neoproterozoic; 5—Neoproterozoic granitic gneiss containing eclogite; 6—Archean granite-greenstone belt; 7—Cretaceous Laoshan granite; 8—Cretaceous Weideshan granite; 9—Cretaceous Guojialing granodiorite; 10—Jurassic granite; 11—Triassic granite; 12—Conformity/unconformity geological boundary; 13—fault; 14—the location of the shallow gold deposits proven in the past (the diameters from large to small indicate super-large gold deposits with resource reserves ≥100 t, large-scale gold deposits with resource reserves of 20~100 t, medium-sized gold deposits with resource reserves of 5~20 t and small-scale gold deposits with reserves <5 t); 15—the location of the newly discovered deep gold deposit (the diameter has the same meaning as in legend 14); 16—altered-rock type gold deposits/quartz-vein type gold deposits/other types of gold deposits; 17—the location of north Sanshan island water gold deposit
|
|
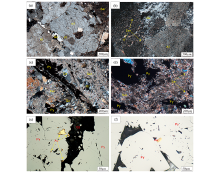
Microscopic characteristics of altered rocks and gold deposits in Haiyu gold deposit
a—potassium, the picture shows potassium feldspar wrapped plagioclase; b—sericification of the hanging wall of the fault, it can be seen that the sericite surface alteration metasomatizes potassium feldspar and plagioclase, and the silicification is embodied as wavy matte quartz; c—pyrite-sericite-quartzized cataclastic rock, where plagioclase and potash feldspar are all corroded into sericite and quartz, and gold-bearing pyrites are distributed in veins; d—scattered pyrite in pyrite-sericite-quartzized cataclastic rocks; e—gold minerals are distributed in pyrite in the form of brecciated inclusion gold and linear interstitial gold; f—gold minerals are encased in pyrite in an oval shape;Kf—potash feldsparl;Pl—plagioclase;Qz—quartz;Ser—sericite;Py—pyrite;Au—gold mineral
|

| 指标 | 测试方法 | 检出限 | 单位 | 一级标准物质合格率/% | 重复样合格率/% | | Au | 无火焰原子吸收光谱法(AAN)
火焰原子吸收光谱法(AAS) | 0.2
100 | 10-9 | 100 | 95.6 | | Ag | 等离子体质谱法(ICP-MS) | 20 | 10-9 | 100 | 97.9 | | As | 氢化物—原子荧光光谱法(HG-AFS) | 1 | 10-6 | 100 | 94.7 | | Ba | 压片法—X射线荧光光谱法(XRF) | 5 | 10-6 | 100 | 100 | | Bi | 等离子体质谱法(ICP-MS) | 0.05 | 10-6 | 100 | 97.9 | | Cd | 等离子体质谱法(ICP-MS) | 20 | 10-9 | 100 | 100 | | Cr | 等离子体光谱法(ICP-AES) | 2 | 10-6 | 100 | 97.9 | | Cu | 等离子体质谱法(ICP-MS) | 1 | 10-6 | 100 | 98.9 | | Ga | 等离子体质谱法(ICP-MS) | 2 | 10-6 | 100 | 100 | | Ge | 氢化物—原子荧光光谱法(HG-AFS) | 0.1 | 10-6 | 100 | 100 | | Mo | 等离子体质谱法(ICP-MS) | 0.2 | 10-6 | 100 | 95.7 | | Pb | 等离子体质谱法(ICP-MS) | 2 | 10-6 | 100 | 92.6 | | S | 压片法—X射线荧光光谱法(XRF) | 50 | 10-6 | 100 | 100 | | Sb | 等离子体质谱法(ICP-MS) | 0.05 | 10-6 | 100 | 96.8 | | Sr | 压片法—X射线荧光光谱法(XRF) | 5 | 10-6 | 100 | 100 | | Ti | 压片法—X射线荧光光谱法(XRF) | 10 | 10-6 | 100 | 100 | | W | 等离子体质谱法(ICP-MS) | 0.2 | 10-6 | 100 | 98.9 | | Zn | 等离子体质谱法(ICP-MS) | 2 | 10-6 | 100 | 96.8 | | Zr | 压片法—X射线荧光光谱法(XRF) | 2 | 10-6 | 100 | 100 | | SiO2 | 压片法—X射线荧光光谱法(XRF) | 0.1 | % | 100 | 100 | | Al2O3 | 等离子体光谱法(ICP-AES) | 0.1 | % | 100 | 98.9 | | TFe2O3 | 压片法—X射线荧光光谱法(XRF) | 0.1 | % | 100 | 98.9 | | MgO | 压片法—X射线荧光光谱法(XRF) | 0.05 | % | 100 | 100 | | CaO | 等离子体光谱法(ICP-AES) | 0.05 | % | 100 | 100 | | Na2O | 等离子体光谱法(ICP-AES) | 0.05 | % | 100 | 98.9 | | K2O | 等离子体光谱法(ICP-AES) | 0.05 | % | 100 | 100 |
|
Sample test method and the result statistics of quality monitoring
|

| 指标 | 变辉长岩
(n=61) | 二长花岗岩
(n=316) | 上盘花岗岩
(n=105) | 构造蚀变带
(n=160) | 下盘花岗岩
(n=102) | 花岗闪长岩
(n=21) | | | C | q | C | q | C | q | C | q | C | q | C | q | | Au | 4.0 | 4.7 | 23 | 46 | 21 | 42 | 3037 | 6074 | 166 | 333 | 7.0 | 10 | | Ag | 210 | 3.1 | 390 | 6.5 | 840 | 14 | 3900 | 65 | 1300 | 21 | 87 | 1.4 | | As | 8.5 | 5.7 | 8.0 | 6.7 | 17 | 14 | 69 | 58 | 26 | 21 | 1.0 | 0.8 | | Cd | 280 | 2.5 | 710 | 12.5 | 1500 | 27 | 690 | 12 | 1000 | 18 | 48 | 0.6 | | Cu | 46 | 0.8 | 9.12 | 1.7 | 14 | 2.5 | 87 | 16 | 32 | 5.8 | 4.3 | 0.2 | | Ga | 21 | 1.1 | 21.43 | 1.2 | 20 | 1.1 | 20 | 1.1 | 21 | 1.1 | 20 | 1.1 | | Ge | 1.31 | 1.2 | 1.2 | 1.0 | 1.2 | 0.96 | 1.4 | 1.1 | 1.1 | 0.9 | 0.78 | 0.7 | | Pb | 26 | 1.7 | 83 | 3.2 | 533 | 20 | 473 | 18 | 435 | 16.7 | 22 | 1.4 | | Sb | 0.55 | 3.4 | 0.48 | 3.7 | 0.75 | 5.8 | 0.88 | 6.7 | 0.73 | 5.6 | 0.24 | 1.7 | | Zn | 109 | 1.0 | 156 | 3.9 | 353 | 8.8 | 177 | 4.4 | 291 | 7.3 | 24 | 0.4 | | Cr | 111 | 0.5 | 24 | 3.6 | 24 | 3.6 | 43 | 6.4 | 18 | 2.7 | 8.8 | 0.2 | | Ti | 3178 | 0.4 | 774 | 0.6 | 838 | 0.61 | 1047 | 0.8 | 840 | 0.6 | 915 | 0.3 | | Ba | 776 | 1.7 | 1098 | 1.6 | 1154 | 1.70 | 478 | 0.7 | 1081 | 1.6 | 1640 | 1.8 | | Sr | 363 | 0.6 | 376 | 1.7 | 332 | 1.51 | 113 | 0.5 | 293 | 1.3 | 659 | 1.5 | | Zr | 91 | 0.8 | 60 | 0.4 | 69 | 0.44 | 84 | 0.5 | 75 | 0.5 | 75 | 0.4 | | Mo | 4.60 | 10 | 2.0 | 2.8 | 0.96 | 1.37 | 1.2 | 1.6 | 1.0 | 1.4 | 0.72 | 1.5 | | W | 1.24 | 2.5 | 1.2 | 1.2 | 1.4 | 1.42 | 4 | 4.3 | 2.3 | 2.3 | 0.85 | 2.2 | | Bi | 0.15 | 1.6 | 0.29 | 1.2 | 0.12 | 0.49 | 8.2 | 34 | 0.73 | 3.0 | 0.06 | 0.5 | | S | 701 | 1.4 | 382 | 4.2 | 632 | 7.0 | 6573 | 73 | 2727 | 30 | 53 | 0.2 | | SiO2 | 58.49 | 1.20 | 65.15 | 0.90 | 63.86 | 0.88 | 59.80 | 0.83 | 69.95 | 0.97 | 64.31 | 0.98 | | Al2O3 | 14.49 | 0.89 | 13.89 | 1.00 | 13.83 | 1.00 | 13.08 | 0.95 | 15.11 | 1.09 | 14.40 | 0.95 | | TFe2O3 | 6.16 | 0.64 | 1.34 | 0.59 | 1.78 | 0.78 | 4.76 | 2.08 | 2.58 | 1.13 | 0.71 | 0.15 | | CaO | 2.64 | 0.27 | 1.73 | 1.29 | 1.83 | 1.36 | 1.22 | 0.91 | 1.90 | 1.42 | 1.88 | 0.59 | | MgO | 2.40 | 0.31 | 0.58 | 0.90 | 0.52 | 0.81 | 0.76 | 1.19 | 0.21 | 0.33 | 0.26 | 0.13 | | Na2O | 2.78 | 1.11 | 3.44 | 0.97 | 2.49 | 0.70 | 0.41 | 0.12 | 3.53 | 1.00 | 4.54 | 1.23 | | K2O | 3.13 | 3.23 | 4.05 | 0.93 | 4.31 | 0.99 | 4.31 | 0.99 | 4.40 | 1.01 | 3.38 | 1.16 |
|
Statistical table of element content and enrichment coefficient in different geological units of Haiyu gold deposit
|
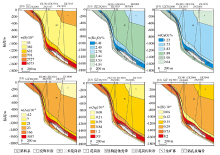
|
Borehole rock survey anomaly diagram of the Haiyu gold deposit
|
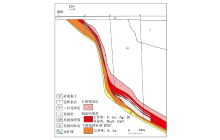
|
Ore-induced anomaly pattern diagram of the Haiyu gold deposit
|
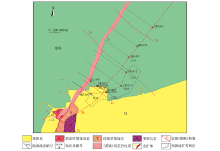
|
Prospective ore-forming location of of Haiyu gold deposit
|
| [1] |
宋明春. 胶东金矿深部找矿主要成果和关键理论技术进展[J]. 地质通报, 2015,34(9):1758-1771.
|
| [1] |
Song M C. The main achievements and key theory and methods of deep-seated prospecting in the Jiaodong gold concentration area,Shandong Province[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 2015,34(9):1758-1771.
|
| [2] |
Li J W, Vasconcelos P M, Zhang J, et al. 40Ar/39Ar constraints on a temporal link between gold mineralization, magmatism, and continental margin transtension in the Jiaodong gold Province, eastern China [J]. Journal of Geology, 2003,111:741-751.
|
| [3] |
Li J W, Vasconcelos P, Zhou M F, et al. Geochronology of the Pengjiakuang and Rushan Gold deposits, eastern Jiaodong gold Province, northeastern China: Implications for regional mineralization and geodynamic setting[J]. Economic Geology, 2006,101:1023-1038.
|
| [4] |
Mao J W, Wang Y T, Li H M, et al. The relationship of mantle-derived fluids to gold metallogenesis in the Jiaodong Peninsula: Evidence from D-O-C-S isotope systematics[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2008,33(3):361-381.
|
| [5] |
钱建平, 陈宏毅, 孙涛, 等. 山东招远前孙家金矿床地质和元素地球化学研究[J]. 地球化学, 2010,39(3):213-228.
|
| [5] |
Qian J P, Chen H Y, Sun T, et al. Study on geology and element geochemistry of Qiansunjia gold mine in Zhaoyuan,Shandong,eastern China[J]. Geochimica, 2010,39(3):213-228.
|
| [6] |
翟裕生, 姚书振, 蔡克勤 .矿床学( 第三版)[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2011.
|
| [6] |
Zhai Y S, Yao S Z, Cai K Q. Mineral deposits(third edition)[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 2011.
|
| [7] |
Zhai M G, Santosh M. Metallogeny of the North China Craton: Link with secular changes in the evolving Earth[J]. Gondwana Research, 2013,24(1):275-297.
|
| [8] |
Goldfarb R J, Santosh M. The dilemma of the Jiaodong gold deposits: Are they unique?[J]. Geoscience Frontiers, 2014,5(2):139-153.
|
| [9] |
毛景文, 李厚民, 王义天, 等. 地幔流体参与胶东金矿成矿作用的氢氧碳硫同位素证据[J]. 地质学报, 2005,79(6):839-857.
|
| [9] |
Mao J W, Li H M, Wang Y T, et al. The relationship between mantle-derived fluid and gold ore-formation in the eastern Shandong peninsula: Evidences from D-O-C-S isotopes[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2005,79(6):839-857.
|
| [10] |
杨进辉, 刘文军, 翟明国. 胶东大型黄金矿集区及大规模成矿作用[J]. 中国科学:D辑, 2001,31(7):545-552.
|
| [10] |
Yang J H, Liu W J, Zhai M G. Large-scale gold mining area in Jiaodong large-scale metallogenesis[J]. Science in China:Series D, 2001,31(7):545-552.
|
| [11] |
翟明国, 范宏瑞, 杨进辉, 等. 非造山带型金矿—胶东型金矿的陆内成矿作用[J]. 地学前缘, 2004,11(1):85-98.
|
| [11] |
Zhai M G, Fan H R, Yang J H, et al. Large-scale cluster of gold deposits in east shandong:anorogenic metallogenesis[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2004,11(1):85-98.
|
| [12] |
Kerrich R, Goldfarb R, Groves D, et al. The characteristics, origins, and geodynamic settings of supergiant gold metallogenic provinces[J]. Science in China, 2000,43(s1):1-68.
|
| [13] |
马生明, 朱立新, 刘崇民, 等. 斑岩型Cu(Mo)矿床中微量元素富集贫化规律研究[J]. 地球学报, 2009,30(6):821-830.
|
| [13] |
Ma S M, Zhu L X, Liu C M, et al. A study of the enrichment and depletion regularity of trace elements in porphyry Cu (Mo) deposits[J]. Acta Geoscientica Sinica, 2009,30(6):821-830.
|
| [14] |
梁胜跃, 马生明, 朱立新, 等. 乌努格吐山斑岩型铜钼矿床地球化学异常结构研究[J]. 物探与化探, 2010,34(2):127-133.
|
| [14] |
Liang S Y, Ma S M, Zhu L X, et al. Geochemical anomaly structure of the Wunugetushan porphyry copper and molybdenum deposit[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2010,34(2):127-133.
|
| [15] |
孙跃, 马生明, 刘显凡, 等. 浙江大岭口银铅锌矿床异常结构及深部矿体预测方法研究[J]. 矿产勘查, 2011,2(3):272-278.
|
| [15] |
Sun Y, Ma S M, Liu X F, et al. A study of the structure of geochemical anomaly and prediction of deep ore body in Dalingkou Ag-Pb-Zn deposit,Zhejiang province[J]. Mineral Exploration, 2011,2(3):272-278.
|
| [16] |
马生明, 朱立新, 韩方法, 等. 胶西北焦家式金矿控矿构造蚀变带的地球化学标志[J]. 地学前缘, 2017,24(2):64-72.
|
| [16] |
Ma S M, Zhu L X, Han F F, et al. Geochemical marks of the ore-controlling tectonic alteration zone in the Jiaojia-type gold deposit, Northwestern Jiaodong Peninsula[J]. Geoscience Frontiers, 2017,24(2):64-72.
|
| [17] |
马生明, 朱立新, 刘海良, 等. 甘肃北山辉铜山铜矿地球化学异常结构研究[J]. 地球学报, 2011,32(4):405-412.
|
| [17] |
Ma S M, Zhu L X, Liu H L, et al. A study of geochemical anomaly structure of the Huitongshan copper deposit in Beishan area, Gansu Province[J]. Acta Geoscientica Sinica, 2011,32(4):405-412.
|
| [18] |
宋明春. 山东省大地构造单元组成、背景和演化[J]. 地质调查与研究, 2008,31(3):165-175.
|
| [18] |
Song M C. The composing,setting and evolution of tectonic units in Shandong Province[J]. Geological Survey and Research, 2008,31(3):165-175.
|
| [19] |
李士先, 刘长春, 安郁宏, 等. 胶东金矿地质[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2007.
|
| [19] |
Li S X, Liu C C, An Y H, et al. Jiaodong gold deposits geology[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 2007.
|
| [20] |
宋明春, 崔书学, 伊丕厚, 等. 山东省胶西北金矿集中区深部大型—超大型金矿找矿与成矿模式[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2010.
|
| [20] |
Song M C, Cui S X, Yi P H, et al. Prospecting and metallogenic model of deep large-ultra-large gold deposits in Jiaodong Northwest gold deposit concentration area, Shandong Province [M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 2010.
|
| [21] |
张军进, 丁正江, 刘殿浩, 等. 山东莱州三山岛北部海域超大型金矿勘查实践与找矿成果[J]. 黄金科学技术, 2016,24(1):1-10.
|
| [21] |
Zhang J J, Ding Z J, Liu D H, et al. Exploration practice and prospecting results of super-large gold mine of Sanshandao northern sea area in Laizhou City,Shandong Province[J]. Gold Science and Technology, 2016,24(1):1-10.
|
| [22] |
宋明春. 胶东三山岛北部海域超大型金矿床的发现及其构造岩浆背景[J]. 地质学报, 2015,89(2):365-383.
|
| [22] |
Song M C. Discovery and tectonic-magmatic background of superlarge gold deposit in offshore of northern Sanshandao,Shandong Peninsula,China[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2015,89(2):365-383.
|
| [23] |
张亮亮, 马生明, 朱立新, 等. 胶东焦家断裂带蚀变岩非镜像对称特征及其地质意义[J]. 大地构造与成矿学, 2020,44(2):276-288.
|
| [23] |
Zhang L L, Ma S M, Zhu L X, et al. Non-mirrored symmetrical feature of altered rocks in the fault zone of Jiaojia, Jiaodong peninsula and its geological significance[J]. Geotectonica et Metallogenia, 2020,44(2):276-288.
|
| [24] |
鄢明才, 迟清华, 顾铁新, 等. 中国东部上地壳化学组成[J]. 中国科学:地球科学, 1997(3):193-199.
|
| [24] |
Yan M C, Chi Q H, Gu T X, et al. Chemical composition of the upper crust in eastern China[J]. Science in China:Series D, 1997(3):193-199.
|
| [25] |
吕古贤. 胶东玲珑—焦家式金矿床矿源岩系(序)列研究[J]. 地球与环境, 2001,29(3):140-143.
|
| [25] |
Lyu G X. Research on ore source series of the Linglong-Jiaojia-type gold deposits[J]. Geology-Geochemistry, 2001,29(3):140-143.
|
| [26] |
刘翠, 邓晋福, 李胜荣, 等. 胶东燕山期大型超大型金矿集区形成的壳幔结构探讨:来自致矿火成岩(组合)的约束[J]. 地学前缘, 2018,25(6):296-307.
|
| [26] |
Liu C, Deng J F, Li S R, et al. Discussions on crust-mantle structure during the formation of Yanshanian of large-super large scale deposits in the Jiaodong gold ore district: Constraints from ore-forming igneous assemblage[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2018,25(6):296-307.
|
| [27] |
马生明, 朱立新, 苏磊, 等. 矿化剂元素硫(S)与成矿[J]. 地质学报, 2016,90(9):2427-2436.
|
| [27] |
Ma S M, Zhu L X, Su L, et al. Mineralizing agent sulfur and metallogenic process[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2016,90(9):2427-2436.
|
| [28] |
马生明, 朱立新, 张亮亮, 等. 关于胶西北金矿成矿地球化学机制的思考[J]. 物探与化探, 2019,43(5):925-931.
|
| [28] |
Ma S M, Zhu L X, Zhang L L, et al. Thoughts on the geochemical mechanism of gold mineralization in the northwest Jiaodong gold province[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2019,43(5):925-931.
|
| [1] |
KANG Ming, LIU Chen, SIQIN Bilige, MA Zu-fei. THE DISCOVERY OF THE XISHANWANYANGCHANG VOLCANICS-HOSTED SILVER DEPOSIT IN ZHA'ERTAISHAN AREA, INNER MONGOLIA[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2013, 37(1): 11-16. |
| [2] |
LIU Chong-min, LI Ying-gui, SHI Chang-yi . A STUDY OF GEOCHEMICAL EXPLORATION TECHNIQUES SUITABLE FOR DIFFERENT LANDSCAPE REGIONS[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2002, 26(1): 23-26. |
|
|
|
|

