|
|
|
| The evaluation of soil environmental quality of main walnut producing areas based on various methods of heavy metal contamination assessment in Tianjin |
XIE Wei1( ), YANG Yao-Dong1( ), YANG Yao-Dong1( ), HOU Jia-Yu2, JIAN Gui-Qin1, LI Guo-Cheng1, ZHAO Xin-Hua1 ), HOU Jia-Yu2, JIAN Gui-Qin1, LI Guo-Cheng1, ZHAO Xin-Hua1 |
1. Tianjin Geological Mineral Test Center, Tianjin 300191, China
2. Geological Center of Tianjin Planning and Natural Resources Bureau, Tianjin 300042, China |
|
|
|
|
Abstract In this study, the soil and walnut samples were taken in the main walnut producing area of Tianjin, and the content characteristics of heavy metals Cd, Hg, Pb, As, Cr, Zn and Cu in the soil were analyzed. Three methods were used to evaluate soil environmental quality in the study area, i.e., Nemerow index method, geo-accumulation index method and pollution load index.The safety of walnut samples was analyzed. The results show that the average values of Cd, Hg, Pb, As, Cr, Zn and Cu in the soil samples are 0.19×10-6, 0.06×10-6, 24.1×10-6, 11.9×10-6, 75.5×10-6, 78.9×10-6 and 30.6×10-6, respectively. The average values of Cd, Hg, As and Cu exceed the background values of Tianjin, and 11.7% and 1.7% of the samples of Cd and Cu exceed the risk screening values. For the single evaluation results, Nemerow single index method shows that 10.0% of the samples of Cd have slight pollution, 1.7% of the samples have moderate pollution, and 1.7% of the samples of Cu have slight pollution. According to the method of Nemerow comprehensive index, the soil environmental quality of the study area is generally better, but according to the evaluation results of geo-accumulation index and pollution load index, it can be found that there is heavy metal accumulation caused by human factors in the study area, and the pollution points are evenly distributed in the study area. The average values of Cd, Hg, Pb, As and Cr in walnut samples are 0.003 ×10-6, 0.004 ×10-6, 0.044 ×10-6, 0.043 ×10-6 and 0.760 ×10-6, respectively, which meet the requirements of food safety standards.
|
|
Received: 17 January 2020
Published: 01 March 2021
|
|
|
|
Corresponding Authors:
YANG Yao-Dong
E-mail: Chinav2012@163.com;fivess@139.com
|
|
|
|
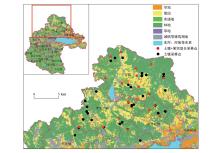
|
Sampling locations in study area
|

| 污染等级 | 单项污染指数分级标准 | 综合污染指数分级标准 | | 污染指数 | 污染水平 | 污染指数 | 污染水平 | | Ⅰ | Pi<1 | 清洁 | I<0.7 | 清洁 | | Ⅱ | 1≤Pi<2 | 轻污染 | 0.7≤I<1 | 尚清洁 | | Ⅲ | 2≤Pi<3 | 中污染 | 1≤I<2 | 轻污染 | | Ⅳ | Pi≥3 | 重污染 | 2≤I<3 | 中污染 | | Ⅴ | | | I≥3 | 重污染 |
|
Evaluation standard of single factor pollution index and Nemerow comprehensive index
|

| 地累积指数Igeo | 分级 | 污染程度 | | Igeo≤0 | 0级 | 无污染 | | 0<Igeo≤1 | 1级 | 无污染—中度污染 | | 1<Igeo≤2 | 2级 | 中度污染 | | 2<Igeo≤3 | 3级 | 中度污染—强污染 | | 3<Igeo≤4 | 4级 | 强污染 | | 4<Igeo≤5 | 5级 | 强污染—极强污染 | | Igeo>5 | 6级 | 极强污染 |
|
Classification table for geo-accumulation index
|

| IPLzone | <1 | 1~2 | 2~3 | ≥3 | | 污染等级 | 0 | I | Ⅱ | Ⅲ | | 污染程度 | 无污染 | 中等污染 | 强污染 | 极强污染 |
|
The grade of pollution load index
|

| 元素 | 最小值/10-6 | 最大值/10-6 | 平均值/10-6 | 中位数/10-6 | 标准差/10-6 | 变异系数/% | 天津市背景值[12]/10-6 | | Cd | 0.08 | 0.73 | 0.19 | 0.18 | 0.12 | 0.63 | 0.17 | | Hg | 0.02 | 0.17 | 0.06 | 0.06 | 0.03 | 0.44 | 0.04 | | Pb | 11.8 | 112.8 | 24.1 | 23.5 | 13.95 | 0.57 | 26.2 | | As | 2.44 | 23.8 | 11.9 | 11.9 | 4.42 | 0.37 | 10 | | Cr | 33.6 | 138.7 | 75.5 | 72.9 | 15.9 | 0.21 | 77.8 | | Zn | 34.3 | 214.3 | 78.9 | 76.8 | 29.6 | 0.37 | 86.2 | | Cu | 13.4 | 134.5 | 30.6 | 29.7 | 29.6 | 0.51 | 30.6 | | pH | 4.46 | 7.88 | 7.03 | 7.31 | 0.81 | 0.11 | 8.07 |
|
Statistical values of heavy metals concentrations in soil
|

| 元素 | 单项污染指数Pi | 样点占比/% | | 最小值 | 最大值 | 平均值 | 中位数 | 清洁 | 轻污染 | 中污染 | 重污染 | | Cd | 0.14 | 2.44 | 0.57 | 0.44 | 88.3 | 10.0 | 1.7 | 0 | | Hg | 0.01 | 0.10 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 0 | | Pb | 0.09 | 0.94 | 0.21 | 0.18 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 0 | | As | 0.08 | 0.79 | 0.42 | 0.42 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 0 | | Cr | 0.13 | 0.69 | 0.38 | 0.36 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 0 | | Zn | 0.11 | 0.86 | 0.33 | 0.30 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 0 | | Cu | 0.13 | 1.35 | 0.39 | 0.34 | 98.3 | 1.7 | 0 | 0 |
|
Statistical results of single pollution index
|

| 评价结果 | 综合污染指数 | 样本数 | 占比/% | | 最小值 | 最大值 | 平均值 | | 清洁 | 0.16 | 0.65 | 0.45 | 51 | 85.0 | | 尚清洁 | 0.70 | 0.92 | 0.80 | 5 | 8.3 | | 轻度污染 | 1.08 | 1.82 | 1.34 | 4 | 6.7 | | 中度污染 | — | — | — | — | — | | 重度污染 | — | — | — | — | — |
|
Statistical results of Nemerow comprehensive pollution index
|

| 元素 | 地累积指数Igeo | | 污染等级样点占比/% | | | 最小值 | 最大值 | 平均值 | 无污染 | 无—中污染 | 中污染 | 中污染—强污染 | 强污染—极强污染 | 极强污染 | | Cd | -0.43 | 2.69 | 0.77 | | 5.0 | 68.3 | 21.7 | 5.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | | Hg | -0.15 | 2.69 | 1.03 | | 1.7 | 41.7 | 50.0 | 6.7 | 0.0 | 0.0 | | Pb | -0.57 | 2.69 | 0.47 | | 15.0 | 78.3 | 5.0 | 1.7 | 0.0 | 0.0 | | As | -1.45 | 1.84 | 0.73 | | 8.3 | 56.7 | 35.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | | Cr | -0.63 | 1.42 | 0.51 | | 5.0 | 90.0 | 5.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | | Zn | -0.74 | 1.90 | 0.46 | | 11.7 | 80.0 | 8.3 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | | Cu | -0.60 | 2.72 | 0.59 | | 8.3 | 78.3 | 11.7 | 1.7 | 0.0 | 0.0 |
|
Statistical results of geo-accumulation index
|
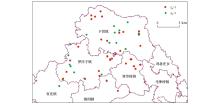
|
Risk assessment map of calculated indices IPL in study area
|

| 元素 | 最小值/10-6 | 最大值/10-6 | 平均值/10-6 | 中位数/10-6 | 标准差 | 变异系数/% | 限量标准/10-6 | | Cd | 0.001 | 0.020 | 0.003 | 0.002 | 0.004 | 129.2 | 0.5 | | Hg | 0.001 | 0.007 | 0.004 | 0.003 | 0.002 | 52.9 | 0.02 | | Pb | 0.021 | 0.114 | 0.044 | 0.040 | 0.022 | 49.7 | 0.2 | | As | 0.027 | 0.142 | 0.043 | 0.037 | 0.026 | 60.4 | 0.5 | | Cr | 0.613 | 0.981 | 0.760 | 0.744 | 0.105 | 13.8 | 1.0 | | Zn | 16.43 | 33.94 | 25.48 | 27.58 | 6.27 | 24.6 | — | | Cu | 8.90 | 18.88 | 14.68 | 14.69 | 2.87 | 19.6 | — |
|
Statistics of heavy metal contents in walnuts
|
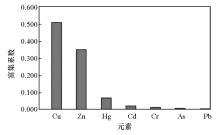
|
Bioaccumulaion factors of different elements in walnuts
|
| [1] |
张红桔, 赵科理, 叶正钱, 等. 典型山核桃产区土壤重金属空间异质性及其风险评价[J]. 环境科学, 2018,39(6):2893-2903.
|
| [1] |
Zhang H J, Zhao K L, Ye Z Q, et al. Spatial variation of heavy metals in soils and its ecological risk evaluation in a typical carya cathayensisproduction area[J]. Environmental Science, 2018,39(6):2893-2903.
|
| [2] |
李世亮, 倪张林, 莫润宏, 等. 云贵川主产区核桃中重金属污染水平及其风险评估[J]. 林业科学, 2017,53(11):52-59.
|
| [2] |
Li S L, Ni Z L, Mo R H, et al. The contents and risk assessments of heavy metals in walnuts from the main producing area of Yunnan, Guizhou, Sichuan provinces[J]. Scientia Silvae Sinicae, 2017,53(11):52-59.
|
| [3] |
Zhang M M, He P, Qiao G, et al. Heavy metal contamination assessment of surface sediments of the Subei Shaol, China: Spatial distribution, source apportionment and ecological risk[J]. Chemosphere, 2019,223:211-222.

|
| [4] |
Chai Y, Guo J, Chai S L, et al. Source identification of eight heavy metals in grassland soils by multivariate analysis from the Baicheng-Songyuan area, Jilin Province, Northeast China[J]. Chemosphere, 2015,134:67-75.

|
| [5] |
李裕瑞, 王志炜, 门大威, 等. 平原农区空心村典型土壤的重金属污染评价——以山东省禹城市为例[J]. 农业资源与环境学报, 2017,34(4):328-334.
|
| [5] |
Li Y R, Wang Z W, Men D W, et al. Consolidation and using oriented evaluation of heavy metal pollution in typical soils of hollowed villages of plain agricultural zones: A case study of Yucheng city, Shandong province, China[J]. Journal of Agricultural Resources and Environment, 2017,34(4):328-334.
|
| [6] |
Müller G. Schwermetalle in den sedimenten des rheins-veranderungen seit 1971[J]. Umschau, 1979,79:778-783.
|
| [7] |
Håkanson L. An ecological risk index for aquatic pollution control: A sedimentological approach[J]. Water Research, 1980,14(8):975-1001.

|
| [8] |
Tomlinson D L, Wilson J G, Harris C R, et al. Problems in theassessment of heavy-metal levels in estuaries and the formation of a pollutionindex[J]. Helgoland Marine Research, 1980,33(1):566.
|
| [9] |
张又文, 韩建华, 涂棋, 等. 天津市郊农田土壤重金属积累特征及评价[J]. 生态与农村环境学报, 2019,35(11):1445-1452.
|
| [9] |
Zhang Y W, Han J H, Tu Q, et al. Accumulation characteristics and evaluation of heavy metals in suburban farmland soils of Tianjin[J]. Journal of Ecology and Rural Environment, 2019,35(11):1445-1452.
|
| [10] |
纪冬丽, 曾琬晴, 张新波, 等. 天津近郊农田土壤重金属风险评价及空间主成分分析[J]. 环境化学, 2019,38(9):1955-1965.
|
| [10] |
Ji D L, Zeng W Q, Zhang X B, et al. Ecological risk assessment and principal component analysis of heavy metals in suburban farmland soils of Tianjin[J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2019,38(9):1955-1965.
|
| [11] |
祝培甜, 赵中秋, 陈勇, 等. 江苏省某镇土壤重金属污染评价[J]. 环境工程学报, 2017,11(4):2535-2541.
|
| [11] |
Zhu P T, Zhao Z Q, Chen Y, et al. Evaluation of soil heavy metals pollution in a town, Jiangsu province[J]. Chinese Journal of Environmental Engineering, 2017,11(4):2535-2541.
|
| [12] |
王卫星, 曹淑萍, 李攻科, 等. 天津板栗品质分析及其立地地质背景研究[J]. 物探与化探, 2017,41(4):972-976.

|
| [12] |
Wang W X, Cao S P, Li G K, et al. Chemical composition analysis and site geological background of castanea mollissima blume quality in Tianjin[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2017,41(5):972-976.

|
| [13] |
Zhang X Y, Sui Y Y, Zhang X D, et al. Spatial variability of nutrient properties in black soil of Northeast China[J]. Pedosphere, 2007,17(1):19-29.

|
| [14] |
孟昭虹, 高玉娟. 黑龙江生态省土壤重金属分布特征及其生态风险评价[J]. 安徽农业科学, 2008,36(31):13819-13821.
|
| [14] |
Meng Z H, Gao Y J. Distribution characteristics of heavy metals in soils of Heilongjiang ecological province and its ecological risk assessment[J]. Journal of Anhui Agricultural Sciences, 2008,36(31):13819-13821.
|
| [15] |
师荣光, 张又文, 许萌萌, 等. 天津市郊区土壤重金属的污染评价与来源解析[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2019,38(5):1069-1078.
|
| [15] |
Shi R G, Zhang Y W, Xu M M, et al. Pollution evaluation and source apportionment of heavy metals in soils from Tianjin suburbs, China[J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 2019,38(5):1069-1078.
|
| [16] |
孟令仪, 徐梦洁, 李小曼, 等. 基于多种方法的苏南镇域土壤重金属污染评价[J]. 安徽农业科学, 2016,44(34):114-118.
|
| [16] |
Meng L Y, Xu M J, Li X M, et al. Evaluation of soil heavy metal pollution in southern towns of Jiangsu province by multiple methods[J]. Journal of Anhui Agricultural Sciences, 2016,44(34):114-118.
|
| [17] |
虎海防, 郑伟华, 张强, 等. 新疆6个核桃品种种仁主要营养成分比较分析[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2010,47(6):1122-1125.
|
| [17] |
Hu H F, Zheng W H, Zhang Q, et al. Comparative analysis on main nutrient components in the kernel of six walnut varieties in Xinjiang[J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2010,47(6):1122-1125.
|
| [18] |
刘道荣, 郑基滋, 占玄, 等. 临安山核桃主产区林地土壤重金属生态风险评价[J]. 物探与化探, 2019,43(6):1382-1388.

|
| [18] |
Liu D R, Zheng J Z, Zhan X, et al. Ecological risk evaluation of heavy metals in soils of carya cathayensis plantations, Lin’an[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2019,43(6):1382-1388.

|
| [19] |
方如康. 环境学词典[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2003: 127-128.
|
| [19] |
Fang R K. Dictionary of environmental sciences[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2003: 127-128.
|
| [20] |
Han Y, Ni Z, Li S, et al. Distribution, relationship, and risk assessment of toxic heavy metals in walnuts and growth soil[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research International, 2018,25(18):17434-17443.

|
| [1] |
YAN Kun, PANG Guo-Tao, LI Wei, MAO Fang-Song. Assessing the distribution and ecological risks of heavy metals in surface sediments of the Maowei Sea estuary, Guangxi[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2022, 46(4): 1030-1036. |
| [2] |
FAN Chen-Zi, YUAN Ji-Hai, LIU Cheng-Hai, GUO Wei, SUN Dong-Yang, LIU Wei, ZHAO Jiu-Jiang, HU Jun-Dong, ZHAO Ling-Hao. Eco-geochemical survey and evaluation of heavy metals and other elements in soil in Anning City, Yunnan Province[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2022, 46(3): 761-771. |
|
|
|
|

