|
|
|
| Large scale tectonic geochemical characteristics and prospecting prediction in eastern Laochang orefield, Gejiu, Yunnan Province |
HUANG Da-Zheng1( ), CHEN Shou-Yu1,2( ), CHEN Shou-Yu1,2( ), ZHAO Jiang-Nan1, WU Shuai-Ji1, ZHANG Yu-Ce1 ), ZHAO Jiang-Nan1, WU Shuai-Ji1, ZHANG Yu-Ce1 |
1. School of Earth Resources, China University of Geosciences(Wuhan), Wuhan 430074, China
2. State Key Laboratory of Geological Processes and Mineral Resources, Wuhan 430074, China |
|
|
|
|
Abstract In the past half a century, with the consumption of resources, the Laochang orefield has entered the rank of resource crisis. In order to alleviate the shortage of mineral resources in the Gejiu tin deposit and prolong the life of the mine, the authors, on the basis of 1∶10 000 tectonic geochemical survey in the study area, analyzed and summarized the geochemical characteristics of 12 elements, used correlation analysis to determine the correlation of elements, used content-area (C-A) fractal method to determine the anomaly threshold, delineated the abnormal range, and then divided the prospecting area.The results show that the 12 elements are highly dispersed, differentiated and enriched in different degrees, among which Pb, Sn, Cu, Bi, As and Cd are the main ore-forming elements in the eastern part of Laochang, Sn and Cu elements have good correlation with Ag, Sb, Zn, Pb, As and Bi elements, and are closely related to mineralization; five prospecting area were delineated, and tin-copper orebodies were found through engineering verification,which shows that the application of tectonic geochemical method in this area can effectively provide scientific basis for the prospecting work.
|
|
Received: 31 December 2019
Published: 29 December 2020
|
|
|
|
Corresponding Authors:
CHEN Shou-Yu
E-mail: huangdz@cug.edu.cn;sychen@cug.edu.cn
|
|
|
|
25] modified)
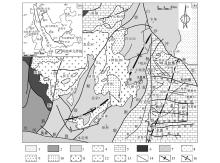
1—Quaternary; 2—slate, sandstone, glutenite of the Huobachong formation; 3—sandstone, shale intercalated with tuff and basaltic lava of the Falang formation; 4—basaltic lava of the Falang formation ; 5—carbonate rock of the Gejiu formation ; 6—purple-red sandstone with green sandstone and marl of lower Triassic ; 7—Ailaoshan metamorphic belt; 8—gabbro; 9—nepheline syenite; 10—alkali-feldspar granite; 11—alkaline granite; 12—porphyritic biotite granite; 13—equigranular biotite granite; 14—fault; 15—syncline; 16—anticline
">
|
Geotectonic location(a) and geological sketch(b) of mining area in Gejiu area, Yunnan province(according to Mao J W,et al [25] modified)
1—Quaternary; 2—slate, sandstone, glutenite of the Huobachong formation; 3—sandstone, shale intercalated with tuff and basaltic lava of the Falang formation; 4—basaltic lava of the Falang formation ; 5—carbonate rock of the Gejiu formation ; 6—purple-red sandstone with green sandstone and marl of lower Triassic ; 7—Ailaoshan metamorphic belt; 8—gabbro; 9—nepheline syenite; 10—alkali-feldspar granite; 11—alkaline granite; 12—porphyritic biotite granite; 13—equigranular biotite granite; 14—fault; 15—syncline; 16—anticline
|
|
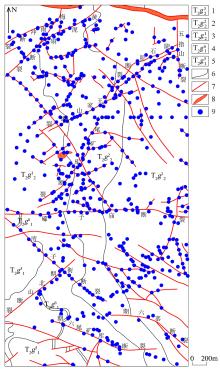
Geological sketch and sampling location of the eastern part of the Laochang ore field in Gejiu
1—the third layer of the Malage section of the Gejiu formation,dolomite with lime dolomite; 2—the second layer of the Malage section of the Gejiu formation,interbedded dolomite and dolomitic limestone; 3—the first layer of the Malage section of the Gejiu formation,thick layered dolostone; 4—the sixth layer of the Kafang section of the Gejiu formation,interbedded limestone and lime dolomite; 5—the fifth layer of the Kafang section of the Gejiu formation,limestone with lime dolomite; 6—stratigraphic boundary; 7—fault; 8—faulted and shattered zone; 9—sampling location
|

| 元素 | 分析方法 | 检出限/10-6 | 报出率/% | | Ag | ES | 0.01 | 100 | | Sn | ES | 0.2 | 100 | | Sb | AFS | 0.05 | 100 | | As | AFS | 0.2 | 97.8 | | Bi | ICP-MS | 0.01 | 98.8 | | Cu | ICP-MS | 0.2 | 100 | | Zn | ICP-MS | 2 | 99.6 | | Mo | ICP-MS | 0.05 | 100 | | Cd | ICP-MS | 0.2 | 100 | | W | ICP-MS | 0.1 | 100 | | Pb | ICP-MS | 0.5 | 100 | | Mn | ICP-MS | 5 | 100 |
|
Analytic technique and parameter of tectonic geochemical samples
|

| 元素 | 样品数 | 最大值 | 最小值 | 平均值 | 标准离差 | 中位数 | 变异系数 | 富集系数 | 全球碳酸盐岩[38] | | Ag | 597 | 44.80 | 0.01 | 0.75 | 2.66 | 0.14 | 3.53 | >1 | 0.0n | | Sn | 597 | 2000.00 | 0.74 | 13.07 | 90.34 | 2.00 | 6.91 | >1 | 0.n | | Sb | 597 | 370.27 | 0.02 | 8.72 | 27.03 | 2.20 | 3.10 | 43.60 | 0.20 | | Bi | 597 | 315.37 | 0.02 | 0.74 | 12.91 | 0.07 | 17.48 | >1 | — | | Mn | 597 | 119900.00 | 0.03 | 1676.00 | 7827.60 | 312.60 | 4.67 | 1.52 | 1100.00 | | Cu | 597 | 8816.00 | 0.50 | 29.37 | 362.80 | 5.60 | 12.34 | 7.34 | 4.00 | | Zn | 597 | 23020.00 | 5.00 | 361.60 | 1200.62 | 89.70 | 3.32 | 18.08 | 20.00 | | Mo | 597 | 200.00 | 0.22 | 2.41 | 12.78 | 0.67 | 5.29 | 6.03 | 0.40 | | Cd | 597 | 2217.00 | 0.03 | 9.28 | 95.45 | 0.51 | 10.28 | 232 | 0.04 | | W | 597 | 114.60 | 0.08 | 2.46 | 8.23 | 1.30 | 3.35 | 4.10 | 0.60 | | Pb | 597 | 40506.75 | 3.98 | 467.86 | 2575.58 | 73.20 | 5.50 | 57.98 | 9.00 | | As | 597 | 93305.00 | 1.00 | 181.07 | 3818.84 | 7.10 | 21.07 | 181.07 | 1.00 |
|
The statistical characteristics of the content parameters of tectonic geochemical elements in the eastern area of Laochang ore field
|
|
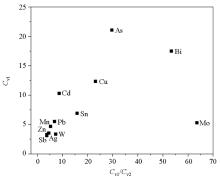
The coefficient of variation of tectonic geochemical elements in the eastern area of Laochang ore field
|
|
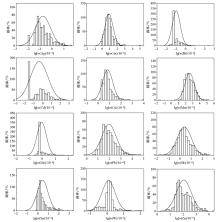
Histogram of the logarithmic content distribution of tectonic geochemical elements in the eastern area of Laochang ore field
|

| 元素 | Ag | Sn | Sb | Bi | Mn | Cu | Zn | Mo | Cd | W | Pb | As | | Ag | 1.00 | | | | | | | | | | | | | Sn | 0.61 | 1.00 | | | | | | | | | | | | Sb | 0.64 | 0.61 | 1.00 | | | | | | | | | | | Bi | 0.35 | 0.49 | 0.40 | 1.00 | | | | | | | | | | Mn | 0.76 | 0.57 | 0.66 | 0.26 | 1.00 | | | | | | | | | Cu | 0.53 | 0.64 | 0.57 | 0.60 | 0.44 | 1.00 | | | | | | | | Zn | 0.71 | 0.61 | 0.74 | 0.27 | 0.75 | 0.54 | 1.00 | | | | | | | Mo | 0.44 | 0.53 | 0.41 | 0.48 | 0.30 | 0.56 | 0.31 | 1.00 | | | | | | Cd | 0.64 | 0.48 | 0.54 | 0.34 | 0.63 | 0.50 | 0.70 | 0.30 | 1.00 | | | | | W | 0.52 | 0.57 | 0.67 | 0.39 | 0.49 | 0.46 | 0.47 | 0.50 | 0.29 | 1.00 | | | | Pb | 0.74 | 0.66 | 0.74 | 0.37 | 0.76 | 0.60 | 0.83 | 0.44 | 0.67 | 0.62 | 1.00 | | | As | 0.64 | 0.69 | 0.75 | 0.63 | 0.57 | 0.70 | 0.68 | 0.53 | 0.58 | 0.57 | 0.70 | 1.00 |
|
Correlation analysis of tectonic geochemical elements in the eastern part of Laochang ore field
|

| 元素 | 原始数据 | 剔除特高低值 | | 样品数 | 峰度 | 偏度 | 样品数 | 峰度 | 偏度 | | Ag | 597 | 0.76 | 0.83 | 590 | 0.40 | 0.70 | | As | 597 | 6.39 | 1.57 | 578 | 0.11 | 0.53 | | Bi | 597 | 10.32 | 2.39 | 556 | 1.19 | 1.23 | | Cu | 597 | 5.72 | 1.68 | 560 | 0.12 | 0.67 | | Pb | 597 | 1.22 | 0.88 | 584 | -0.03 | 0.53 | | Sb | 597 | 0.64 | 0.42 | 580 | -0.14 | 0.31 | | Sn | 597 | 4.00 | 1.89 | 504 | 0.56 | 1.03 | | Zn | 597 | 0.55 | 0.71 | 594 | 0.20 | 0.61 |
|
Normal test characteristic values of tectonic geochemical elements in the eastern part of Laochang ore field
|
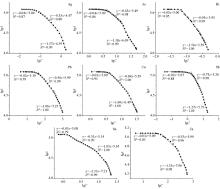
|
C-A double logarithmic scatter of different elements and piecewise fitting graph
|

| 元素 | 特征值 | | D1 | D2 | D3 | D4 | C1 | C2 | C3 | | Ag | 0.04 | 0.53 | 1.37 | — | 0.08 | 0.78 | — | | As | 0.04 | 0.65 | 1.18 | — | 4.07 | 17.38 | — | | Bi | 0.05 | 0.95 | 1.54 | — | 0.07 | 0.23 | — | | Cu | 0.03 | 0.84 | 1.60 | — | 3.80 | 17.78 | — | | Pb | 0.02 | 0.56 | 1.06 | — | 36.31 | 398.11 | — | | Sb | 0.02 | 0.15 | 1.27 | — | 1.55 | 9.55 | — | | Sn | 0.03 | 0.51 | 1.05 | 2.33 | 1.38 | 9.12 | 18.62 | | Zn | 0.01 | 0.53 | 1.35 | — | 46.77 | 281.84 | — |
|
C-A fractal statistical characteristics of elements
|

| 元素 | Ag | As | Bi | Cu | Pb | Sb | Sn | Zn | | 一级异常 | 0.78 | 17.38 | 0.23 | 17.78 | 398.11 | 9.55 | 9.12 | 281.84 | | 二级异常 | 1.55 | 34.76 | 0.46 | 35.57 | 796.21 | 19.10 | 18.24 | 563.68 | | 三级异常 | 3.10 | 69.51 | 0.92 | 71.13 | 1592.43 | 38.20 | 36.48 | 1127.35 |
|
Statistics of abnormal lower bound of tectonic geochemical elements
|
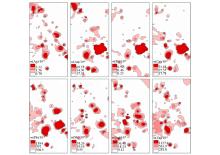
|
Single element anomoly diagram of 1:10 000 tectonic geochemical survey in the eastern part of Laochang ore field
|
Fig.2
">
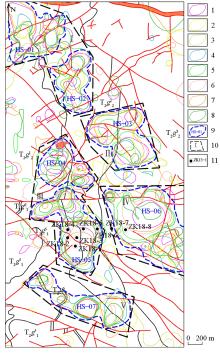
|
Comprehensive anomaly distribution and prospecting prospect zoning in the eastern part of Laochang ore field
1—Ag element anomaly; 2—As element anomaly; 3—Bi element anomaly; 4—Cu element anomaly; 5—Pb element anomaly; 6—Sb element anomaly; 7—Sn element anomaly; 8—Zn element anomaly; 9—comprehensive anomaly area and number; 10—prospecting area and number; 11—drilling hole and number;other legends are the same as Fig.2
|

综合异
常编号 | 面积
/km2 | 元素组合 | 异常特征 | | HS-01 | 0.52 | Sb-Bi-Pb-Cu-Zn-As-Sn-Ag | 出露地层为个旧组马拉格段二层(T2g22)白云岩与含白云质灰岩互层、个旧组马拉格段一层(T2g12)厚层状白云岩,异常区内异常元素套合好,各元素三级浓度分带明显,异常区内断裂较为发育 | | HS-02 | 0.34 | Sb-Cu-Sn-Pb-As-Zn-Ag | 出露地层为个旧组马拉格段二层(T2g22)白云岩与含白云质灰岩互层,异常区内断裂较为发育,Sb、Cu、Sn聚于核部,Pb、Zn、Ag、As异常分布于外围,Ag、As、Pb、Sb、Zn三级浓度分带明显,但异常面积较小 | | HS-03 | 0.34 | Zn-Cu-As-Sn-Sb-Ag-Pb-Bi | 出露地层为个旧组马拉格段三层(T2g32)白云岩夹灰质白云岩、个旧组马拉格段二层(T2g22)白云岩与含白云质灰岩互层,异常区内断裂构造发育,Ag、Pb、Sb、Zn三级浓度分带明显 | | HS-04 | 0.34 | Pb-Zn-Sb-Ag-Sn-Cu-Bi-As | 出露地层为个旧组马拉格段二层(T2g22)白云岩与含白云质灰岩互层、个旧组马拉格段一层(T2g12)厚层状白云岩,异常区内断裂极为发育,元素套合较好,Sn、Cu、Sb出现三级浓度分带,但面积较小 | | HS-05 | 0.61 | Zn-Sn-Ag-Bi- Sb-Cu-As-Pb | 出露地层为个旧组马拉格段二层(T2g22)白云岩与含白云质灰岩互层、个旧组马拉格段一层(T2g12)厚层状白云岩,元素套合较好,具有2个浓集中心,元素三级浓度分带明显 | | HS-06 | 0.94 | Zn-Ag-Sn-Sb-Pb-Cu-Bi-As | 岩性较为简单,出露地层为个旧组马拉格段三层(T2g32)白云岩夹灰质白云岩,具有1个明显的浓集中心,异常套合较好,异常元素浓度高,异常面积较大,Ag、Pb、Sb、Sn三级浓度分带明显 | | HS-07 | 0.47 | Sn-Ag-Sb-Zn-Pb-As-Bi-Cu | 出露地层为个旧组马拉格段二层(T2g22)白云岩与含白云质灰岩互层、个旧组马拉格段一层(T2g12)厚层状白云岩、个旧组卡房段六层(T2g61)石灰岩与灰质白云岩互层,具有3个明显的浓集中心,异常套合较好,异常元素浓度较大,但异常面积较小 |
|
Comprehensive abnormal feature statistics
|

|
Photographs field and core in the eastern part of Laochang ore field
a—tectonic fracture zone breccia; b—limonitization; c—net-shaped and thin-shaped calcite veins; d—limonitization cataclastic rock; e—ore-bearing skarn; f—skarn sulfide ore; g—diopsideskarn; h—chlorite marble
|
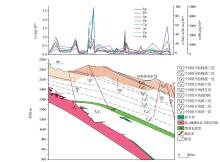
|
Geological-geochemical information section in the eastern part of Laochang ore field
|
| [1] |
Liao S, Chen S, Deng X, et al. Fluid inclusion characteristics and geological significance of the Xi’ao copper-tin polymetallic deposit in Gejiu, Yunnan Province[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2014,79(79):455-467.
|
| [2] |
Cheng Y, Mao J, Chang Z, et al. The origin of the world class tin-polymetallic deposits in the Gejiu district, SW China: Constraints from metal zoning characteristics and 40Ar-39Ar geochronology[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2013,53:50-62.
|
| [3] |
Zhang J, Dai C, Huang Z, et al. Age and petrogenesis of Anisian magnesian alkali basalts and their genetic association with the Kafang stratiform Cu deposit in the Gejiu supergiant tin-polymetallic district, SW China[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2015,69:403-416.
|
| [4] |
曹华文, 裴秋明, 张寿庭, 等. 个旧老厂钾质煌斑岩矿物学特征及其锆石U-Pb和黑云母40Ar-39Ar年龄[J]. 地球化学, 2016,45(6):545-568.
|
| [4] |
Cao H W, Pei Q M, Zhang S T, et al. Mineralogical characteristics, zircon U-Pb and biotite 40Ar-39Ar ages of potassic lamprophyres in the Gejiu tin deposit, Yunnan Province[J]. Geochimica, 2016,45(6):545-568.
|
| [5] |
陈守余, 赵鹏大, 张寿庭, 等. 个旧超大型锡铜多金属矿床成矿多样性与深部找矿[J]. 地球科学:中国地质大学学报, 2009,34(2):319-324.
|
| [5] |
Chen S Y, Zhao P D, Zhang S T, et al. Mineralizing multiformity and deep prospecting of Gejiu super Sn-Cu multi-metal deposit, Yunnan, China[J]. Earth science:Journal of China University of Geosciences, 2009,34(2):319-324.
|
| [6] |
何光辉, 周涛发, 范裕, 等. 庐江沙溪斑岩型铜金矿床绿泥石的地球化学特征及找矿指示[J]. 矿床地质, 2018,37(6):1247-1259.
|
| [6] |
He G H, Zhou T F, Fan Y, et al. Geochemical characteristics and exploration implications of chlorite in Shaxi porphyry copper gold deposit, Lujiang[J]. Mineral Deposits, 2018,37(6):1247-1259.
|
| [7] |
孙岩. 论构造地球化学研究[J]. 地球科学进展, 1993,8(3):1-6.
|
| [7] |
Sun Y. On the study of structural geochemistry[J]. Advance in Earth Sciences, 1993,8(3):1-6.
|
| [8] |
Han R S. Main study progress for ten years of Tectono-geochemistry[J]. Bulletin of Mineralogy Petrology & Geochemistry, 2013(2):198-203.
|
| [9] |
Han R S, Deyun M A, Peng W U, et al. Ore-finding method of fault tectono-geochemistry in the Tongchang Cu-Au polymetallic orefield,Shaanxi, China: I. Dynamics of tectonic ore-forming processes and prognosis of concealed ores[J]. Chinese Journal of Geochemistry, 2009,28(4):397-404.
|
| [10] |
钱建平, 黄德阳, 谢彪武, 等. 西藏谢通门县斯弄多铅锌矿区矿床地质特征和构造地球化学找矿研究[J]. 大地构造与成矿学, 2013,37(1):29-41.
|
| [10] |
Qian J P, Huang D Y, Xie B W, et al. Study on geology and tectono-geochemistry of the Silongduo Lead-Zinc deposit in Xietongmen County, Tibet[J]. Geotectonica et Metallogenia, 2013,37(1):29-41.
|
| [11] |
谢彪武, 钱建平, 黄德阳, 等. 西藏阿里住浪铜银矿区构造地球化学找矿研究[J]. 地质与勘探, 2012,48(4):807-814.
|
| [11] |
Xie B W, Qian J P, Huang D Y, et al. A study of structural geochemical prospecting in the alexilang copper silver ore area, Tibet[J]. Geology and Exploration, 2012,48(4):807-814.
|
| [12] |
金浚. 构造地球化学在某矿区的应用[J]. 物探与化探, 1981,5(3):174-177.
|
| [12] |
Jin J. Application of structural geochemistry in a mining area[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 1981,5(3):174-177.
|
| [13] |
吕古贤, 孙岩, 刘德良, 等. 构造地球化学的回顾与展望[J]. 大地构造与成矿学, 2011,35(4):479-494.
|
| [13] |
Lyu G X, Sun Y, Liu D L, et al. Review and prospect of tectonic geochemistry[J]. Geotectonica et Metallogenia, 2011,35(4):479-494.
|
| [14] |
齐家喆, 麦广田. 地质构造地球化学特征要素及其在区域化探解释中的应用[J]. 物探与化探, 1993,17(1):14-21.
|
| [14] |
Qi J Z, Mai G T. Geochemistry characteristic elements of geological structure and their application in regional geochemical exploration interpretation[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 1993,17(1):14-21.
|
| [15] |
安国英. 青海省东昆仑中段地区构造地球化学特征及地质意义[J]. 物探与化探, 2015,39(1):69-75.
|
| [15] |
An G Y. Tectonic geochemistry of the central segment of the East Kunlun Mountainsin Qinghai Province and its geological significance[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2015,39(1):69-75.
|
| [16] |
Han R S, Liu C, Huang Z, et al. Geological features and origin of the Huize carbonate-hosted Zn-Pb-(Ag) District, Yunnan, South China[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2007,31(1):360-383.
|
| [17] |
韩润生, 陈进, 高德荣, 等. 构造地球化学在隐伏矿定位预测中的应用[J]. 地质与勘探, 2003,39(6):25-28.
|
| [17] |
Han R S, Chen J, Gao D R, et al. Application of tectonic geochemistry ore-finding method in orientation prognosis of concealed ores[J]. Geology and Exploration, 2003,39(6):25-28.
|
| [18] |
郭泽华, 王雷, 韩润生, 等. 滇西云县红豆山铜矿构造地球化学特征及找矿预测[J]. 中国地质, 2019,46(1):178-190.
|
| [18] |
Guo Z H, Wang L, Han R S, et al. Tectonic geochemical characteristics and ore prediction in Hongdoushan copper deposit, Yunxian area, Western Yunnan[J]. Geology in China, 2019,46(1):178-190.
|
| [19] |
韩润生. 隐伏矿定位预测的矿田(床)构造地球化学方法[J]. 地质通报, 2005,24(10):104-110.
|
| [19] |
Han R S. Orefield/deposit tectonic-geochemistry method for the localization and prognosis of concealed orebodies[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 2005,24(10):104-110.
|
| [20] |
邓军, 孙忠实, 杨立强, 等. 吉林夹皮沟金矿带构造地球化学特征分析[J]. 高校地质学报, 2000,6(3):405-411.
|
| [20] |
Deng J, Sun Z S, Yang L Q, et al. Tectono-Geochemical Analysis of Jiapigou Gold Belt, Jilin Province[J]. Geological Journal of China Universities, 2000,6(3):405-411.
|
| [21] |
韩润生, 陈进, 李元, 等. 云南会泽麒麟厂铅锌矿床构造地球化学及定位预测[J]. 矿物学报, 2001(4):667-673.

|
| [21] |
Han R S, Chen J, Li Y, et al. Tectono-geochemical features and orientation prognosis of concealed ores of Qilinchang Lead-Zinc deposit in Huize, Yunnan[J]. Acta Mineralogica Sinica, 2001(4):667-673
|
| [22] |
钱建平, 何胜飞, 王富民, 等. 安徽省廖家地区地质地球化学特征和构造地球化学找矿[J]. 物探与化探, 2008,32(5):519-524.

|
| [22] |
Qian J P, He S F, Wang F M, et al. Geological and geochemical characteristics and tectono-geochemical prospecting work in Liaojia area, Anhui Province[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2008,32(5):519-524.
|
| [23] |
范柱国, 秦德先, 谈树成, 等. 个旧老厂锡多金属矿田东部断裂构造地球化学异常特征[J]. 矿物学报, 2004,24(2):129-135.
|
| [23] |
Fan Z G, Qin D X, Tan S C, et al. Geochemical anomaly signatures in the eastern Gejiu laochang tin polymetallic ore field[J]. Acta Mineralogica Sinica, 2004,24(2):129-135.
|
| [24] |
王力, 孟昭君, 毛政利. 构造地球化学方法在个旧锡矿外围找矿预测中的应用[J]. 矿床地质, 2002,21(S1):1197-1200.
|
| [24] |
Wang L, Meng Z J, Mao Z L, et al. Application of tectogeochemistry in metallogenic prognosis in periphery of Gejiu Tin ore deposit[J]. Mineral Deposits, 2002,21(S1):1197-1200.
|
| [25] |
毛景文, 程彦博, 郭春丽, 等. 云南个旧锡矿田:矿床模型及若干问题讨论[J]. 地质学报, 2008,82(11):1455-1467.

|
| [25] |
Mao J W, Chen Y B, Guo C L, et al. Gejiu Tin polymetallic ore-field: Deposit model and discussion for several points concerned[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2008,82(11):1455-1467.
|
| [26] |
Cheng Y, Mao J, Zhu X, et al. Iron isotope fractionation during supergene weathering process and its application to constrain ore genesis in Gaosong deposit, Gejiu district, SW China[J]. Gondwana Research, 2015,27(3):1283-1291.

|
| [27] |
Sun S Y. Study on the multi-episodic activity of faults in the Gaosong field of Gejiu tin deposits[J]. Acta Mineralogica Sinica, 2004.
|
| [28] |
庄永秋, 王任重, 杨书培, 等. 云南个旧锡铜多金属矿床[M]. 北京: 地震出版社, 1996.
|
| [28] |
Zhuang Y Q, Wang R Z, Yang S P, et al. Gejiu tin copper polymetallic deposit, Yunnan[M]. Beijing: Earthquake Press, 1996.
|
| [29] |
Zhao J, Zuo R, Chen S, et al. Application of the tectono-geochemistry method to mineral prospectivity mapping: a case study of the Gaosong tin-polymetallic deposit, Gejiu district, SW China[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2015,71:719-734.

|
| [30] |
He F P, Wang Z, Chen F, et al. Identification and assessment of Sn-polymetallic prospects in the Gejiu western district, Yunnan (China)[J]. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 2014,145:106-113.

|
| [31] |
Cheng Y, Mao J. Age and geochemistry of granites in Gejiu area, Yunnan province, SW China: Constraints on their petrogenesis and tectonic setting[J]. Lithos, 2010,120(3):258-276.

|
| [32] |
秦德先, 黎应书, 范柱国, 等. 个旧锡矿地球化学及成矿作用演化[J]. 中国工程科学, 2006(1):30-39.

|
| [32] |
Qin D X, Li Y S, Fan Z G, et al. The geochemistry and mineralization evolvement of Gejiu Tin ore deposits[J]. Strategic Study of CAE, 2006(1):30-39.
|
| [33] |
廖时理, 陈守余, 姚涛, 等. 个旧西凹铜—锡多金属矿床地球化学特征及地质意义[J]. 大地构造与成矿学, 2014,38(3):635-646.
|
| [33] |
Liao S L, Chen S Y, Yao T, et al. Geochemical characteristics and geological significance of the Xi’ao Cu-Sn polymetallic deposit in the Gejiu area[J]. Geotectonica et Metallogenia, 2014,38(3):635-646.
|
| [34] |
杨宝富, 李彬, 魏超. 个旧老厂矿田东部矿床控矿因素、成矿规律及找矿预测[J]. 矿物学报, 2016,36(4):479-487.
|
| [34] |
Yang B F, Li B, Wei C, et al. Ore-controlling factors, metallogenetic regularity and prospecting of eastern Laochang deposits, Gejjiu mine, Yunnan Province, China[J]. Acta Mineralogica Sinica, 2016,36(4):479-487.
|
| [35] |
陈守余, 赵鹏大, 童祥, 等. 个旧东区蚀变花岗岩型锡铜多金属矿床成矿特征及找矿意义[J]. 地球科学:中国地质大学学报, 2011,36(2):277-281.
|
| [35] |
Chen S Y, Zhao P D, Tong X, et al. Metallogenic characteristics of western low altered Tin-Copper polymetallic deposit and its prospecting significance in east part of Gejiu, Yunnan[J]. Earth science:Journal of China University of Geosciences, 2011,36(2):277-281.
|
| [36] |
Caron M E, Grasby S E, Ryan M C. Spring water trace element geochemistry: A tool for resource assessment and reconnaissance mineral exploration[J]. Applied Geochemistry, 2008,23(12):3561-3578.

|
| [37] |
Zhu W, Sun Y, Guo J, et al. Prospects for study of tectono-geochemistry[J]. Progress in Natural Science:Materials International, 2003,13(3):161-165.
|
| [38] |
Turekian K K, Wedepohl K H. Distribution of the elements in some major units of the earth’s crust[J]. Geological Society of America Bulletin, 1961,72(2):175.

|
| [39] |
罗先熔. 勘查地球化学[M]. 北京: 冶金工业出版社, 2007.
|
| [39] |
Luo X R. Exploration geochemistry [M]. Beijing: Metallurgical Industry Press, 2007.
|
| [40] |
袁玉涛. 化探数据处理方法对比研究[D]. 北京:中国地质大学(北京), 2015.
|
| [40] |
Yuan Y T. Comparative study on geochemical data processing methods[D]. Beijing:China University of Geosciences (Beijing), 2015.
|
| [41] |
向中林, 顾雪祥, 王恩营, 等. 新疆博罗科努成矿带东段地球化学分形特征及找矿预测[J]. 河南理工大学学报:自然科学版, 2019,38(4):49-57.
|
| [41] |
Xiang Z L, Gu X X, Wang E Y, et al. Geochemical fractal characteristics and prospecting prediction of the eastern section of theBoluokenu metallogenic belt, Xinjiang[J]. Journal of Henan Polytechnic University:Natural Science, 2019,38(4):49-57.
|
| [42] |
Cheng Q, Agterberg F P, Ballantyne S B. The separation of geochemical anomalies from background by fractal methods[J]. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 1994,51(2):109-130.

|
| [43] |
Zuo R, Xia Q, Zhang D. A comparison study of the C-A and S-A models with singularity analysis to identify geochemical anomalies in covered areas[J]. Applied Geochemistry, 2013,33:165-172.

|
| [44] |
Zuo R, Jian W. Fractal/multifractal modeling of geochemical data: A review[J]. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 2016,164:33-41.

|
| [45] |
Zhao J, Chen S, Zuo R. Identification and mapping of lithogeochemical signatures using staged factor analysis and fractal/multifractal models[J]. Geochemistry: Exploration, Environment, Analysis, 2017,17(3):239-251.

|
| [46] |
谢淑云, 鲍征宇. 地球化学场的连续多重分形模式[J]. 地球化学, 2002,31(2):191-200.
|
| [46] |
Xie S Y, Bao Z Y. Continuous multifractal model of geochemical field[J]. Geochimica, 2002,31(2):191-200.
|
| [47] |
成秋明. 多维分形理论和地球化学元素分布规律[J]. 地球科学, 2000,25(3):311-318.
|
| [47] |
Cheng Q M. Multidimensional fractal theory and distribution law of geochemical elements[J]. Earth Science, 2000,25(3):311-318.
|
| [48] |
刘世宝, 陈鑫, 国显正, 等. 分形(多重分形)在区域化探数据处理中的应用——以柴北缘荒漠戈壁景观区为例[J]. 物探与化探, 2016(3):550-556.

|
| [48] |
Liu S B, Chen X, Guo X Z, et al. Fractal/multifractal modeling of geochemical exploration data in desert landscape area of QaidamBasin[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2016(3):550-556.
|
| [1] |
ZHAO Ji-Chang, FAN Ying, LEI Yi-Lan, YAO Bin-Bin. The application of tectonogeochemical cuttings survey to gold prospecting in Nanshan area of Danghe, Gansu Province[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2021, 45(4): 923-932. |
| [2] |
Jing-Jing GONG, Jian-Zhou YANG, Sheng-Ming MA, Lei SU. Recognition of ore-induced geochemical anomaly by combined factor and fractal analysis in Heiyingshan, Inner Mongolia[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2020, 44(1): 122-131. |
|
|
|
|

