|
|
|
| Characteristics of selenium content in soil of eastern Baoqing County and its relationship with soil properties |
Yue-Ping WANG, Li ZHANG( ), Yu-Jun CUI, Shi-Jia LYU ), Yu-Jun CUI, Shi-Jia LYU |
| Heilongjiang Institute of Geological Survey, Haerbin 150036, China |
|
|
|
|
Abstract In order to study the soil selenium content in the eastern part of Baoqing County and its relationship with soil properties, the authors collected 17 470 soil samples in the depth of 0~20 cm from the main agricultural areas in eastern Baoqing County according to the density of 4 points/km 2. Physical and chemical indicators such as selenium content, organic carbon and pH were analyzed. The results show that the selenium content in the topsoil is between 0.01×10 -6 and 1.17×10 -6, the average content is 0.326×10 -6, 73.53% of the soil is selenium-sufficient, 21.14% of the soil is selenium-abundant, and 4.56% of soil is of potential selenium-deficiency. Selenium-deficient soil only accounts for 0.77%, and there is no selenium poisoning area. The average content of selenium in different soil parent materials is arranged in decreasing order of alluvial deposits>alluvial deposits>granite>sedimentary rocks>basic-neutral volcanic rocks; the average content of selenium in different soil types in arranged in decreasing order of albic soil>meadow soil>black soil>marshy soil>dark brown soil>paddy soil; the average content of selenium in different land use is arranged in decreasing order of irrigated farmland>dry farmland>grassland>construction land>unused land>forest land. Correlation analysis shows that soil organic carbon (TOC) and pH are the main factors affecting the selenium content in the surface soil of the study area.
|
|
Received: 08 January 2019
Published: 15 August 2019
|
|
|
|
Corresponding Authors:
Li ZHANG
E-mail: 11741785@qq.com
|
|
|
|
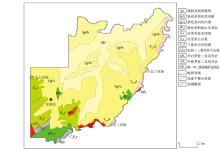
|
Geological sketch map of eastern Baoqing County
|

| 土壤性质 | 平均值 | 变幅 | 标准差 | 变异系数/% | | 总硒 | 0.326 | 0.01~1.17 | 0.116 | 35.58 | | TOC | 2.684 | 0.03~32.96 | 1.655 | 61.65 | | pH | 6.13 | 3.95~8.56 | 0.632 | 10.32 |
|
Basic physicochemical properties of soil (n=17 470)
|

| 硒含量分级 | 硒含量范围/10-6 | 硒效应 | 面积比例/% | | 缺乏 | <0.125 | 缺硒 | 0.77 | | 边缘 | 0.125~0.175 | 硒潜在不足 | 4.56 | | 适中 | 0.175~0.4 | 足硒 | 73.53 | | 高 | 0.4~3.0 | 富硒 | 21.14 | | 过剩 | >3.0 | 硒中毒 | 0 |
|
Limit value and statistical result of selenium content of soil in research area
|
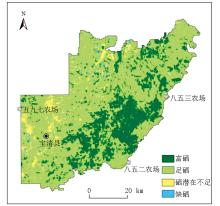
|
Distribution characteristics of selenium content in soil in eastern Baoqing County
|

| 成土母质 | 样本数 | 平均值/10-6 | 变幅/10-6 | 标准差/10-6 | 变异系数/% | | 冲积—洪积物 | 7463 | 0.304 | 0.01~1.17 | 0.107 | 35.20 | | 残坡积物 | 6639 | 0.370 | 0.07~0.99 | 0.120 | 32.43 | | 基性—中性火山岩 | 1195 | 0.270 | 0.08~1.15 | 0.094 | 34.81 | | 沉积岩 | 1889 | 0.296 | 0.09~0.92 | 0.100 | 33.78 | | 花岗岩 | 284 | 0.298 | 0.10~0.57 | 0.086 | 28.86 |
|
Characteristics of selenium content in different soil-forming material
|

| 土壤类型 | 样本数 | 平均值/10-6 | 变幅/10-6 | 标准差/10-6 | 变异系数/% | | 草甸土 | 6396 | 0.353 | 0.01~1.17 | 0.116 | 33.14 | | 沼泽土 | 4876 | 0.298 | 0.05~1.13 | 0.112 | 37.33 | | 白浆土 | 2943 | 0.358 | 0.01~0.84 | 0.108 | 30.00 | | 暗棕壤 | 1606 | 0.270 | 0.07~0.85 | 0.102 | 37.78 | | 黑土 | 1593 | 0.300 | 0.10~0.83 | 0.104 | 34.67 | | 水稻土 | 56 | 0.253 | 0.13~0.47 | 0.080 | 32.00 |
|
Characteristics of selenium content in different soil types
|

| 土地利用 | 样本数 | 平均值/10-6 | 变幅/10-6 | 标准差/10-6 | 变异系数/% | | 旱地 | 10943 | 0.330 | 0.05~1.17 | 0.116 | 34.98 | | 水田 | 3157 | 0.343 | 0.01~0.89 | 0.109 | 31.82 | | 草地 | 976 | 0.307 | 0.05~1.13 | 0.140 | 45.43 | | 林地 | 1712 | 0.284 | 0.08~0.80 | 0.102 | 36.08 | | 建设用地 | 300 | 0.305 | 0.1~0.74 | 0.115 | 37.84 | | 未利用地 | 382 | 0.303 | 0.01~0.72 | 0.117 | 38.51 |
|
Characteristics of selenium content in different land use patterns
|
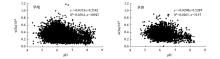
|
Relations between pH and Se content in soil
|
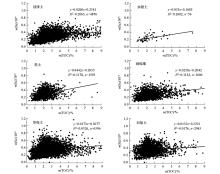
|
Relations between TOC and Se content in soil
|
| [1] |
Rayman M P . The importance of selenium to human health[J]. Lancet, 2000,356(9225):233-241.
|
| [2] |
Finley J W . Selenium accumulation in plant foods[J]. Nutrition Reviews, 2005,63(1):196-202.
|
| [3] |
Abdulah R, Miyazaki K, Nakazawa M , et al. Chemical forms of selenium for cancer prevention[J]. Journal of Trace Elements in Medicine & Biology, 2005,19(2/3):141-150.
|
| [4] |
Schwarz M . Selenium as an integral part of factor against dietary Necrotic liver degeneration[J]. Chemical Society, 1957,70(32):92-93.
|
| [5] |
Rotriek J, Pope A, Gather H , et al. Selenium: Biochemical role as a component of glutathione Peroxides[J]. Science, 1973,179(5):88-90.
|
| [6] |
张明中 . 番茄施硒的生理和品质效应及分子调控研究[D]. 重庆: 西南大学, 2014: 1-2.
|
| [6] |
Zhang M Z . Studies on the effect of selenium on physiological characteristics and qualities of tomato and its molecular regulation[D]. Chongqing: Southwestern University, 2014: 1-2.
|
| [7] |
杨忠芳, 余涛, 侯青叶 , 等. 海南岛农田土壤Se的地球化学特征[J] . 现代地质, 2012,26(5):837-849.
|
| [7] |
Yang Z F, Yu T, Hou Q Y , et al. Geochemical characteristics of soil selenium in farmland of Hainan Island[J]. Geoscience, 2012,26(5):837-849.
|
| [8] |
夏学齐, 杨忠芳, 薛圆 , 等. 黑龙江省松嫩平原南部土壤硒元素循环特征[J]. 现代地质, 2012,26(5):850-858, 864.
|
| [8] |
Xia X Q, Yang Z F, Xue Y , et al. Geochemical circling of soil Se on the Southern Song-Nen Plain, Heilongjiang Province[J]. Geoscience, 2012,26(5):850-858,864.
|
| [9] |
戴慧敏, 宫传东, 董北 , 等. 东北平原土壤硒分布特征及影响因素[J]. 土壤学报, 2015,52(6):1356-1364.
|
| [9] |
Dai H M, Gong C D, Dong B , et al. Distribution of soil selenium in the northeast china plain and its influencing factors[J]. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 2015,52(6):1356-1364.
|
| [10] |
迟凤琴, 徐强, 匡恩俊 , 等. 黑龙江省土壤硒分布及其影响因素研究[J]. 土壤学报, 2016,53(5):1262-1274.
|
| [10] |
Chi F Q, Xu Q, Kuang E J , et al. Distribution of selenium and its inlfuencing factors in soils of Heilongjiang Province[J]. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 2016,53(5):1262-1274.
|
| [11] |
张慧, 马鑫鹏, 李昕阳 , 等. 泰来县耕地土壤硒含量特征及空间分布[J]. 中国农业大学学报, 2018,23(9):100-107.
|
| [11] |
Zhang H, Ma X P, Li X Y , et al. Characteristics and spatial distribution of selenium content in cultivated soils of Tailai County[J]. Journal of China Agricultural University, 2018,23(9):100-107.
|
| [12] |
徐强, 迟凤琴, 匡恩俊 , 等. 方正县土壤硒的分布特征及其与土壤性质的关系[J]. 土壤通报, 2015,46(3):597-602.
|
| [12] |
Xu Q, Chi F Q, Kuang E J , et al. Distribution characteristics of selenium in Fangzheng County and its relationship with soil properties[J]. Chinese Journal of Soil Science, 2015,46(3):597-602.
|
| [13] |
DZ/T 0295-2016 土地质量地球化学评价规范 [S]. 中华人民共和国国土资源部, 北京: 地质出版社, 2016.
|
| [13] |
DZ/T 0295-2016 Specification of land quality geochemical assessment [S]. Ministry of Land and Resources of the People’s Republic of China, Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 2016.
|
| [14] |
谭见安 . 环境生命元素与克山病 [M]. 北京: 中国医药科技出版社, 1996: 1-13.
|
| [14] |
Tan J A. Environmental life element sand Keshan disease [M]. Beijing: China Medical Science Press, 1996: 1-13.
|
| [15] |
刘铮 . 中国土壤微量元素 [M]. 南京: 江苏科学技术出版社, 1996: 21-24.
|
| [15] |
Liu Z. Chinese soil trace elements [M]. Nanjing: Jiangsu Science and Technology Press, 1996: 21-24.
|
| [16] |
Fordyce F M . Selenium deficiency and toxicity in the environment[J]. Essentials of Medical Geology: Revised Edition, 2013: 375-416.
|
| [17] |
张建东, 王丽, 王浩东 , 等. 紫阳县土壤硒的分布特征研究[J]. 土壤通报, 2017,48(6):1404-1408.
|
| [17] |
Zhang J D, Wang L, Wang H D , et al. Distribution of soil total selenium in Ziyang, Shaanxi[J]. Chinese Journal of Soil Science, 2017,48(6):1404-1408.
|
| [18] |
吴文良, 张征, 卢勇 , 等. 江西省丰城市“中国生态硒谷”创意产业的发展战略[J]. 农产品加工: 创新版, 2010(3):72-75.
|
| [18] |
Wu W L, Zhang Z, Lu Y , et al. Expand strategy on creative industry for Chinese ecological Se-tech at Jiangxi Fengcheng[J]. Agricultural Products Processing: Innovational Edition, 2010(3):72-75.
|
| [19] |
Qin H B, Zhu J M, Liang L , et al. The bioavailability of selenium and risk assessment for human selenium poisoning in high - Se areas[J]. Environment International, 2013,52:66-74.
|
| [20] |
王美珠, 章明奎 . 我国部分高硒低硒土壤的成因初探[J]. 浙江农业大学学报, 1996,22(1):89-93.
|
| [20] |
Wang M Z, Zhang M K . A discussion on the cause of high-Se and low-Se soil formation[J]. Journal of Zhejiang Agricultural University, 1996,22(1):89-93.
|
| [21] |
李家熙 . 人体硒缺乏与过剩的地球化学环境特征及其预测 [M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2000, 1-204.
|
| [21] |
Li J X. Geochemical environment and prediction of human selenium deficiency and excess features [M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 2000, 1-204.
|
| [22] |
黑龙江省土地管理局, 黑龙江省土壤普查办公室编. 黑龙江土壤 [M]. 北京: 农业出版社, 1992: 149-179.
|
| [22] |
Land Administration Bureau of Heilongjiang Province, Soil Survey Office of Heilongjiang Province. Heilongjiang soil [M]. Beijing: Agriculture Press, 1992: 149-179.
|
| [23] |
吴俊 . 福建省寿宁县富硒土壤地球化学特征[J]. 物探与化探, 2018,42(2):386-391.
|
| [23] |
Wu J . Geochemical characteristics of selenium-rich soil in Shouning County of Fujian Province[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2018,42(2):386-391.
|
| [1] |
ZHAO Ze-Lin, LI Jun-Jian, ZHANG Tong, NI Zhen-Ping, PENG Yi, SONG Li-Jun. Geological characteristics and prospecting direction of rare earth element deposits in North China[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2022, 46(1): 46-57. |
| [2] |
CHEN Da-Lei, WANG Run-Sheng, HE Chun-Yan, WANG Xun, YIN Zhao-Kai, YU Jia-Bin. Application of integrated geophysical exploration in deep spatial structures: A case study of Jiaodong gold ore concentration area[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2022, 46(1): 70-77. |
|
|
|
|

