0 引言
倒谱分析自1963年由Bogert等[7]用于识别核爆炸和地震信号以来,目前已被广泛应用于地震子波的恢复、地震道的去卷积、微地震和遥感事件分析、地层厚度预测以及烃类检测[4,6,8⇓⇓⇓⇓⇓-14]。2011年,曹俊兴等[1]借鉴声纹识别方法将倒谱分析应用于地震信号谱分解技术,并发展了基于倒谱分析算法的烃类检测方法,命名为地震纹分析法。近年来随着倒谱概念的发展,倒谱已经由早期的以傅里叶变换为核心运算的功率倒谱[7,15],复倒谱[16]和实倒谱拓展到核心运算为小波包变换的小波包倒谱[17],从而,地震信号的倒谱分解技术也包括基于傅里叶变换的倒谱和基于小波包变换的倒谱几种形式。地震信号倒谱分解技术具有较常规频谱分解技术更高的时空分辨率,能够给出更好的成像效果和计算精度。
我们将基于傅里叶变换的倒谱分解技术和基于小波包变换的倒谱分解技术应用于顺北地区超深层碳酸盐岩储层地震数据,对比两种方法谱分解的特性,并对两种方法含气性检测的结果进行对比分析。
1 地震数据倒谱分解理论
1.1 基于傅里叶变换倒谱的地震倒谱分解技术
式中:F、F-1为傅里叶正、反变换;c(n)为倒谱序列;x(n)为地震信号。
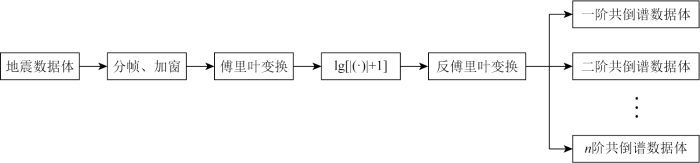
图1
图1
基于傅里叶变换倒谱的地震数据倒谱分解技术流程
Fig.1
Flow chart of seismic data cepstrum decomposition technology based on Fourier-based cepstrum
1.2 基于小波包倒谱的地震倒谱分解技术
式中:
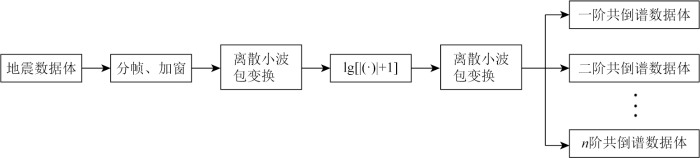
图2
图2
基于小波包变换倒谱的地震数据倒谱分解技术流程
Fig.2
Flow chart of seismic data cepstrum decomposition technology based on wavelet-based cepstrum
式中:
1.3 基于倒谱的烃类检测算法
式中:
式中:
地震幅度异常剖面
由于基于倒谱的烃类检测算法中包含了对数操作,它会增强弱孔隙流体响应,通过算法中去除平均振幅信息又抑制了骨架信息,因此,基于倒谱的烃类检测算法是一种弱信号检测方法,有利于超深层碳酸盐岩储层烃类检测。
2 模型测试
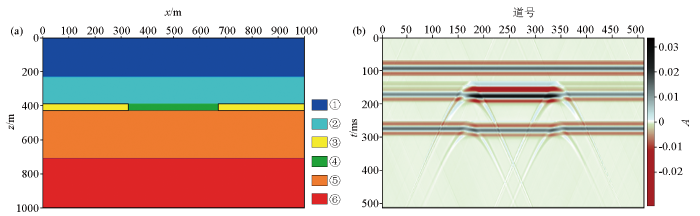
图3
图3
地质模型(a)及其地震响应剖面(b)
Fig.3
Geological model(a) and its seismic response profile(b)
表1 地质模型参数
Table 1
| 层号 | Vp | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ① | 5000 | 2.500 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 200 |
| ② | 5260 | 2.539 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 200 |
| ③ | 5320 | 2.548 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 200 |
| ④ | 5100 | 2.515 | 5 | 400 | 5 |
| ⑤ | 5550 | 2.583 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 200 |
| ⑥ | 5800 | 2.620 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 200 |
注:
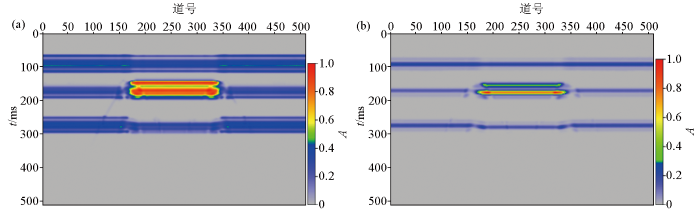
图4所示为基于傅里叶倒谱、小波包倒谱的烃类检测结果。从图中可以看到,基于傅里叶倒谱、小波包倒谱的烃类检测方法都能准确识别到含气层,但是,小波包倒谱检测到的含气层的上下界面区分更清晰,分辨率更高,而傅里叶倒谱检测到的含气层的上下界面区分不够清晰,分辨率较低。此外,小波包倒谱检测到的含气层异常振幅起始响应值较傅里叶倒谱的更低一些。
图4
图4
地震振幅异常剖面
a—傅里叶倒谱;b—小波包倒谱
Fig.4
Seismic amplitude anomaly section
a—Fourier-based cepstrum;b—wavelet-based cepstrum
由于本模型采用的是顺北地区超深层碳酸盐岩储层地震数据和储层测井参数,本模型地震响应的烃类检测结果也表明基于倒谱的烃类检测方法适用于顺北地区超深层碳酸盐岩储层烃类检测。
3 实际地震数据应用
3.1 地震数据
这里,我们利用顺北地区超深层碳酸盐岩储层地震数据进行分析。该地区主要目的层为奥陶系碳酸盐岩储集层,目的层埋深大,有效储集空间类型主要为经过多期次构造挤压作用以及溶蚀改造等形成的柱状溶蚀孔、洞储集体,储层纵向、横向变化快,非均质性极强。研究区岩性主要为黄灰色泥晶灰岩、含砂屑泥晶灰岩、砂屑泥晶灰岩。研究区地震数据能量时强时弱,频率偏低。因此,缝洞型储集空间的空间预测是该地区超深层碳酸盐岩储层气藏勘探的关键。
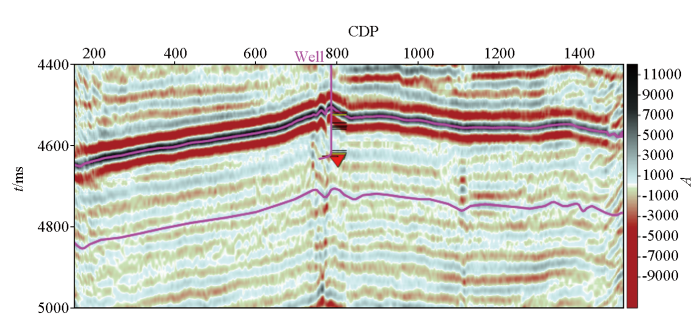
这里,我们利用该地区的过井叠后宽带偏移二维剖面(图5)分析基于倒谱的地震数据分解技术的应用特征和效果。该地震数据采样频率为2 ms。图中目标区为粉色上下层位线之间区域。该剖面过含气井Well。图中测井解释的含气区在井轨迹上进行了标识。
图5
3.2 共倒谱剖面对比
首先,我们对过井剖面分别利用傅里叶变换倒谱和小波包倒谱进行分频处理,可以得到一系列共倒谱剖面。这里,我们首先对比分析共倒谱剖面和基于传统时频分析方法的共频率剖面的特征。
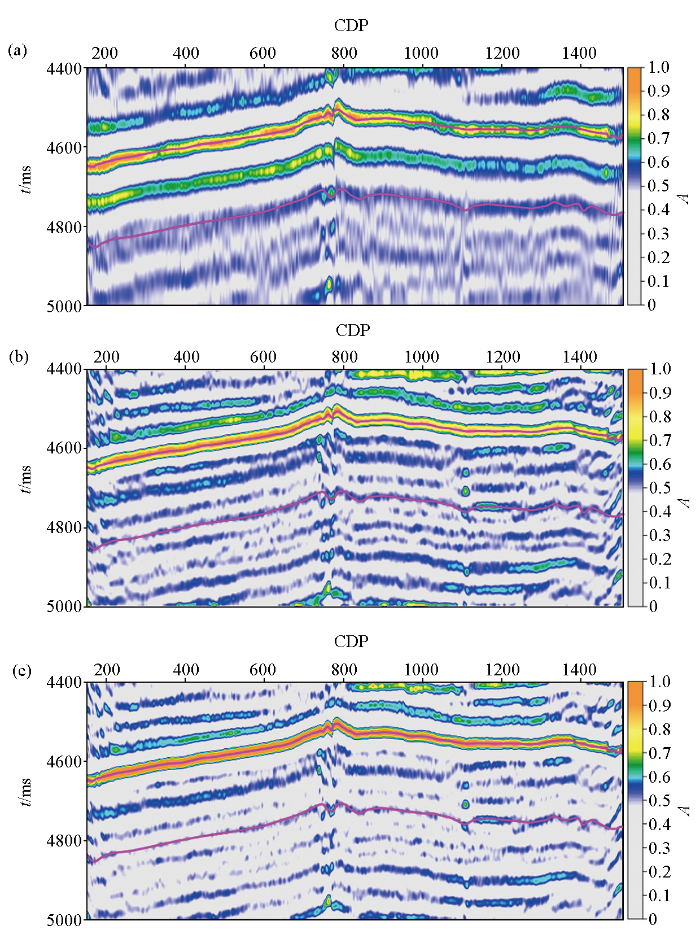
图6所示为过井剖面利用连续小波变换(CWT)获得的共频率剖面和利用傅里叶倒谱、小波包倒谱获得的共倒频剖面的对比。图4展示了共倒频剖面与共频率剖面的对应关系。该地震剖面数据主频约为20 Hz,采样频率为500 Hz。根据式(3),小波包倒谱中滑动窗的长度约为500/(2×20)=12.5,考虑到滑动窗需要为2的幂次方,所以我们选择滑动窗长度16进行计算。为了保持一致,傅里叶倒谱中滑动窗长度也选择为16。此时,一阶共倒频剖面(图6b、c)的频率范围为(0,500/(2×16)≈15.6 Hz)。为了对比,我们给出了使用CWT提取的8 Hz共频率剖面(图6a),注意,这里8 Hz是利用频率范围(0,16 Hz)计算的。注意这里为了对比,我们对所有结果进行了归一化。将图6b、c与图6a对比可知,一阶共倒谱剖面与CWT分别提取的8 Hz共频率剖面类似。这个事实说明了傅里叶倒谱、小波包倒谱的有效性及其与传统共频率剖面的关系。同时,我们可以发现,一阶共倒谱剖面的时空分辨率较CWT提取的8 Hz共频率剖面的时空分辨率更高,可以给出更多的细节信息。
图6
图6
过井剖面的一阶共倒谱剖面和共频率剖面
a—CWT提取的8 Hz共频率剖面,小波变换中使用Morlet小波;b—傅里叶变换倒谱提取的一阶共倒谱剖面;c—小波包倒谱提取的一阶共倒谱剖面
Fig.6
First-order common quefrency and common frequency sections of the seismic section intersecting the known well
a—8 Hz common frequency section extracted by the CWT,Morlet wavelet is used in wavelet transform;b—first-order common quefrency section extracted by Fourier-based ceptrum;c—first-order common quefrency section extracted by the wavelet-based cepstrum
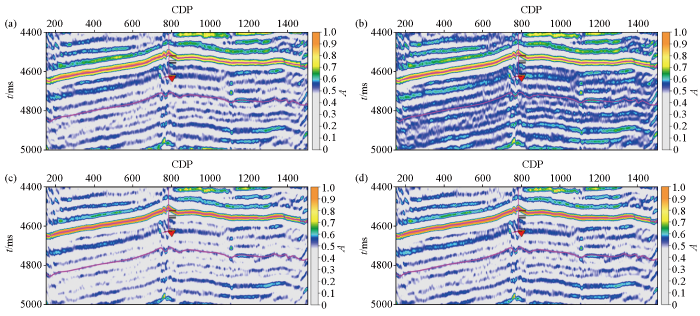
下面再对比分析傅里叶变换倒谱和小波包倒谱提取的一阶共倒谱剖面和二阶共倒谱剖面的特征差异。从图7可以看出,傅里叶变换倒谱和小波包倒谱提取的共倒谱剖面总体能量分布较为一致,但是在能量强弱分布上有差异,傅里叶变换倒谱提取的一阶共倒谱剖面和二阶共倒谱剖面中能量分布在中间部分区域,较小波包倒谱提取的结果更强,而小波包倒谱提取的一阶和二阶共倒谱剖面在上层位处能量分布较傅里叶变换倒谱更强,此外,傅里叶变换倒谱提取的二阶共倒谱剖面没有小波包倒谱提取的二阶共倒谱剖面时空分辨率高。
图7
图7
傅里叶倒谱和小波包倒谱提取的一阶和二阶共倒谱剖面
a—傅里叶变换倒谱提取的一阶共倒谱剖面;b—傅里叶变换倒谱提取的二阶共倒谱剖面;c—小波包倒谱提取的一阶共倒谱剖面;d—小波包倒谱提取的二阶共倒谱剖面
Fig.7
First and second-order common quefrency sections extracted from Fourier-based cepstrum and wavelet-based cepstrum
a—first-order common quefrency section extracted by Fourier-based cepstrum;b—second-order common quefrency section extracted by Fourier-based cepstrum;c—first-order common quefrency section extracted from wavelet-based cepstrum;d—second-order common quefrency section extracted from wavelet-based cepstrum
3.3 烃类检测
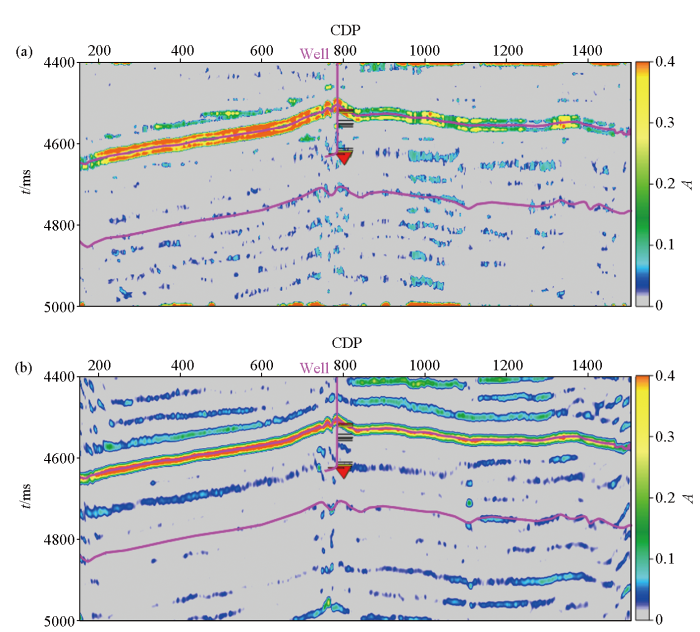
含烃类区域通常在基于倒谱的烃类检测技术检测到的地震幅度异常剖面中表现为强振幅异常特征区域,排除岩性、地层等其他因素影响,通常认为地震幅度异常剖面中的强振幅异常特征可以给出含烃类信息的解释结果。
图8
图8
地震振幅异常剖面
a—傅里叶倒谱;b—小波包倒谱
Fig.8
Seismic amplitude anomaly section
a—Fourier-based cepstrum;b—wavelet-based cepstrum
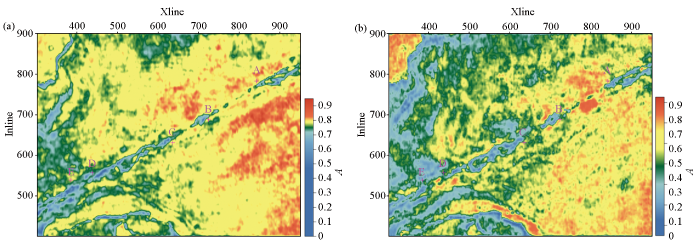
图9
图9
地震振幅异常切片
a—傅里叶倒谱;b—小波包倒谱
Fig.9
Seismic amplitude anomaly slice
a—Fourier-based cepstrum;b—wavelet-based cepstrum
4 结论
本文对比研究了傅里叶变换倒谱和小波包倒谱分解技术。地震数据倒谱分解技术可以得到类似谱分解一样的系列分频数据体,能有效避免调谐效应,提高剖面的空间分辨率。模型分析表明小波包倒谱较傅里叶倒谱检测到的含气层的上下界面区分更清晰,分辨率更高。顺北实际地震数据处理结果表明,应用地震数据倒谱分解技术能有效地对该地区超深层碳酸盐岩储层进行很好的预测,且小波包倒谱分解技术较傅里叶变换倒谱分解技术具有更高的时空分辨率,能体现更多细节信息。
参考文献
龙门山前陆盆地深层海相碳酸盐岩储层地震预测研究
[J].
Seismic prediction of carbonate reservoirs in the deep of Longmenshan foreland basin
[J].
Seismic-print Analysis and Hydrocarbon Identification
[C]//
地震分倒频处理技术
[J].
Seismic sub-inverted frequency processing technology
[J].
深层碳酸盐岩储层含气性检测方法技术研究
[J].
DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1000-1441.2019.01.002
[本文引用: 2]

我国深层海相碳酸盐岩地层蕴藏有丰富的天然气资源,但因演化历史长、埋深大等因素影响,储层含气性评价困难。评述了现有储层含气性地震检测技术(包括亮点、AVO异常、低频阴影等)在深层天然气储层识别中的适用性,认为亮点和AVO异常反映的是界面响应,而低频阴影反映的是储层的“体”响应。储层含气性检测不仅要确定储层是否含气,还要确定储层含气量。为此,介绍了一种新的基于地震纹倒谱分析的储层含气性检测方法,指出①雷克子波的地震纹倒谱参数随子波频率呈非线性变化;②地震纹倒谱参数对储层参数变化反应灵敏;③含气储层地震响应的1阶倒谱系数呈高值异常,而2阶倒谱系数呈低值异常,且二者呈镜像对称。地震纹倒谱对弱反射的敏感性使得该方法能够发现“暗点”型气藏,同时因与模型无关而克服了诸多建模带来的弊端,能够对深层超深层储层含气性进行较为可靠的检测。探讨了基于地震的深层碳酸盐岩储层产能评价问题,认为地震纹分析与频散分析相结合有望能确定储层的含气性并估算其可采储量。
Advances in hydrocarbon detection in deep carbonate reservoirs
[J].
DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1000-1441.2019.01.002
[本文引用: 2]

<p>There are abundant natural gas resources in deep marine carbonate strata onshore China.It is necessary but difficult to discover gas-bearing reservoirs and evaluate their gas content,due to their long evolutionary history and large buried depth.This paper reviews existing hydrocarbon detection techniques,such as bright spot,AVO,and low-frequency shadow,in the identification of deep gas carbonate reservoir.Bright spots and AVO anomalies reflect the interface response,while low-frequency shadows reflect the response of the “body” of the reservoir.In this paper a hydrocarbon detection technique is proposed based on seismic cepstrum analysis.The cepstrum of the Ricker wavelet varies nonlinearly with frequency and the seismic cepstrum is sensitive to reservoir parameters.In addition,the first-order cepstral coefficient of the seismic cepstrum of gas-bearing reservoirs is of a high-value anomaly,while the second-order cepstral coefficient represents a low-value anomaly,and the two anomalies are mirror-symmetric.The sensitivity of the seismic cepstrum to weak reflection enables the method to detect “dim spot” gas reservoirs.In addition,the method is independent of reservoir modeling.Discussion on capacity evaluation based on seismic data analysis suggested that combined analysis of seismic print and dispersion could effectively detect gas-bearing reservoir and estimate the recoverable reserves for a deep carbonate reservoir.</p>
Wavelet-based cepstrum decomposition of seismic data and its application in hydrocarbon detection
[J].
The state-of-the-art techniques of hydrocarbon detection and its application in ultra-deep carbonate reservoir characterization in the Sichuan Basin,China
[J].
The quefrency analysis of time series for echoes:Cepstrum,pseudo-autocovariance,cross-cepstrum and saphe cracking
[G]//
Application of homomorphic deconvolution to seismology
[J].
Homomorphic deconvolution of some teleseismic events
[J].
Cepstrum analysis for determination of rupture length of microearthquakes
[J].
The application of homomorphic deconvolution to shallow-water marine seismology:Part ii:Real data
[J].
Deconvolution by autocepstral windowing
[J].
Application of fractional Fourier transform in cepstrum analysis
[C]//
Predicting bed thickness with cepstral decomposition
[J].
Discrete-time signal processing
[M].
Wavelet-based cepstrum calculation
[J].
Seismic low-frequency effects in monitoring fluid-saturated reservoirs
[J].