|
|
|
| Speciation characteristics and bioavailability of cadmium in paddy soils, western Zhejiang Province |
LIU Dao-Rong( ), ZHOU Yi ), ZHOU Yi |
| Zhejiang Geological Prospecting Institute of China Chemical Geology and Mine Bureau, Hangzhou 310002, China |
|
|
|
|
Abstract The bioavailability of cadmium (Cd) in soil is affected by many factors, while the morphological distribution characteristic is one of the important factors. In order to find out the bioavailability of Cd in paddy soil in western Zhejiang Province and analyze the relationship between the forms of Cd in soil and Cd content in rice grains, the authors collected and analyzed 32 samples of paddy soil and 15 samples of paddy rice. First, the morphological distribution characteristics and biological characteristics of Cd in soil under different pH and parent materials conditions were discussed. And then, by linear correlation analysis, the correlation between the Cd content in rice and different forms of Cd in soil was studied.The results show that Cd in paddy soil is mainly in the form of ion exchange (about 35% of the total amount), and the content of water soluble Cd is the least (about 1% of the total amount), with other forms of Cd in between. Under acidic condition (pH 5.0~6.5), both of the ion-exchange Cd and the bioavailability of Cd are the highest.The morphological distribution characteristics of Cd in soil between the weathered limestone and the other parent materials are quite different.Varying measures should be taken to control the Cd pollution in different parent material areas. The correlation analysis shows that there is a significant correlation between the Cd content of rice and the ion-exchange Cd content (P<0.01), but the correlation with other forms of Cd is not obvious.
|
|
Received: 29 November 2019
Published: 26 October 2020
|
|
|
|
|
|

| 指标 | 土壤样品(n=32) | 水稻(n=15) | | 总Cd | F1 | F2 | F3 | F4 | F5 | F6 | F7 | pH | 稻谷Cd | | 最大值 | 13.0 | 0.091 | 8.200 | 1.980 | 0.800 | 1.730 | 0.640 | 0.610 | 7.66 | 3.513 | | 最小值 | 0.23 | 0.001 | 0.047 | 0.006 | 0.025 | 0.025 | 0.022 | 0.015 | 4.58 | 0.016 | | 平均值 | 1.71 | 0.013 | 0.705 | 0.292 | 0.163 | 0.245 | 0.107 | 0.101 | 5.37 | 0.740 | | 标准偏差 | 2.76 | 0.020 | 1.516 | 0.596 | 0.218 | 0.368 | 0.117 | 0.111 | 0.76 | 1.010 | | 变异系数/% | 161.60 | 148.04 | 215.09 | 204.36 | 133.32 | 149.91 | 109.99 | 110.19 | 14.15 | 136.47 |
|
The total and fraction Cd content and pH in soil as well as Cd content in rice grains
|

| Cd形态 | F1 | F2 | F3 | F4 | F5 | F6 | F7 | 合计 | | 形态分布百分率/% | 1.06 | 34.96 | 10.45 | 11.65 | 15.34 | 11.20 | 11.16 | 95.82 |
|
The percentage of fraction Cd with its total content in paddy soil
|
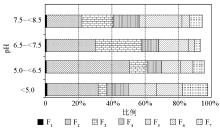
|
The ratio of Cd with different forms in soil under different pH
|
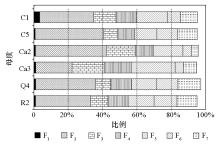
|
The ratio of Cd with different forms in soil under different parent materials
|

| Cd形态 | F1 | F2 | F3 | F4 | F5 | F6 | F7 | | r | 0.473 | 0.690** | 0.189 | 0.296 | 0.080 | 0.301 | 0.370 |
|
Correlation between different forms of Cd in soil and Cd content in rice
|
| [1] |
环境保护部, 国土资源部. 全国土壤污染状况调查公报[N]. 中国国土资源报, 2014-04-18(002).
|
| [1] |
Ministry of Environmental Protection, Ministry of Land and Resources. Bulletin of national soil pollution survey[N]. China Land and Resources News, 2014-04-18(002).
|
| [2] |
王梦梦, 何梦媛, 苏德纯. 稻田土壤性质与稻米镉含量的定量关系[J]. 环境科学, 2018,39(4):1918-1925.
|
| [2] |
Wang M M, He M Y, Su D C. Quantitative relationship between paddy soil properties and cadmium content in rice grains[J]. Environmental Science, 2018,39(4):1918-1925.
|
| [3] |
朱智伟, 陈铭学, 牟仁祥, 等. 水稻镉代谢与控制研究进展[J]. 中国农业科学, 2014,47(18):3633-3640.
|
| [3] |
Zhu Z W, Chen M X, Mou R X, et al. Advances in research of cadmium metabolism and control in rice plants[J]. Scientia Agricultural Sinica, 2014,47(18):3633-3640.
|
| [4] |
Chen H M, Zheng C R. Heavy metal pollution in soils in China:Status and countermeasures[J]. Ambio, 1999,28(2):130-134.
|
| [5] |
宗良纲, 徐晓炎. 水稻对土壤中镉的吸收及其调控措施[J]. 生态学杂志, 2004,23(3):120-123.
|
| [5] |
Zong L G, Xu X Y. Cadmium absorption of rice from soils and remediations[J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 2004,23(3):120-123.
|
| [6] |
肖振林, 王果, 黄瑞卿, 等. 酸性土壤中有效态镉提取方法研究[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2008,27(2):795-800.
|
| [6] |
Xiao Z L, Wang G, Huang R Q, et al. Extraction method for available cadmium in acid soils[J]. Journal of Agro-environment Science, 2008,27(2):795-800.
|
| [7] |
Tessier A, Campbell P G C, Bisson M. Sequential extraction procedure for the speciation of particulate trace metals[J]. Analytical Chemistry, 1979,51(7):844-851.
|
| [8] |
陈学诚, 董文庚, 郎志敏, 等. A.Tessier逐级提取程序应用于土镉形态研究的可靠性[J]. 环境科学, 1991,12(6):25-28,36.
|
| [8] |
Chen X C, Dong W G, Lang Z M, et al. Reliability of Tessier’s fractional extraction procedure for cadmium species in soil[J]. Environmental Science, 1991,12(6):25-28,36.
|
| [9] |
朱亮, 邵孝侯. 耕作层中重金属Cd形态分布规律及植物有效性研究[J]. 河海大学学报, 1997,25(3):50-56.
|
| [9] |
Zhu L, Shao X H. Chemical form distribution and plant availability of Cd in plough horizon[J]. Journal of Hohai University, 1997,25(3):50-56.
|
| [10] |
崔妍, 丁永生, 公维民, 等. 土壤中重金属化学形态与植物吸收的关系[J]. 大连海事大学学报, 2005,31(2):59-63.
|
| [10] |
Cui Y, Ding Y S, Gong W M, et al. Study on the correlation between the chemical forms of the heavy metals in soil and the metal uptake by plant[J]. Journal of Dalian Maritime University, 2005,31(2):59-63.
|
| [11] |
周国华. 土壤重金属生物有效性研究进展[J]. 物探与化探, 2014,38(6):1097-1106.

|
| [11] |
Zhou G H. Recent progress in the study of heavy metal bioavailability in soil[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2014,38(6):1097-1106.

|
| [12] |
张季惠, 王黎虹, 张建奎. 土壤中镉的形态转化、影响因素及生物有效性研究进展[J]. 广东农业科学, 2013(6):169-171.
|
| [12] |
Zhang J H, Wang L L, Zhang J K. Transformation and influence factors of existing form of cadmium in soils and its effect on cadmium bioavailability[J]. Guangdong Agricultural Sciences, 2013(6):169-171.
|
| [13] |
喻华, 秦鱼生, 陈琨, 等. 水稻土镉形态分布特征及其生物效应研究[J]. 西南农业学报, 2017,30(2):452-457.
|
| [13] |
Yu H, Qin Y S, Chen K, et al. Distribution characteristics of cadmium forms and its correlation with biological effect in paddy soil[J]. Southwest China Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 2017,30(2):452-457.
|
| [14] |
王昌全, 代天飞, 李冰, 等. 稻麦轮作下水稻土重金属形态特征及其生物有效性[J]. 生态学报, 2007,27(3):889-897.

|
| [14] |
Wang C Q, Dai T F, Li B, et al. The speciation and bioavailability of heavy metals in paddy soils under the rice-wheat cultivation rotation[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2007(3):889-897.
|
| [15] |
李冰, 王昌全, 代天飞, 等. 水稻子实对不同形态重金属的累积差异及其影响因素分析[J]. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2007,13(4):602-610.
|
| [15] |
Li B, Wang C Q, Dai T F, et al. Accumulation of heavy metals in rice seeds as influenced bymetal speciation and soil properties[J]. Plant Nutrition and Fertilizer Science, 2007,13(4):602-610.
|
| [16] |
周国华, 董岩翔, 张建明, 等. 浙江省农业地质环境调查评价方法技术[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2007.
|
| [16] |
Zhou G H, Dong Y X, Zhang J M, et al. Methodology of evaluation on agro-geology environment survey in Zhejiang[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 2007.
|
| [17] |
黄涓, 刘昭兵, 谢运河, 等. 土壤中Cd形态及生物有效性研究进展[J]. 湖南农业科学, 2013(17):56-61.
|
| [17] |
Huang J, Liu Z B, Xie Y H, et al. Progress of form and bioavailability of cadmium in soil[J]. Hunan Agricultural Sciences, 2013(17):56-61.
|
| [18] |
DD 2005-03 生态地球化学评价样品分析技术要求(试行)[S].
|
| [18] |
DD 2005-03 Technical requirements for analysis of eco geochemical evaluation samples (Trial)[S].
|
| [19] |
DZ/T 0258-2014 多目标区域地球化学调查规范(1:250000)[S].
|
| [19] |
DZ/T 0258-2014 Specification of multi-purpose regional geochemical survey(1:250000)[S].
|
| [20] |
邓朝阳, 朱霞萍, 郭兵, 等. 不同性质土壤中镉的形态特征及其影响因素[J]. 南昌大学学报:工科版, 2012,34(4):341-346.
|
| [20] |
Deng Z Y, Zhu X P, Guo B, et al. Distribution and influence factors of Cd speciation on the soil with different properties[J]. Journal of Nanchang University:Engineering and Technology, 2012,34(4):341-346.
|
| [21] |
郝汉舟, 靳孟贵, 李瑞敏, 等. 耕地土壤铜、镉、锌形态及生物有效性研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2010,19(1):92-96.
|
| [21] |
Hao H Z, Jin M G, Li R M, et al. Fractionations and bioavailability of Cu, Cd and Zn in cultivated land[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 2010,19(1):92-96.
|
| [22] |
汪霞, 南忠仁, 武文飞, 等. 干旱区绿洲土壤中重金属的形态分布及生物有效性研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2010,19(7):1663-1667.
|
| [22] |
Wang X, Nan Z R, Wu W F, et al. Experiments on speciation and bioavailability of selected heavy metalsin arid oasis soil, northwest China[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 2010,19(7):1663-1667.
|
| [23] |
杜彩艳, 祖艳群, 李元. pH和有机质对土壤中镉和锌生物有效性影响研究[J]. 云南农业大学学报, 2005,20(4):539-544.
|
| [23] |
Du C Y, Zu Y Q, Li Y. Effect of pH and organic matter on the bioavailability Cd and Zn in soil[J]. Journal of Yunnan Agricultural University, 2005,20(4):539-544.
|
| [24] |
秦余丽, 熊仕娟, 徐卫红, 等. 不同镉浓度及pH条件下纳米沸石对土壤镉形态及大白菜镉吸收的影响[J]. 环境科学, 2016,37(10):539-544.
|
| [24] |
Qin Y L, Xiong S J, Xu W H, et al. Effect of nano zeolite on chemical fractions of Cd in soil and uptake by Chinese cabbage at different soil pH and cadmium levels[J]. Environmental Science, 2016,37(10):539-544.
|
| [25] |
冯佳蓓. 纳米羟基磷灰石对重金属污染农用土壤的修复研究[D]. 杭州:浙江大学, 2015.
|
| [25] |
Fen J B. Research on heavy metal polluted agricultural soil remediation by nano-hydroxyapatite[D]. Hangzhou:Zhejiang University, 2015.
|
| [1] |
Shi-Qi TANG, Neng WAN, Ming-Zhong ZENG, Ke YANG, Fei LIU, Min PENG, Kuo LI, Zheng YANG. Geochemical characteristics of selenium and cadmium in soil and crops in Enshi area[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2020, 44(3): 607-614. |
| [2] |
ZHOU Guo-Hua. Recent progress in the study of heavy metal bioavailability in soil[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2014, 38(6): 1097-1106. |
|
|
|
|

