0 引言
张掖盆地处于甘肃省河西走廊,是全国最大的玉米种植区和重要的粮食、蔬菜、瓜果、油料、牛羊生产基地及国家现代农业示范区,对该区域土壤性状和成分的研究一直受到重视。20世纪90年代,张掖地区农科所完成了区域农田耕作层土壤化学性状测试,并将其与1986年的区域土壤普查结果作了对比[6];甘肃省地矿系统在张掖盆地第四系和南北山地分别完成了土壤测量和水系沉积物测量,利用张掖盆地土壤测量结果总结了生土层与表土层土壤中微量元素的富集状况,并提出了适宜种植作物的建议[7-8]。2000年以来,陆续出现多项针对河西走廊和盆地绿洲农业区的土壤地球化学调查成果,并利用调查数据对相应工作范围的重金属污染状况和生态风险进行了评价[9⇓⇓⇓-13]。上述各项成果中,甘肃省地矿系统于1990s的勘查成果覆盖面积最广,采样点位最多,采样深度相当于表土层深部的犁底层或耕作层与生土层的过渡部位,有别于其他工作者以耕作层和生土层为采样对象的工作方法,而且1990s是该区至今唯一区域地球化学勘查与农业土壤调查相重合的时代;然而,至今未能对该数据在探讨区域土壤环境地球化学特征方面的作用给予重视。本文将张掖盆地土壤与南北山地看作一个整体,选择20世纪90年代在张掖盆地和周围山地进行的32种元素的岩石、表土层深部土壤和水系沉积物测量数据,以重金属元素为主线,从区域和第四系地层两个层次,利用元素的背景分析结果,总结表土层深部土壤重金属元素的丰缺状况及其与同期耕作层土壤农化性状调查结果的差异,进一步探讨盆地土壤中重金属的物质来源,为深入理解该区域土壤物质成分的时空演化规律及土壤元素累积与趋势预测[14]奠定基础。
1 研究区概况
张掖盆地处于北祁连与龙首山之间,按地貌及水系展布特点,本文对该盆地的研究范围局限在高台、民乐、山丹围限的第四系分布地带,面积约8 700 km2(图1a)。盆地内地层主体为第四系(Q),边部零星出露新近系(N)。北部山地龙首山主体为下白垩统庙沟组(K1m)砂砾岩建造和古近系白杨河组(Eb)砂岩泥岩建造,出露基底岩石为龙首山岩群(Ar3-Pt1L)碎屑岩建造和碳酸盐岩建造。南部山地北祁连主体为下古生界奥陶系和志留系组成的复理石夹火山岩建造(O-S),上覆少量上古生界石炭系和二叠系细碎屑岩建造(C-P),以及下白垩统下沟组砂砾岩—泥岩建造(K1x);沿羊毛达板至老君山由北而南依次发育香毛山蛇绿岩和北祁连蛇绿混杂岩。新生代以来青藏高原持续隆升,并有沉积物粒度和古地震活动响应[15-16],其中,160 ka和40 ka的构造活动最为强烈[17]。
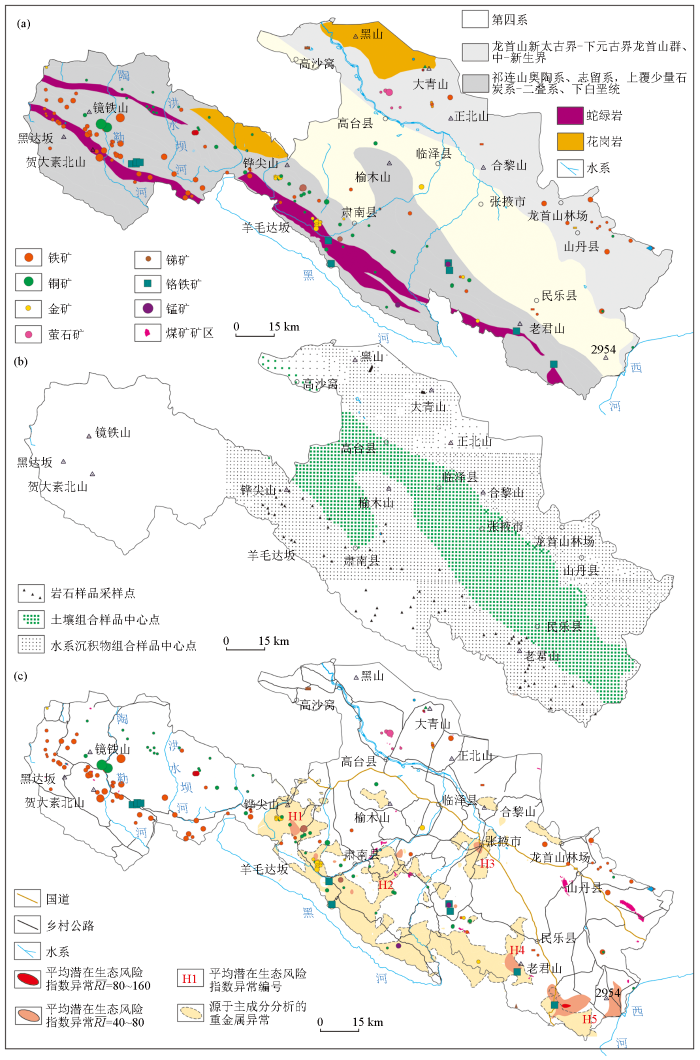
图1
图1
张掖盆地地质背景(a)、1990s表土层深部土壤样品采样位置(b)、重金属异常分布(c)
Fig.1
The geological background of Zhanye Basin (a),and its location of deep topsoil samples (b) and heavy metal anomalies(c) in 1990s
2 材料与方法
区域地球化学勘查样品的采样介质有岩石、土壤和水系沉积物,采样记录来源于20世纪90年代完成的祁连山幅、祁连幅、张掖幅、临泽幅、高台幅等5个1:20万图幅的区域化探报告。按照区域地球化学勘查规范[31],在北祁连和龙首山的每个系级单元采集岩石样品30件以上,在地质单元内均匀布置采样点,样品由多点法采集同一岩性岩石样品组合而成,每件样品质量大于200 g;同步采集水系沉积物样品,采样密度为1~4点/km2,样品采自一级水系或二级水系。在山前、山间及河西走廊第四系覆盖区和农田区采集土壤样品,采样密度1点/4 km2,采样深度10~30 cm,相当于表土层深部的犁底层;其中,在张掖幅的农田区同点采集浅层(10~30 cm)和深层(60~90 cm)两种样品,本文采用其浅层样品测试数据。在采样过程中完整地记录了采样位置、采样层位、样品性质、水系级别、地形等级、植被等若干参数。本文采用85件岩石样品、1 710件表土层深部土壤样品、3 913件水系沉积物样品(图1b)的测试数据进行分析。
土壤样品截取粒级为-60目,水系沉积物样品截取粒级为-20~+80目(北祁连)和-4~+60目(龙首山)[7-8,32]。所有样品过筛后质量大于250 g,并按4 km2单元形成的组合样为分析样品。所有样品均由甘肃省地质矿产局兰州中心实验室按区域地球化学勘查规范进行定量分析,共测试元素39种,本文从中选择了重金属元素和能反映物质成分和示踪物源的SiO2、Al2O3、K2O、Na2O、CaO、MgO、Fe2O3、Ti、Zr、Nb、La、Th、Co、Y、Ni、B、P 等32种元素或氧化物来进行张掖盆地表土层深部土壤成分和物质来源研究,各元素的分析方法是:Sb、As为原子荧光法,其余元素为X-射线荧光法;各元素的分析报出率(88.01%~100%)、一标对数偏差(100%)、二标批次合格率(97.2%~100%)、内检相对误差合格率(96.9%~100%)4项质量监控指标完全满足规范(DZ/T 0167—1995)[31]要求。SiO2、Al2O3、K2O、Na2O、CaO、MgO和Fe2O3的含量单位为%,Hg和Cd的含量单位为10-9,其余元素的含量单位为10-6。
表1 张掖盆地第四系与毗邻地质单元的重金属及其他元素的背景值
Table 1
| 介质 | 地质 单元 | 代码 | 样数 | Cu | Zn | Mo | Cr | Hg | Cd | Pb | As | Al2O3 | SiO2 | Na2O | CaO | MgO | Fe2O3 | Mn | K2O |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 岩石 (R) | 大青山 花岗岩 | DGR | 10 | 51.46 | 63.57 | 0.11 | 18.94 | 35.52 | 73.09 | 11.65 | 1.96 | 15.72 | 61.67 | 3.09 | 5.67 | 3.09 | 4.95 | 945.00 | 1.63 |
| 龙首山 | LSS | 8 | 18.72 | 69.92 | 0.48 | 17.87 | 19.62 | 65.52 | 18.91 | 2.14 | 14.84 | 63.65 | 3.20 | 4.54 | 2.39 | 4.84 | 887.28 | 2.05 | |
| 北祁连 | NQL | 56 | 43.46 | 59.44 | 0.33 | 63.17 | 31.80 | 95.09 | 19.42 | 8.79 | 9.44 | 57.48 | 1.02 | 3.64 | 2.59 | 4.97 | 859.58 | 1.40 | |
| 北祁连 蛇绿岩 | NQO | 11 | 21.95 | 50.09 | 0.36 | 55.54 | 34.68 | 76.40 | 25.15 | 8.79 | 10.59 | 65.24 | 1.19 | 2.53 | 2.16 | 4.06 | 585.05 | 1.83 | |
| 土壤 (So) | 第四系 | Q | 1710 | 23.04 | 50.99 | 0.62 | 85.03 | 30.04 | 103.65 | 19.36 | 5.11 | 10.46 | 66.35 | 1.47 | 4.33 | 2.44 | 4.10 | 590.23 | 1.97 |
| 全国背 景值[39] | 860 | 20.00 | 67.70 | 1.20 | 53.90 | 40.00 | 74.00 | 23.60 | 9.20 | 12.11 | 3.61 | 0.99 | 1.04 | 3.90 | 482.00 | 2.16 | |||
| 1990耕 作层[6] | 35.03 | 89.99 | 15.47 | 50.13 | 105.10 | 326.50 | 4.31 | 0.14 | 5.61 | 1.98 | 3.33 | 611.80 | 0.94 | ||||||
| 水系 沉积 物(St) | 大青山 花岗岩 | DGRS | 5 | 24.77 | 73.14 | 0.42 | 34.26 | 9.15 | 101.91 | 41.86 | 3.27 | 11.69 | 67.24 | 2.45 | 3.60 | 1.75 | 4.08 | 648.90 | 3.38 |
| 龙首山 | LSSS | 560 | 12.36 | 33.93 | 0.58 | 35.98 | 16.60 | 73.81 | 22.83 | 1.38 | 9.53 | 69.44 | 1.54 | 3.37 | 1.54 | 2.56 | 470.46 | 2.40 | |
| 北祁连 | NQLS | 1482 | 27.55 | 62.91 | 0.64 | 83.49 | 28.71 | 107.22 | 20.82 | 11.05 | 12.41 | 63.90 | 1.44 | 3.03 | 2.18 | 4.86 | 646.96 | 2.32 | |
| 北祁连 蛇绿岩 | NQOS | 153 | 36.46 | 69.73 | 0.78 | 153.84 | 31.93 | 136.77 | 19.74 | 15.83 | 11.80 | 62.90 | 1.22 | 3.47 | 3.44 | 5.59 | 765.5 | 1.91 | |
| R/St 相对 偏差 RE/% | 大青山 花岗岩 | -70.03 | 14.01 | 115.31 | 57.60 | -118.10 | 32.94 | 112.93 | 50.08 | -29.38 | 8.65 | -23.02 | -44.72 | -55.16 | -19.26 | -37.15 | 70.02 | ||
| 龙首山 | -40.91 | -69.31 | 19.73 | 67.25 | -16.65 | 11.90 | 18.78 | -43.16 | -43.58 | 8.69 | -69.90 | -29.61 | -43.50 | -61.73 | -61.40 | 15.33 | |||
| 北祁连 | -44.80 | 5.67 | 63.50 | 27.72 | -10.20 | 12.00 | 6.97 | 22.78 | 27.20 | 10.57 | 34.42 | -18.39 | -17.06 | -2.36 | -28.23 | 49.89 | |||
| 北祁连 蛇绿岩 | 49.68 | 32.78 | 74.89 | 93.89 | -8.25 | 56.64 | -24.09 | 0.15 | 10.77 | -3.65 | 1.99 | 31.32 | 45.84 | 31.85 | 26.72 | 4.33 | |||
| 介质 | 地质 单元 | 代码 | 样数数 | P | B | F | Sb | Ag | Co | La | Li | Nb | Ni | Sn | Sr | Th | Ti | Y | Zr |
| 岩石 (R) | 大青山 花岗岩 | DGR | 10 | 645.92 | 20.92 | 480.93 | 0.30 | 39.75 | 17.37 | 29.47 | 10.05 | 9.23 | 15.83 | 1.71 | 405.92 | 7.50 | 4151.57 | 22.41 | 159.37 |
| 龙首山 | LSS | 8 | 719.21 | 11.01 | 458.75 | 1.24 | 63.91 | 13.87 | 28.69 | 18.69 | 11.08 | 11.01 | 1.66 | 382.43 | 9.16 | 3932.44 | 21.01 | 146.00 | |
| 北祁连 | NQL | 56 | 268.86 | 23.83 | 487.02 | 2.24 | 78.49 | 13.34 | 16.63 | 16.32 | 10.25 | 35.20 | 2.12 | 140.00 | 9.09 | 2587.70 | 19.99 | 109.13 | |
| 北祁连 蛇绿岩 | NQO | 11 | 363.37 | 18.42 | 368.63 | 5.12 | 83.10 | 11.18 | 24.27 | 13.71 | 9.68 | 22.94 | 1.79 | 122.87 | 9.14 | 2443.03 | 19.25 | 126.00 | |
| 土壤 (So) | 第四系 | Q | 1710 | 541.90 | 37.21 | 471.51 | 0.83 | 58.29 | 11.27 | 34.47 | 21.23 | 11.98 | 33.42 | 2.35 | 160.10 | 9.10 | 3144.46 | 21.02 | 187.83 |
| 全国背 景值[39] | 860 | 440.00 | 38.70 | 440.00 | 1.06 | 110.00 | 11.20 | 37.40 | 29.10 | 23.40 | 2.30 | 121.00 | 12.80 | 3800.00 | 21.80 | 237.00 | |||
| 1990耕 作层[6] | 1413.00 | 88.29 | 19.94 | 38.65 | 51.15 | 92.68 | |||||||||||||
| 水系 沉积 物(St) | 大青山 花岗岩 | DGRS | 5 | 656.10 | 521.26 | 0.36 | 82.45 | 9.60 | 37.27 | 35.20 | 13.93 | 24.12 | 5.32 | 151.99 | 17.22 | 3473.82 | 26.30 | 183.21 | |
| 龙首山 | LSSS | 560 | 402.39 | 448.11 | 0.47 | 48.01 | 6.35 | 37.15 | 12.40 | 11.19 | 11.06 | 2.20 | 170.83 | 8.48 | 2318.19 | 20.11 | 173.19 | ||
| 北祁连 | NQLS | 1482 | 606.62 | 518.04 | 0.98 | 61.65 | 13.75 | 35.81 | 25.89 | 12.72 | 36.73 | 2.50 | 145.35 | 11.38 | 3762.23 | 22.50 | 186.96 | ||
| 北祁连 蛇绿岩 | NQOS | 153 | 589.64 | 594.70 | 1.30 | 72.34 | 16.83 | 35.06 | 28.37 | 12.99 | 76.11 | 2.30 | 118.17 | 11.31 | 4087.15 | 21.61 | 178.67 | ||
| R/St 相对 偏差 RE/% | 大青山 花岗岩 | 1.56 | 8.05 | 18.63 | 69.88 | -57.64 | 23.39 | 111.19 | 40.64 | 41.49 | 102.80 | -91.03 | 78.69 | -17.78 | 15.97 | 13.92 | |||
| 龙首山 | -56.49 | -2.35 | -90.67 | -28.42 | -74.37 | 25.68 | -40.48 | 0.97 | 0.42 | 27.79 | -76.49 | -7.67 | -51.65 | -4.35 | 17.04 | ||||
| 北祁连 | 77.16 | 6.17 | -78.81 | -24.04 | 3.03 | 73.16 | 45.38 | 21.53 | 4.24 | 16.43 | 3.74 | 22.40 | 36.99 | 11.81 | 52.57 | ||||
| 北祁连 蛇绿岩 | 47.48 | 46.93 | -118.97 | -13.84 | 40.31 | 36.36 | 69.68 | 29.15 | 107.38 | 24.85 | -3.89 | 21.19 | 50.35 | 11.53 | 34.58 |
注:氧化物含量单位为%,Hg、Cd含量单位为10-9,其余元素含量单位为10-6。
元素在地表风化产物中的稳定性与区域地理条件或地球化学景观有关,本文利用元素在岩石和水系沉积物中背景值的相对偏差(RE)来确定该区域地表环境中的稳定元素,计算公式为:
3 结果与讨论
3.1 区域表土层深部土壤地球化学特征
与1990年张掖地区农科所对耕作层的调查成果[6]相比,研究区表土层深部土壤重金属元素Cr显著富集,Cu、Zn、Pb和As显著贫化;其他指标中,Al2O3、Na2O、Fe2O3和K2O显著富集,CaO、P、B、Co、Li、Ni和Sn显著贫化;说明耕作层中的重金属主要来源于人类活动,可能与施肥对耕作层上部产生影响,灌溉使黏粒沉积在犁底层和干旱地区,并产生蒸发作用有关。
与大青山花岗岩、龙首山、北祁连和北祁连蛇绿岩的岩石地球化学背景值比较,研究区表土层深部土壤重金属元素中Cd、Cr相对北祁连和龙首山全面富集,Pb和As较龙首山富集,但较北祁连贫化。与大青山花岗岩、龙首山、北祁连和北祁连蛇绿岩的水系沉积物地球化学背景值比较,研究区表土层深部土壤较北祁连和龙首山均富集Hg和Cr,较北祁连贫化但较龙首山富集的有Cd和As。表土层深部土壤中重金属的这种富集特点和由南到北的渐变趋势说明其富集过程分别与人类活动和机械混合过程有关。
3.2 地层的表土层深部土壤地球化学特征
表2 张掖盆地第四纪沉积层重金属及其他元素背景值
Table 2
| 地质单元 | 代码 | 样数 | Cu | Zn | Mo | Cr | Hg | Cu | Zn | Mo | Cr | Hg | Al2O3 | SiO2 | Na2O | CaO | MgO | Fe2O3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 第四系 | Q | 1710 | 23.04 | 50.99 | 0.62 | 85.03 | 30.04 | 23.04 | 50.99 | 0.62 | 85.03 | 30.04 | 10.46 | 66.35 | 1.47 | 4.33 | 2.44 | 4.10 |
| 下更新统玉 门组洪积层 | Qp1y | 4 | 19.87 | 48.04 | 0.46 | 93.73 | 39.44 | 19.87 | 48.04 | 0.46 | 93.73 | 39.44 | 10.95 | 69.67 | 1.57 | 3.51 | 2.58 | 3.91 |
| 中更新统酒 泉组洪积— 冰积层 | Qp2j | 17 | 20.64 | 47.80 | 0.60 | 66.97 | 30.57 | 20.64 | 47.80 | 0.60 | 66.97 | 30.57 | 11.57 | 67.22 | 1.30 | 3.62 | 2.12 | 4.21 |
| 上更新统近 河道洪积层 | 119 | 15.81 | 44.03 | 1.00 | 43.70 | 17.59 | 15.81 | 44.03 | 1.00 | 43.70 | 17.59 | 10.79 | 64.69 | 1.29 | 4.87 | 2.83 | 3.35 | |
| 上更新统河 道北砂砾层 | 53 | 9.38 | 24.34 | 0.48 | 29.26 | 15.72 | 9.38 | 24.34 | 0.48 | 29.26 | 15.72 | 7.54 | 75.93 | 1.69 | 2.51 | 0.97 | 1.94 | |
| 上更新统河 道南洪积层 | 262 | 17.79 | 43.53 | 0.50 | 76.00 | 28.53 | 17.79 | 43.53 | 0.50 | 76.00 | 28.53 | 9.84 | 71.60 | 1.47 | 3.25 | 1.97 | 3.64 | |
| 全新统河道 北冲洪积层 | Qhalpln | 7 | 9.75 | 26.60 | 0.23 | 23.19 | 16.26 | 9.75 | 26.60 | 0.23 | 23.19 | 16.26 | 10.02 | 73.28 | 2.11 | 2.98 | 1.20 | 1.96 |
| 全新统河道 南冲洪积层 | Qhalpls | 123 | 23.46 | 52.13 | 0.69 | 84.81 | 35.49 | 23.46 | 52.13 | 0.69 | 84.81 | 35.49 | 11.09 | 63.93 | 1.50 | 4.74 | 2.86 | 4.00 |
| 全新统河道 北坡残积层 | Qhdeln | 14 | 5.66 | 16.33 | 0.29 | 19.48 | 14.55 | 5.66 | 16.33 | 0.29 | 19.48 | 14.55 | 6.83 | 81.09 | 1.46 | 1.81 | 0.58 | 1.20 |
| 全新统河道 南坡残积层 | Qhdels | 10 | 12.76 | 34.03 | 0.48 | 54.89 | 24.93 | 12.76 | 34.03 | 0.48 | 54.89 | 24.93 | 8.74 | 76.04 | 1.48 | 2.57 | 1.28 | 2.87 |
| 全新统风积层 | Qheol | 88 | 20.45 | 43.99 | 0.51 | 79.82 | 22.13 | 20.45 | 43.99 | 0.51 | 79.82 | 22.13 | 9.78 | 70.13 | 1.52 | 3.33 | 2.26 | 3.69 |
| 全新统湖 沼相堆积 | Qhl | 44 | 28.87 | 55.26 | 1.08 | 79.65 | 32.27 | 28.87 | 55.26 | 1.08 | 79.65 | 32.27 | 10.41 | 59.55 | 1.81 | 6.26 | 4.34 | 3.82 |
| 全新统河道 南洪积层 | Qhpls | 262 | 25.88 | 60.73 | 0.76 | 103.75 | 41.08 | 25.88 | 60.73 | 0.76 | 103.75 | 41.08 | 12.01 | 63.32 | 1.35 | 4.99 | 3.03 | 4.42 |
| 全国背景值[39] | 860 | 20.00 | 67.70 | 1.20 | 53.90 | 40.00 | 20.00 | 67.70 | 1.20 | 53.90 | 40.00 | 12.11 | 3.61 | 0.99 | 1.04 | 3.90 | ||
| 地质单元 | 代码 | 样数 | Cd | Pb | As | Sb | Ag | Co | La | Li | Nb | Ni | Sn | Sr | Th | Ti | Y | Zr |
| 第四系 | Q | 1710 | 103.65 | 19.36 | 5.11 | 0.83 | 58.29 | 11.27 | 34.47 | 21.23 | 11.98 | 33.42 | 2.35 | 160.09 | 9.10 | 3144.46 | 21.02 | 187.83 |
| 下更新统玉 门组洪积层 | Qp1y | 4 | 87.82 | 14.09 | 1.19 | 0.57 | 58.66 | 11.10 | 36.66 | 15.19 | 10.89 | 30.50 | 1.85 | 149.04 | 6.85 | 3040.35 | 19.85 | 149.36 |
| 中更新统酒 泉组洪积— 冰积层 | Qp2j | 17 | 71.02 | 13.39 | 1.52 | 0.76 | 46.99 | 12.42 | 38.28 | 18.59 | 12.37 | 22.60 | 2.19 | 175.35 | 7.30 | 3259.46 | 20.67 | 157.68 |
| 上更新统近 河道洪积层 | 119 | 67.50 | 17.66 | 1.46 | 0.67 | 39.24 | 8.80 | 43.18 | 14.58 | 14.75 | 16.49 | 2.08 | 183.66 | 8.26 | 2993.64 | 21.72 | 195.60 | |
| 上更新统河 道北砂砾层 | 53 | 60.82 | 26.76 | 1.25 | 0.35 | 50.27 | 4.55 | 29.50 | 9.65 | 8.44 | 7.58 | 2.08 | 166.94 | 7.83 | 1739.95 | 17.86 | 154.30 | |
| 上更新统河 道南洪积层 | 262 | 80.93 | 19.92 | 1.84 | 0.64 | 48.52 | 9.96 | 35.89 | 17.53 | 10.90 | 23.93 | 2.02 | 145.90 | 7.48 | 2772.55 | 19.32 | 156.04 | |
| 全新统河道 北冲洪积层 | Qhalpln | 7 | 51.79 | 17.29 | 1.74 | 0.23 | 40.84 | 4.12 | 38.18 | 7.02 | 10.41 | 6.38 | 2.29 | 295.45 | 7.03 | 1540.52 | 17.99 | 139.54 |
| 全新统河道 南冲洪积层 | Qhalpls | 123 | 98.25 | 21.11 | 1.92 | 0.79 | 56.37 | 11.78 | 40.50 | 19.70 | 12.75 | 32.66 | 2.30 | 203.29 | 9.39 | 3225.36 | 21.66 | 179.09 |
| 全新统河道 北坡残积层 | Qhdeln | 14 | 60.79 | 25.76 | 1.06 | 0.25 | 44.25 | 2.63 | 29.62 | 7.78 | 7.85 | 4.57 | 1.85 | 150.15 | 6.47 | 1244.29 | 16.30 | 110.40 |
| 全新统河道 南坡残积层 | Qhdels | 10 | 80.66 | 22.05 | 1.43 | 0.61 | 58.44 | 7.15 | 33.88 | 13.17 | 9.33 | 12.86 | 1.99 | 138.50 | 7.66 | 2299.24 | 17.94 | 147.67 |
| 全新统风积层 | Qheol | 88 | 84.84 | 19.09 | 2.06 | 0.63 | 52.26 | 10.29 | 36.33 | 17.81 | 10.81 | 24.02 | 2.27 | 160.61 | 8.60 | 2844.98 | 19.30 | 150.79 |
| 全新统湖 沼相堆积 | Qhl | 44 | 99.71 | 19.04 | 1.62 | 0.79 | 65.44 | 12.20 | 43.59 | 23.20 | 11.78 | 32.20 | 2.34 | 326.81 | 8.60 | 3213.38 | 21.06 | 177.54 |
| 全新统河道 南洪积层 | Qhpls | 262 | 106.65 | 22.23 | 2.03 | 0.85 | 60.45 | 13.64 | 42.35 | 22.47 | 13.54 | 41.54 | 2.35 | 193.43 | 8.53 | 3562.90 | 22.73 | 190.24 |
| 全国背景值[39] | 860 | 74.00 | 23.60 | 9.20 | 1.06 | 110.00 | 11.20 | 37.40 | 29.10 | 23.40 | 2.30 | 121.00 | 12.80 | 3800.00 | 21.80 | 237.00 |
注:氧化物含量单位为%,Hg、Cd含量单位为10-9,其余元素为10-6。
表3 第四纪沉积层中元素的丰缺状况
Table 3
| 地质单元 | 代码 | 重金属 | 其他元素 | 平均潜在生态 风险指数( | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 富集 | 贫化 | 富集 | 贫化 | |||
| 下更新统玉门组 | Qp1y | Cr、Cd | Cu、Zn | CaO、MgO、Fe2O3、P、Mn、F、Ni、Sr | K2O、Mo | 13.47~15.03 |
| 中更新统酒泉组 | Qp2j | Cu、Cr | Zn | CaO、MgO、Fe2O3、P、Mn、Co、Sr | K2O、Mo | 5.63~34.37 |
| 上更新统近河道洪积层 | Cu、Zn | CaO、MgO、K2O、P、Mn、F、La、Sr | Fe2O3、Mo | 5.63~30.48 | ||
| 上更新统河道北砂砾层 | Pb | Cu、Zn | CaO、K2O、Sr | MgO、Fe、P、Mn、Mo | 5.00~14.57 | |
| 上更新统河道南洪积层 | Cr | Cu、Zn | CaO、MgO、Mn、Ni、Sr | Fe、K2O、P、Mo | 7.53~29.09 | |
| 全新统河道北冲洪积层 | Qhalpln | Cu、Zn | CaO、MgO、K2O、Sr | Fe2O3、P、Mn、Mo | 7.18~11.38 | |
| 全新统河道南冲洪积层 | Qhalpls | Cu、Cr、Cd | Zn | CaO、MgO、Fe2O3、P、B、Mn、 Co、F、La、Ni、Sr | K2O、Mo | 13.98~49.89 |
| 全新统河道北坡残积层 | Qhdeln | Pb | Cu、Zn | CaO、K2O、Sr、Mo | MgO、Fe2O3、P、Mn | 6.49~14.33 |
| 全新统河道南坡残积层 | Qhdels | Cr、Cd | Cu、Zn | CaO、MgO、Sr、Mo | Fe2O3、K2O、P、Mn | 9.60~23.80 |
| 全新统风积层 | Qheol | Cu、Cr、Cd | Zn | CaO、MgO、P、Mn、Ni、Sr、Mo | Fe2O3、K2O | 6.97~39.71 |
| 全新统湖沼相堆积 | Qhl | Cu、Cr、Cd | Zn | CaO、MgO、P、B、Mn、Co、F、 La、Ni、Sn、Sr、Mo | Fe2O3、K2O | 0.91~1.13 |
| 全新统河道南洪积层 | Qhpls | Cu、Cr、Hg、Cd | Zn | CaO、MgO、Fe2O3、K2O、P、B、 Mn、Co、F、La、Ni、Sn、Sr、Y、Mo | 6.23~49.89 | |
3.3 表土层深部土壤的平均潜在生态风险指数
利用表土层深部土壤样品中的 Zn、Pb、Ni、Hg、Cu、Cr、Cd和As含量求得第四系地层的平均潜在生态风险指数
表4
H3平均潜在生态风险指数
Table 4
| 参数 | Zn | Pb | Ni | Hg | Cu | Cr | Cd | As | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 样品数 | 6 | 6 | 6 | 6 | 6 | 6 | 6 | 6 | 6 |
| 平均值 | 69.75 | 20.87 | 58.20 | 109.50 | 32.15 | 131.12 | 148.33 | 3.22 | 45.80 |
| 标准差 | 2.36 | 1.38 | 4.43 | 10.08 | 2.57 | 5.60 | 9.83 | 0.97 | 2.93 |
| 最小值 | 65.70 | 20.10 | 49.80 | 103.00 | 27.60 | 119.70 | 130.00 | 1.50 | 43.91 |
| 最大值 | 71.20 | 23.50 | 60.70 | 123.00 | 33.70 | 133.80 | 160.00 | 3.80 | 49.89 |
| 偏度 | -0.75 | 1.06 | -1.02 | 0.54 | -0.82 | -1.36 | -0.80 | -0.83 | 0.55 |
| 峰度 | 1.59 | 2.30 | 2.23 | 1.05 | 1.75 | 2.91 | 2.35 | 1.76 | 1.07 |
注:Hg、Cd含量单位为10-9,其余元素为10-6。
3.4 区域主成分异常指示的人类活动痕迹
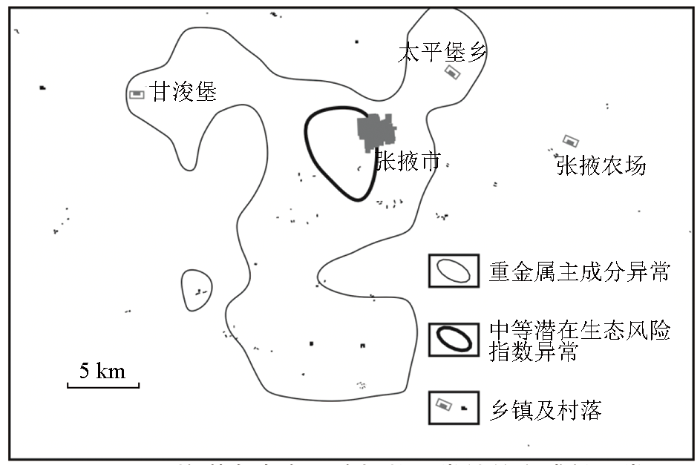
因子分析法常被用来分析重金属的来源[41⇓-43],本研究采用主成分分析结果来示踪污染物来源,纳入分析的变量为32种元素或氧化物,获得主成分F1(方差贡献=29.07%,载荷aij>0.4)的元素或化合物组合是Al2O3、Be、Bi、Y、W、V、U、Ti、P、Ni、Nb、Mn、Mg、Li、La、Fe2O3、F、Co、Cr、Cu、Zn、Cd、As,反映了北祁连蛇绿岩及重金属矿区,其异常的分布如图1c所示。H3处F1主要围绕张掖市区及村落分布;近张掖市区的重金属异常与人口密度呈正相关,但张掖农场未表现出重金属异常(图2),显著地表现为非农业人类活动污染迹象,如金属加工[11]、商业活动和道路结点等[13,42-43]。
图2
图2
H3平均潜在生态风险指数异常处的主成分异常
Fig.2
The princinpal component anomalies around H3 anomaly of average potential ecological risk indexes
3.5 元素地球化学混合模型指示的物质源区
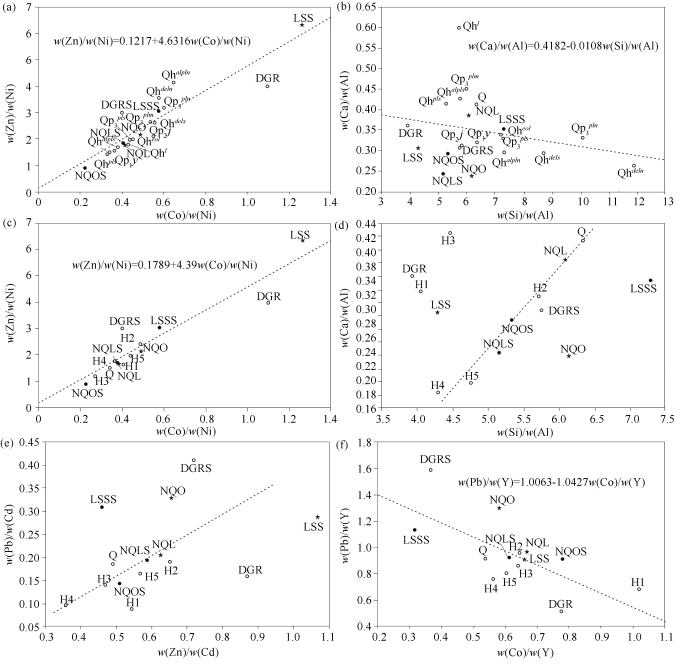
H1、H2、H4和H5潜在生态风险异常均毗邻北祁连蛇绿岩和重金属矿区,季节性洪水是搬运重金属的主要因素,风力作用影响相对较小;然而,由于狭管效应的存在,盆地内表土层深部土壤及其中的H3潜在生态风险指数异常的风成作用不能忽视。下面基于碱性条件下稳定元素的比值来判别风成作用对盆地内表土层深部土壤及其中H3潜在生态风险异常的影响。依照同一地质单元中元素在岩石和水系沉积物中背景值的相对偏差(RE)计算结果(表1)判断,在龙首山和北祁连,含量相对稳定的元素或化合物(RE<33%)有14种:SiO2、CaO、Hg、Cd、Pb、Zn、Ag、F、Nb、Ni、Sn、Th、Y、Co。进一步遵循元素的亲合性和通用混合方程[35⇓-37],选择碱性土壤中与铁氧化物相容的稳定元素[25⇓⇓⇓⇓-30,33-34]对比值图解,如w(Zn)/w(Ni)-w(Co)/w(Ni)图解和w(Pb)/w(Cd)-w(Zn)/w(Cd)图解(图3a、3c和3e)示踪土壤和重金属的物质源区;选择碱性土壤中与铁氧化物不相容的稳定元素[29]对比值图解,如w(Ca)/w(Al)-w(Si)/w(Al)图解和w(Pb)/w(Y)-w(Co)/w(Y)图解(图3b、3d和3f)示踪引起元素发生分异的地质作用。
图3
图3
张掖盆地表土层深部土壤与潜在生态风险指数异常物源地球化学图解
DGR—大青山花岗岩岩石;LSS—龙首山岩石;NQL—北祁连岩石;NQO—北祁连蛇绿岩岩石;DGRS—大青山花岗岩水系沉积物;LSSS—龙首山水系沉积物;NQLS—北祁连水系沉积物;NQOS—北祁连蛇绿岩水系沉积物;Q—第四系表土层深部土壤;Qp1y—玉门组洪积层表土层深部土壤;Qp2j—酒泉组洪积-冰积层表土层深部土壤;
Fig.3
Geochemical diagrams for origins of deep subsoil and potential ecological risk index anomalies in Zhangye Basin
DGR—Daqing mountain granite rocks; LSS—Longshou mountain rocks; NQL—north Qilian rocks; NQO—north Qilian ophiolite rocks; DGRS—Daqing mountain granite stream sediment; LSSS—Longshou mountain drainage sediment; NQLS—north Qilian stream sediment; NQOS—north Qilian ophiolite stream sediment; Q—Quaternary deep topsoil; Qp1y—diluvium layer of deep topsoil from Yumen Formation; Qp2j—diluvium-glacial layer of deep topsoil from Jiuquan Formation;
w(Zn)/w(Ni)-w(Co)/w(Ni)图解(图3a)和w(Pb)/w(Y)-w(Co)/w(Y)图解(图3f)显示,第四系地层整体和绝大部分第四系地层表土深层土壤处于北祁连水系沉积物附近,或介于北祁连水系沉积物与北祁连蛇绿岩水系沉积物之间,富集基性组分,即其主要源于北祁连;少部分黑河河道北的第四系地层接近于龙首山水系沉积物,或受风成作用和风化残积作用影响而趋于接近龙首山岩石样品成分,富集酸性组分,如上更新统河道北砂砾层(
w(Zn)/w(Ni)-w(Co)/w(Ni)图解中(图3c),表土深层土壤异常H3处于北祁连岩石(NQL)与北祁连蛇绿岩水系沉积物(NQOS)之间;w(Pb)/w(Cd)-w(Zn)/w(Cd)图解(图3e)和w(Pb)/w(Y)-w(Co)/w(Y)图解显示,H2、H3、H4、H5、NQL、NQLS和NQOS基本呈线性排列,即围绕张掖市区的H3异常除与西北侧的H2、北祁连水系沉积物和北祁连蛇绿岩有关外,还与位于其东南侧的H4和H5有关,表明除西北风的搬运作用外,夏秋季(7月)的东南风在重金属迁移中发挥了作用;这一点得到黑河流域季节性水质分析结果佐证,水中的Cd、Zn和Hg在7月份最高,Pb、Cr、Cu和As在7月份较低[44]。
3.6 物质来源综合分析
张掖盆地自第四纪以来承受了巨厚的松散堆积物,呈NW向带状分布,粒度自两侧向中心由粗变细,地貌上形成一倾斜平原。前人认为盆地物质皆取于祁连山、北山两地[40],但从元素在区域地质单元中的分配状况、区域主成分异常和碱性条件下稳定元素混合模型图解可知,盆地土壤主要来源于祁连山,少部分黑河河道北第四纪地层源于龙首山,不能排除人类活动和风成作用的影响。
山地水系沉积物是盆地土壤的直接来源。与周围主要地质单元的水系沉积物相比,盆地表土层深部土壤较北祁连和龙首山均富集Hg和Cr,较北祁连贫化但较龙首山富集Cd和As。结合稳定元素对比值图解判断,重金属Zn、Cd和As主要源于北祁连;Pb在河道北岸上更新统砂砾层和全新统残坡积层富集,指示其来源于龙首山;重金属Hg和Cr显著富集于盆地的表土层深部土壤中,难以完全用机械混合模型解释,主要与人类活动有关。
碱性条件下稳定元素混合模型图解显示,盆地表土层深部土壤中的H3异常与西北侧的H2、东南侧的H4和H5、北祁连水系沉积物和北祁连蛇绿岩有关,表明除西北风的搬运作用外,夏秋季(7月)的东南风在重金属迁移中发挥了作用。
4 结论
1)与全国土壤背景值相比,张掖盆地表土层深部土壤中重金属元素Cu和Cd富集,Zn和Mo贫化;其他富集元素或化合物中包含CaO、MgO、P、Sr、Ba,反映了钙成土的成分特征。与同时期耕作层土壤相比,重金属元素Cr显著富集,Cu、Zn、Mo、Pb和As显著贫化。
2)物质来源综合分析表明,Zn、Cd和As主要源于北祁连,Pb来源于龙首山,Hg和Cr主要与人类活动有关。
3)重金属元素在上更新统和全新统河道北沉积层中相对贫化,对应于晚更新世剧烈的新构造运动。下—中更新统富集重金属Cr、Cd或Cu;全新统河道南沉积层全面富集重金属Cu、Cr和Cd;Hg仅在全新统河道南洪积层中富集。该现象大致表明,重金属在表土层深部土壤中的富集程度与人类活动强度呈正相关,与新构造运动强度呈负相关。
4)碱性条件下稳定元素混合模型图解表明,除西北风的搬运作用外,夏秋季(7月)的东南风在重金属迁移中发挥了作用。
致谢
甘肃省地质学会及甘肃省地质调查院的各级领导在文献查阅和学术交流方面给予了支持,在此表示衷心感谢!
参考文献
辽阳市土壤重金属含量特征及潜在风险评价
[J].
Characteristics and potential risk assessment of heavy metal contents in urban soil,Liaoyang City
[J].
上海农田土壤重金属的环境质量评价
[J].
Evaluation on environmental quality of heavy metals in agricultural soils of Shanghai
[J].
微波消解—电感耦合等离子体质谱法同时测定垃圾渗滤液中8种生物毒性元素
[J].
Simultaneous determination of 8 kinds of biotoxicity elements in landfill leachate by inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry with microwave digestion
[J].
张掖地区农田土壤农化性状测试结果与分析
[J].
Test results and analysis of agrochemical characteristics of farmland soil in Zhangye area
[J].
张掖幅(J-47-Ⅺ)、山丹幅(J-47-Ⅻ)地球化学图说明书
[R].
Direction of Zhangye map-sheet(J-47-Ⅺ) and Shandan map-sheet (J-47-Ⅻ) geochemical map
[R].
酒泉幅(J-47-Ⅲ)、祁连山幅(J-47-Ⅸ)地球化学图说明书
[R].
Direction of Jiuquan map-sheet(J-47-Ⅲ) and Qilianshan map-sheet (J-47-Ⅸ) geochemical map
[R].
甘肃省河西灌漠土微量元素的空间变异特征
[J].
Spatial variabilitiy of trace elements of irrigated desert soil in Zhangye and Wuwei,Gansu Province
[J].
绿洲农田土壤主要微量元素的影响因素及分布特征研究——以张掖甘州区和临泽县为例
[J].
Spatial distribution and affecting factors of main trace elements in oasis cropland—A case of Ganzhou District and Linze of Zhangye
[J].
甘肃省张掖—永昌地区土壤有机碳密度算及其空间分布特征
[J].
The soil organic carbon density and its distribution charactoristics in Zhangye-Yongchang area,Gansu Province
[J].
张掖市甘州区北部土壤重金属污染特征及生态风险评价
[J].
Pollution characteristics and ecological risk assessment of soil heavy metals in northern Ganzhou District,Zhangye City
[J].
基于1:25万和1:5万土地质量地球化学调查评价的土壤元素累积趋势预测——以广西南宁市西乡塘区为例
[J].
Prediction of the soil element accumulation trends based on 1:250,000 and 1:50,000 geochemical surveys and assessments of land quality:A case study of Xixiangtang District,Nanning City,Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region
[J].
Relationship model of sediment grain size and Tibetan Plateau uplift in middle-west parts of Qilian Mountain
[J].
祁连山东段天桥沟—黄羊川断裂古地震活动习性研究
[J].天桥沟-黄羊川断裂位于祁连山东段主峰冷龙岭以东,是祁连山东段的重要活动断裂之一。该断裂以关家台为界分为东西2段,全新世以来均有过明显的活动。沿断裂开挖了6个古地震探槽,通过综合对比得到了该断裂全新世以来的7次古地震事件和1次历史地震事件,其年代分别为事件Ⅰ(10743±343)aBP,事件Ⅱ(9038±39)aBP,事件Ⅲ(7050±577)aBP,事件Ⅳ(4847±185)aBP,事件Ⅴ(3562±190)aBP,事件Ⅵ(2476±194)aBP,事件Ⅶ(1505±253)aBP,事件Ⅷ为1927年古浪8级大地震。这表明该断裂可能也参与了1927年古浪8级地震的活动。各次古地震事件在时空分布上相对较均匀,大致具有准周期复发的特征。
Characteristics of palaeo-earthquake activity along the active Tianqiaogou-Huangyangchuan fault on the eastern section of the Qilianshan Mountains
[J].
Impact of tectonics on alluvial landforms in the Hexi Corridor,Northwest China
[J].
黑河地区行星边界层大气的气候分析
[J].分析指出:气温和比湿的季节变化基本上呈峰谷相当波型;各月气温和比湿的直减率分别小于和略大于自由大气的直减率。整层各月为准无辐散和弱有旋的西北气流,风速的季节变化在近地层也呈谷峰相当波型,其振幅随高度迅速增强,但位相恰与温、湿波型相反。张掖单站分时次的月平均资料分析表明,风向、风速和层结稳定度都有明显的气候日变化;当考虑湿度层结时,夏季7月19时的平均层结是真潜不稳定,其余季节和时次仍为稳定层结。扩展域边界层月平均温、湿、风场的分析指出,黑河地区近地层在1、4、10月基本上位在平浅温度槽区,而7月却处在纬向水平温度梯度矢端;该区比湿7月相对最高,而其余各月很低;全域近地层流场仅7月稍复杂点,黑河试验区位于弱辐合流场中,其余月份黑河地区边界层平均基本上为平直西北气流所控制。
Climatic analyses of the planetary boundary layer atmosphere in the Heihe Region
[J].In this paper, the climate characters of the temperature, humidity and wind fields on the planetary boundary layer (PBL) over the Heihe region and its neighbourhood have been analysed utilizing the multi-year monthly mean data at grided points and some sta tions of the area. The results indicate that the seasonal variations of the temperature and specific humidity on the PBL appear a waveform with basically equivalent value for the peak and valley; the lapse rates of the temperature and specific humidity on the PBL for each month are less and large than those on the free atmosphere, respectively. There is a northwest flow with quasi-nondivergence and weak rotation in the whole PBL. The seasonal variation of wind speed also appears a waveform with a equivalent value for the peak and valley in the surface layer, the wave amplitude increases rapidly with height, however, the phase is just contrary to the waveform of the temperature and specific humidity. The analyses of the monthly mean data at the Zhanye station for 07-and 19-hrs. (BLT) indicate that there is a pronounced climatically diurnal variation for the wind direction, wind speed and stratified stability. The monthly mean stratification only at 19(BLT) in July is true potential instability when the stratification of the temperature and humidity in the PBL was analysed at the same time, in the rest seasons and times are still stable stratification. The briefly analyses of monthly mean fields of the wind, temperature and specific humidity in the PBL of extension domain indicate that the surface layer of the Heihe region in the January, April, October is located at the shallow temperature trough area, however, the region in July is just located at the end of zonal temperature gradient vector; the specific humidity in July in the region is the a highest, the other months are very low; the streamlines on the surface layer in extension domain only in July are something complex, the surface layer over Heihe region is located a weak convergence flow field; the PBL over the Heihe region for rest months are basically controlled by the straight north west flow.
Wind erosion forces and wind direction distribution for assessing the efficiency of shelterbelts in Northern China
[J].
地形高差对风速影响的探讨
[J].
Discussing into influence of topographic height difference on wind velocity
[J].
不同生态保护地植物特征和土壤性质的对比研究——以黑河中游湿地为例
[J].
Comparative study of plant characteristics and soil properties in different ecological protected areas:A case study of middle reaches of the Heihe River
[J].
张掖市城市湿地土壤盐分、pH值和含水量的空间异质性分析
[J].
Zhangye city wetland soil salinity,PH value and the spatial heterogeneity of water content
[J].
风化成土过程中稀土元素地球化学特征
[J].
Geochemical features of rare earth elements in process of rock weathering and soil formation
[J].
不同pH条件下有色冶炼厂周边道路尘及土壤中重金属释放特征
[J].
Release characteristics of heavy metal in road dust and soil around non-ferrous smelters under different pH conditions
[J].
残坡积土壤层中铁锰氧化物的吸附特性及其地球化学找矿意义
[J].
Absorption characteristics of Fe-Mn oxides in residual soils and its significance in geochemical prospecting
[J].
陕西渭北苹果园土壤中汞、镉污染与分布特征研究
[J].
Spatial distribution and pollution of mercury and cadmium in Weibei apple orchard soils of Shaanxi Province
[J].
土壤pH值对重金属形态的影响及其相关性研究
[J].
Effect of pH value on heavy metals form of soil and their relationship
[J].
重金属在松花江沉积物中的竞争吸附行为及pH的影响
[J].
Competitive adsorption of heavy metals on Songhua River sediments and effect of pH
[J].
甘肃省景观地球化学特征及区域化探工作方法研究
[J].
Landscape geochemistry features and working methods of regional geochemistry in Gansu Province
[J].
白云岩风化剖面元素地球化学特征:对黔中九架炉组“三稀金属” 富集机制的启示
[J].
Geochemical characteristics of dolomite weathering profiles and revelations to enrichment mechanism of trace elements in the Jiujialu Formation,central Guizhou Province
[J].
鄂西南利川三叠纪须家河组地球化学特征及其对风化、物源与构造背景的指示
[J].
Geochemistry of clastic rocks from the Triassic Xujiahe Formation,Lichuan area,southwestern Hubei:Implications for weathering,provenance and tectonic setting
[J].
A general mixing equation with applications to Icelandic basalts
[J].
Genetic aspects of basalts from the Carlsberg Ridge
[J].
新元古代以来甘肃西秦岭造山过程的地球化学证据及其成矿背景
[J].
Geochemical evidence for the orogenic process of West Qinling in Gansu since Neoproterozoic and its metallogenic background
[J].
潜在生态危害指数法评价中重金属毒性系数计算
[J].
Calculation of heavy metals' toxicity coefficient in the evaluation of potential ecological risk index
[J].
中国土壤环境背景值研究
[J].
Study on the background contents on 61 elements of soils in China
[J].
J-47-Ⅺ(张掖)幅区域地质测量报告
[R].
J-47-Ⅺ(Zhangye)map-sheet regional geological survey report
[R].
渭干河—库车河绿洲土壤重金属分布特征与生态风险评价
[J].
Distribution of heavy metal pollution and assessment of its potential ecological risks in Ugan-Kuqa River Delta of Xinjiang
[J].
川南山区土壤与农作物重金属特征及成因
[J].
Characteristics and origins of heavy metals in soil and crops in mountain area of southern Sichuan
[J].