0 引言
在深埋隧道的地质勘探中应用综合物探方法,能够从多个角度对同一目标体进行描述,这种方式使解释结果更贴近实际地质情况[5
乐山至西昌高速公路马边至昭觉段的大风顶隧道位于四川省凉山彝族自治州雷波县,隧道全长5 696 m,最大埋深1 006 m,是典型的深埋特长隧道,具有埋深大、山体宽厚等特点,其地形地貌、地层岩性及水文地质条件极为复杂。区域地震活动性较高,地震基本烈度为Ⅶ度,属强震区。在详细分析区域地质情况的基础上,针对大风顶隧道勘查的重难点,本文采用音频大地电磁测深和高密度电法数据进行综合物探分析。通过充分发挥各种物探方法的优势,全面查明了隧址区整体地质情况,重点详查隧道洞口的地质特征。多种勘查方法的相互补充和验证,有效地解决了单一物探方法“多解性”的问题,提升了勘查的精度和效率。在此基础上,进一步分析了区域内不同程度岩石破碎带对周边地震活动的响应特性,为隧道设计与施工提供了可靠的地质信息,同时也为制定更有针对性的防震措施提供了理论依据。
1 研究区概况
1.1 地质概况
大风顶隧道位于四川省凉山彝族自治州雷波县北西方向,与雷波县城直线距离约30 km。区域海拔在2 000~3 000 m之间,地形深切,主要呈SN向和EW向的大型深沟,为构造剥蚀型高中山地貌区。
研究区位于川滇SN向构造带与四川盆地新华夏系沉降带交接处,SN向构造带自马边县刹水坝、森捏罗向南延伸至雷波大谷堆、马颈子及牛牛寨一带,宽度约5~6 km,主要由褶皱和断裂组成。褶皱以向斜和背斜为主,形成复式紧密褶皱,轴面多为直立或高角度西倾,少数东倾,部分轴部或翼部不完整。区域内主要断层包括刹水坝—马颈子断层、上田坝断层、硝滩断层和猴儿沟断层,呈平行排列,局部呈叠瓦状,以压性和压扭性为主。区域新构造运动强烈,表现为强侵蚀的峡谷山丘地形,以及夷平面、多级阶地、瀑布、跌水分布,古滑坡和地震活动频繁,断层复活现象明显。隧道场地未穿越区域性断裂,但岩层产状变化频繁,地质构造较为复杂,新构造运动强烈,地震基本烈度为Ⅶ度区,属Ⅱ类场地。
大风顶隧道场地内部地层复杂,包含多种岩性,且结构不均,局部存在溶蚀和断层现象,主要包括新生界第四系、中生界和古生界的多个地层。第四系地层包括残坡积碎石角砾土、崩坡积碎块石土和冲洪积泥砾卵石土,结构松散,厚度变化显著。中生界三叠系主要岩性为灰岩、砂岩和粉砂质泥岩,局部溶蚀裂隙发育,岩质坚硬。二叠系上统峨眉山组为玄武岩,质地坚硬,节理发育;宣威组为泥质砂岩夹煤线。志留系龙马溪组为钙质泥岩和炭质页岩,岩质较软。奥陶系巧家组为灰岩、泥质灰岩,岩质较硬,结构完整,具有较好的稳定性。
长河断层位于大谷堆—西苏角一带,全长约37 km,宽约10~15 m,总体呈NW向展布。该断层北段位于测区西部区域,主要发育于三叠系地层之中,断层走向为NNW向,属左行—逆冲断层。谷堆向斜位于雷波大谷堆乡,呈NW方向延伸,长度约21 km,宽度3~7 km。该褶皱由上二叠统至下侏罗统组成,形态不对称,东翼陡峭(50°~70°),西翼缓和(30°~50°),轴面约80°倾向东,区域构造活动复杂。通过区域地质资料分析和初步地质调绘,初步判定隧址区主体构造为大风顶背斜。背斜地层包括二叠系和志留系,两翼不对称分布于新地层。
隧址区降水较丰富,地表水体稀少,主要通过溪沟排泄,可划分为两个水文地质单元。以马捏姑河为排泄基准面,主要为垂直循环带;以马颈子—刹水坝断层为界,涵盖水平循环与垂直循环的交汇区域。隧道穿越雷口坡组岩溶裂隙含水层,厚度较薄,较少涌水。
1.2 地球物理特征
隧址区内主要岩(矿)石的电性测试结果(表1)显示,区内不同岩石类型之间展现出明显的电阻率差异;同时较完整岩体与充水破碎带、软弱岩体及断层破碎带之间也存在明显的电性差异。这为后续的区分地层岩性,划分断层破碎带等构造提供了良好的物性基础。
表1 隧址区矿物电阻率范围统计
Table 1
| 岩性 | ρ/(Ω·m) | 岩性 | ρ/(Ω·m) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 灰岩 | 500~6000 | 白云岩 | 200~3000 |
| 砂岩 | 100~2000 | 碳质页岩 | 100~2000 |
| 粉砂岩 | 50~1000 | 玄武岩 | 1500~8000 |
2 勘查方法与工作布置
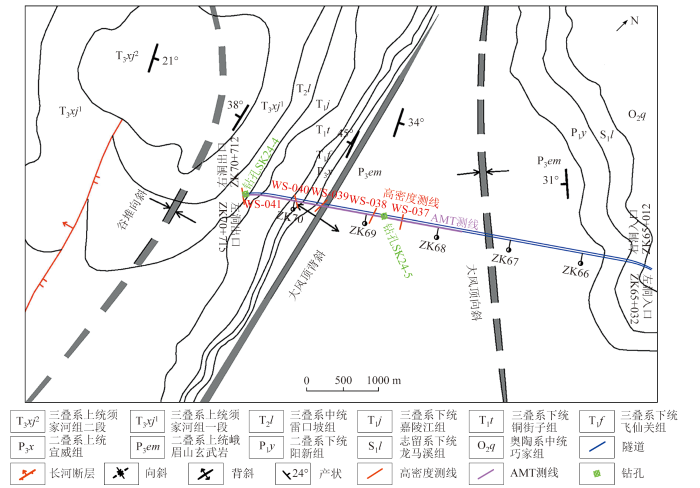
大风顶隧道为分离式隧道,左线起止桩号为 ZK65+032~ZK70+715,全长5 683 m,右线起止桩号桩号为(ZK65+012)~(ZK70+712),全长5 700 m;最大埋深达到1 006 m,是一条典型的深埋特长隧道,区域地形地貌、地层岩性、地质构造和水文地质条件复杂。因此,在区域地质分析和初步地质调绘的基础上,明确主体构造形式,并进一步通过轴线物探、构造分析,以构建隧址区的构造格架。
图1
图1
隧址区地质构造及物探测线示意
Fig.1
Schematic of geological structures and geophysical survey lines in the tunnel area
音频大地电磁法的采集工作使用美国EMI公司生产的EH4 连续电导剖面仪,属于混合源方法的仪器,利用的场源可以是天然场,也可以是人工场。工作频率设定10~1 000 Hz范围内,采集天然电磁场信号,可测量地下几米至1 km范围内介质电阻率的连续分布。高密度电法采用深圳市赛盈地脉技术有限公司和北京桔灯地球物理勘探有限公司研发生产的GD-10 分布式高密度电法系统。由于测区地形起伏大,为降低地形起伏的造成的干扰,工作时主要以温纳排列装置为主,MN的距离与AB距离保持1∶3的关系。
在AMT数据采集过程中,系统实时监测了4个相关分量的振幅、相位及视电阻率曲线,以确保信号质量。当信号较弱或视电阻率曲线出现较大波动时,采取增加迭加次数或延长记录时间等手段,以增强数据的信噪比。此外,大部分野外测点采用十字型布设,确保电极的接地电阻不大于2 000 Ω,并通过加水或垫土等措施优化电极接地条件。在测量过程中,定期检查测点质量,确保数据连续性并避免脱节现象。对于较难测量的点位,采用不同电压进行复测,最大限度地排除外部干扰。
在高密度电法勘探中,布设电极时确保其接触良好,避免电极悬空或接地不均。在测量过程中,如出现异常现象,立即对电极连接与接地情况进行检查,以确保接收信号的稳定性。为提高数据的可靠性,采用了延长采集时间和增加采样点数等手段。测量完成后,即时进行现场数据处理,发现并纠正问题,以确保勘测数据的质量。
针对地形的起伏程度、大气条件及电磁干扰源情况,在勘探前不仅进行了详细的踏勘,并根据实际情况制定了合理的施工方案,以避免高压输电线及居民电器设备的电磁干扰。此外,在冰雪天气条件下,采取了防寒、防潮等措施,以保障设备与人员的安全,从而确保数据采集的顺利进行和有效性。
3 勘探结果与分析
3.1 资料处理
在AMT资料处理过程中,对时间序列数据进行了再处理。首先,逐段筛选采集的时间序列数据,剔除含有干扰信号的时间段,以减少噪声对数据质量的影响。随后,使用采集软件对筛选后的数据进行重新处理,以确保大地电磁响应的质量。此外,通过阻抗张量分解,识别了地下构造的复杂性及其走向特征。大部分测点在频段范围内表现出二维构造特征,且与测线方向近乎垂直。因此,采用二维共轭梯度反演法,通过联合反演视电阻率和阻抗相位数据,获得最佳拟合的地下电性模型。在反演过程中,选择测线方向作为剖面方向,以确保反演结果能够准确反映与区域二维构造平行和垂直的电磁响应。
在高密度电阻率法资料预处理阶段,对原始数据进行了质量控制,剔除坏点、进行数据拼接并实施地形校正,以消除外部因素对数据质量的干扰,确保数据的准确性与一致性。结合已有的地质信息,使用瑞典Res2dinv高密度电法数据处理与解释软件进行反演分析,得到视电阻率成像断面图,揭示了地下不同层次的电性分布及其结构特征,为后续的地质分析与区域构造研究提供了重要依据。
3.2 岩石电性特征分析
由于区域内岩石种类较多,不同的岩石物性差异大,因此结合各类岩石的物性特征和岩石破碎情况,对围岩划分标准细分如表2所示。
表2 各岩类解释划分标准
Table 2
| 地质 背景 | 推断解释 | ρs/ (Ω·m) | lg[ρs/ (Ω·m)] | 围岩 级别 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 碳酸盐岩地层 | 极破碎、富水溶洞 | ≤50 | ≤1.7 | V |
| 风化破碎、溶蚀发育区 | 50~2200 | 1.7~2.3 | IV | |
| 弱风化带岩石 | 200~700 | 2.3~2.8 | III | |
| 微风化、完整坚硬岩石 | ≥700 | ≥2.8 | II | |
| 碎屑岩地层 | 极破碎、富水岩石 | ≤50 | ≤1.7 | V |
| 破碎、富水性强、强风化带 | 50~200 | 1.7~2.3 | IV | |
| 较破碎、富水性中、弱风化带 | 200~500 | 2.3~2.7 | III | |
| 富水性弱、微风化带 | ≥500 | ≥2.7 | II | |
| 火山岩地层 | 岩石破碎、极软弱或 富水岩体 | ≤300 | ≤2.5 | V |
| 破碎、软弱或含水岩体 | 300~1000 | 2.5~3 | IV-V | |
| 较破碎、富水性中到弱 | 1000~2000 | 3~3.3 | IV | |
| 岩体较完整、富水性弱 | ≥2000 | ≥3.3 | III |
3.3 音频大地电磁测深法成果解释
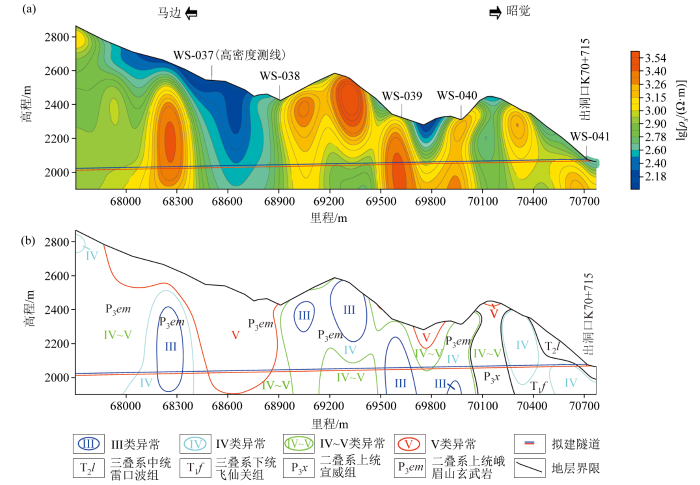
勘测段为大风顶隧道左线中部偏出口段方向(图2),其地层岩性主要为两段。出口段为碎屑岩和碳酸盐岩,岩性主要为砂岩、粉砂岩、岩屑砂岩等以及雷口坡组的白云岩和白云质灰岩;洞身大部分为二叠系峨眉山玄武岩。出口段(昭觉方向)视电阻率在200~1 500 Ω·m之间;洞身段视电阻率100~3 500 Ω·m,电性变化大。
图2
图2
大风顶隧道左线AMT视电阻率断面(a)岩性异常分类剖面(b)
Fig.2
AMT apparent resistivity section of the left line of Dafengding tunnel (a) lithological anomaly classification profile (b)
1)(ZK67+677)~(ZK68+912)段主要发育有峨眉
山玄武岩。其中,(ZK67+677)~(ZK68+157)段低电阻率特征反映了显著的岩体破碎以及中等的含水性,为IV~V类异常。(ZK68+307)~(ZK68+367)段,围岩电阻率稳定在高值区,展现出较好的岩体完整性及较弱的富水性,岩体较为稳定。(ZK68+367)~(ZK68+912)段,低电阻率的特征尤为明显,表明此处的岩石极破碎,存在丰富的导水条件。
2)(ZK68+912)~(ZK69+996)段主要发育有峨眉山玄武岩,视电阻率值整体变化幅度较大,高阻值多呈半圈闭和圈闭近直立状由地表延伸至深部。其中,(ZK69+117)~(ZK69+432)段围岩视电阻率在上部高阻出现两处较明显的错断现象,向下分别对应凹字形东西两支,结合地质资料分析,该段可能为背斜轴部,岩体裂隙发育。(ZK69+697)~(ZK69+773)段的围岩视电阻率在900~1 000 Ω·m之间,整体曲线呈凹字状,表明存在负地形和沼泽分布。
3)(ZK69+996)~(ZK70+651)段地层由东至西发育有二叠系上统宣威组,岩性组合为灰绿色岩屑砂岩、炭质页岩及薄煤层等;三叠系下统飞仙关组,岩性组合为细粒岩屑砂岩、粉砂岩、泥岩等。电阻率在400~1 000 Ω·m之间,显示出明显的西倾趋势,推断为IV~V类异常,围岩破碎且富水性中等。
4)(ZK70+651)~(ZK70+715)段为隧道出口段,发育有三叠系中统雷口坡组,岩性组合为白云岩、灰岩等。隧道围岩视电阻率在500~1 000 Ω·m之间。推断该段为IV~V类异常,围岩破碎且富水。
3.4 高密度电法成果解释
通过WS-037~WS-041高密度测线结果与AMT视电阻率反演结果(图1a)的对比验证,可以获得浅部高精度的视电阻率分布,特别是在洞口附近的详细视电阻率特征,为洞口开挖工作提供了详细的地质资料,以提升施工的安全性。
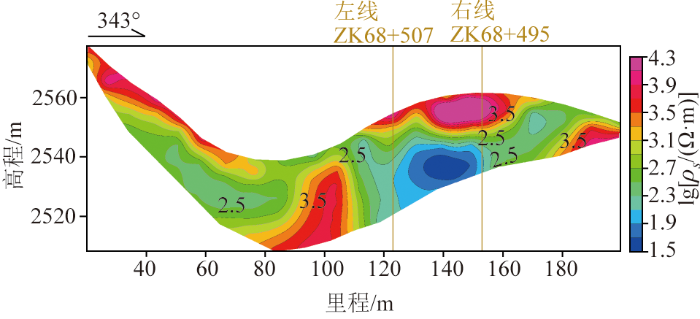
1)隧道左右两线视电阻率值(图3)表现为浅部高阻,深部低阻。浅部的高阻视电阻率值在3 200 Ω·m以上,推测为地表玄武岩碎块堆积影响。深部低阻视电阻率值在50~100 Ω·m,向下无收敛迹象,与AMT成果显示的低阻异常吻合,推测为柱状节理发育的玄武岩岩体。
图3
图3
大风顶隧道左线ZK68+507处WS-037高密度电法视电阻率断面
Fig.3
High-density apparent resistivity profile at ZK68+507 (WS-037) for the left line of the Dafengding tunnel
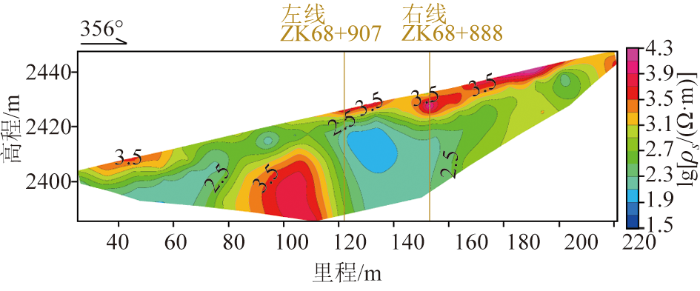
2)隧道左右两线视电阻率值(图4)表现为浅部偏高阻,深部偏低阻。浅部偏高阻呈平行于地形的条带状展布,推测为地表乱石堆积层的反映。深部偏低视电阻率值在200~600 Ω·m,呈近似直立的半圈闭状展布。AMT对应为近直立的条带状偏低阻,视电阻率值在600~800 Ω·m,两者较为吻合,推测该段为柱状节理较发育的玄武岩。
图4
图4
大风顶隧道左线ZK68+907处WS-038高密度电法视电阻率断面
Fig.4
High-density apparent resistivity profile at ZK68+907 (WS-038) for the left line of the Dafengding tunnel
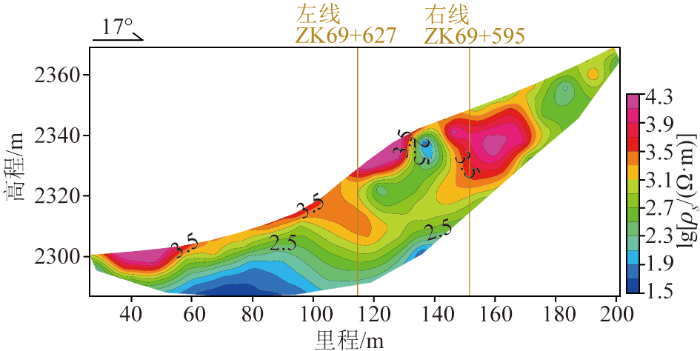
3)隧道左右线视电阻率(图5)表现为上中部高阻,向下视电阻率值逐渐降低。右线AMT显示视电阻率值在1 000~1 500 Ω·m之间,两者比较吻合,推测可能为较完整的玄武岩。而左线60~100 m范围,深部低视电阻率区域逐渐扩大,向下无收敛趋势,视电阻率值在50~100 Ω·m,推测低阻值区可能与AMT在 WS-039处左右两端邻近的浅地表显示的低阻异常相同,为富水破碎的玄武岩。
图5
图5
大风顶隧道左线ZK69+627处WS-039高密度电法视电阻率断面
Fig.5
High-density apparent resistivity profile at ZK69+627 (WS-039) for the left line of the Dafengding tunnel
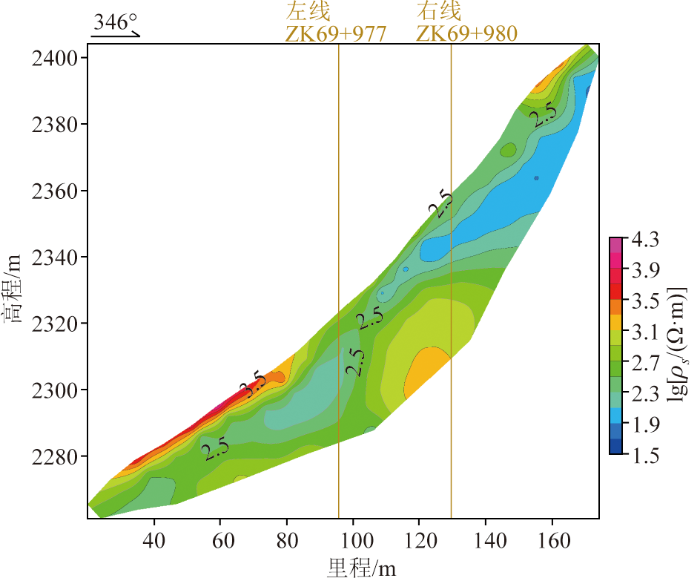
4)图6中隧道左右线范围内浅部视电阻率较低,深部视电阻率逐渐升高,电阻率高值约为850 Ω·m,AMT显示视电阻率值在1 200~1 500 Ω·m之间,两者较为吻合,推测深度可能为较完整的玄武岩。
图6
图6
大风顶隧道左线ZK69+977处WS-040高密度电法视电阻率断面
Fig.6
High-density apparent resistivity profile at ZK69+977 (WS-040) for the left line of the Dafengding tunnel
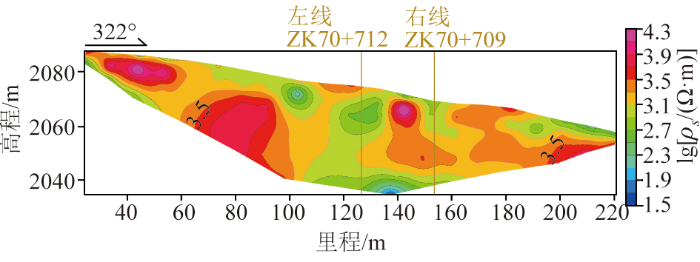
5)隧道左右两线整体视电阻率值(图7)在800~1 000 Ω·m,AMT视电阻率值在500~900 Ω·m范围,两者较为吻合。左线位置在高程2 065 m左右,视电阻率值在500 Ω·m左右,推测可能为含砂砾石的溶洞;而左右线正下方高程2 040 m处,视电阻率值在50~200 Ω·m,推测可能为含水溶洞。
图7
图7
大风顶隧道左线ZK70+712处WS-041高密度电法视电阻率断面
Fig.7
High-density apparent resistivity profile at ZK70+712 (WS-041) for the left line of the Dafengding tunnel
4 钻探验证
为进一步验证以上推断的准确性,在分析收集隧道地质资料和综合物探工作成果后,于隧道左线ZK70+670处布置SK24-4钻孔;左线ZK68+746处布置SK24-5钻孔(图1)。
SK24-4钻孔位于左线出洞口附近,孔深60.4 m,物探推断该处为IV~V类异常,围岩破碎且富水。SK24-4岩芯0~0.9 m为粉质黏土;0.9~60.4 m为中风化灰岩,节理裂隙较发育,岩芯较完整,节理长10~60 cm,含方解石脉和少量溶孔。钻孔验证结果与物探推断结果基本吻合。
SK24-5钻孔孔深209.4 m,该处低电阻率的特征尤为明显,物探推断此处岩石极破碎,存在丰富的导水条件。SK24-4岩芯0~8 m为碎石,母岩主要为玄武岩;8~29.7 m为块石,呈松散—稍密状,母岩成分以玄武岩为主,粒径20~150 cm,以碎石泥质充填;29.7~147.5 m为玄武岩,整体发育两组节理,倾角分别为85°和63°,岩体较破碎,节理裂隙发育;147.5~157.4 m为凝灰岩,岩质极软,岩体极破碎,岩芯以扁柱状、大块状为主。157.4~209.4 m为玄武岩,岩体较完整,岩芯以短柱状为主,夹大块状(节理裂隙发育),节长5~15 cm。钻孔验证结果与物探推断一致,进一步验证了综合物探在岩性异常分类及构造识别中的准确性。
5 结论
通过结合可控源音频大地电磁和高密度电阻率法,揭示隧道区域的整体视电阻率分布及洞口附近的精细电性特征,从而进一步推断隧道区域岩体的破碎程度及富水性特征,为隧道抗震支护设计提供理论依据。此外,借助多种物探技术的相互验证,同时结合钻孔验证,提高了勘查结果的可靠性和准确性。
综合物探结果评估了隧道区域岩体的破碎程度和富水性特征,而岩石破碎程度决定了岩体的抗震能力,验证了综合物探在地震活动影响评估中的有效性,为在类似山岭强震区特长深埋隧道勘查和建设提供了借鉴。
参考文献
西部区域重大交通基础设施互联互通协同发展的挑战与推进路径
[J].
Challenges and paths to coordinated development of regional mega-transportation infrastructure interconnection in the western region
[J].
截至2023年底中国10 km以上特长公路隧道统计与分析
[J].
Statistics and analysis of super-long highway tunnels over 10 km in China by the end of 2023
[J].
西部山区深埋特长公路隧道综合勘查技术研究
[J].
Research on comprehensive survey technology of deep-buried and extra-long highway tunnels in western mountainous areas
[J].
我国西南部山区隧道施工期支护结构力学行为特征案例分析
[J].
Cases analysis of mechanical behavior characteristics of tunnel supporting structure in mountainous areas in southwest China
[J].
综合物探方法在复杂地质条件下公路隧道勘查中的应用
[J].
Application of comprehensive geophysical methods in highway tunnel investigation under complex geological conditions
[J].
瞬变电磁法指导复杂地质隧道超前水平钻探应用
[J].
The application of TEM to guiding advance exploration drilling of complex geological tunnel
[J].
西部山区公路隧道音频大地电磁正演研究
[J].
Study on audio magnetotelluric forward of highway tunnel in mountainous area of western China
[J].
广域电磁法在深埋隧道勘查中的应用研究
[J].

研究目的: 广域电磁法是一种适应艰险复杂山区勘察并满足工程勘察精度要求的大深度勘察方法,本文通过对广域电磁法基本原理和特点的分析,并通过九天山隧道多测线的勘察应用以及与音频大地电磁法和大地电磁法的成果对比,旨在研究广域电磁法在艰险复杂山区深埋隧道勘察中的效果。研究结论: (1)广域电磁法在本次勘察中,有效深度达到2.8 km,完全满足大深度隧道勘察的需要;(2)本次工作最大发射电流达到20 A,对地形和地表不均匀体产生的静态效应进行了较好的压制;(3)通过和大地电磁法(MT)以及音频大地电磁法(AMT)的对比,浅部信息比AMT丰富,深部信息比MT丰富,纵向分辨率提高很多,可以实现大深度隧道全范围的精细化勘察;(4)广域电磁法有效进行了地层的精细化划分,推断了构造位置与倾向,提示了软弱风险区,适用于艰险复杂山区深埋隧道地质勘察。
Application research on the wide field electromagnetic method for deep-buried tunnel investigation
[J].

<b>Research purposes:</b> The wide field electromagnetic method(WFEM) is a kind of large depth survey method which is suitable for difficult and complex mountainous area exploration and meet the requirement of engineering survey precision. Based on the analysis of the basic principles and characteristics of WFEM, through the investigation of the multi-line in Jiutianshan Tunnel and the comparison with the results of the audio magnetotelluric method(AMT) and magnetotelluric method(MT), this paper aims to study the effect of WFEM in deep buried tunnel exploration in difficult and complex mountainous areas.<br><b>Research conclusions:</b> (1) The effective exploration depth was 2.8 km in this survey, which fully met the needs of large-depth tunnel exploration. (2) The maximum emission current adopted in this survey reached 20 A, which made a good suppression of the static effects caused by terrain and surface unevenness. (3) Compared with the magnetotelluric method (MT) and the audio magnetotelluric method (AMT), the shallow information of WFEM is richer than that of the AMT and the deep information of WFEM is richer than that of the MT. The vertical resolution is much improved, which can realize the full-scale detailed survey of the large-depth tunnel. (4)The WFEM effectively carried out the fine division of the stratum, inferred the structural position and tendency, and suggested the weak risk zone, which is applicable to the geological exploration of deep-buried tunnels in difficult and complex mountainous areas.
隧道勘查中的综合物探方法
[J].
The comprehensive geophysical survey in tunnel exploration
[J].
综合物探技术在隧道勘查中的应用研究
[J].
Application and study of comprehensive geophysical prospecting methods in the geotechnical investigation of tunnel
[J].
综合物探在新兴都斛铜矿床勘查中的应用
[J].
Application of comprehensive geophysical prospecting in exploration of the Duhu copper deposit in Xinxing County
[J].
综合物探技术在云南龙堡隧道地层勘查中的应用研究
[J].
Research on the application of comprehensive geophysical techniques in stratigraphic survey of Longbao tunnel in Yunnan province
[J].
基于水文地质综合勘查的隧道导水特性研究
[J].
DOI:10.20174/j.JUSE.2024.04.28
[本文引用: 1]

深埋特长隧道是高速公路建设中的关键控制性工程,查明水文地质条件和准确预测涌水量是保证施工安全的重要前提。本文以拟建的深圳外环高速公路三期工程田头山隧道为例,采用水文地质测绘、物探、钻探、水文地质试验和室内试验相结合的水文地质综合勘察方法,对隧道围岩分段分级、富水段落划分、涌水量预测等方面进行了分析研究。隧道经过向斜轴部地段,为良好的储水构造,富水段落集中在K84+680~K84+840,预测在施工时将产生大涌水,将此范围洞身段划为Ⅴ级围岩,判定为主要导水岩体;隧道受断裂构造影响,富水段落中的断层带及宽张裂隙将会成为重要导水通道。进一步,在获取隧址区典型深度段岩体的渗透系数后,分别采用降水入渗系数法、裘布依理论式及古德曼经验式对隧道涌水量展开预测,表明水文地质综合勘察方法可以很好地评估隧道导水特性及估算涌水量。
Study on water diversion characteristics of tunnel based on hydrogeological comprehensive investigation
[J].
DOI:10.20174/j.JUSE.2024.04.28
[本文引用: 1]

Deep-buried long tunnel is a key control project in highway construction. Identifying hydrogeological conditions and accurately predicting water inflow are important prerequisites for ensuring construction safety. This paper takes the Tiantoushan tunnel of the third phase project of Shenzhen outer ring expressway as an example, and uses the hydrogeological comprehensive survey method combining hydrogeological surveying and mapping, geophysical prospecting,drilling, hydrogeological test and indoor test to analyze and study the segmentation and classification of tunnel surrounding rock,the division of water-rich sections,and the prediction of water inflow. The tunnel passes through the synclinal axis section,which is a good water storage structure. Geophysical exploration also shows that the water-rich section is concentrated in K84 + 680 ~ K84 + 840. It is predicted that large water gushing will occur during construction. The tunnel section in this range is divided into V-level surrounding rock,which is determined as the main water-conducting rock mass. At the same time, the tunnel is affected by the fracture structure,and the fault zone and wide tensile cracks in the water-rich section will become important water-conducting channels. Furthermore,after obtaining the permeability coefficient of the rock mass in the typical depth section of the tunnel site,the tunnel water inflow is predicted by using the precipitation infiltration coefficient method,the Dupuit theoretical formula and the Goodman empirical formula respectively,indicating that the hydrogeological comprehensive survey method can well evaluate the tunnel water conductivity characteristics and estimate the water inflow.
综合物探技术在北京延庆松山隧道勘查中的应用
[J].
Application of integrated geophysical exploration technology to the survey of the Songshan tunnel in Yanqing,Beijing
[J].
长大深埋隧道勘查中的综合地球物理方法应用研究
[J].
DOI:10.6038/pg2024II0089
[本文引用: 1]

作为市域铁路全线岩土工程勘察的重难点之一,山岭隧道勘察常采用地质测绘、钻探与物探相结合的方式,而长大深埋隧道由于其复杂的地质地貌条件和外部环境,单一的物探方法存在一定的技术局限性,因此,需要多种物探技术进行综合勘察.在宁波西舟岭隧道勘察中,采用瞬态面波法、高密度电法和地震共振频率成像法相结合的综合物探技术,取得了较好的勘察成效,为后续工程设计、施工提供了可靠的工程地质依据.研究和实践表明,瞬态面波法能精确查明隧道覆盖层的厚度,高密度电法能有效查明浅埋段断层破碎带等地质问题,而地震共振频率成像法能有效弥补瞬态面波和高密度电法对深部地下介质探测的短板,三种物探方法起到了较好的相互补充和验证作用.
Application research of integrated geophysical methods in long and deeply-buried tunnel exploration
[J].
DOI:10.6038/pg2024II0089
[本文引用: 1]

As one of the key and difficult geotechnical engineering surveys of the suburban railway lines, the survey of mountain tunnels usually adopts the combination of geological survey, drilling and geophysical prospecting, however, there are technical limitations of single geophysical method due to the complicated geological and geomorphological conditions and external environment of long and deeply-buried tunnels, multiple geophysical prospecting techniques are needed for comprehensive exploration. The integrated geophysical prospecting technology combining the transient surface wave method, the high-density resistivity method and the seismic resonant frequency imaging technology are used in the survey of Xizhouling tunnel in Ningbo, and a satisfactory survey result is achieved, which provides a reliable engineering geological basis for the subsequent engineering design and construction. Research and practice show that the transient surface wave method can accurately ascertain the thickness of the tunnel cover layer, the high-density resistivity method can identify the geological problems like shallow-buried sections and fault fracture zones of the tunnel effectively, and the seismic resonant frequency imaging technology can effectively make up for the shortcomings of transient surface wave and the high-density resistivity method for deep underground media detection. The three geophysical prospecting methods are mutually complementary and verified quite well.
音频大地电磁在长大深埋隧道勘探中的研究与应用
[J].
Research and application of audio magnetotelluric in deeply-buried tunnel exploration
[J].
吊脚楼隧道断裂构造识别与定位:来自音频大地电磁测深的证据
[J].
Identification and location of fracture sturcture in Diaojiaolou tunnel:Evidence from audio-frequency magnetotelluric sounding AMT survey
[J].
高密度电阻率法在余凯高速公路岩溶隧道浅埋段地质探测中的应用研究
[J].
Study on the application of high density resistivity method in geological exploration of shallow buried section of Yukai Expressway Karst tunnel in Yu Kai Expressway
[J].
改进电测深法探测山区深埋隧道隐伏构造
[J].
Improved electric sounding method for detecting concealed structures in deep-buried tunnels in mountainous areas
[J].
高密度电法和音频大地电磁测深法在西南岩溶地区地下水勘探中的应用
[J].
Application of high-density electrical resistivity tomography and audio magnetotellurics for groundwater exploration in the karst area in southwestern China
[J].
高密度电法与音频大地电磁法在城市输水隧洞勘查中的应用
[J].
Application of multi-electrode resistivity method and audio-frequency magnetotelluric method in the investigation of urban water tunnel
[J].