|
|
|
| An analysis of the input flux and source of elements in dry and wet atmospheric deposition of southwest plain of Shandong:A case study of Juye County |
Zeng-Hui WANG( ) ) |
| Shandong Institute of Geological Survey,Shandong Engineering Research Center of Land Quality Geochemistry and Pollution Prevention,Ji'nan 250014,China |
|
|
|
|
Abstract Dry and wet atmospheric deposition is a main input pathway of some elements in the surface soil of agricultural areas, and its heavy metalelementcomponents mayhave a great influence on the environmental qualityof soil. Research on the dry and wet atmosphericdeposition of Juye County in Shandong Province shows that, with the rapid development of coal mining and chemical industry in recent years, total amount of dry and wet atmospheric deposition has been significantly increased in this area, and is also significantly higher than that of several other regions of China.The deposition flux of heavy metal elements in this region is also higher,the deposition fluxes of Pb, Cr, Cu, Ni can be 2~ 3 times those of other regions inChina. The enrichment degree of Cd, Pb, Hg and other elements in atmospheric deposition is higher, and the high value area of the enrichment factor(EF) coincides with the position of the emission source of coal mining and coal chemical industry, which indicates that the dry and wet atmospheric deposition in the industrial area is an important way for heavy metal elements like Cd, Pb, Hg to enter the soil. Industrial activities have an important influence on the increase of dry and wet atmospheric deposition in thisarea. In addition, the enrichment factor shows thatcoal burning dusts should be the main source of S and Se in atmospheric deposition and soil. Ni, Cr, As in atmospheric deposition should mainly originate from soil dusts, and thesources of Ca and Mg are closely related to the stone mining and cement manufacturing industry.
|
|
Received: 01 November 2019
Published: 28 August 2020
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Bitmap of sampling points for atmospheric wet and dry deposition
|
|
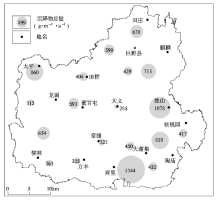
Total atmospheric dry and wet deposits in the study area
|

| 元素 | As | Cd | Cr | Cu | Hg | Pb | Ni | Zn | Se | Fe | S | Ca | Mg | P | K | | 区内通量算数均值 | 2.75 | 0.71 | 26.93 | 19.68 | 0.032 | 31.82 | 15.47 | 127 | 1.37 | 9.27 | 22.3 | 41.0 | 12.0 | 0.31 | 8.71 | | 区内通量几何均值 | 2.49 | 0.67 | 22.24 | 17.72 | 0.030 | 30.23 | 13.76 | 115 | 1.14 | 8.21 | 12.8 | 28.5 | 9.5 | 0.24 | 7.45 | | 区内通量最小值 | 1.14 | 0.38 | 9.04 | 8.11 | 0.020 | 17.77 | 5.95 | 56 | 0.35 | 3.75 | 4.5 | 8.5 | 2.6 | 0.09 | 2.96 | | 区内通量最大值 | 5.61 | 1.16 | 73.20 | 42.45 | 0.070 | 57.07 | 34.50 | 243 | 3.11 | 22.36 | 123.5 | 203.4 | 40.4 | 1.27 | 21.46 | | 区内(2005~2006) | 1.10 | 0.31 | 18.69 | 7.15 | 0.025 | 13.65 | 4.02 | 43 | 0.45 | | | | | 0.19 | 2.79 | | 北京(2005~2006)[11] | 2.9 | 0.236 | 11.855 | 14.195 | 0.024 | 21.995 | 6.601 | 54.492 | | | | 9.264 | 3.236 | | 3.328 | | 长春(2006~2007)[18] | 4.79 | 0.25 | 10.67 | 8.22 | 0.03 | 12.31 | | 48.15 | | | | | | | | | 成都(2004~2005)[19] | 2.77 | 1.77 | | | 0.1 | 45.95 | | 147.83 | | | | 18.074 | 1.016 | | 2.009 |
|
Statistics and comparison of atmospheric dry and wet deposition element fluxes in Juye County
|
|
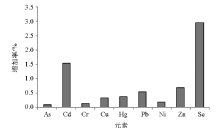
Comparison of annual increase rate of soil elements in plough layer caused by atmospheric deposition
|
|
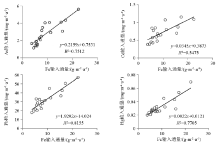
Scatter diagram of correlation between input fluxes of Fe and As, Cd, Pb, Hg in atmospheric sediment
|

| 项目 | As | Cd | Cr | Cu | Hg | Pb | Ni | Zn | Se | Fe | S | Ca | Mg | P | K | | 区内降尘含量均值 | 4.78 | 1.33 | 45.55 | 34.10 | 0.05 | 58.61 | 26.45 | 224.91 | 2.46 | 1.57 | 3.70 | 6.24 | 2.07 | 0.05 | 1.44 | | 区内表层土壤背景值 | 10.85 | 0.17 | 68.2 | 21.9 | 0.03 | 21.24 | 28.27 | 66.88 | 0.17 | 3.15 | 0.023 | 4.28 | 1.31 | 0.108 | 1.93 | | 菏泽表层土壤背景值 | 10.30 | 0.15 | 61.90 | 21.90 | 0.03 | 19.90 | 27.90 | 63.00 | 0.17 | 2.92 | 0.020 | 4.07 | 1.24 | 0.101 | 1.92 | | 富集系数 | 0.44 | 7.81 | 0.67 | 1.56 | 1.75 | 2.76 | 0.94 | 3.36 | 14.33 | 0.50 | 160.38 | 1.46 | 1.58 | 0.47 | 0.75 | | 富集因子(EF) | 0.86 | 16.45 | 1.37 | 2.89 | 3.47 | 5.47 | 1.76 | 6.63 | 26.93 | 1.00 | 344.16 | 2.85 | 3.10 | 0.94 | 1.39 |
|
Average enrichment coefficient and enrichment factor of heavy metals and other elements in atmospheric deposits in the area
|
|
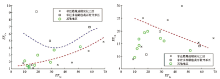
Enrichment factors scatter diagram of Se with Cd, Ca in the atmospheric deposition of the study area
|
|
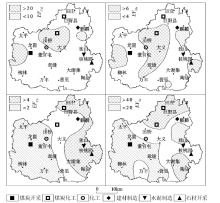
Enrichment factors distribution map of Cd, Pb, Ca and Se of the atmospheric deposition in the study area
|
| [1] |
王梦梦, 原梦云, 苏德纯. 我国大气重金属干湿沉降特征及时空变化规律[J]. 中国环境科学, 2017,37(11):4085-4096.
|
| [1] |
Wang M M, Yuan M Y, Su D C. Characteristics and spatial-temporal variation of heavy metals in atmospheric dry and wet deposition of China[J]. China Environmental Science, 2017,37(11):4085-4096.
|
| [2] |
邹海明, 李粉茹, 官楠, 等. 大气中TSP和降尘对土壤重金属累积的影响[J]. 中国农学通报, 2006,22(5):393-395.
|
| [2] |
Zou H M, Li F R, Guan N, et al. Effects of TSP and dustfall on heavy metal accumulation in soil[J]. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin, 2006,22(5):393-395.
|
| [3] |
张国忠, 黄威, 潘月鹏, 等. 河北典型农田大气重金属干沉降通量及来源解析[J]. 中国生态农业学报, 2019,27(8):1245-1254.
|
| [3] |
Zhang G Z, Huang W, Pan Y P, et al. Dry deposition flux of atmospheric heavy metals and its source apportionment in a typical farmland of Hebei Province[J]. Chinese Journal of Eco-Agriculture, 2019,27(8):1245-1254.
|
| [4] |
张乃明. 大气沉降对土壤重金属累积的影响[J]. 土壤与环境, 2001,10(2):91-93.
|
| [4] |
Zhang N M. Effects of air settlement on heavy metal accumulation in soil[J]. Soil And Environmental Sciences, 2001,10(2):91-93.
|
| [5] |
李晋昌, 董治宝. 大气降尘研究进展及展望[J]. 干旱区资源与环境, 2010,24(2):102-109.
|
| [5] |
Li J C, Dong Z B. Research progress and prospect of dustfall research[J]. Journal of Arid Land Resources and Environment, 2010,24(2):102-109.
|
| [6] |
张云峰, 于瑞莲, 胡恭任, 等. 泉州市大气PM2.5中有毒金属元素的环境风险评价[J]. 地球与环境, 2018,46(5):456-462.
|
| [6] |
Zhang Y F, Yu R L, Hu G R, et al. Environmental risk assessment of toxic metal elements in PM2.5 of Quanzhou City[J]. Earth and Environment, 2018,46(5):456-462.
|
| [7] |
张忠地, 邵天杰, 卫佩茹. 开封市大气降尘中重金属污染及潜在生态危害评价[J]. 干旱区资源与环境, 2019,33(11):156-162.
|
| [7] |
Zhang Z D, Shao T J, Wei P R. Assessment of heavy metal pollution and potential ecological hazards in atmospheric dust in Kaifeng city[J]. Journal of Arid Land Resources and Environment, 2019,33(11):156-162.
|
| [8] |
Pawel K, Malgorzata S, Grazyna S, et al. Long-term moss monitoring of atmospheric deposition near a large steelworks reveals the growing importance of local non-industrial sources of pollution[J]. Chemosphere, 2019,230:29-39.

|
| [9] |
Hissler C, Stille P, Geagea M L, et al. Identifying the origins of local atmospheric deposition in the steel industry basin of Luxembourg using the chemical and isotopic composition of the lichen Xanthoria parietina[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2008,405(1/3):338-344.
|
| [10] |
王洋, 刘景双, 王金达, 等. 土壤pH值对冻融黑土重金属Cd赋存形态的影响[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2008,27(2):574-578.
|
| [10] |
Wang Y, Liu J S, Wang J D, et al. Effects of pH on the fraction transformations of Cd in phaiozem soil at the condition of freeze/thaw cycles[J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 2008,27(2):574-578.
|
| [11] |
丛源, 陈岳龙, 杨忠芳, 等. 北京平原区元素的大气干湿沉降通量[J]. 地质通报, 2008,27(2):257-264.
|
| [11] |
Cong Y, Chen Y L, Yang Z F, et al. Dry and wet atmospheric deposition fluxes of elements in the plain area of Beijing Municipality, China[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 2008,27(2):257-264.
|
| [12] |
张良璧, 娄长庚. 大气降尘采样影响因素的研究[J]. 中国环境监测, 1986,2(1):9-12.
|
| [12] |
Zhang L B, Lou C G. Study on the influence factors of atmospheric dust sampling[J]. Environmental Monitoring in China, 1986,2(1):9-12.
|
| [13] |
侯佳渝, 刘金成, 曹淑萍, 等. 天津市城区大气干湿沉降地球化学研究[J]. 地质调查与研究, 2013,36(2):131-135.
|
| [13] |
Hou J Y, Liu J C, Cao S P, et al. Study on the dry and wet atmospheric deposition in the urban area of Tianjin[J]. Geological Survey and Research, 2013,36(2):131-135.
|
| [14] |
李延生. 黑龙江省松嫩平原南部大气降尘地球化学特征[J]. 物探与化探, 2011,35(4):536-540.
|
| [14] |
Li Y S. Geochemical characteristics of atmosphleric dust in southern songnen plain, Heilongjiang Province[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2011,35(4):536-540.
|
| [15] |
罗莹华, 戴塔根, 梁凯. 广东韶关市大气降尘及尘中金属元素分布特征研究[J]. 地质调查与研究, 2006,29(1):64-68.
|
| [15] |
Luo Y H, Dai T G, Liang K. Study on distribution of the atmospheric dust-fall and its metal element contents in Shaoguan City, Guangdong Province[J]. Geological Survey and Research, 2006,29(1):64-68.
|
| [16] |
焦荔, 沈建东, 姚琳, 等. 杭州市大气降尘重金属污染特征及来源研究[J]. 环境污染与防治, 2013,35(1):73-76.
|
| [16] |
Jiao L, Shen J D, Yao L, et al. Pollution characteristics and sources of heavy metals in atmospheric dustfall of Hangzhou[J]. Environmental Pollution and Control, 2013,35(1):73-76.
|
| [17] |
陈天虎, 徐惠芳. 大气降尘TEM观察及其环境矿物学意义[J]. 岩石矿物学杂志, 2003,22(4):425-428.
|
| [17] |
Chen T H, Xu H F. TEM investigation of atmospheric particle settlings and its significance in environmental mineralogy[J]. Acta Petrologica et Mineralogica, 2003,22(4):425-428.
|
| [18] |
杨忠平, 卢文喜, 龙玉桥, 等. 长春市城区大气湿沉降中重金属及pH值调查[J]. 吉林大学学报:地球科学版, 2009,39(5):887-892.
|
| [18] |
Yang Z P, Lu W X, Yu L Q, et al. Current situation of pH and wet deposition of heavy metals in precipatation in Changchun City, China[J]. Journal of Jilin University:Earth Science Edition, 2009,39(5):887-892.
|
| [19] |
汤奇峰, 杨忠芳, 张本仁, 等. 成都经济区As等元素大气干湿沉降通量及来源研究[J]. 地学前缘, 2007,14(3):213-222.
|
| [19] |
Tang Q F, Yang Z F, Zhang B R, et al. A study of elements flux and sources from atmospheric bulk deposition in the Chengdu economic region[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2007,14(3):213-222.
|
| [20] |
毕木天. 关于富集因子及其应用问题[J]. 环境科学, 1984(5):68-70.
|
| [20] |
Bi M T. About the enrichment factor and its application[J]. Environmental Science, 1984(5):68-70.
|
| [21] |
杨丽萍, 陈发虎, 张成君. 兰州市大气降尘的化学特性[J]. 兰州大学学报, 2002,38(5):115-120.
|
| [21] |
Yang L P, Chen F H, Zhang C J. Chemical characteristics of atmospheric dust in Lanzhou[J]. Journal of Lanzhou University, 2002,38(5):115-120.
|
| [22] |
张秀芝, 鲍征宇, 唐俊红. 富集因子在环境地球化学重金属污染评价中的应用[J]. 地质科技情报, 2006,25(1):65-72.
|
| [22] |
Zhang X Z, Bao Z Y, Tang J H. Application of the enrichment factor in evaluating of heavy metals contamination in the environmental geochemistry[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information, 2006,25(1):65-72.
|
| [23] |
顾家伟. 我国城市大气颗粒物重金属污染研究进展与趋势[J]. 地球与环境, 2019,47(3):385-396.
|
| [23] |
Gu J W. A review on heavy metals in atmospheric suspended particles of China cities and its implication for future references[J]. Earth and Environment, 2019,47(3):385-396.
|
| [24] |
Mikhailova E A, Goddard M A, Post C J, et al. Potential contribution of combined atmospheric Ca2+ and Mg2+ wet deposition within the continental U.S. to soil Inorganic carbon sequestration[J]. Pedosphere, 2013,23(6):808-814.
|
| [25] |
代杰瑞, 祝德成, 庞绪贵, 等. 济宁市近地表大气降尘地球化学特征及污染来源解析[J]. 中国环境科学, 2014,34(1):40-48.
|
| [25] |
Dai J R, Zhu D C, Pang X G, et al. Geochemical characteristics and pollution sources identification of the near-surface atmosphere dust-fall in Jining City[J]. China Environmental Science, 2014,34(1):40-48.
|
| [26] |
邹本东, 徐子优, 华蕾, 等. 因子分析法解析北京市大气颗粒物PM10的来源[J]. 中国环境监测, 2007,23(2):79-85.
|
| [26] |
Zou B D, Xu Z Y, Hua L, et al. Sources apportionment of atmospheric particles PM10 in Beijing by factor analysis[J]. Environmental Monitoring in China, 2007,23(2):79-85.
|
| [27] |
赵西强, 王增辉, 王存龙, 等. 济南市近地表大气降尘元素地球化学特征及污染评价[J]. 物探与化探, 2016,40(1):154-159.
|
| [27] |
Zhao X Q, Wang Z H, Wang C L, et al. Geochemical characteristics and pollution assessment of near-surface atmospheric dust in Jinan[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2016,40(1):154-159.
|
| [28] |
Xing J W, Song J M, Yuan H M, et al. Atmospheric wet deposition of dissolved organic carbon to a typical anthropogenic-influenced semi-enclosed bay in the western Yellow Sea, China:Flux, sources and potential ecological environmental effects[J]. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 2019,182:109371.

|
| [29] |
姚瑞珍, 张勇, 王亚良, 等. 黄石市大气降尘中重金属污染特征与评价[J]. 地球与环境, 2016,44(2):212-218.
|
| [29] |
Yao R Z, Zhang Y, Wang Y L, et al. Distribution characteristics and risk assessment of heavy metals in atmospheric dustfall of Huangshi City, China[J]. Earth and Environment, 2016,44(2):212-218.
|
| [30] |
王明仕, 刘艳萍, 曹景丽, 等. 焦作市采暖期大气降尘重金属的分布特征和健康风险评估[J]. 地球与环境, 2018,46(1):59-65.
|
| [30] |
Wang M S, Liu Y P, Cao J L, et al. Distribution characteristics and health risk assessment of heavy metals in atmospheric dust-fall in Jiaozuo City, Henan Province, China[J]. Earth and Environment, 2018,46(1):59-65.
|
| [1] |
MENG Wei, MO Chun-Hu, LIU Ying-Zhong. Geochemical background and management target values of heavy metals in soil in northwestern Guizhou Province[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2022, 46(1): 250-257. |
| [2] |
ZHAO Chen, SUN Bin-Bin, ZHOU Guo-Hua, HE Ling, ZENG Dao-Ming. The study and application of eco-geological adaptibility model for Myricarubra in Longhai,Fujian Province[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2021, 45(5): 1121-1129. |
|
|
|
|

