0 引言
目前,在我国东部油田,石油勘探工作已经进入到了精细勘探阶段,工作的重点在于确定薄互层储集层的空间展布规律及其性质。而新生代含油气盆地大多以薄砂层、泥岩沉积为主,这类薄互层的地震反射波场特征与常规厚层有很大的差别,其地震反射效应并非单一的顶底界面反射波,而是顶底反射与层间多次波混叠而成的复合波,若仍按照厚层条件下的方法对薄互层的地震反射效应做研究则会导致薄互层层间信息的缺失。长久以来,由于分辨率的限制,地震数据无法达到薄互层储集层的分辨要求,为了识别薄层并尽可能清晰地分辨出薄互层的层间信息,国内外的专家学者很早就对此展开了研究。
探究地震波在地层中的传播特征需做正演模拟,而反射率法是层状薄层及薄互层条件下最为有效的正演方法。反射率法最早由Thomson[5]运用到计算面波的频散曲线中。在此基础上,Fuchs等[6-7]运用反射率法合成地震记录,并预测了该方法在层状介质和横向各向同性介质的可行性。Mueller[8]在考虑透射损失等现象的条件下运用反射率法对层状介质做正演模拟,并将反射率法扩展到激发点源震源的层状半空间中。Kennett等[9⇓⇓⇓-13]对层状介质中反射率法震源点与检波点相对关系的设定、算法稳定性和地震记录合成方式等问题做了详细研究,并提出了一种运用递归矩阵法计算反射与透射系数的方法,该方法通常称为KRM(kennett reflectivity method)方法并被广泛使用,但该方法计算量很大且传递矩阵的求解比较复杂。为了解决这一问题,Phinney等[14]将反射率法正演模拟的过程向量化,极大地提升了效率以使反射率法正演适用于实际生产。与递归矩阵相似,Carcione[15]将传递矩阵法引入到粘弹性横向各向同性介质的研究中,本文中垂直入射时的反射率法就是以Carcione所提出的传递矩阵法为基础。
对于薄层和厚层反射特征的差异,很难从时域上准确区分,对此专家学者们纷纷从频域上寻找解决方法。杨凯等[16]在子波已知的情况下在频率域中对薄层厚度和反射系数进行了近似求取。张玉芬等[17]论证了相邻的两个频率极值的差与薄层时间厚度之间的关系,并对具有不同的层间组合以及反射系数序列的薄互层时频域谱的变化特征进行了详细的讨论。邵治龙等[18]运用小波变换和最大熵分析的方法提取出对薄层敏感的参数,并在该参数的基础上用神经网络算法来估算薄层及薄互层厚度,取得了较好效果。蒋龙聪[19]综合运用短时傅立叶变换(STFT)、连续小波变换(CWT)、S变换(ST)等方法,研究了薄互层地震波特征的影响因素及这些因素对波形特征的影响。张晶[20]运用广义S变换获取薄层和薄互层的瞬时频谱,寻找出了可表征薄层、薄互层特性的稳定性参数。
近年来,对于薄层和薄互层的研究进入了新的发展阶段。王赟等[21]对薄层及薄互层反演方法做了总结,详细列举出了薄层研究中存在的问题,并预测弹性波用于研究薄层问题将成为时代必然。相较于传统薄层的定义,马跃华等[22]建立了以“岩性组合—阻抗组合—地质成因”为标准的多维度薄层分类标准,并根据该分类标准得出3类调谐模式对薄层的地震响应研究。李佳欣等[23]对于长波长假设下薄互层等效各向同性方法的研究现状和现存问题做了详细的描述,并预测薄互层等效各向异性理论将适用于先验信息约束下的薄互储层反演。倪长宽等[24]基于地震沉积学理论提出了两种薄互层层内分布预测方法,该类方法对薄互层内的地层做切片处理以达到压制邻层干涉的效果,实现了在平面中检测剖面中难以界定的单砂体分布的情况,但该类方法仅适用于薄互层层内分层较少的情况。杨震等[25]提出了以快速反射率法为核心的叠前AVA反演方法并将其应用到薄互层模型和实际数据中,结果表明该方法在反演过程中收敛速度更快且具有抗噪能力。
本文主要针对地震波垂直入射的情况,以层状介质中的传递矩阵法为基础推导出垂直入射时反射率法的公式,并分别考虑地层结构和砂泥比的变化建立两大类、共26个典型模型,然后运用垂直入射时的反射率法分别对各个薄互层模型的地震反射波场进行了正演模拟,并对所有正演模拟结果做频谱分析,最后对比分析不同薄互层模型对地震波反射的滤波效应。
1 垂直入射时的反射率法
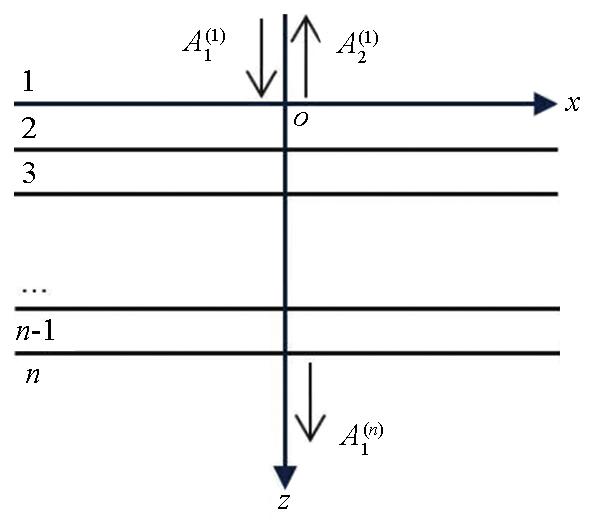
在常规地震勘探中,炮检距通常小于目的层深度。为简化起见,我们仅讨论垂直入射的情形。对于水平介质而言,此时层中无转换波产生,但存在层间多次反射,这种情况适合利用反射率法求解。如图1,设整个模型共有
图1
式中:
在第
式中:矩阵
根据弹性界面处的位移和应力连续条件,第
式中:
将式(4)代入式(2),有:
式中:
式中:
考虑到仅有纵波自顶层介质1入射,设入射波振幅为1,即
求解此方程可以得到自第1层入射时整个层系的反射系数和透射系数。将反射系数序列与地震子波褶积,就可以得到地震记录。这个方法的优点在于合成的反射波场包含了层间多次反射[26]。
2 模型的建立
考虑到地下地层厚度、速度、分层情况以及子波波长的影响,构建了两大类、6组、共26个典型模型。假设模型的总大小均为300 m×400 m,薄互层的埋深均为200 m。
2.1 考虑地层结构变化的薄互层模型
第一类模型的总厚度参考地震子波的1/4、1/2及1个波长来设计,故地层总厚度可设计为21 m、42 m和84 m,单层厚度设计为1 m和2 m。考虑上述因素,建立3组、共12个典型模型。
2.1.1 韵律型薄互层模型
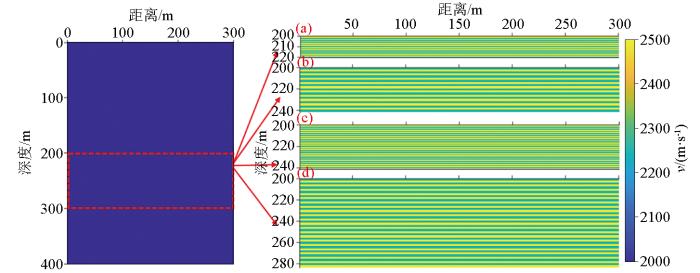
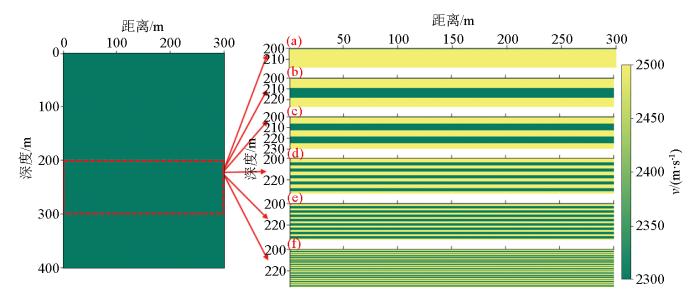
图2
图2
韵律型薄互层模型
薄互层的层厚分别为:a—21×1 m;b—21×2 m;c—42×1 m;d—42×2 m
Fig.2
Rhythmic thin interlayer models
the thickness of thin interlayer is:a—21×1 m;b—21×2 m;c—42×1 m;d—42×2 m
2.1.2 递增型薄互层模型
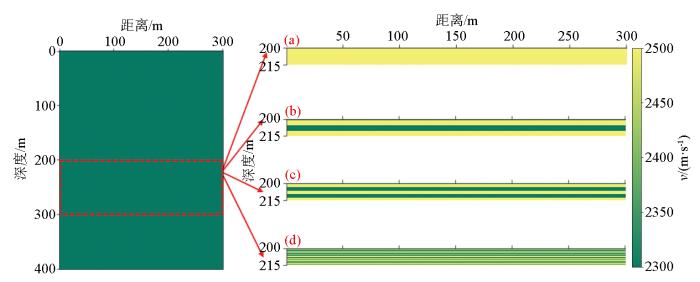
图3
图3
递增型薄互层模型
薄互层的层厚分别为:a—21×1 m;b—21×2 m;c—42×1 m;d—42×2 m
Fig.3
Incremental thin interlayer models
the thickness of thin interlayer is:a—21×1 m;b—21×2 m;c—42×1 m;d—42×2 m
2.1.3 递减型薄互层模型
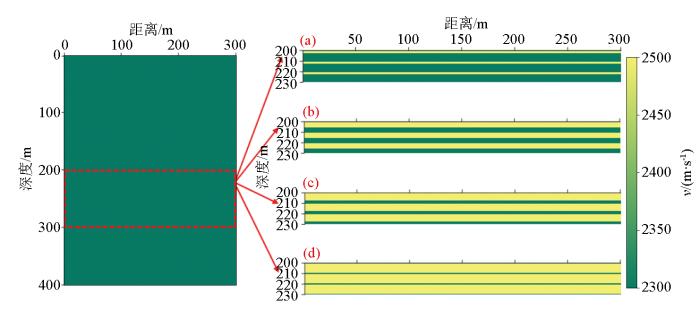
图4
图4
递减型薄互层模型
薄互层的层厚分别为:a—21×1 m;b—21×2 m;c—42×1 m;d—42×2 m
Fig.4
Decreasing thin interlayer models
the thickness of thin interlayer is:a—21×1 m;b—21×2 m;c—42×1 m;d—42×2 m
2.2 考虑砂泥比变化的薄互层模型
第二类模型考虑到薄互层砂泥岩厚度、互层数以及砂泥比的变化情况,砂岩的速度为2 500 m/s,泥岩的速度为2 300 m/s。考虑上述因素,建立3组、共14个模型。
2.2.1 砂岩累计厚度不变的薄互层模型
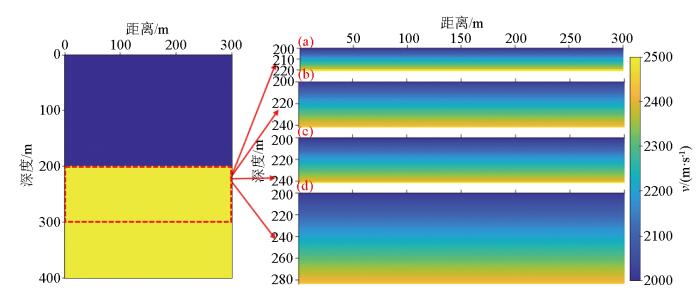
图5
图5
砂岩累计厚度不变的薄互层模型
砂岩的分层情况分别为:a—1×18 m;b—2×9 m;c—3×6 m;d—6×3 m;e—9×2 m;f—18×1 m
Fig.5
Sandstone cumulative thickness invariant thin interlayer models
the stratification of sandstone is:a—1×18 m;b—2×9 m;c—3×6 m;d—6×3 m;e—9×2 m;f—18×1 m
2.2.2 总厚度不变的薄互层模型
图6
图6
总厚度不变的薄互层模型
薄互层的分层情况分别为:a—1×15 m;b—3×5 m;c—5×3 m;d—15×1 m
Fig.6
Total thickness invariant thin interlayer models
the stratification of thin interlayer is:a—1×15 m;b—3×5 m;c—5×3 m;d—15×1 m
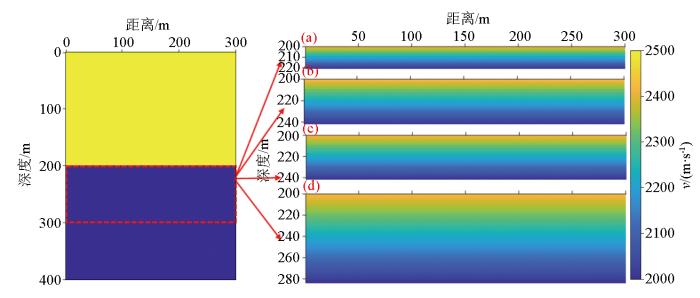
2.2.3 单套砂泥层砂泥比变化的薄互层模型
图7
图7
单套砂泥层砂泥比变化的薄互层模型
单套砂泥层砂泥比分别为:a—0.3;b—1;c—3;d—9
Fig.7
Sand to mud ratio in a single set of sand and mud layers variant thin interlayer models
the sand to mud ratio of a single set of sand and mud layer is:a—0.3;b—1;c—3;d—9
3 模型反射波场正演
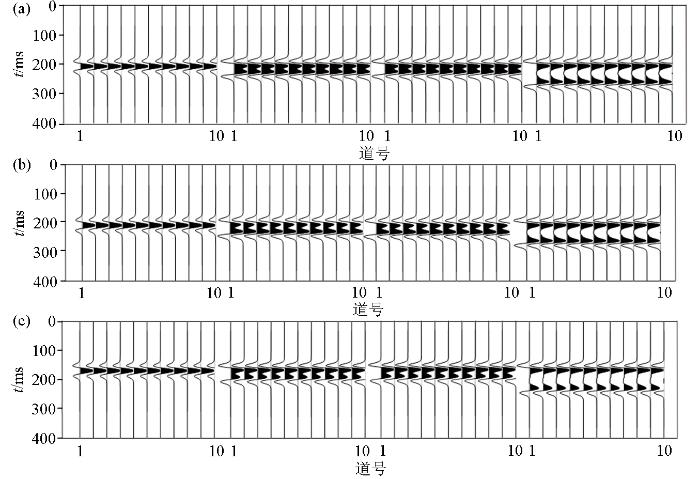
图8
图8
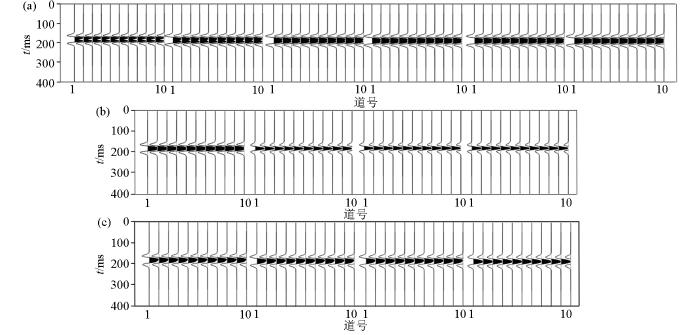
地层结构变化的薄互层模型的正演炮记录
a—韵律型薄互层模型的正演炮记录;b—递增型薄互层模型的正演炮记录;c—递减型薄互层模型的正演炮记录;从左至右薄互层的层厚分别为:21×1 m;21×2 m;42×1 m;42×2 m
Fig.8
Forward shot record of stratigraphic structure variant thin interlayer models
a—forward shot record of rhythmic thin interlayer models;b—forward shot record of incremental thin interlayer models;c—forward shot record of decreasing thin interlayer models;the thickness of the thin interlayer from left to right is:21×1 m;21×2 m;42×1 m;42×2 m
图9
图9
砂泥比变化的薄互层模型的正演炮记录
a—砂岩累计厚度不变的薄互层模型的正演炮记录,从左至右砂岩的分层情况分别为:1×18 m,2×9 m,3×6 m,6×3 m,9×2 m,18×1 m;b—总厚度不变的薄互层模型的正演炮记录,从左至右薄互层的分层情况分别为:1×15 m,3×5 m,5×3 m,15×1 m;c—单套砂泥层砂泥比变化的薄互层模型的正演炮记录从左至右单套砂泥层砂泥比分别为:0.3,1,3,9
Fig.9
Forward shot record of sand to mud ratio variant thin interlayer models
a—forward shot record of sandstone cumulative thickness invariant thin interlayer models,the stratification of sandstone from left to right is:1×18 m,2×9 m,3×6 m,6×3 m,9×2 m,18×1 m;b—forward shot record of total thickness invariant thin interlayer models,the stratification of thin interlayer from left to right is:1×15 m,3×5 m,5×3 m,15×1 m;c—forward shot record of sand to mud ratio in a single set of sand and mud layers variant thin interlayer models,the sand to mud ratio of a single set of sand and mud layer from left to right is:0.3,1,3,9
3.1 地层结构变化的薄互层模型
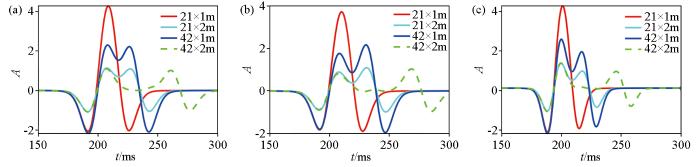
抽取正演炮记录中的第1道,得到各组模型的反射波波形如图10所示。
图10
图10
地层结构变化的薄互层模型的反射波波形
a—韵律型薄互层模型;b—递增型薄互层模型;c—递减型薄互层模型
Fig.10
Reflected waveform of stratigraphic structure variant thin interlayer models
a—rhythmic thin interlayer models;b—incremental thin interlayer models;c—decreasing thin interlayer models
对比分析3组模型的反射波波形,发现3组模型反射波波形的整体变化趋势一致,即随着薄互层总厚度增加,反射波的振幅会减小,反射波的波长会增大;这是由于随着薄互层总厚度的增加,地震波在薄互层中的传播时间会延长,且越深处的薄互层反射强度会越小。薄互层厚度为21×2 m和42×1 m的模型由于总厚度一样,故两组模型反射波的形态和波长一样,基本重合。递减型薄互层模型由于薄互层上层的速度较高,反射波波形相位会提前。且随着薄互层总厚度的变化,3组模型中反射波的形态会发生变化,当薄互层总厚度为21 m(λ/4)时,反射波只有一个波峰;而当薄互层总厚度为42 m(λ/2)和84 m(λ)时,反射波有两个波峰。
3.2 砂泥比变化的薄互层模型
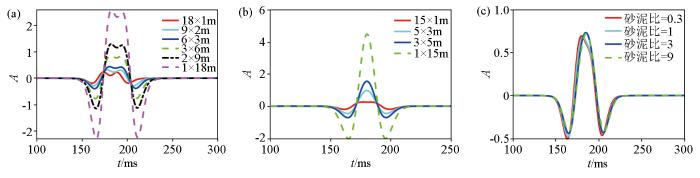
抽取正演炮记录中的第1道,得到各组模型的波形如图11所示。
图11
图11
砂泥比变化的薄互层模型的反射波波形
a—砂泥累计厚度不变的薄互层模型;b—总厚度不变的薄互层模型;c—单套砂泥比变化薄互层模型
Fig.11
Reflected waveform of sand to mud ratio variant thin interlayer models
a—sandstone cumulative thickness invariant thin interlayer models;b—total thickness invariant thin interlayer models;c—sand to mud ratio in a single set of sand and mud layers variant thin interlayer models
4 薄互层反射的滤波效应
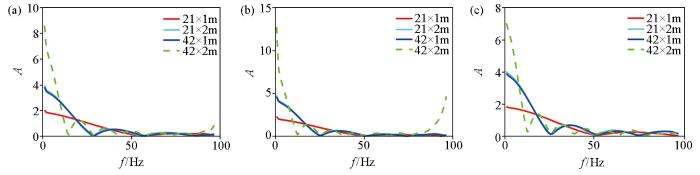
图12
图12
地层结构变化的薄互层模型的频谱
a—韵律型薄互层模型;b—递增型薄互层模型;c—递减型薄互层模型
Fig.12
Spectrogram of stratigraphic structure variant thin interlayer models
a—rhythmic thin interlayer models;b—incremental thin interlayer models;c—decreasing thin interlayer models
图13
图13
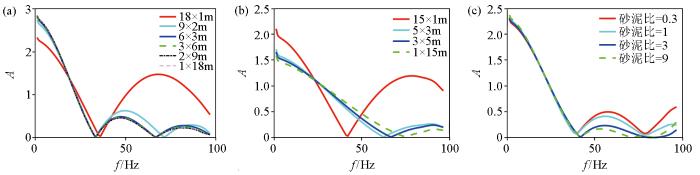
砂泥比变化的薄互层模型的频谱
a—砂岩累计厚度不变的薄互层模型;b—总厚度不变的薄互层模型;c—单套砂泥层砂泥比变化的薄互层模型
Fig.13
Spectrogram of sand to mud ratio variant thin interlayer models
a—sandstone cumulative thickness invariant thin interlayer models;b—total thickness invariant thin interlayer models;c—sand to mud ratio in a single set of sand and mud layers variant thin interlayer models
对比分析图12所示的3组模型的频谱,发现随着薄互层总厚度的增加,陷波点会增加,且陷波点会向低频移动;当薄互层总厚度为21 m(λ/4)时,有1个陷波点;当薄互层总厚度为42 m(λ/2)时,有2个陷波点;当薄互层总厚度为84 m(λ)时,有4个陷波点。这说明在薄互层反射波频谱曲线中陷波点的数量与地层总层厚除以1/4子波波长的值对应。而薄互层厚度为21×2 m和42×1 m的模型的频谱曲线重合,说明当薄互层总厚度不变时,单层厚度的变化不会影响频谱曲线。
对比分析图13所示的3组模型的频谱,由图13a可得,在保持薄互层中砂岩累计厚度不变时,随着砂岩分层的增加,中高频的频谱曲线的幅值会减小;而随着薄互层总厚度的增加,陷波点会由一个变为两个。由图13b可得,在保持薄互层总厚度不变时,随着砂泥岩互层数的增加,中高频的频谱曲线的幅值也会减小;且陷波点会随着砂泥岩互层数的增加而向高频移动,但由于薄互层总厚度没变,陷波点个数未变。由图13c可得,在保持单套砂泥层厚度和薄互层互层数不变时,中高频的频谱曲线的幅值会随着单套砂泥层砂泥比的增大而减小;这是由于砂、泥岩分别对不同的频率成分敏感,当薄互层中的砂、泥比变化时,频谱中不同的频率成分会升高或降低,最终会综合体现在频谱图中高频幅值的变化。
5 结论
本文基于垂直入射时的反射率法,建立了多个薄互层模型,通过波场正演和频谱分析,研究了薄互层对地震反射波的滤波效应,结果表明:
1)地震波在薄互层中调谐现象的变化,本质上是薄互层层厚与子波波长之间相对关系的体现。即地震子波在薄互层中传播时,子波的速度和频率的变化会导致子波波长的变化,而子波波长变化则会导致调谐厚度的变化。
2)在薄互层条件下,频谱曲线陷波点的数量与地层总层厚除以1/4子波波长的值对应,且陷波点会随着地层总厚度的增加向低频移动。当薄互层总厚度一定时,陷波点会随着互层数的增加向高频移动,且中高频处(陷波点后)的幅值会随着互层数的增加而减小。而随着薄互层中砂泥比的增大,频谱曲线在中高频处(陷波点后)的幅值会减小。
3)薄互层频谱曲线中频率域的变化特征在本质上是由薄互层单层厚度引起的,薄互层中互层数的变化也是通过影响单层厚度从而影响频率域的特征变化。
4)当地震波非垂直入射时,由于受到炮检距和地层厚度的双重影响,薄层顶底反射的干涉程度会随着炮检距而变化,滤波效应同时受炮检距、地层厚度、速度、波长等多个因素影响,需要针对具体情况进行分析。
参考文献
Wavelet contraction,wavelet expansion,and the control of seismic resolution
[J].
Interpretation of synthetic seismograms
[J].
The limits of resolution of zero-phase wavelets
[J].
Transmission of elastic waves through a stratified solid medium
[J].
The reflection of spherical waves from transition zones with arbitrary depth-dependent elastic moduli and density
[J].
Computation of synthetic seismograms with the reflectivity method and comparison with observations
[J].
The reflectivity method:A tutorial
[J].
Seismic waves in laterally inhomogeneous media
[J].
Seismic waves in a stratified half space
[J].
Seismic waves in a stratified half space—II.Theoretical seismograms
[J].
Seismic waves in a stratified half space—III.Piecewise smooth models
[J].
Rapid generation of synthetic seismograms in layered media by vectorization of the algorithm
[J].
在频率域中求取薄层厚度和反射系数的新方法
[J].
A new method for calculating the thickness and reflection coefficient of thin layer in frequency domain
[J].
石油地震勘探中的薄层解释研究方法综述
[J].
Advancement of thin-bed studies in oil seismic exploration
[J].
小波变换与最大熵法联合计算薄层厚度
[J].
Thin-layer thickness estimation using wavelet transform and maximum entropy method
[J].
薄互层弹性波反演面临的困境
[J].
DOI:10.6038/cjg2018L0404
[本文引用: 1]

对于薄互层地震传播特征的研究我们已有了充分的认识,这是一种完全不同于现有的基于厚层单阻抗差界面地震反射理论的、具有频率依赖性的调谐反射.因而也使得对具有N层结构的弹性介质薄互层反演时,现有有限带宽的基于空间-频率域采样的地震观测难以规避多解性问题.长波长假设下的薄互层VTI近似似乎可以为我们提供一种待反演弹性参数只有5个的可行性方案,使得我们可以将薄互层背景下任一目标薄层的反演看作VTI厚层介质背景下单薄层的反演.但是,我们首先面临薄互层VTI近似的误差和适用性条件等问题;其次,既使对于单薄层厚度的反演,目前地震领域也未能提供一种通用有效的解决方案,实际地震勘探中薄层厚度的预测依然是一个悬而未决的难题.因此在此基础上再进行单薄层的物性参数、裂缝隙和流体的预测则更叠加了难以预知的多解性.显然单纯P波已难以应对,弹性波的介入成为必然;而且单薄层含裂缝与流体的预测更需要横波分裂和双相介质理论的支撑.可以预见的是,除了纵、横波速度,薄互层反射系数的频率依赖性是我们试图给出相对可靠的、单薄层物性精细刻画必须使用的一种重要地震属性.
Dilemma faced by elastic wave inversion in thinly layered media
[J].
薄层分类及其地震响应分析——以大港油田两个应用研究为例
[J].
DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1000-1441.2018.06.013
[本文引用: 1]

薄层研究不应过于强调单一地层的厚度,而应关注地层的组合形式。重新定义了薄层,并从地质学和地球物理学角度分别对薄层进行分类,初步建立了多维度薄层分类标准。基于新的分类标准,研究调谐效应,并根据调谐响应的不同特征,将调谐分为3类:TPⅠ、TPⅡ和TPⅢ。实例1研究了中、浅层欠压实情况下,地质学中泥包砂型薄层对应于地球物理学中高包低(低阻抗地层介于高阻抗地层之间)型薄层,利用沉积微相与响应频率之间的关系(microfacies versus frequency,MVF)研究该类型薄层的沉积微相,分别预测了边滩、分支河道、泛滥平原等。实例2讨论了两套正旋回、油气同出、反射特征差异明显的薄层类型,针对地质特征相似,地震响应差别较大的薄层,依次进行了岩石物理分析、数值正演模拟、高压物性分析和气油比分析等研究,预测了凝析气藏和轻质油藏的分布范围。
Classification and seismic response analysis of thin bed:Two cases study from Dagang oilfield,China
[J].
DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1000-1441.2018.06.013
[本文引用: 1]

<p>Thin layer research should focus on composition form,rather than the thickness of a single layer.In this study,a thin layer is redefined and classified from the standpoint of both geology and geophysics to establish a multi-dimensional classification standard.Based on the proposed classification,the tuning effect was classified into three types (i.e.,TP Ⅰ,TP Ⅱ and TP Ⅲ).In the first case from Dagang oilfield in China,with regard to the undercompacted beds,a geological thin layer structure with the characteristic of “sand encased by shale” corresponded to a geophysical characteristic of “low-impedance layer distributing between high-impedance layers”.The relationship between sedimentary microfacies and response frequency was used to predict the sedimentary microfacies of the thin layers,including point bar,branch channel and flood plain.In the second case,two sets of geological thin layers with “positive cycles” were studied; both had co-production of oil and gas,but one layer exhibited weak seismic reflection response whereas the other had a strong response.For thin layers with similar geological characteristics and different seismic response,methods such as rock physics analysis,numerical forward modeling,high-pressure physical property analysis,and gas-oil ratio analysis were employed to predict the distribution ranges of both condensate gas reservoirs and light oil reservoirs.</p>
薄互层等效各向异性的研究现状与存在问题
[J].
DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1000-1441.2021.02.004
[本文引用: 1]

在长波长假设下,薄互层是一种典型的横向各向同性介质;长波长各向异性假设使得薄互层复杂结构反演成为可能。通过综述长波长假设下薄互层等效各向异性的理论发展、数值模拟和物理实验,发现该理论的适用条件较为严苛:对于韵律型薄互层,波长与互层单元厚度的比值需大于等于10;对于随机型薄互层,需满足等效的平均长度远大于单层厚度,且远小于主波长的条件。综合分析与总结薄互层等效各向异性理论研究进展发现:韵律型薄互层的等效各向异性理论与薄互层的互层结构、波长与互层单元或单层厚度比值、薄储层内部的物性差异等因素密切相关;随机型薄互层的等效各向异性理论相较于韵律型薄互层更为复杂,除与上述条件有关外,还应考虑等效的平均长度与非均匀性尺度、主波长的关系。
A state of the art on the equivalent anisotropy of thin interbeds
[J].
基于地震沉积学的薄互层储集层分布预测方法
[J].
DOI:10.11698/PED.20210805
[本文引用: 1]

针对薄互层地震识别难题,以地震沉积学为理论基础,采用对地层切片开展相关处理达到压制邻层干涉的研究思路,提出两种薄互层储集层分布预测方法,实现在平面上识别薄互层中单砂体平面展布的目的。①最小干涉频率切片方法,利用基于小波变换的振幅-频率特征寻找对目标层切片干涉作用最小的地震频率,进而提取最小干涉频率下的地层切片;②基于地层切片的叠加方法,通过计算对目标地质体储集层与相邻层的多个干涉系数,然后按上述系数将邻层与目标层的地层切片加权叠加形成叠加切片。在准噶尔盆地风南地区应用这两种方法预测三叠系克拉玛依组3套薄互层储集层中厚度为6 m的目标油层分布,通过与钻井信息及常规地层切片对比,证明这两种方法均可有效提高薄互层中单砂体分布的预测精度。
Thin-interbedded reservoirs prediction based on seismic sedimentology
[J].
基于快速反射率法的AVA反演技术在致密砂岩薄储层勘探中的应用
[J].
DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1000-1441.2023.01.011
[本文引用: 1]

致密砂岩储层成层性明显且具有储层厚度薄的特点。传统的地震数据处理技术不能有效地压制地层内部的多次波,也不能准确地补偿传输损耗,使得基于Zoeppritz方程或其近似值的AVA反演理论不适用于致密砂岩储层。提出了一种以快速反射率算法为驱动核心的叠前AVA反演方法,快速反射率法可以计算全波响应,包括反射、透射、转换波和内部多次波,适用于致密砂岩储层,并利用薄层模型对方法进行了验证分析。目标函数的构建基于Gauss-Newton法,并推导出雅可比矩阵的解析解,提高了反演的准确度和收敛速度。将该方法分别应用于不含噪声和含噪声的薄互层模型数据,测试结果表明,基于快速反射率法的反演结果更加准确且具有一定的抗噪能力。四川崇州工区的实际数据应用结果表明,基于快速反射率法的正演模拟结果与实际地震数据更加接近,此外基于快速反射率法的反演结果更接近于测井曲线,更准确地反映地层变化的趋势,能更好地识别致密砂岩储层。
Application of AVA inversion technique based on rapid reflectivity method in thin tight gas reservoir exploration
[J].
DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1000-1441.2023.01.011
[本文引用: 1]

Tight gas reservoirs are characterized by apparent stratification and thin reservoirs,in which internal multiples are difficult to suppress and accurate compensation of transmission loss is difficult.Therefore,AVA inversion methods based on the Zoeppritz equations or their approximations are not applicable to thin interbeds.In this study,we propose a prestack AVA inversion method based on the rapid reflectivity method.The rapid reflectivity method can compute full-wave responses,including reflections,transmissions,mode conversions,and internal multiples,and it is beneficial for the seismic inversion of tight gas reservoirs.Another advantage of the rapid reflectivity method is that the partial derivatives of the reflection coefficient with respect to the elastic parameters can be expressed as analytical solutions.Based on the theories of the rapid reflectivity method,we established an objective function using the Gauss-Newton approach.To estimate the elastic parameters (P- and S-wave velocities and density),the objective function was established by minimizing the difference between the simulated and observed data in the angle domain.Eventually,we implemented the rapid reflectivity method-based inversion on the thin interbed model and field data and then compared it with the inversion method based on the exact Zoeppritz equation.The forward simulation results based on the rapid reflectivity method were closer to the field seismic data.The inversion results demonstrate that the rapid reflectivity method-based inversion can accurately reflect the trend of reservoir change and identify tight gas reservoirs.
弱连接界面地层地震反射波场的正演方法
[J].当介质中存在按照一定方向排列的裂隙时,会形成弱连接界面。地震波传播时,界面两侧的质点不再满足位移的连续性条件,位移差与该点的应力呈线性关系。界面的这种弱连接特性可以用法向柔量和切向柔量来表示,柔量值越大,界面的接触程度和质点位移的连续性就越差。讨论了界面柔量对PP反射波的影响,并通过数值算例说明了法向柔量对反射系数的影响大于切向柔量;建立了基于反射率法的弱连接界面地层地震反射波场正演方法;通过用正演方法合成的(τ,p)域地震记录,讨论了含有弱连接界面模型的波场特征,给出了(τ,p)域波场的动校正方法。模拟试验和动校正结果说明方法正确可行。
Forward modeling of reflected wavefield from strata with weakly bonded interfaces
[J].Weakly bonded interfaces can be formed when some aligned cracks exist in the media. The particles beside the interface don’t satisfy the continuity condition of the displacement any more. The displacement difference has linear relationship with the stress of the point. The weakly bonded characteristic can be expressed by normal compliance and shear compliance. With the increasing of interface compliances, the bonding level and the displacement continuity becomes poorer. The influences of interface compliances on PP wave reflections were discussed. Numerical models were utilized to illustrate that the normal compliance had much influence on PP reflections than shear compliance did. A forward modeling method for reflected wavefield of strata with weakly bonded interfaces was developed based on the reflectivity method. The synthetic seismograms in (τ, p) domain were obtained by this method, and the wavefield characteristics of weakly bonded interface models were discussed. Meanwhile, the NMO correction procedure in (τ, p) domain was established. Simulated test and NMO correction results show that the method is feasible and accurate.