|
|
|
| Research on fast three-dimensional forward algorithm of magnetotelluric sounding based on vector finite element |
GU Guan-Wen1,2( ), WU Ye1,2, SHI Yan-Bin1,2 ), WU Ye1,2, SHI Yan-Bin1,2 |
1. School of Earth Sciences, Institute of Disaster Prevention, Langfang 065201, China
2. Hebei Key Laboratory of Earthquake Dynamics, Langfang 065201, China |
|
|
|
|
Abstract The finite element method has the characteristics of strong adaptability in simulating the electromagnetic response of rugged topography and complex geological bodies. In recent years, it has been widely used in the three-dimensional (3D) forward modeling of magnetotelluric (MT) sounding. However, the finite element method also has some shortcomings in terms of computational efficiency. The large amount of calculation and long running time of the method are the main factors that lead to the lag of the practical process of the 3D MT inversion technology based on the finite element method compared with the 3D MT inversion technology based on the finite difference method. In order to improve the 3D forward speed of MT, the authors adopt the forward modeling scheme which uses the direct solver PARDISO and does not need divergence correction to solve the large-scale linear equations corresponding to the vector finite element method, and obtain the MT response of the geoelectric model under such different terrain conditions as flat and rugged topography. Under the conditions of medium-scale calculation, through the comparison between the direct solution method without divergence correction and the iterative solution method with divergence correction, the authors have detected that the direct solution method without divergence correction has advantages in calculation accuracy and calculation time, especially in the calculation. In terms of time, the ratio of the calculation speed of the direct solution and the iterative solution is raised by more than ten times.
|
|
Received: 02 July 2020
Published: 29 December 2020
|
|
|
|
|
|
11]
">
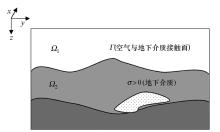
|
Section diagram of numerical modeling domain for 3D MT with topography[11]
|
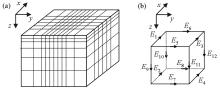
|
Domain subdivision of the vector finite element method
a—domain subdivision; b—location of electric field components
|

频点
/Hz | 视电阻率(ρxy,ρyx)/(Ω·m) | 相位φ/(°) | | 矢量有限元解 | 解析解 | 误差/% | 矢量有限元解 | 解析解 | 误差/% | | 10000 | 99.4934 | 100 | 0.5066 | 44.9824 | 45 | 0.039111 | | 8000 | 99.5168 | 100 | 0.4832 | 44.9800 | 45 | 0.044444 | | 5000 | 99.5580 | 100 | 0.442 | 44.9782 | 45 | 0.048444 | | 2000 | 99.6149 | 100 | 0.3851 | 44.9802 | 45 | 0.044 | | 1000 | 99.6266 | 100 | 0.3734 | 44.9895 | 45 | 0.023333 | | 500 | 99.7002 | 100 | 0.2998 | 44.9601 | 45 | 0.088667 | | 200 | 99.8467 | 100 | 0.1533 | 45.0661 | 45 | 0.14689 | | 100 | 99.4868 | 100 | 0.5132 | 45.1051 | 45 | 0.23356 | | 50 | 99.2563 | 100 | 0.7437 | 45.0452 | 45 | 0.10044 | | 10 | 99.4329 | 100 | 0.5671 | 44.9565 | 45 | 0.096667 | | 5 | 99.5295 | 100 | 0.4705 | 44.9596 | 45 | 0.089778 | | 2 | 99.6083 | 100 | 0.3917 | 44.9717 | 45 | 0.062889 | | 1 | 99.6484 | 100 | 0.3516 | 44.9776 | 45 | 0.049778 | | 0.5 | 99.6599 | 100 | 0.3401 | 44.9970 | 45 | 0.006667 | | 0.1 | 99.7267 | 100 | 0.2733 | 44.9301 | 45 | 0.155333 | | 0.05 | 99.9013 | 100 | 0.0987 | 44.9393 | 45 | 0.134889 | | 0.01 | 100.0090 | 100 | 0.009 | 44.9873 | 45 | 0.028222 | | 0.005 | 100.0070 | 100 | 0.007 | 44.9949 | 45 | 0.011333 | | 0.001 | 100.0010 | 100 | 0.001 | 44.9995 | 45 | 0.001111 | | 0.0005 | 100.0000 | 100 | 0 | 44.9998 | 45 | 0.000444 | | 0.0001 | 100.0000 | 100 | 0 | 45.0000 | 45 | 0 |
|
Comparison of vector finite element solution and analytical solution of uniform half space model
|
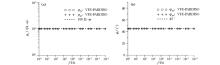
|
Comparison of 3D forward apparent resistivity (a) and phase (b) of homogeneous half space model with analytical solution
|

| 层参数 | 第一层 | 第二层 | 第三层 | | 电阻率/(Ω·m) | 100 | 10 | 1000 | | 层厚/m | 370 | 268 | ∞ |
|
Parameters of H-type layered model
|

频点
/Hz | 视电阻率(ρxy,ρyx)/(Ω·m) | 相位φ/(°) | | 矢量有限元解 | 解析解 | 误差/% | 矢量有限元解 | 解析解 | 误差/% | | 10000 | 99.4944 | 100 | 0.505638 | 44.9825 | 45.00002 | 0.03894 | | 8000 | 99.5156 | 99.99967 | 0.484074 | 44.9807 | 45.00007 | 0.00043 | | 5000 | 99.564 | 100.0036 | 0.439562 | 44.9729 | 44.9985 | 0.000569 | | 2000 | 99.1812 | 99.72298 | 0.543282 | 45.0089 | 45.02392 | 0.000334 | | 1000 | 100.138 | 100.1248 | 0.01314 | 44.3103 | 44.43167 | 0.002732 | | 500 | 108.223 | 107.9785 | 0.22646 | 44.9127 | 44.67756 | 0.00526 | | 200 | 112.433 | 113.6883 | 1.104134 | 51.6513 | 51.46143 | 0.00369 | | 100 | 94.4807 | 95.60484 | 1.175822 | 59.265 | 59.07526 | 0.00321 | | 50 | 63.587 | 64.76429 | 1.817807 | 63.9834 | 63.85949 | 0.00194 | | 10 | 28.0673 | 28.37355 | 1.079333 | 45.849 | 46.13936 | 0.006293 | | 5 | 32.2082 | 32.33247 | 0.384363 | 32.3095 | 32.54673 | 0.007289 | | 2 | 55.1794 | 55.21716 | 0.06839 | 21.4561 | 21.55953 | 0.004797 | | 1 | 89.6415 | 89.67347 | 0.035652 | 18.7262 | 18.78408 | 0.003081 | | 0.5 | 143.375 | 143.3732 | 0.00122 | 19.0537 | 19.09105 | 0.001956 | | 0.1 | 348.002 | 347.851 | 0.04341 | 25.4995 | 25.50588 | 0.00025 | | 0.05 | 457.716 | 457.5438 | 0.03763 | 29.036 | 29.03635 | 1.19E-05 | | 0.01 | 692.088 | 691.9579 | 0.0188 | 36.1384 | 36.13554 | 7.9E-05 | | 0.005 | 769.11 | 769.008 | 0.01327 | 38.3803 | 38.37769 | 6.8E-05 | | 0.001 | 888.395 | 888.3428 | 0.00588 | 41.8079 | 41.80643 | 3.5E-05 | | 0.0005 | 919.642 | 919.6043 | 0.0041 | 42.7015 | 42.70037 | 2.7E-05 | | 0.0001 | 963.197 | 963.179 | 0.00187 | 43.9466 | 43.94614 | 1.1E-05 |
|
Comparison of vector finite element solution and analytical solution of H-type layered model
|
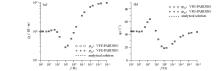
|
Comparison of apparent resistivity (a) and phase (b) of 3D forward modeling of H-type layered model with analytical solutions
|

| 层参数 | 第一层 | 第二层 | 第三层 | | 电阻率/(Ω·m) | 100 | 1000 | 10 | | 层厚/m | 370 | 268 | ∞ |
|
Parameters of K-type layered model
|

频点
/Hz | 视电阻率(ρxy,ρyx)/(Ω·m) | 相位φ/(°) | | 矢量有限元解 | 解析解 | 误差/% | 矢量有限元解 | 解析解 | 误差/% | | 10000 | 99.4928 | 99.99995 | 0.507154 | 44.9823 | 44.99998 | 0.039291 | | 8000 | 99.5179 | 100.0004 | 0.482464 | 44.9795 | 44.99994 | 0.04542 | | 5000 | 99.5522 | 99.9958 | 0.443615 | 44.9822 | 45.00155 | 0.042987 | | 2000 | 99.9938 | 100.3013 | 0.306591 | 44.9731 | 44.9962 | 0.05134 | | 1000 | 98.5514 | 99.11594 | 0.569571 | 45.4799 | 45.46765 | 0.02695 | | 500 | 94.8705 | 94.84442 | 0.0275 | 43.8641 | 44.11071 | 0.55908 | | 200 | 111.446 | 109.5436 | 1.73666 | 42.1518 | 41.35312 | 1.93136 | | 100 | 124.19 | 128.152 | 3.091671 | 47.226 | 45.89309 | 2.90438 | | 50 | 115.34 | 122.0064 | 5.46397 | 54.8037 | 54.506 | 0.54618 | | 10 | 55.4147 | 56.83843 | 2.504864 | 64.9559 | 65.42769 | 0.721085 | | 5 | 38.6174 | 39.2693 | 1.660063 | 64.5842 | 64.96375 | 0.584241 | | 2 | 25.6211 | 25.88921 | 1.03559 | 61.7858 | 62.03061 | 0.394665 | | 1 | 20.052 | 20.20837 | 0.773778 | 58.9626 | 59.13016 | 0.28337 | | 0.5 | 16.5801 | 16.68206 | 0.611172 | 56.1309 | 56.24364 | 0.200444 | | 0.1 | 12.6035 | 12.65607 | 0.415342 | 50.8822 | 50.92886 | 0.091626 | | 0.05 | 11.7748 | 11.82107 | 0.391403 | 49.346 | 49.36433 | 0.037132 | | 0.01 | 10.7493 | 10.77999 | 0.284731 | 46.9822 | 47.06061 | 0.166611 | | 0.005 | 10.5349 | 10.54576 | 0.102932 | 46.4109 | 46.47605 | 0.140175 | | 0.001 | 10.2412 | 10.24057 | 0.00616 | 45.6579 | 45.67163 | 0.030065 | | 0.0005 | 10.17 | 10.16953 | 0.00462 | 45.4711 | 45.47688 | 0.012716 | | 0.0001 | 10.0755 | 10.07547 | 0.00035 | 45.2136 | 45.21445 | 0.001873 |
|
Comparison between vector finite element solution and analytical solution of K-type layered model
|
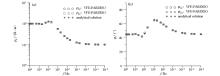
|
Comparison of 3D forward apparent resistivity (a) and phase (b) of K-type layered model with analytical solution
|
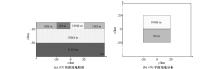
|
Schematic diagram of COMMEMI3D-2
|
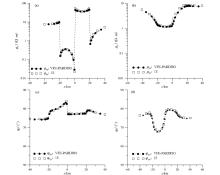
|
Comparison between the calculation results of vector finite element forward algorithm and IE method
a—Zxy mode forward apparent resistivity;b—Zyx mode forward apparent resistivity;c—Zxy mode forward impedance phase;d—Zyxmode forward impedance phase
|

|
3D topography and grid
a—sketch of 3D topography; b—topography meshing and distribution of MT measurement sites
|
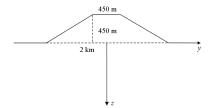
|
Sketch of 2D ridge
|
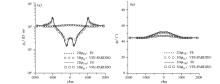
|
Comparision between modeling results of 3DVFEM(PARDISO) and 2DFEM for 2D ridge
a—forward apparent resistivity; b—forward impedance phase
|

|
Comparison of calculation results of VFE-PARDISO without divergence correction and VFE-BICG with divergence correction
a—forward apparent resistivity; b—forward impedance phase
|
| [1] |
Wannmaker P E. Advances in three-dimensional magnetotelluric modeling using integral equations[J]. Geophysics, 1991,56:1716-1728.
|
| [2] |
徐凯军, 李桐林, 张辉, 等. 利用积分方程法的大地电磁三维正演[J]. 西北地震学报, 2006(2):104-107.
|
| [2] |
Xu K J, Li T L, Zhang H, et al. Three-dimensional magnetotelluric forward modeling using integral equation[J]. Northwestern Seismological Journal, 2006(2):104-107.
|
| [3] |
任政勇, 陈超健, 汤井田, 等. 一种新的三维大地电磁积分方程正演方法[J]. 地球物理学报, 2017,60(11):4506-4515.
|
| [3] |
Ren Z Y, Chen C J, Tang J T, et al. A new integral equation approach for 3D magnetotelluric modeling[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2017,60(11):4506-4515.
|
| [4] |
Mackie R L, Madden T R, Wannamaker P. 3-D magnetotelluric modeling using difference equations-theory and comparisons to integral equation solutions[J]. Geophysics, 1993,58:215-226.
|
| [5] |
Mackie R L, Smith T J, Madden T R. 3-D electromagnetic modeling using difference equations:The Magnetotelluric Example[J]. Radio Sci., 1994,29:923-935.
|
| [6] |
Newman G A, Alumbaugh D L. Three-dimensional induction logging problems.Part I. An integral equation solution and model comparisons[J]. Geophysics, 2002,67:484-491.
|
| [7] |
谭捍东, 余钦范, John Booker, 等. 大地电磁三维交错网格有限差分正演[J]. 地球物理学报, 2003,46(5):705-711.
|
| [7] |
Tan H D, Yu Q F, Booker J, et al. Magnetotelluric three-dimension modeling using the staggered-grid finite difference method[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2003,46(5):705-711.
|
| [8] |
董浩, 魏文博, 叶高峰, 等. 基于有限差分正演的带地形三维大地电磁反演方法[J]. 地球物理学报, 2014,57(3):939-952.
|
| [8] |
Dong H, Wei W B, Ye G F, et al. Study of three-dimensional magnetotelluric inversion including surface topography based on Finite-difference method[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2014,57(3):939-952.
|
| [9] |
Mitsuhata Y, Uchida T. 3D magnetotelluric modeling using the T-Ω finite-element method[J]. Geophysics, 2004,69(1):108-119.
|
| [10] |
汤井田, 张林成, 公劲喆, 等. 三维频率域可控源电磁法有限元—无限元结合数值模拟[J]. 中南大学学报:自然科学版, 2014,45(4):1251-1260.
|
| [10] |
Tang J T, Zhang L C, Gong J Z, et al. 3D frequency domain controlled source electromagnetic numericalmodeling with coupled finite-infinite element method[J]. Journal of Central South University:Science and Technology, 2014,45(4):1251-1260.
|
| [11] |
Shi X, Utada H, Wang J, et al. Three-dimensional magnetotelluric forward modelling using vector finite element method combined with divergence corrections(VFE++)[R]// 2004,17th IAGA WG1.2 Workshop on electromagnetic Induction in the Earth.Hyderabad.
|
| [12] |
Nam N J, Kim H J, Song Y, et al. 3D magnetotelluric modelling inluding surface topography[J]. Geophysical Prospecting, 2007,55(2):277-287.
|
| [13] |
Ren Z Y, Kaischeuer T, Greenhalgh S, et al. A goal-oriented adaptive finite-element approach for plane wave 3D electromagnetic modeling[J]. Geophys. J. Int., 2013,194:700-718.
|
| [14] |
顾观文, 吴文鹂, 李桐林. 大地电磁场三维地形影响的矢量有限元数值模拟[J]. 吉林大学学报:地球科学版, 2014,44(5):1678-1686.
|
| [14] |
Gu G W, Wu W L, Li T L. Modeling for the effect of magnetotelluric 3D topography based on the vector finite-element method[J]. Journal of Jilin University:Earth Science Edition, 2014,44(5):1678-1686.
|
| [15] |
殷长春, 张博, 刘云鹤, 等. 面向目标自适应三维大地电磁正演模拟[J]. 地球物理学报, 2017,60(1):327-336.
|
| [15] |
Yin C C, Zhang B, Liu Y H, et al. A goal-oriented adaptive algorithm for 3D magnetotelluric forward modeling[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2017,60(1):327-336.
|
| [16] |
王刚, 魏文博, 金胜, 等. 冈底斯成矿带东段的电性结构特征研究[J]. 地球物理学报, 2017,60(8):2993-3003.
|
| [16] |
Wang G, Wei W B, Jin S, et al. A study on the electrical structure of eastern Gangdese metallogenic belt[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2017,60(8):2993-3003.
|
| [17] |
余辉, 邓居智, 陈辉, 等. 起伏地形下大地电磁L-BFGS三维反演方法[J]. 地球物理学报, 2019,62(8):3175-3188.
|
| [17] |
Yu H, Deng J Z, Chen H, et al. Three-dimensional magnetotelluric inversion under topographic relief based on the limited-memory quasi-Newton algorithm(L-BFGS)[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2019,62(8):3175-3188.
|
| [18] |
崔腾发, 陈小斌, 詹艳, 等. 安徽霍山地震区深部电性结构和发震构造特征[J]. 地球物理学报, 2020,63(1):256-269.
|
| [18] |
Cui T F, Chen X B, Zhan Y, et al. Characteristics of deep electrical structure and seismogenic structure beneath Anhui Huoshan earthquake area[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2020,63(1):256-269.
|
| [19] |
杨文采, 金胜, 张罗磊, 等. 青藏高原岩石圈三维电性结构[J]. 地球物理学报, 2020,63(3):817-827.
|
| [19] |
Yang W C, Jin S, Zhang L L, et al. The three-dimensional resistivity structures of the lithosphere beneath the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2020,63(3):817-827.
|
| [20] |
汤井田, 任政勇, 化希瑞. 地球物理学中的电磁场正演与反演[J]. 地球物理学进展, 2007,22(4):1181-1194.
|
| [20] |
Tang J T, Ren Z Y, Hua X R. The forward modeling and inversion ingeophysical electromagnetic field[J]. Progress in Geophysics, 2007,22(4):1181-1194.
|
| [21] |
Smith J T. Conservative modeling of 3D electromagnetic fields, Part I, Properties and error analysis[J]. Geophysics, 1996,61:1308-1318.

|
| [22] |
Farquharson C G, Miensopust M P. Three-dimensional finite-element modeling of magnetotelluric data with a divergence correction[J]. Journal of Applied Geophysics, 2011,75(4):699-710.

|
| [23] |
Schenk O, Gärtner K. Solving unsymmetric sparse systems of linear equations with PARDISO[J]. Future Generation Computer Systems, 2004,20:475-487.

|
| [24] |
AmestoyP R, Duff I S, L’Excellent J Y, et al. A fully asynchronous multifrontal solver using distributed dynamic scheduling[J]. SIAM J. Matrix Anal. Appl., 2002,23(1):15-41.

|
| [25] |
Amestoy P R, Guermouche A, L’Excellent J Y, et al. Hybrid schedulingfor the parallel solution of linear systems[J]. Parallel Computing, 2006,32(2):136-156.

|
| [26] |
Streich R. 3D finite-difference frequency-domain modeling of controlled-source electromagnetic data: Direct solution and optimization for high accuracy[J]. Geophysics, 2009,74(5):F95-F105.

|
| [27] |
Puzyrev V, Koldan J, De La Puente J, et al. A parallel finite-element method for three-dimensional controlled-source electromagnetic forward modeling[J]. Geophysical Journal International, 2013,193(2):678-693.

|
| [28] |
Kordy M, Wannamaker K, Maris V, et al. 3D magnetotelluric inversion including topography using deformed hexahedral edge finite elements and direct solvers parallelized on SMP computers—Part I: forward problem and parameter Jacobians[J]. Geophys. J. Int., 2016,204:74-93.

|
| [29] |
汤井田, 任政勇, 周聪. 浅部频率域电磁勘探方法综述[J]. 地球物理学报, 2015,58(8):2681-2705.
|
| [29] |
Tang J T, Ren Z Y, Zhou C, et al. Frequency-domain electromagnetic methods for exploration of the shallow subsurface: A review[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2015,58(8):2681-2705.
|
| [30] |
Siripunvaraporn W, Egbert G, Lenbury Y. Numerical accuracy of magnetotelluric modeling: A comparison of finite difference approximations[J]. Earth Planets Space, 2002,54:721-725.

|
| [31] |
徐世浙. 地球物理中的有限单元法[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 1994.
|
| [31] |
Xu S Z. Finite element method in Geophysics[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 1994.
|
| [32] |
金建铭. 电磁场有限元方法[M]. 西安: 西安电子科技大学出版社, 1998: 176-189.
|
| [32] |
Jin J M. The Finite element method in electromagnecic fields [M]. Xi’an: Xidian University Press, 1998: 176-189.
|
| [33] |
Gould N I M, Scott J A, H Y F. A numerical evaluation of sparse direct solvers for the solution of large sparse symmetric linear systems of equations[J]. ACM Transactions on Mathematical Software, 2007,33(2):300-325.
|
| [34] |
Newman G A, Alumbaugh D L. Three-dimensional magnetotelluric inversion using non-linear conjugate gradients[J]. Geophys. J. Int., 2000,140:410-424.

|
| [35] |
谭捍东, 魏文博, 邓明, 等. 大地电磁法张量阻抗通用计算公式[J]. 石油地球物理勘探, 2004,39(1):113-116.

|
| [35] |
Tan H D, Wei W B, Deng M, et al. General use formula in MT tensor impedance[J]. Oil Geophysical Prospecting, 2004,39(1):113-116.
|
| [36] |
Zhdanov M S, Varentov I M, Weaver J T, et al. Methods for modeling electromagnetic fields: Results from COMMEMI——The international project on the comparison of modeling methods for electromagnetic induction[J]. Journal of Applied Geophysics, 1997,37:133-271.

|
| [37] |
Wannamaker P E, Stodt J A, Rijo L. Two-dimensional topographic responses in magnetotelluric model using finite elements[J]. Geophysics, 1986,51(11):2121-2144.
|
| [38] |
秦策, 王绪本, 赵宁. 基于二次场方法的并行三维大地电磁正反演研究[J]. 地球物理学报, 2017,60(6):2456-2468.
|
| [38] |
Qin C, Wang X B, Zhao N. Parallel three-dimensional forward modeling and inversion of magnetotelluric based on a secondary field approach[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2017,60(6):2456-2468.
|
| [39] |
Chen P F, Hou Z H, Fan G H. Three-dimension topographic responses in MT using finite difference method[J]. Acta Seismologica Sinica, 1998,11(5):631-635.

|
| [1] |
CHEN Da-Lei, WANG Run-Sheng, HE Chun-Yan, WANG Xun, YIN Zhao-Kai, YU Jia-Bin. Application of integrated geophysical exploration in deep spatial structures: A case study of Jiaodong gold ore concentration area[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2022, 46(1): 70-77. |
| [2] |
CHEN Jun, YAN Liang-Jun, ZHOU Lei. Denoising of magnetotelluric data based on Hilbert-Huang transform[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2021, 45(6): 1462-1468. |
|
|
|
|

