|
|
|
| A study of the effect of hyperparameters GRU-CNN hybrid deep learning EI inversion |
LIANG Li-Feng1( ), LIU Xiu-Juan1( ), LIU Xiu-Juan1( ), ZHANG Hong-Bing2, CHEN Cheng-Hao1, CHEN Jin-Hua1 ), ZHANG Hong-Bing2, CHEN Cheng-Hao1, CHEN Jin-Hua1 |
1. Department of Geography,Lingnan Normal University,Zhanjiang 524057,China
2. School of Earth Science and Engineering,Hohai University,Nanjing 210098,China |
|
|
|
|
Abstract Previous studies have shown that CNN-GRU hybrid deep learning inversion EI has the advantages of strong applicability and strong generalization capability.However,there are many pre-stack inversion parameters based on deep learning,such as internal deep learning network learnable parameters and external hyperparameters.At present,there is still no systematic research on the impact of hyperparameter selection on network performance and computing speed,which will directly affect the further promotion and application of the method.Therefore,based on the hybrid deep learning inversion elastic impedance,this paper discusses the impact of five hyperparameters,i.e.,learning rate,Epoch,batch_size,regularization parameter,and the number of wells participating in network training on network performance and calculation speed,thus providing a basis for studying the selection of seismic inversion hyperparameters.The research results can provide a feasible quality control method for three-dimensional large-area deep learning inversion,which is of certain significance for promoting the wide application of deep learning methods in petroleum geophysical prospecting.
|
|
Received: 02 January 2020
Published: 01 March 2021
|
|
|
|
Corresponding Authors:
LIU Xiu-Juan
E-mail: 121436068@qq.com;544022065@qq.com
|
|
|
|
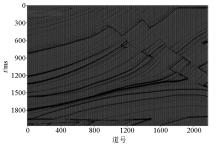
|
Time domain seismic profile of marmorsi2 model(local)
|
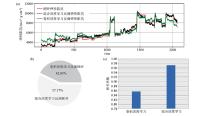
|
Comparison of inversion efficiency and result between convolution deep learning and hybrid deep learning
a—inversion results comparison;b—time consmption comparison;c—correlation coefficient comparison
|
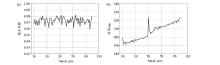
|
Batch-size effect on correlation coefficient(a) and calculation time(b)
|
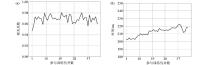
|
Influence of number of wells participating in the training on correlation coefficient(a) and calculation time(b)
|
|
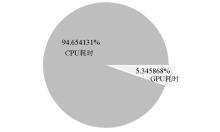
Comparison of operation time between GPU and CPU with the same hyper-parameters
|
|
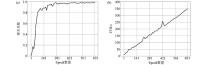
Relation diagram of Epoch vs the correlation coefficient(a) and time consumption(b)
|
|
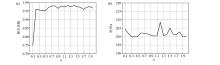
Relation diagram of regularization parameter α vs correlation coefficient(a) and time consumption(b)
|
|
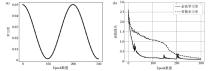
Learning rate curve and improvement method
a—cosinc learning rate curve;b—loss curve comparison between constant learning rate and cosinc learning rate
|
| [1] |
王逸宸, 柳林涛, 许厚泽. 基于卷积神经网络识别重力异常体[J]. 物探与化探, 2020,44(2):394-400.

|
| [1] |
Wang Y C, Liu L T, Xu H Z. The identification of gravity anomaly body based on the convolutional neural network[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2020,44(2):394-400.

|
| [2] |
Russakovsky O, Deng J, Su H, et al. Image net large scale visual recognition challenge[J]. Int. J. Comput. Vis., 2015,115(3):211-252.

|
| [3] |
王文强, 孟凡顺, 孙文亮. 优化卷积神经网络在道编辑中的应用[J]. 地球物理学进展, 2019,34(1):214-220.
|
| [3] |
Wang W Q, Meng F S, Sun W L. Application of optimized convolutional neural network in Dao editing[J]. Progress in Geophysics, 2019,34(1):214-220.
|
| [4] |
韩卫雪, 周亚同, 池越. 基于深度学习卷积神经网络的地震数据随机噪声去除[J]. 石油物探, 2018,57(6):862-869,877.
|
| [4] |
Han W X, Zhou Y T, Chi Y. Deep learning convolutional neural networks for random noise attenuation in seismic data[J]. Geophysical Prospecting for Petroleum, 2018,57(6):862-869,877.
|
| [5] |
刘力辉, 陆蓉, 杨文魁. 基于深度学习的地震岩相反演方法[J]. 石油物探, 2019,58(1):123-129.
|
| [5] |
Liu L H, Lu R, Yang W K. Seismic rock inversion method based on deep learning[J]. Geophysical Prospecting for Petroleum, 2019,58(1):123-129.
|
| [6] |
林年添, 付超, 张栋, 等. 无监督与监督学习下的含油气储层预测[J]. 石油物探, 2018,57(4):601-610.
|
| [6] |
Lin N T, Fu C, Zhang D, et al. Prediction of petroleum reservoirs under unsupervised and supervised learning[J]. Geophysical Prospecting for Petroleum, 2018,57(4):601-610.
|
| [7] |
Wu X M, Shi Y Z, Fomel S, et al. Fault net 3D:Predicting fault probabilities,strikes,and dips with a single convolutional neural network[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2019,57(11):9138-9155.

|
| [8] |
Alfarraj M, AlRegib G. SEG technical program expanded abstracts 2018[M]. Houston:Society of Exploration Geophysicists, 2018: 2141-2146.
|
| [9] |
安鹏, 曹丹平, 赵宝银, 等. 基于LSTM循环神经网络的储层物性参数预测方法研究[J]. 地球物理学进展, 2019,34(5):1849-1858.
|
| [9] |
An P, Cao D P, Zhao B Y, et al. Research on prediction method of reservoir physical property parameters based on LSTM recurrent neural network[J]. Progress in Geophysics, 2019,34(5):1849-1858.
|
| [10] |
张东晓, 陈云天, 孟晋. 基于循环神经网络的测井曲线生成方法[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2018,45(4):598-607.
|
| [10] |
Zhang X D, Chen Y T, Meng J. Logging curve generation method based on cyclic neural network[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2018,45(4):598-607.
|
| [11] |
汤梦, 朱杰. 一种基于LSTM的合成语音自然度评价方法的研究[J]. 信息技术, 2019,43(5):41-44.
|
| [11] |
Tang M, Zhu J. Research on an evaluation method of naturalness of synthesized speech based on LSTM[J]. Information Technology, 2019,43(5):41-44.

|
| [12] |
卢鹏飞, 须成杰, 张敬谊, 等. 基于SARIMA-LSTM的门诊量预测研究[J]. 大数据, 2019,5(6):101-110.
|
| [12] |
Lu P F, Xu C J, Zhang J Y, et al. Research on outpatient forecast based on SARIMA-LSTM[J]. Big Data Research, 2019,5(6):101-110.
|
| [13] |
Alfarraj M, AlRegib G.Semisupervised sequence modeling for elastic impedance inversion[J]. Interpretation, 2019,7(3):237-249.
|
| [14] |
邓帅. 基于改进贝叶斯优化算法的CNN超参数优化方法[J]. 计算机应用研究, 2019,36(7):1984-1987.
|
| [14] |
Deng S. Hyper-parameter optimization of CNN based on improved Bayesian optimization algorithm[J]. Application Research of Computers, 2019,36(7):1984-1987.
|
| [15] |
Smith L N. Cyclical learning rates for training neural networks[C]// 2017 IEEE Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision (WACV),IEEE, 2017: 464-472.
|
| [16] |
Breuel T M. The effects of hyperparameters on SGD training of neural networks[EB/OL]. Computer Science, 2015. [2015-08-12]. https://arxiv.org/abs/150802788.

|
| [17] |
Martin G S, Wiley R, Marfurt K J. Marmousi2:An elastic upgrade for marmousi[J]. The Leading Edge, 2006,25:156-166.

|
|
|
|

