0 引言
电磁法是获取地下电性结构分布的重要地球物理探测方法之一,该方法通过在地表测量不同位置或不同频率的电场或磁场,计算解析地下不同深度的电性信息。其中,电场分量对地下介质的电阻率、介电常数等电性参数的灵敏度较高,是电磁法探测中常用的观测参数。例如,大地电磁法、音频大地电磁法、可控源音频大地电磁法和广域电磁法都要求测量单个或多个电场分量[1-2]。因此,高精度电场测量是电磁探测的关键技术问题。尤其是在大地电磁等天然源电磁探测中,由于天然源信号微弱,地表响应电场信号幅度最低接近数十μV/km数量级,以100 m接收极距合算至响应电压为百nV~μV数量级[3⇓-5],如此微弱的电场信号对电场传感器的极差漂移与本底噪声提出的要求较高[6⇓-8]。
不极化电极是电磁法探测系统中最常用的电场传感器,该传感器通过将金属阳极浸入相应的电解质溶液中,利用金属与溶液之间快速可逆的氧化还原反应实现导电,从而隔绝纯金属电极与土壤的直接接触,相比纯金属电极具有低极差、耐腐蚀、耐氧化等优势。国际上先进的不极化电极当属乌克兰LEMI公司生产的LEMI701电极,其极差漂移达到50 μV/144 days[9]。近几年,国内也出现了几款性能较优的商用电极,以Pb-PbCl2体系固态电极为代表[10⇓⇓⇓-14],此类电极的极差漂移一般小于100 μV/d,本底噪声一般接近50nV/
在此背景下,国内一些专家开展了Ag-AgCl体系固态电极的研发工作[15⇓⇓-18],例如申振等[16]用烧结法制备了全固态Ag-AgCl电极,并在海洋电场测量中开展了性能测试与应用,避免了Pb-PbCl2电极的污染问题,且取得了有益的电场测量效果。此类工作研究并阐述了保持固态不极化电极的极化电位稳定性的方法,即增大反应界面的交换电流密度,保证双电层两侧有充足的反应离子。交换电流密度越大,相同电流在流经时产生的极化电位越小,同时电极双电层两侧吸附的离子数量更多,外界扩散到双电层的离子数量相对于双电层两侧的反应离子数量较小,扩散离子对电极表面的双电层影响减弱,电极的极化电位越稳定[19⇓-21]。李红霞等[22]通过在Ag-AgCl电极中添加石墨烯,引入层状结构进一步增加了电极的比表面积、增大反应界面的交换电流密度,缩短了极差稳定时间,减小了电极的极差,提升了电极稳定性。测试结果表明,加入3%的石墨烯材料可将电极的极差稳定时间缩短至1 h,极差低至70 μV。该方法有效降低了不极化电极的极差,提升了电极稳定性,为本文研究提供指导与参考[23⇓-25]。本文为进一步降低电场传感器的极差、极差漂移及本底噪声,提出一种新型石墨烯基电场传感器。通过攻克基于Ag-AgCl体系的石墨烯基稳定电解质凝胶制备工艺,优化设计基于高分子微孔隔膜的多触角、多仓式电场传感器结构,减缓了外部离子的扩散影响,降低了本身的内阻和接触电阻,从而有效降低了电场传感器极差漂移与本底噪声。
1 电场传感器的基本原理与研制需求
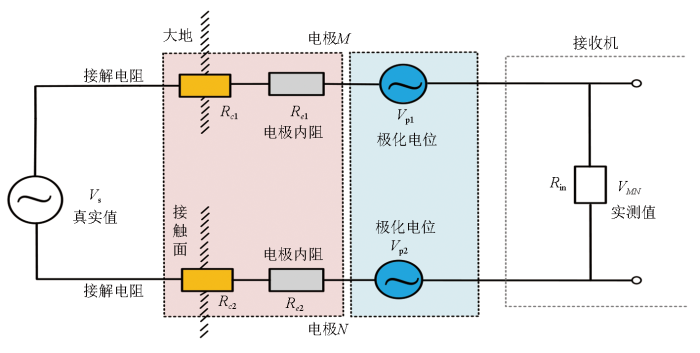
要实现低极差、低极差漂移、低噪声的电场传感器设计,首先需要从电场传感器的基本工作原理和极化电位的产生机理入手。不极化电极在测量电场时,利用相距一定极距的一对电极与大地接触,通过测量不极化电极对之间的电位差,间接测量电场。理想情况下,假设电极对之间的电场基本均匀,电极对中点处的电场等于电位差与极距的商。但实际测量时由于电极对本身存在极化电位和本底噪声,会在电位差测量时引入误差从而影响电场测量精度,如图1所示,其中,对交流电磁法而言,极化电位的影响主要体现在电极对的极化电位差随时间变化而产生的极差漂移。因此,要提高电场传感器的电场测量精度,要求电场传感器具有低极差漂移和低本底噪声。
图1
1.1 极化电位产生机理
其中:ε0表示电极的标准电势;R表示理想气体常数,8.314 J/(mlo·K);T表示环境温度;n为化合价;F为法拉第常数;co为稳定条件下的离子浓度。
图2
图2
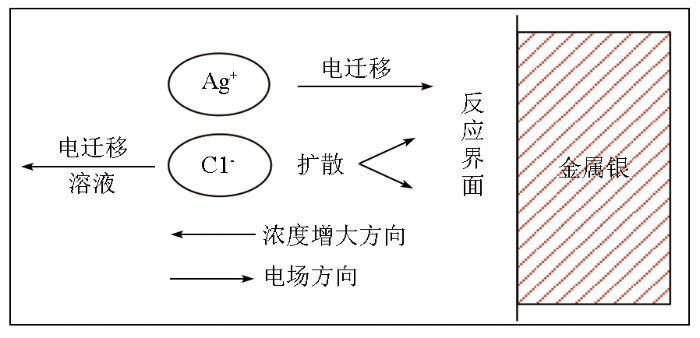
Ag-AgCl体系不极化电极的电化学反应过程示意
Fig.2
Schematic diagram of electrochemical reaction process of non-polarized electrode with Ag-AgCl system
当外加交变电压时,反应区阴阳离子在电压作用下发生定向移动,诱导金属、离子和掺杂物构成的三项反应界面上发生氧化还原反应,从而导致电位偏离平衡状态,直至再次达到稳定,此时稳定电位计算公式为:
其中:cs为再次达到稳定时的离子浓度。平衡电位和稳定电位之差值即为电极的极化电位,计算公式为:
选定电极的电解质反应体系后,电极对的极化电位大小和极差稳定性主要受离子浓度和温度等变化因素的影响,尤其是当离子浓度呈现的非线性变化趋势时,将直接影响电极的极差漂移。要研制低极差漂移的电场传感器,首先要考虑尽可能减缓离子的浓度变化。
1.2 本底噪声产生机理
不极化电极的本底噪声主要来源于电极本身的内阻及其与大地接触电阻引入的电阻热噪声。如图1所示,假设电极M的内阻为Re1、接触电阻为Rc1,电极N的内阻为Re2、接触电阻为Rc2,各电阻产生的热噪声分别为:
其中:k为玻尔兹曼常数;T为环境温度;Bw为传感器等效带宽。
则电阻热噪声产生的总噪声功率谱密度为:
由于在电场测量时,要求传感器和信号采集系统的带宽需保持一致,因此,上述电阻产生的总噪声功率谱密度可等效为:
因此,若要实现低噪声电场传感器设计,主要应考虑减小电场传感器的内阻和接触电阻。
2 石墨烯基电场传感器研制
优选了电极反应体系,改良了电解质溶液配比,优化设计了稳定电极结构。因金属Ag具有较高电流交换密度、温度系数适中且环保等优异特性,本文首选Ag-AgCl体系。通过反复试验对比了在不同涂覆工艺及不同溶液配比、不同酸碱度和不同粘稠度电解质凝胶情况下,电极的极差和漂移情况。结合机理研究基础,围绕低极差、低漂移的设计需求,确定了固体Ag电极涂覆工艺和电解质凝胶配比的优化方向。
2.1 石墨烯基电解质凝胶制备
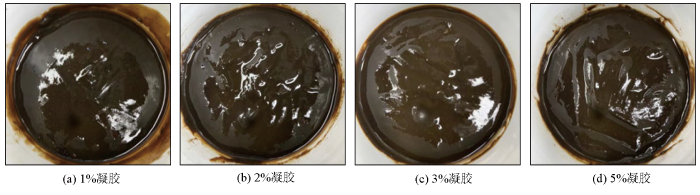
氧化石墨烯电解质凝胶的形态会随着石墨烯材料质量比重的变化而变化,粘度和锁水性也随之改变。为探究氧化石墨烯质量比重对氧化石墨烯电解质凝胶的影响,制备了4组石墨烯溶液,其中石墨烯的质量比重分别是1%、2%、3%、5%,再通过添加电解质及粘稠剂等材料制备石墨烯基电解质凝胶,所制备出的氧化石墨烯凝胶形貌如图3所示,测试比对了4种凝胶的锁水性,进而评估凝胶的离子保持能力。
图3
图3
不同质量比重的氧化石墨烯凝胶形态
Fig.3
Morphology of graphene oxide gel with different mass ratio
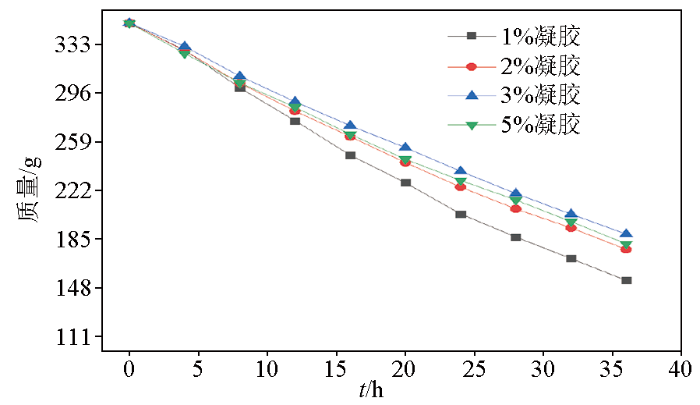
将制备好的凝胶放置于50 ℃干燥箱内进行干燥,不同质量比重的氧化石墨烯凝胶随着时间的推移,水分出现不同程度的挥发(图4)。经过36 h的干燥,当氧化石墨烯质量比重为1%时,损失水分质量为196.2 g;当氧化石墨烯质量比重为2%时,损失水分质量为172.6 g;当氧化石墨烯质量比重为3%时,损失水分质量为161 g;当氧化石墨烯质量比重为5%时,损失水分质量为168.3 g。通过数据可以看出,当氧化石墨烯比重在3%以下时,保水效果随着氧化石墨烯质量比重的增加而有所提升,但当氧化石墨烯的质量比重达到5%时,保水效果反而没有预想的高,此时其保水性高于质量比重为2%的石墨烯凝胶而低于质量比重为3%的石墨烯凝胶。经分析得知,过高的氧化石墨烯比重会影响其在水中的分散效果,并随之影响到凝胶的交联效果。因此,可通过比对试验方式确定最佳的石墨烯质量比重,以保证石墨烯基电解质凝胶具备最强的保水性,进而提升凝胶的离子保持能力。
图4
图4
不同质量比重氧化石墨烯凝胶保水性能对比
Fig.4
Comparison of water retention properties of graphene oxide gels with different mass ratio
2.2 多触角电场传感器结构设计
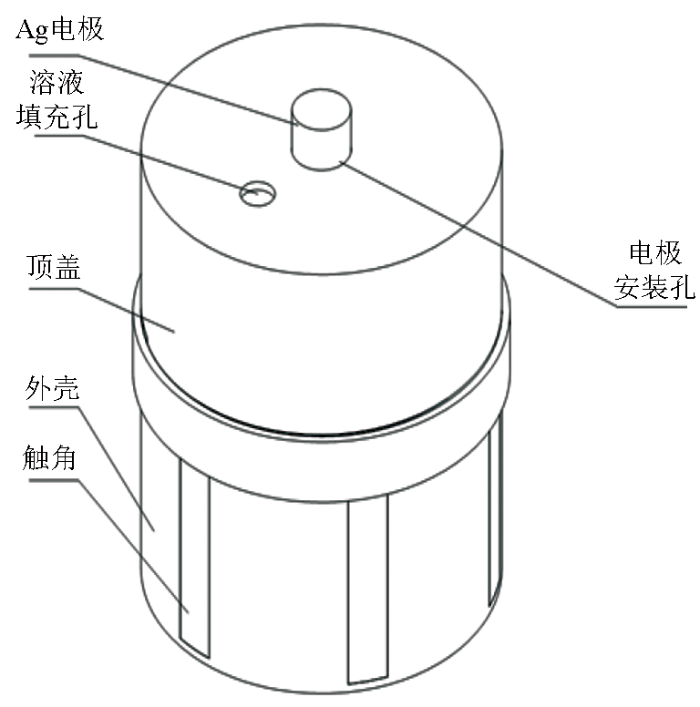
为充分发挥石墨烯基电解质凝胶的性能,降低电极的极差漂移与本底噪声,还需要研究稳定的电极结构。本文提出一种如图5所示的多仓式、多触角电极结构,在外壳的侧壁贯穿开设有若干通孔与大地连通,内壁抵接安装在外壳内腔,用于盛装电解质凝胶,内壁的四周固接有若干个与外壳通孔对应设置的触角,以便伸入通孔并与大地接触。利用侧壁设置的多接触点,增加电极与大地的接触面,增强电极与大地的接触性,降低电极的接触电阻。
图5
图5
多触角电场传感器结构设计
Fig.5
Design diagram of multi-contactor electric field sensor structure
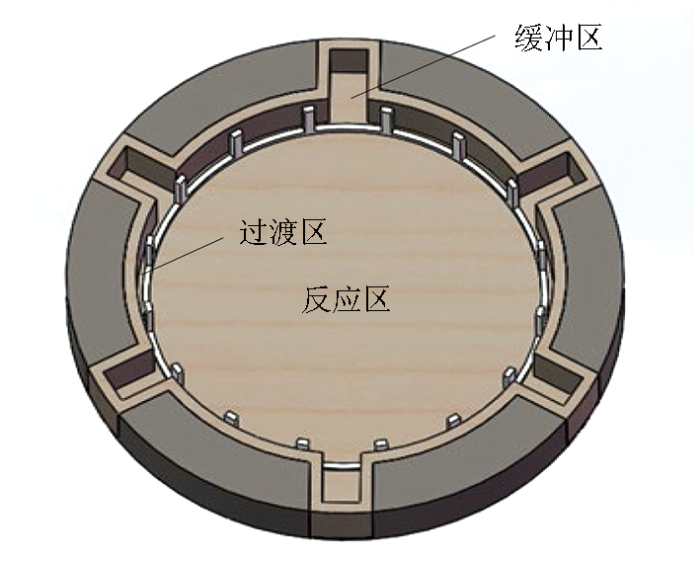
如图6所示,该结构利用高分子微孔隔膜将电极整体分为由反应区、过渡区、缓冲区组成的多仓结构,高分子微孔隔膜通过支撑架固定于电极内壁的内测,距离内壁一定宽度处。隔膜内测为反应区,隔膜外侧为过渡区,凸起的多个触角构成缓冲区。如此,可通过分区隔离减缓外部离子向电极的反应区进行扩散,进而有效减缓反应区离子浓度受外部离子扩散影响而引起的极差变化,增强电极的极差稳定性,降低电极的极差和极差漂移。
图6
图6
多触角电场传感器结构俯视分区示意
Fig.6
Overlooking partition diagram of multi-contactor electric field sensor structure
3 石墨烯基电场传感器测试
3.1 石墨烯基电场传感器性能指标测试
3.1.1 石墨烯基电场传感器极差与极差漂移测试
在可密封容器中加入适量的3.5%浓度NaCl溶液(饱和食盐水),保证所有待测电极的接触角能够充分浸没在溶液中,容器顶部预留适宜接线端口,一端连接待测电极对,另一端接入高精度直流电压表。本文测试中选用精度达到6位半的Keithley 2700数字万用表,能够保证数微伏级电压测量精度。设置数字万用表工作于直流电压测量模式,根据测试需求,每隔1 min记录一次电压值,连续测量120 h。测量结束后,导出测试结果数据,利用Matlab软件进行数据处理成图,每个通道测得直流电压的平均值即为被测电极对的极差,特定时间段内电压的峰峰值对应该时间段内的极差漂移(如图7所示),例如连续5天的测量电压峰峰值即为5日的极差漂移,每日连续24 h测量的电压峰峰值即为每日极差漂移。成图并统计连续5天测量的极差和极差漂移结果,统计每日极差漂移情况,计算5天连续测量的5组每日极差漂移的标准差,分析电场传感器的极差及其极差漂移的稳定性情况。
图7
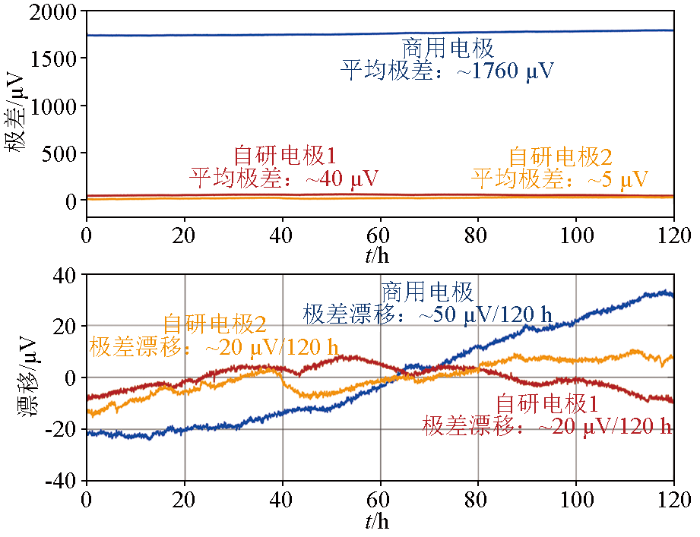
依据测试方案,对所研制的石墨烯基电场传感器的极差和极差漂移进行测试,并与国内主流的商用电极进行比对。按上述数据处理方法处理多次、多天电极极差和漂移测量的结果,得到如图8所示的极差与极差漂移测试比对结果。可知,两对石墨烯基电场传感器连续5天测得的平均极差分别为40 μV和5 μV,远小于商用电极的1 760 μV;而且,两对自研石墨烯基电场传感器连续5天(120 h)的极差漂移约为20 μV,小于商用电极所达到的50 μV。
图8
图8
极差与极差漂移连续5天的测试比对结果
Fig.8
Comparison results for 5 days of the potential difference and drift
图9
表1 连续5天的每日极差漂移测量结果统计
Table 1
| 项目 | 每日极差漂移结果/μV | 标准 差/μV | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 第1天 | 第2天 | 第3天 | 第4天 | 第5天 | ||
| 自研电极1 | 9.1 | 5.3 | 3.1 | 1.4 | 7.8 | 3.2 |
| 自研电极2 | 11.0 | 3.9 | 9.4 | 7.1 | 5.2 | 2.9 |
| 商用电极 | 3.7 | 6.8 | 15.5 | 16.7 | 12.0 | 5.6 |
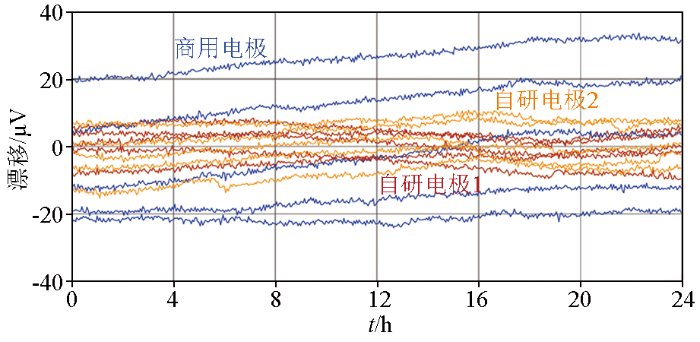
同等测试条件下,同时、同步测量结果显示,自研石墨烯基电场传感器的极差漂移不超过11 μV/24 h,小于商用电极达到的不超过16.7 μV/24 h,而且两对石墨烯基电场传感器连续5天测得的每日极差漂移标准差更小,表示其每日极差漂移更稳定。
3.1.2 石墨烯基电场传感器本底噪声测试
表2 本底噪声测试设备及参数指标
Table 2
| 设备名 | 用途 | 主要技术指标 | 实物图片 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 高精度多路 噪声分析 装置 | 噪声 测量 | 本底噪声 优于10nV/ 观测带宽 DC~1000Hz |
表3 被测电场传感器电阻测试结果 Tabal 3 Resistance of the tested electric field sensors
| 被测项目 | 被测电阻/Ω |
|---|---|
| 自研电极1 | 322 |
| 自研电极2 | 344 |
| 商用电极 | 1256 |
图10
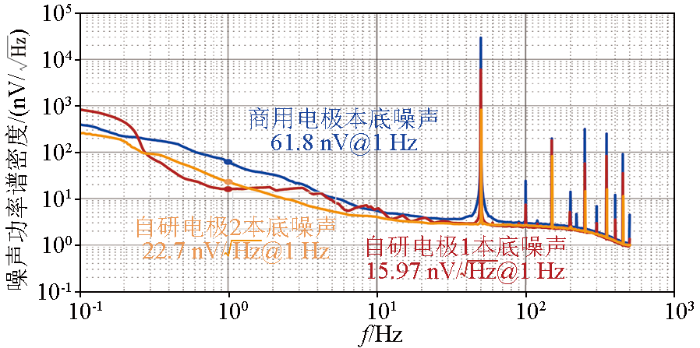
同等测试条件下,同时、同步测量结果显示,自研石墨烯基电场传感器的本底噪声不超过25 nV/
3.2 石墨烯基电场传感器野外探测试验应用
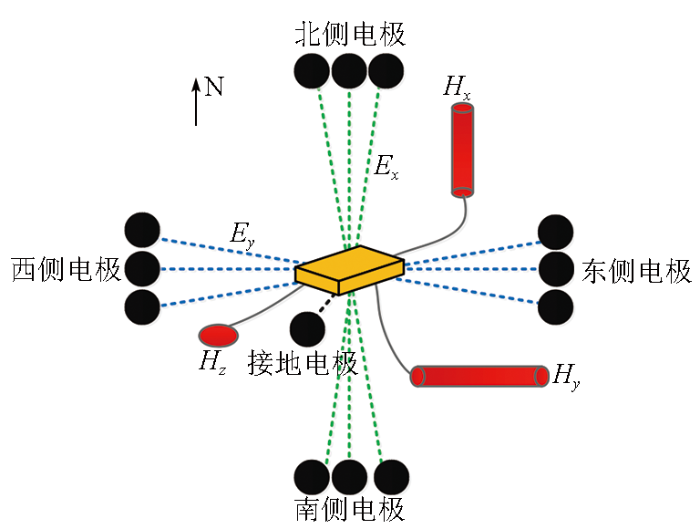
在黑龙江多宝山矿区,使用DRU-3C采集站、磁传感器、石墨烯基电场传感器和商用电极等设备,开展了石墨烯基电场传感器与商用电极的大地电磁(MT)探测对比试验。通过采集时长为24小时的MT试验,测试了石墨烯基电场传感器的野外实际应用效果。按照标准的大地电磁布极方式进行装置布设,整体布置如图11所示,在北、南、东、西4个方向同一点位分别布置两对石墨烯基电极和一对商用电极,电极距为100 m,同时布置三分量的磁场传感器。
图11
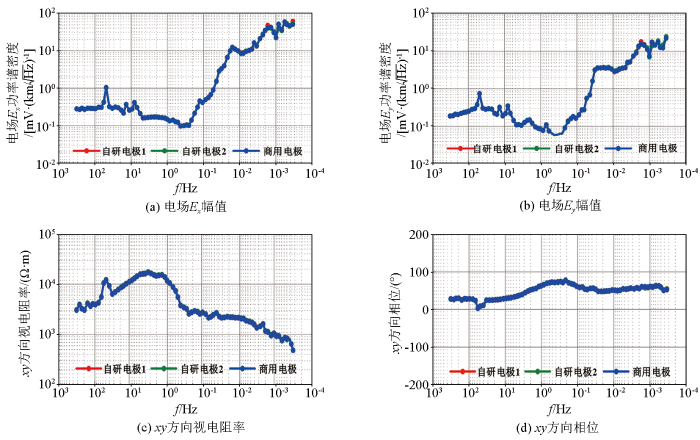
对未经任何处理的原始数据进行电场功率谱和视电阻率相位计算,绘制电场和视电阻率比对曲线,如图12所示。可知,采集的24小时的大地电磁原始数据经简单时频变换处理后,获取了0.000 125~320 Hz频段的有效电场及视电阻率相位结果。电场及视电阻率相位曲线在整个频段内相对平滑,符合大地电磁数据的基本特点。电场和视电阻率相位处理结果表明,在MT模式下,石墨烯基电场传感器与商用电极可获取基本一致的电场和视电阻率相位曲线,验证了石墨烯基电场传感器野外工作的有效性。进一步分析发现,该测点处视电阻率取值范围为400~2 000 Ω·m,表明该区域属于中阻区。对应电场信号取值范围为50 μV/(km/
图12
图12
野外实测电场与视电阻率及相位对比结果
Fig.12
Field comparison results of electric field, apparent resistivity and phase
4 结论及讨论
自主研制石墨烯电场传感器,利用比表面积更大、交换电流密度更大的Ag-AgCl体系石墨烯基电解质凝胶作为反应浆料,结合隔离性更强、接触性更优的基于高分子微孔隔膜结构分割的多仓式、多触角电极结构,有效提升了电场传感器的极差漂移和本底噪声等性能指标,研制的电场传感器极差漂移不高于20 μV/24 h,本底噪声不超过25 nV/
参考文献
Basic theory of the magneto-telluric method of geophysical prospecting
[J].
On determining electrical characteristics of the deep layers of the earth’s crust
[J].
我国大地电磁测深新进展及瞻望
[J].
New advance and prospect of magnetotelluric sounding (MT) in China
[J].
Very long period magnetotellurics at Tucson Observatory:Estimation of impedances
[J].
Very long period magnetotellurics at Tucson Observatory:Implications for mantle conductivity
[J].
Improving of electrical channels for magnetotelluric sounding instrumentation
[J].
电极极化电位对地电场观测影响研究
[J].
Analysis and study on the influence of polarization potential in measuring geoelectric field
[J].
地电场观测过程中的干扰因素分析
[J].
Analysis on the interference factors in geoelectric field observation
[J].
Noise,temperature coefficient,and long time stability of electrodes for telluric observations
[J].
固体不极化电极的研制及其应用效果
[J].
The development and application of solid nonpolarized electrodes
[J].
一种Pb-PbCl2不极化电极试验研究
[J].
Research on a type of Pb-PbCl2 non-polarizable electrode
[J].
Pb-PbCl2不极化电极的设计与实现
[J].
The design and implementation of non-polarizable Pb-PbCl2 electrodes
[J].
Pb-PbCl2不极化电极在长周期大地电磁测深观测中的应用效果
[C]//
Application effect of Pb-PbCl2 non-polarized electrode in Long period magnetotelluric sounding observation
[C]//
免维护超低噪声固体不极化电极的研制与性能测试
[J].
Development and performance tests of maintenance-free ultra-low noise solid nonpolarizing electrodes
[J].
A one-year systematic study of electrodes for long period measurements of the electric field in geophysical environments
[J].
Ag/AgCl和碳纤维海洋电场电极的探测特性研究
[J].
Study on the detection characteristics of Ag/AgCl and carbon fiber marine electric field electrodes
[J].
Design and characterization of an ultralow-potential drift Ag/AgCl electric field sensor
[C]//
Ag/AgCl电极的制备及电化学性能
[J].
The preparation and electrochemical performance of Ag/AgCl electrodes
[J].
Relationship between microstructure of AgCl film and electrochemical behavior of Ag/AgCl electrode for chloride detection
[J].
The electrochemical formation and reduction of a thick AgCl deposition layer on a silver substrate
[J].
Investigation of the AgCl formation mechanism on the Ag wire surface for the fabrication of a marine low-frequency-electric-field-detection Ag/AgCl sensor electrode
[J].
DOI:10.1021/acsomega.2c01481
PMID:35910151
[本文引用: 1]

One of the most widely used electric field sensors for low-frequency electric field detection (LFEFD) in seawater uses the Ag/AgCl electrode. The surface structure of the electrode including AgCl layers plays a critical role in the electrode's electrochemical performance required for the sensor. In this study, the sequential AgCl formation process under the constant current was examined on the Ag wire in an electrode size for actual applications, and an optimal electrode surface structure was suggested for the LFEFD Ag/AgCl sensor. Upon mild anodization (0.2 mA/cm) in 3.3 M KCl solution that permits us to follow the AgCl formation process manageably, Ag dissolution from the wire surface begins leaving cavities on the surface, with the accompanied growth of initial Ag grains. During this period, AgCl deposits in sizes of about several micrometers to 10 μm with crystal planes also form primarily along scratch lines on the wire surface, but in a partial scale. Then, with further anodization, the assumed thin AgCl deposits start to form, covering a large portion of the wire surface. They grow to become deposits in sizes of about several micrometers to 10 μm with no clear facet planes next to one another and are connected to form the network structure, representing the main developing mode of the AgCl deposits. While they cover all the surface, AgCl deposits also form on the surface of the already formed ones, making multiple AgCl layers. All these deposits develop through the nucleation process with a relatively high surface energy barrier, and their formation rate is solely controlled by the release rate of Ag from the wire, thus by the applied current magnitude. The Ag/AgCl electrode with a thick AgCl layer and many holes in the AgCl surface structure like microchannels is considered to work effectively for the LFEFD sensor in terms of both detection sensitivity and service lifetime.© 2022 The Authors. Published by American Chemical Society.
石墨烯对Ag/AgCl电极水下电场探测性能的影响研究
[J].
DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1000-1093.2019.12.018
[本文引用: 1]

利用石墨烯制备新型Ag/AgCl电极,开展其电化学性能及探测性能研究。通过对表面结构表征、电极极差、幅频响应、自噪声、极化曲线、吸水量和扫描振动电极等进行测试,分析石墨烯的加入及其含量对Ag/AgCl电极探测性能的影响规律。研究发现:相对于Ag/AgCl电极,石墨烯-Ag/AgCl电极极差稳定时间短、极差小、电化学性能好,适用于快速部署测量;石墨烯含量不同,对于改变Ag/AgCl电极与溶液界面接触性质有不同的作用机制:石墨烯含量为1%时主要表现在提高电极的孔隙率、增大比表面积;石墨烯含量为3%时主要表现在改善电极表面均匀性、加速溶液介质渗透。不同的作用机制是导致不同石墨烯含量Ag/AgCl电极电化学性能差异的主要原因。
Effect of graphene modification on the detection performance of Ag/AgCl electrode in undersea electric field
[J].
DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1000-1093.2019.12.018
[本文引用: 1]

The electro-chemical properties and detection performance of Ag/AgCl electrode made of grapheme are studied. The influences of addition of graphene and its content on the detection performance of Ag/AgCl electrodes are analyzed from microstructure characterization, electrode potential drifts, amplitude-frequency response, self-noise, polarization curves, water absorption and microstructure of Ag/AgCl electrode. The study shows that the graphene-Ag/AgCl electrode has small potential drift, short stability time, and good electrochemical properties compared to Ag/AgCl electrode, which is suitable for the rapidly deploying measurement. The different contents of graphenes have different mechanisms of action for changing the interface contact properties of Ag/AgCl electrodes/solution. The porosity of electrode and the specific surface area increase with the graphene content of 1%, and the surface uniformity of electrode is improved and the permeation of solution medium is accelerated with the graphene content of 3%. Different mechanisms of action are the main reason for the difference of electrochemical properties of Ag/AgCl electrodes with different contents of graphene. Key
石墨烯和粘胶基碳纤维改性Ag/AgCl海洋电场电极的研究
[J].
Effect of carbon material modification on Ag/AgCl underwater electric field electrode
[J].
石墨烯改性Ag/AgCl电极的表面特性研究
[J].
Study on surface properties of graphene modified Ag/AgCl electrode
[J].