|
|
|
| The advantages of AS350B3 helicopter in aerogeophysical survey in the high mountain area |
Jian LI( ), Liang GUO( ), Liang GUO( ), Gang-Yi XIAO, Zhi-Qiang LIU, Ming XU, Jiu-Qiang JIN, Zhi-Bo WANG, Mao-Sheng DENG, Bing LI ), Gang-Yi XIAO, Zhi-Qiang LIU, Ming XU, Jiu-Qiang JIN, Zhi-Bo WANG, Mao-Sheng DENG, Bing LI |
| China Aero Geophysical Survey and Remote Sensing Center for Land and Resources,Beijing 100083,China |
|
|
|
|
Abstract The airborne geophysical exploration flying vessel which performs operation in middle and high mountain areas needs plateau adaptability.Through a comparative study of the characteristics of AS350B3 helicopter in such aspects as its taking off condition,maximum flying altitude,maximum endurance and plateau flexibility,the authors put forward the type-choosing principle and flying method of the airborne geophysical exploration flying vessel for low altitude and large scale survey.The practical surveying flying in a certain surveying area of Gansu Province has proved the feasibility of the principle and method put forward by the authors.Analysis shows that AS350B3 helicopter can meet the requirement of airborne geophysical exploration in such areas.
|
|
Received: 25 August 2016
Published: 20 February 2018
|
|
|
|
|
|

|
|
|

|
|
|

| 总重量/kg | 1600 | 1800 | 2000 | 2220 | 2250 | 2370 | | 续航能力(无余油) | 3h07min | 4h57min | 4h44min | 4h31min | 4h28min | 4h20min | | 最大航程(无余油)/km | 411 | 699 | 664 | 654 | 650 | 642 | | 升限(ISA)/m | >7000 | >7000 | 6096 | 5242 | 5044 | 4556 | | 爬升率/(m/s) | 12.1 | 11.9 | 11.2 | 10.3 | 10.0 | 9.2 | | 快速巡航下的油耗/(kg/h) | 174 | 174 | 174 | 174 | 174 | 174 | | 推荐巡航速度/(km/h) | 226 | 226 | 226 | 226 | 226 | 226 |
|
|
|

最大巡航公里数/km
(可用载荷时最大燃油1 604 lb) | 2758 | | 远程巡航速/(km/h) | 435 | | 最大巡航时间/h | 6.34 | | 高速巡航速度/(km/h) | 578 | | 满载最短起飞跑道长度(海平面)/m | 1006 | | 满载最短起飞跑道长度(海拔1 500 m)/m | 1639 | | 满载着陆距离/m | 729 | | 双发爬升率(襟翼收上)/(m/s) | 13.8 | | 单发爬升率(起飞襟翼)/(m/s) | 2.8 | | 取证升限/m | 10668 | | 双发升限/m | 10668 | | 单发升限/m | 6553 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|

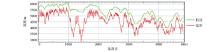
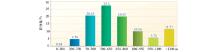
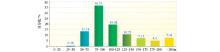
| 高度范围/m | 测点数/个 | 百分比/% | | 0~200 | 2 | 0.04 | | 200~350 | 229 | 4.76 | | 350~500 | 993 | 20.63 | | 500~650 | 1314 | 27.30 | | 650~800 | 959 | 19.93 | | 800~950 | 484 | 10.06 | | 950~1100 | 277 | 5.76 | | >1100 | 555 | 11.53 | | 平均高度:725 | 总测点数: 4813 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|

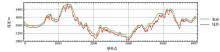
| 高度范围/m | 测点数/个 | 百分比/% | | 0~50 | 19 | 0.38 | | 50~75 | 663 | 13.43 | | 75~100 | 1804 | 36.53 | | 100~125 | 962 | 19.48 | | 125~150 | 531 | 10.75 | | 150~175 | 351 | 7.11 | | 175~200 | 242 | 4.90 | | >200 | 366 | 7.41 | | 平均高度:116 | 总测点数: 4938 |
|
|
|

|
|
|

|
|
|

| 总重量/kg | 1600 | 1800 | 2000 | 2220 | 2250 | 2370 | | 续航能力(无余油) | 3h07min | 4h57min | 4h44min | 4h31min | 4h28min | 4h20min | | 最大航程(无余油)/km | 411 | 699 | 664 | 654 | 650 | 642 | | 升限(爬升率=1 m/s)/m | >7000 | >7000 | 6096 | 5242 | 5044 | 4556 | | 爬升率/(m/s) | 12.1 | 11.9 | 11.2 | 10.3 | 10.0 | 9.2 |
|
|
|

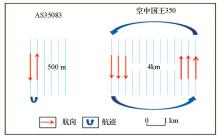
| 型号 | AS350B3 | 空中国王350 | | 作业速度/(节/h) | 100 | 215 | 转弯半
径/m | 坡度角15° | 1006 | 4690 | | 坡度角25° | 579 | 2697 | | 坡度角30° | 467 | 2178 |
|
|
|
|
|
|

|
|
|
| [1] |
熊盛青. 发展中国航空物探技术有关问题的思考[J].中国地质,2009,36(6):1366-1374.
|
| [2] |
许苏鹏,姬泰脉,纪福山,等.AS350B3型直升机硬架航空磁测系统在青藏高原上的应用[J].物探与化探,2013,37(4):640-644.
|
| [3] |
崔志强,胥值礼,孟庆敏.国内主要航空物探飞行平台特点及发展[J].物探与化探,2014,38(6):1107-1113.
|
| [4] |
赵济,陈传庚.中国地理[M].北京:高等教育出版社,1997.
|
| [5] |
鄂国庆,徐英哲,李文杰.固定翼时间域航空电磁系统的选型问题[J].物探与化探,2012,36(4):595-597.
|
| [6] |
牟艳彬. 高原航空天气特征和航空气象服务保障[J].四川气象,2007,27(2):26-31.
|
| [7] |
王金龙,谢汝宽,梁韧,等.高海拔山区航空地球物理飞机选型与飞行性能分析[J].物探与化探,2017,41(3):556-559.
|
| [8] |
熊盛青,周伏洪,姚正熙,等.青藏高原中西部航磁调查[J].物探与化探,2007,31(5):404-407.
|
| [9] |
熊盛青,周伏洪,姚正熙,等.青藏高原中西部航磁调查[M].北京:地质出版社,2001.
|
| [10] |
AS350B3操作手册 EUROCOPTER 350B3 13.101.01E.
|
| [11] |
空中国王350(Kingair-350)操作手册 Beechcraft Kingair-350 TM/SF-200.
|
| [12] |
于长春,熊盛青,刘士毅,等.直升机航磁方法在大冶铁矿区深部找矿中的见矿实例[J].物探与化探,2010,34(4):435-439.
|
| [13] |
薛典军. 航磁测量中飞行高度质量控制的方法技术[J].物探与化探,2001,25(4):253-258.
|
| [14] |
熊盛青,于长春,眭素文,等.中高山区高精度航磁测量方法[M].北京:地质出版社,2009.
|
|
|
|

