0 引言
鉴于此,我们研发了一种低成本、多功能节点式旋转地震仪RBWL。该仪器采用低成本(micro electro mechanical systems,MEMS)传感器测量加速度和角速度以及姿态、温度,从而实现平动分量和旋转分量以及环境因素的测量;在数据传输方面,本仪器采用4G—云端—客户端的数据传输模式,实现了RBWaveLink和客户端同步传输加速度、角速度、姿态角度和温度数据。
1 RBWL节点式旋转地震仪的软硬件设计
1.1 硬件系统设计
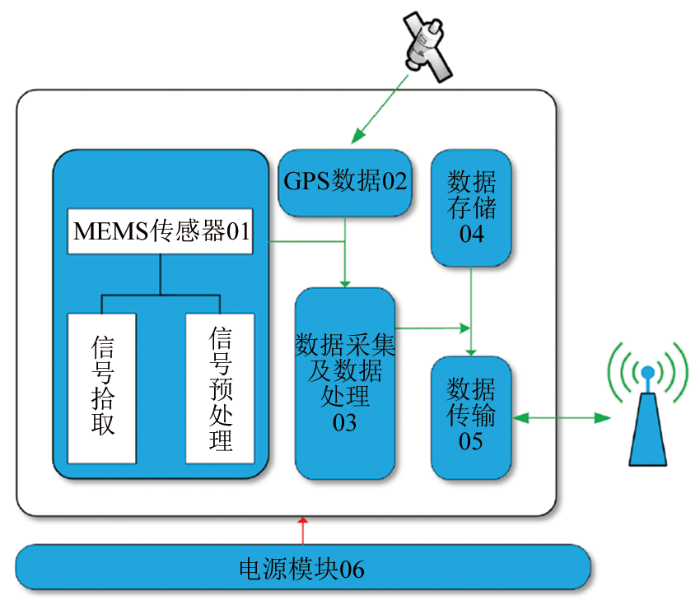
图1
图1
节点式旋转地震仪硬件系统示意
Fig.1
Schematic diagram of the hardware system of the nodal rotary seismometer
表1 RBWL系统主要技术参数
Table 1
| 技术参数 | 取值范围 |
|---|---|
| 最大线性加速度/g | ±2 |
| 线性加速度最高分辨率/(LSB·g-1) | 16384 |
| 角速度最高分辨率/(rad·s-1) | 4E-5 |
| 姿态角度量程/(°) | x、y:±180,z:±90 |
| 温度量程/℃ | -40~85 |
| 频率响应范围/Hz | 7~500 |
| 采样率/Hz | 100、200、500、1000 |
| 工作温度/℃ | -40~85 |
| 实时传输连续工作时间@25℃/d | 3 |
| 存储容量/G | 64 |
| 长、宽、高/mm | 100×75×120 |
| 功耗/W | <2.5 |
硬件系统主要功能为:
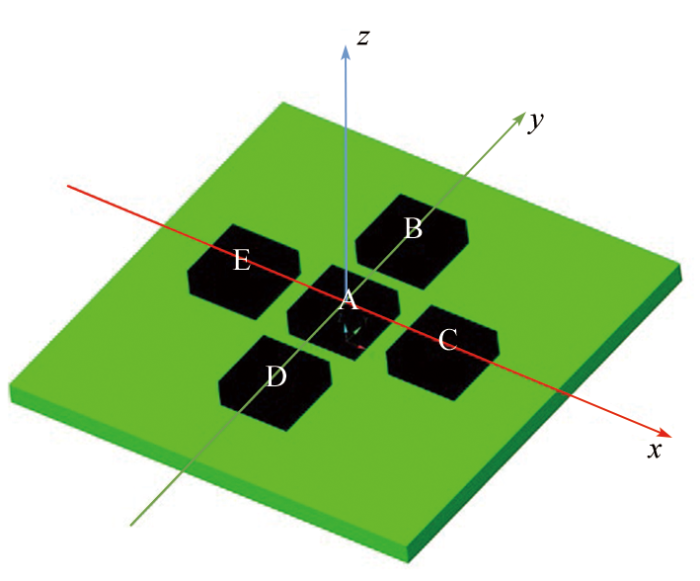
1)MEMS传感器包括由5个加速度计组成的阵列和1个磁场传感器以及1个温度传感器,采集振动信号以及环境数据,加速度计阵列如图2所示。其中,MEMS加速度传感器以十字形分布布置在仪器内部的电路板上,在直角坐标系下,传感器C、E、B、D分别布置在x轴和y轴的正方向和负方向,关于A对称分布。
图2
2)GPS模块用于节点定位以及系统时钟同步,以便后续的数据分析和研究。
3)数据采集模块对各个传感器数据和GPS模块获取的数据进行预处理和解算,通过扩展卡尔曼滤波算法进行姿态角度估计,实现数据校正,从而减小仪器姿态的影响。
4)数据存储模块采用FATFS虚拟文件系统,根据预设记录间隔创建文件夹,负责记录处理好的实时振动信号(实时钟、平动及旋转加速度信号)、状态及环境数据(仪器工作状态、姿态、GPS定位、温度等),并分别存储在两个独立的文件中。
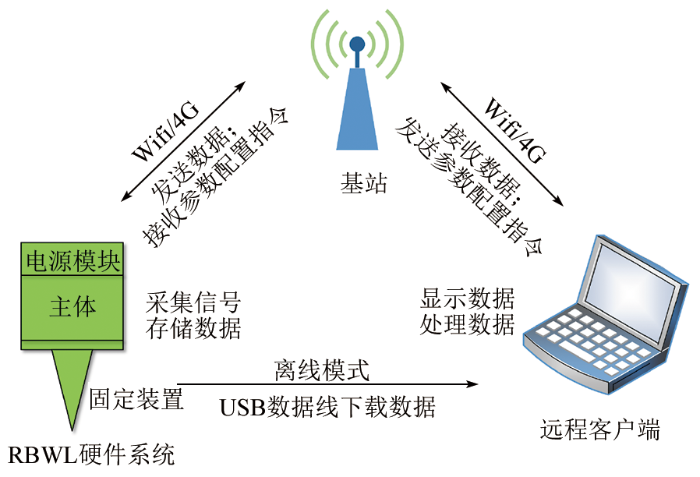
5)数据传输模块如图3所示,数据传输模块用于节点仪与用户端之间的双向数据交互,提供USB和Wifi接口进行离线数据下载,还可以通过4G模块进行远程数据传输。
图3
6)电源模块采用18650锂电池组作为储能单元,同时集成了充放电保护及UPS电路,能够实现野外自容式与室内外供电两种工作模式的自主切换。
1.2 软件平台设计
为方便用户对RBWL进行管理和设置,对利用python语言在RBWL远程监测平台的客户端上位机软件进行开发,具有方便快捷、兼容性高的优点,能够兼容Win10和Linux平台。其主要功能如下:
1)用户界面:包括硬件参数配置,数据显示和时间序列波形显示;
2)数据处理:包括数据预处理(数据解算、客户端将接收到的数据还原为地震信号数据)和补偿与校正(客户端对数据进行温度补偿校正,减小环境因素对数据的影响);
3)文件管理:用于文件格式的转换和数据回放。
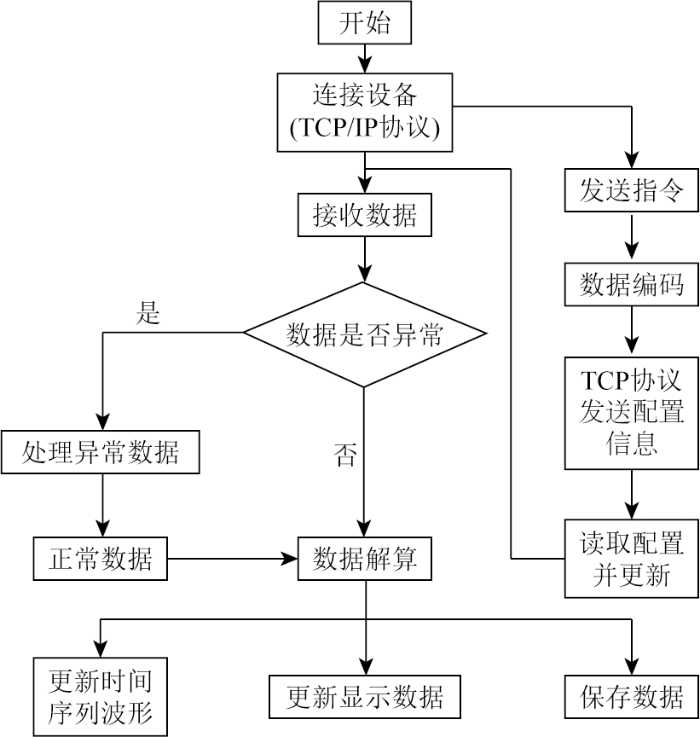
远程监测平台客户端的上位机软件如图4所示。客户端软件首先对默认参数进行初始化,然后通过4G与RBWL建立的连接,建立连接后对仪器参数进行配置并对数据进行接收与解算,实时显示振动信号的时间序列波形数据以及仪器状态数据,随后对数据进行保存。
图4
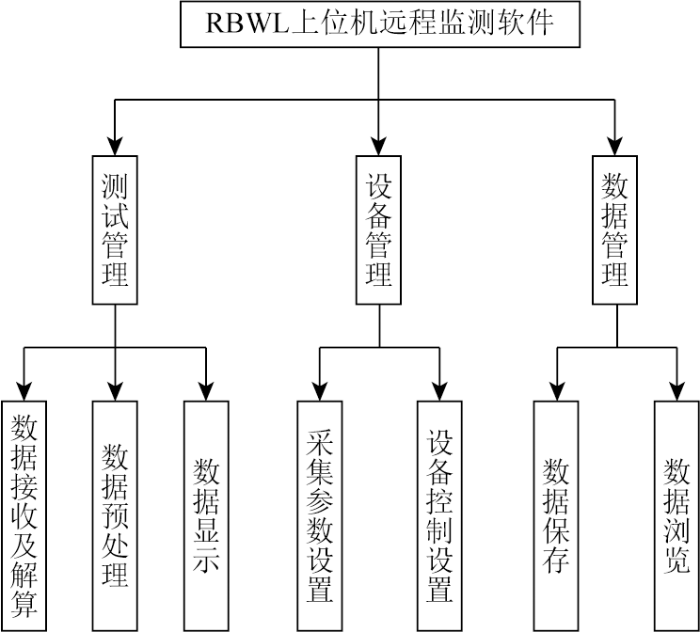
软件的主要功能模块包括测试管理模块、设备测试管理模块、数据管理模块3部分,如图5所示。
图5
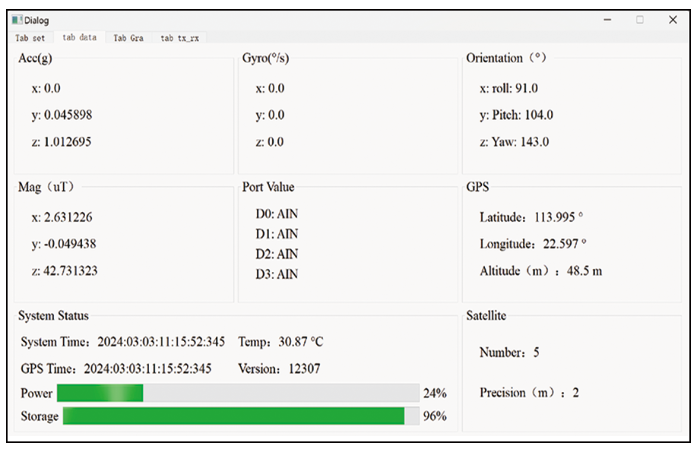
图6
图6
数据显示及设备状态监测界面示意
Fig.6
Schematic diagram of data display and equipment status monitoring interface
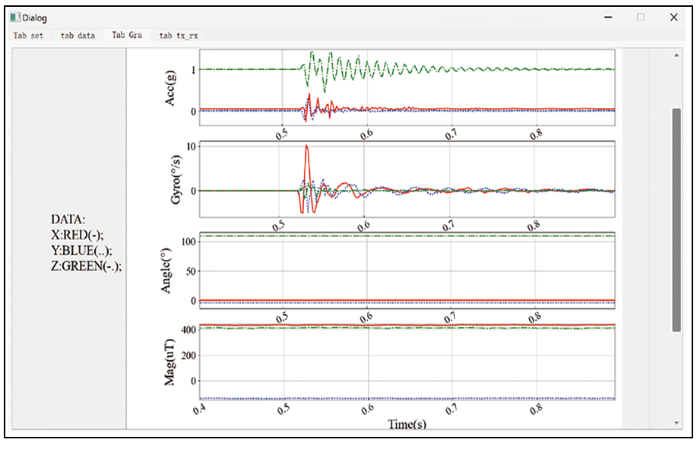
图7
图7
数据可视化界面示意
(加速度、角速度、姿态角度、磁场)
Fig.7
Schematic of the data visualization interface
(acceleration, angular velocity, attitude angle, magnetic field)
数据补偿与校正:接收到的MEMS加速度计数据由于测试时环境温度的变化会导致测量数据产生误差即温漂,需要对数据进行预处理,利用温度数据进行温漂补偿以减小误差,温漂补偿如式(1)所示:
其中:
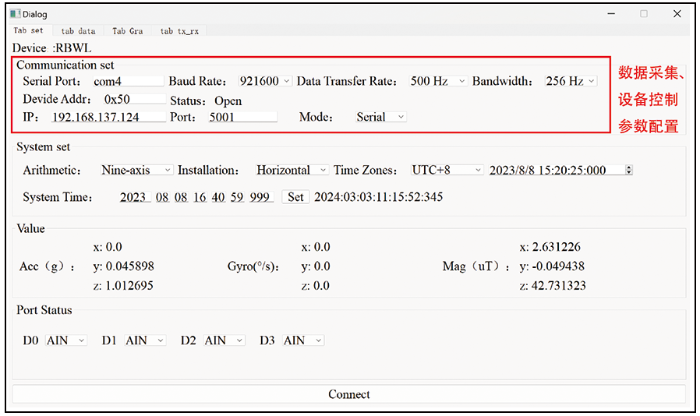
设备管理模块如图8所示,主要负责数据采集参数的设置和设备控制。在采集参数配置中,能够对仪器的采样速率、带宽等进行设置;在设备控制设置中能够对USB端口通信的波特率、远程数据传输端口的IP地址和Port、仪器的设备地址进行设置。
图8
图8
参数配置及数据显示界面示意
Fig.8
Parameter configuration and data display interface diagram
数据管理模块主要负责将振动信号数据和仪器状态及环境数据分类存储,并提供SEED和miniSEED文件格式转换功能,以便于预览和后续的数据处理。
2 间接法旋转分量测量
无论是地震、爆炸还是环境振动都包含平动分量和旋转分量,而旋转分量中含有的波场梯度信息能够进一步揭示地壳的复杂结构等。平动分量和旋转分量的结合能够在地震波场的重建中更加准确、细致地分析地震波的类型、传播特性、波速等,对地震工程领域的结构抗震性能研究具有重大意义,还能够更加细致地分析地层所蕴含的丰富资源,以及提高灾害防御能力等。
如表2所示,直接法通常利于电化学或光学陀螺仪来测量旋转分量,其灵敏度更高,并且在数据测量和预处理方面操作更加简单,但是其成本高、体积和功耗都较大,部署较为复杂。间接法测量旋转分量的优势在于保持高灵敏度的同时降低了成本、功耗和部署难度,因而选择传感器阵列方式间接测量旋转分量。
表2 RBWL与同类测量设备比较
Table 2
| 仪器名称 | 仪器类型 | 观测类型 | 观测分量 | 精度 | 部署难度 | 功耗 | 体积 | 质量 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RBWL | MEMS | 平动+旋转 | 6 | 中 | 低 | 低 | 小 | 小 |
| 6DOF | 速度计阵列 | 平动+旋转 | 6 | 高 | 中 | 中 | 大 | 大 |
| R-1 | 电化学 | 旋转 | 3 | 高 | 中 | 高 | 大 | 大 |
| G-Ring | 激光陀螺仪 | 旋转 | 3 | 超高 | 超高 | 超高 | 超大 | 超大 |
| FOSREM | 光纤陀螺仪 | 旋转 | 3 | 高 | 中 | 高 | 大 | 大 |
| Titan | 加速度计 | 平动 | 3 | 中 | 中 | 低 | 中 | 中 |
平动分量计算旋转分量的方法主要分为单测站法和密集台阵法,其中,密集台阵法包括差分法和测地学法。差分法相对简单和便于理解,任意质点的旋转运动可以分解到x、y、z这3个相互正交的方向上[14]:
根据MEMS加速度传感器阵列的结构,旋转分量计算公式如下:
其中:Tx、Ty和Tz分别x、y、z方向相互正交的平动分量;
3 H/V谱比测试分析
3.1 H/V谱比法
Nakamura提出的H/V的定义[19]如下:
则H/V可表示为:
3.2 H/V谱比法实验及结果分析
图9
表3 共振频率与记录时长关系
Table 3
| fr/Hz | Lw最 小值 /s | 最小有 效周期 数/nc | 最小窗 口数 | 最小有用 信号持续 时间/s | 建议的最 短记录持 续时间/min |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5 | 5 | 200 | 10 | 40 | 3 |
| 10 | 5 | 200 | 10 | 20 | 2 |
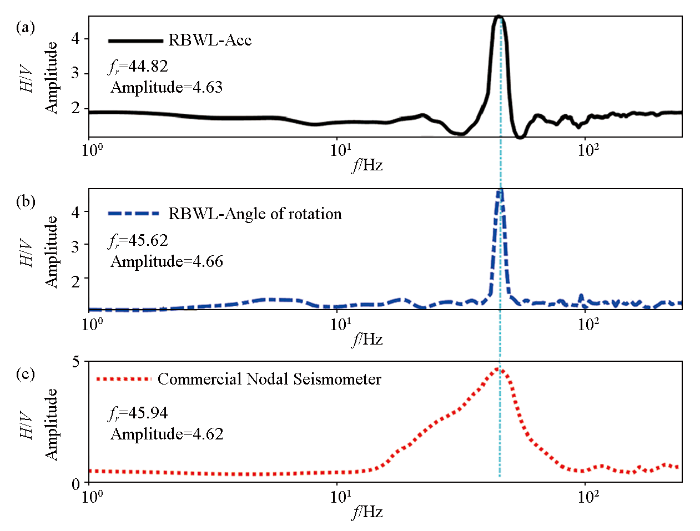
本次测量中,两种仪器的采样率均设置为500 Hz,数据采集时长为20 min,使用Geopsy软件进行数据分析和处理。采用反触发式长短时窗法在采集到的噪声时间序列中选择没有强瞬态信号的窗口计算H/V谱比曲线,如图10所示。
图10
图10
H/V谱比曲线
a—RBWL的3个加速度分量绘制的H/V谱比曲线;b—RBWL计算的旋转分量绘制的H/V谱比曲线;c—节点地震仪三轴数据绘制的H/V谱比曲线
Fig.10
H/V spectral ratio curves
a—H/V curves plotted for the three acceleration components of the RBWL;b—H/V curves plotted for the rotational components calculated by RBWL;c—H/V curves plotted for the three-axis data of the nodal seismometer
假设土层厚度为h,根据Abu等提出的共振频率fr与h的关系[26]:
其中:x是与土层厚度和质地相关的参数,根据Abu等[26]的建议,x取值为0.44,VS0取100 m/s。
表4 土层厚度h估算结果
Table 4
| fr/Hz | h/m | 误差/% |
|---|---|---|
| 44.82 | 0.62 | 3.3 |
| 45.62 | 0.61 | 1.7 |
| 45.94 | 0.61 | 1.7 |
4 结论
RBWL采集节点选用价格低但性能稳定的MEMS传感器元件,并且优化电路设计,将多个传感器集中在一个单元,缩小了系统尺寸,能够一次测量多种类型数据,减少了所需测量仪器的种类和数量,降低了仪器成本,仪器总成本在万元以内,而目前光纤陀螺仪市面价格则在3万元以上。RBWL采集节点采用模块化设计,通过选配不同模块以适应不同环境和需求。在后期维护方面,也仅需更换受损模块即可快速投入工作,不仅降低了制造和后期的维护成本,而且后期维护更加简易和便捷。在功耗方面,MEMS传感器元件功耗相对光纤陀螺仪传感器元件功耗更低,单个MEMS器件功耗仅为2.5 mW,RBWL采集节点整机功耗也不大于2.5 W,远远小于光纤陀螺仪传感器的功耗4 W。RBWL采集节点体积小,仅为1支笔的长度,更加便于携带和部署。RBWL内置电池模块无需外部供电,数据传输采用无线通信设计,无需布置传输电缆,从而使得RBWL更加易于部署。
本研究设计的基于MEMS传感器的低成本、多分量节点式旋转地震仪RBWL,通过MEMS技术将不同类型检波器、主控制器以及电池集成到一个单元,并以低成本、低功耗实现了对平动分量的采集和旋转分量的计算以及监测。该仪器在实现微型化、无线化和模块化的基础上,能够同时采集加速度、角速度、磁场、姿态、温度等多种类型数据,并提供友好的用户界面。RBWL与其他多分量旋转地震仪产品相比,具有更低的制造成本和更强的灵活性和可维护性,有利于在实际工程中的应用与推广。通过与商业三分量地震仪器的H/V谱比对比实验,证实了RBWL仪器在工程地震领域的所采集数据的有效性以及仪器的可靠性。本研究所设计的基于MEMS的多分量节点式旋转地震仪为平动分量和旋转分量在地震观测、资源勘探和工程领域的观测提供了一种新型、经济高效的解决方案。
参考文献
Earthquake geodesy and hazard monitoring
[J].
基于地震动信号分析的地质灾害过程重构方法研究与应用
[J].
Research and application of geological hazards process reconstruction based on seismic signal analysis
[J].
地面运动旋转分量观测综述——以中国台湾地区旋转运动观测为例
[J].
Review of the measurement of rotational component in ground motions:A case study of rotating motion observation in Taiwan,China
[J].
勘探地震中的六分量观测
[J].
DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1000-1441.2021.01.002
[本文引用: 1]

地震旋转分量在天然地震和工程地震等领域都有广泛的应用。在回顾地震旋转运动的基础上,首先介绍了六分量地震数值模拟研究,论证了不同震源类型与地震波型在六分量波场上存在能量与极性的差异。随后,回顾了利用模拟数据与实际观测数据验证差分法与行波法两种旋转分量间接换算方法的可行性与精度。通过数值模拟,分析了勘探地震中广泛应用的面波,在六分量记录上呈现的不同或相似的特征,以及旋转分量记录波场信息具有的不同于平动分量的频散特征。近年来,不断发展的地震旋转分量研究,对波型识别、波场分离、横波成像、微震的高精度预测、探索海底电磁和地震观测的关联等领域均具有重要意义与深入研究价值。
Six-component observation for exploration seismology
[J].
DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1000-1441.2021.01.002
[本文引用: 1]

In recent years,research on seismic rotational components has gained substantial attention for the purpose of wave-type identification,wave field separation,S-wave imaging,high-precision prediction of microseisms,and exploration of the relationship between electromagnetic and seismic observations of ocean bottoms.Seismic rotational components are widely utilized in the study of natural earthquakes,in engineering seismology applications,and in many other fields.Numerical simulations demonstrated that the characteristics of six-component wave fields originating from different source types and seismic wave types are different in both energy and polarity.Based on the analysis of numerical six-component seismic data as well as of actual observed data,it has been verified that both the difference method and the travelling-wave method are applicable and offer a reasonable accuracy when it comes to converting translational components into rotational components.Numerical simulations demonstrated the characteristics of surface waves in six-component records,and that the dispersion characteristics of the rotational components are different from those of the translational components of surface waves.
Application of multi-component seismic exploration in the exploration and production of lithologic gas reservoirs
[J].
地热资源地震勘探方法综述
[J].
An overview of methods for geothermal seismic exploration
[J].
六分量地震观测在工程勘查中的应用试验
[J].
A case study:Application of six-component seismic observations in urban engineering investigation
[J].
地震勘探节点采集系统设计的要点
[J].
Key points of the design of a nodal acquisition system for seismic exploration
[J].
几种旋转地震仪在深部地下巷道的观测对比
[J].
Deep underground observation comparison of rotational seismometers
[J].
Tutorial on rotational seismology and its applications in exploration geophysics
[J].
Estimation of the resonance frequency of rotational and translational signals evoked by mining-induced seismicity
[J].
Ground rotational motions of the 1999 Chi-Chi,Taiwan earthquake as inferred from dense array observations
[J].
Recording rotational and translational ground motions of two TAIGER explosions in northeastern Taiwan on 4 March 2008
[J].
差分法计算地震动旋转分量
[J].
Calculating rotational components of ground motions by finite difference method
[J].
微动H/V谱比方法
[J].
A review on microtremor H/V spectral ratio method
[J].
Rayleigh波ZH幅度比(椭率)研究综述
[J].
Review on rayleigh wave ZH amplitude ratio(ellipticity)
[J].
A microtremor HVSR study of the seismic site effects in the area of the town of brežice (se slovenia)
[J].
S-wave velocity profiling by inversion of microtremor H/V spectrum
[J].
A method for dynamic characteristics estimation of subsurface using microtremor on the ground surface
[J].
On the amplitude characteristics of micro-tremor,Part II
[J].
Effect of transient seismic noise on estimates of H/V spectral ratios
[J].
Inversion of local S-wave velocity structures from average H/V ratios,and their use for the estimation of site-effects
[J].
The nature of noise wavefield and its applications for site effects studies
[J].
Effects of love waves on microtremor H/V ratio
[J].
Guidelines for the implementation of the H/V spectral ratio technique on ambient vibrations measurements,processing and interpretation
[J].
The passive seismic technique ‘HVSR’ as a reconnaissance tool for mapping paleo-soils:The case of the pilastri archaeological site,northern italy
[J].