0 引言
不同地质背景下的储集层预测方法具有一定的差异性[6⇓⇓-9]。地震数据体分为叠后地震数据体和叠前地震数据体。通常对于中浅层低阻砂岩,-90°相移叠后地震即可较好地表征储集层。但是对于深层储层,由于砂泥岩阻抗叠置,常规的-90°相移叠后地震已经不再适用。储集层的表征一方面与地震资料有关,另一方面与储集层本身的岩石物理特征相关。常规叠后地震为全叠加地震数据,不考虑入射角的变化,反映地下综合信息。实际上,地震反射振幅随着入射角的变化会发生变化,即AVO效应[10⇓⇓-13]。利用AVO效应可以分析地层岩性信息,开展岩性和流体的解释[14⇓-16]。不同角度道集表征不同的地球物理信息[17⇓⇓-20]。近道部分叠加数据由于地震波传播距离小,高频成分得到较好保留,因此地震分辨率较高,适合于薄层砂体的刻画,突出沉积细节,但是,由于偏移距较小,多次波较难压制,存在虚假同相轴的干扰。而远道部分叠加数据由于偏移距较大,多次波易于压制,信噪比高,地震轴连续性较好,适用于区域层序界面解释,但是,由于地震波传播距离长,高频成分吸收衰减大,分辨率较低,不适用于岩性体的刻画。相比于部分叠加数据,全叠加数据能压制随机噪音,降低多次波的影响,从而改善地震资料信噪比;但是,全叠加地震未考虑AVO效应,尤其针对近道与远道发生相位变化的情况,对二类AVO储集层刻画能力有限。与全叠加数据相比,优势道叠加数据将优势角度范围内的地震数据叠加,可以大大改善弱相位和相位反转在叠加中被抵消的问题,提高储集层的表征能力[18⇓-20]和烃类检测能力[21⇓⇓-24]。此外,还有叠前AVO梯度属性和叠前反演数据体可以表征储集层岩性。
Z气田储集层埋深大,目的层砂泥阻抗叠置,利用常规地震较难识别储集层,制约了气田开发方案的制定。为了精细表征深层储集层,本文采用基于优势道叠加技术实现深层储集层刻画。首先从研究目的层的井旁叠前道集出发,分析其AVO特征及不同角度范围的地震相位稳定性,确定能准确反映储集层的相位稳定的优势角度地震道。基于优势角度地震道进行部分叠加得到岩性敏感三维数据体。该方法充分挖掘了优势叠前地震信息,未使用过多的数学变换,提供了面向储集层描述的高品质地震资料,支撑了Z气田的高效开发。相关技术可为其他区块深层砂泥阻抗叠置储集层的地球物理预测提供参考。
1 地质概况
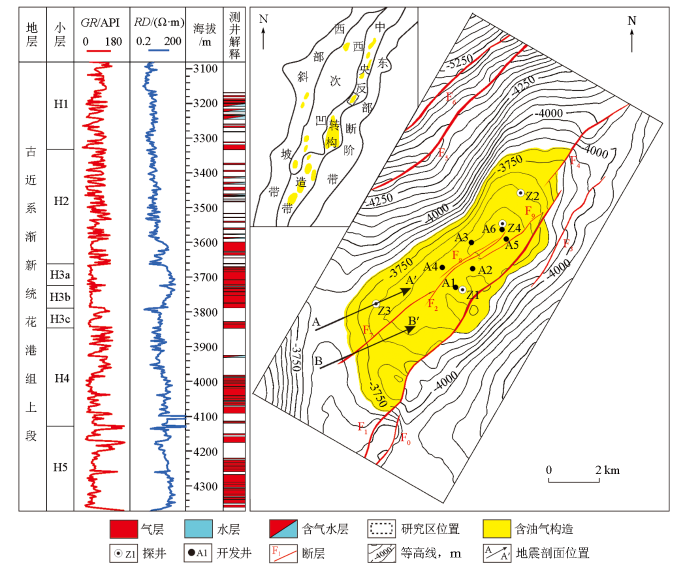
图1
Z气田主要开发层系为H3层(花港组第三层)。H3砂体垂厚约200 m,储集层非均质强,渗透率差异大。H3层进一步可以细分为H3a、H3b、H3c三个小层。随着埋藏深度的增加,孔隙度和渗透率降低,H3a整体埋深大于3 500 m,渗透率0.1~59 mD,渗透率中值0.4 mD;孔隙度7%~11%,孔隙度中值9%;为特低孔特低渗储集层。H3a已钻井揭示砂体垂厚30~70 m,均为气层,含气饱和度48%~69%,平均含气饱和度59%。储集层在常规地震上相位不稳定、连续性差,表现为弱振幅的特征(图2),为“暗点”型储集层。H3a是Z气田后续开发的重要层系,如何有效识别深层“暗点”型储集层是下一步开发方案设计的关键。
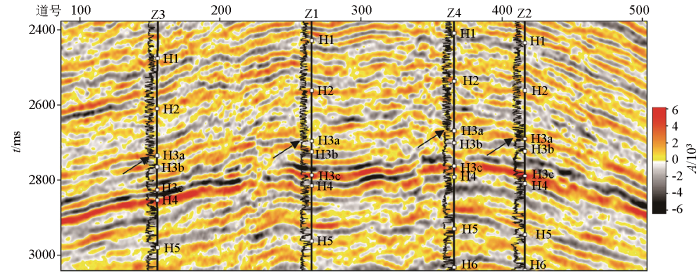
图2
2 深层“暗点”型储集层地震响应特征
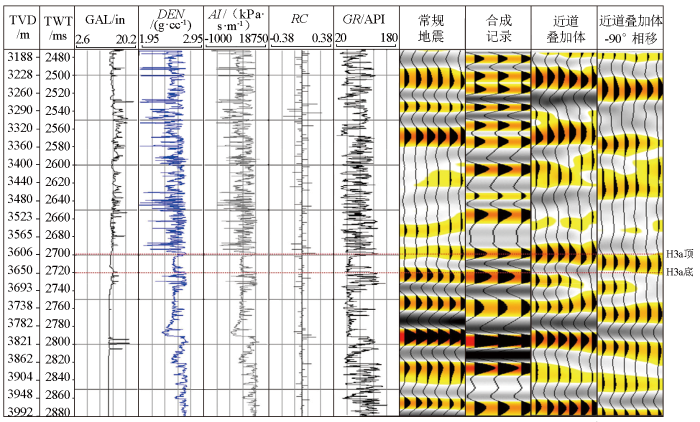
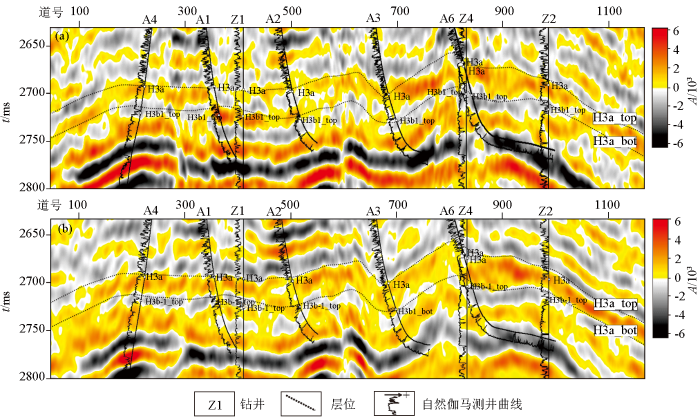
地震的响应特征分析是地球物理识别深层“暗点”型储集层的基础。地震反射与厚度、物性和含气饱和度相关,是地下储集层的综合反映。通过该气田Z1井开展精细的井震标定,发现H3a储集层在常规地震上表现为弱波峰反射特征,且相位较不稳定(图3),属“暗点”型储集层。开展深层“暗点”储集层的地震正演,有助于寻找“暗点”型储集层预测的方法。
图3
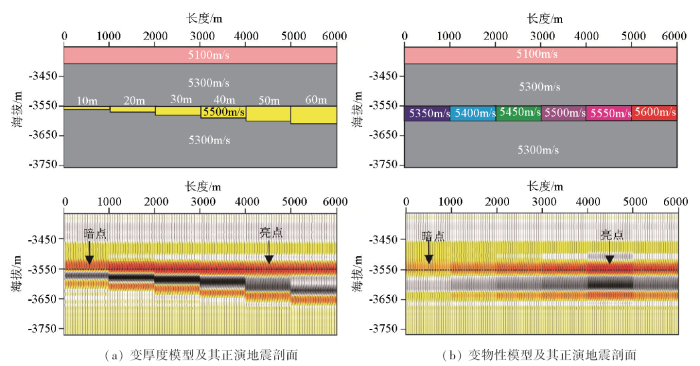
依据研究区实际钻井数据开展地震正演模拟,分别设计厚度变化和物性变化两种情况。
在砂岩物性不变的情况下,改变砂体厚度(10~60 m),通过正演模拟分析砂体厚度变化对地震响应的影响(图4a)。正演结果表明,当砂体厚度小于10 m时,在地震剖面上表现为弱反射特征。但是,研究区H3a砂厚在30~70 m,依据正演模型可形成强反射,因此,砂体厚度不是储集层表现为“暗点”的原因。
图4
在设定砂体厚度50 m不变的情况下,改变物性参数,将速度变化范围设置为5 350~5 600 m/s,开展正演模拟来分析砂体物性的变化对地震响应的影响(图4b)。正演结果表明,储集层物性差,砂岩速度与泥岩速度差异越小,阻抗差异越小,振幅强度越低,表现为“暗点”特征。
研究区H3a储集层物性较差,砂岩与泥岩的阻抗差异小,存在砂泥阻抗叠置的现象。总体上,物性差是“暗点”储集层形成的主要因素。
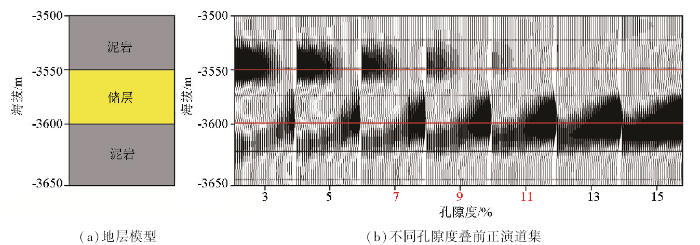
孔隙度是影响地震的最敏感参数,对地震振幅起主控作用。振幅与孔隙度呈线性关系,高孔“甜点”表现为强振幅“亮点”特征,地震上易识别。孔隙度对地震反射影响较大:孔隙度大于11%时,叠前从近道到远道皆表现为强振幅;小于11%时,随着孔隙度减小,近道振幅衰减较快,叠后振幅减弱。孔隙度小于5%时,砂体顶面近道和远道均表现为波峰反射;孔隙度为7%~11%时,砂体顶面近道表现为波峰反射,远道表现为弱波谷反射;孔隙度大于11%时,砂体顶面近道和远道均表现为波谷反射。研究区目的层的孔隙度为7%~11%,是二类AVO特征,近道表现为波峰反射,远道表现为弱波谷反射,叠加后表现为暗点特征(图5)。
图5
图5
不同孔隙度叠前AVO正演
Fig.5
Prestack AVO forward modeling of different porosity reservoir
3 优势道叠加技术
优势道叠加技术主要包括3方面。首先,针对储集层预测的要求开展地震资料针对性处理,如多次波压制,得到高品质道集地震资料。然后,针对目的层储集层开展井旁AVO特征分析,确定优势道集选取的部分。最后,结合VSP和合成记录标定综合优选优势角度,并且将优势叠加数据体进行-90°相移,得到最终的地震岩性数据体。
3.1 多次波的处理
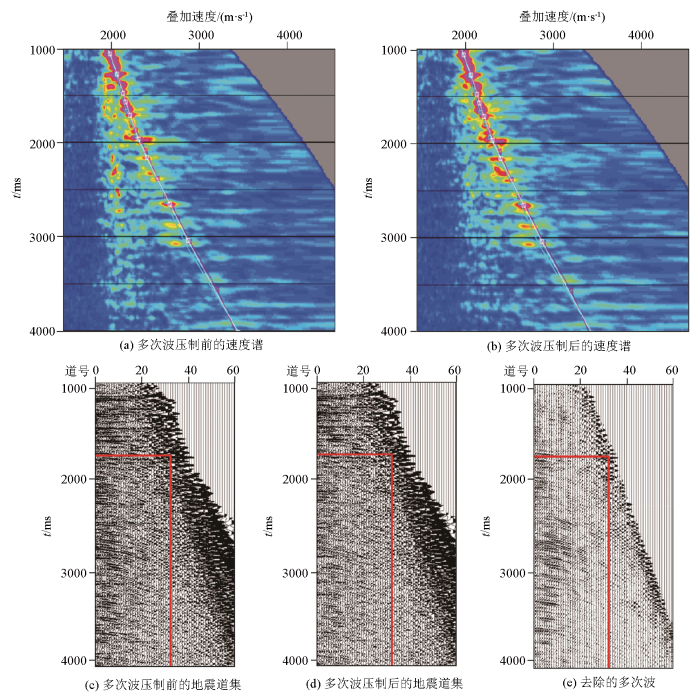
地震资料的针对性处理为储集层预测提供了合适的资料基础,高品质的地震道集是开展优势道地震叠加的资料处理前提。由于近道地震多受到多次波的影响,制约了近道地震在储集层表征精度,因此,本次采用3项针对性技术去除多次波:①利用基于波动方程的3DSRME技术来压制海底相关多次波;②利用拉冬域去多次波技术压制海底相关多次波以外的长周期多次波;③利用AVO预测法压制剩余的绕射多次波。
研究区地震速度的分析结果显示,处理后的道集反射能量较集中,不存在明显的多次波反射特征(图6)。通过地震资料的针对性处理,多次波得到较好的压制,有效信号得到更好的突出,有效信号同相轴的连续性得到提高,最终得到较好的多次波压制效果,为后续处理提供了更好的基础数据。
图6
图6
研究区地震资料多次波去除前后对比
Fig.6
Comparison of seismic data by removing multiple waves
3.2 目的层AVO特征分析
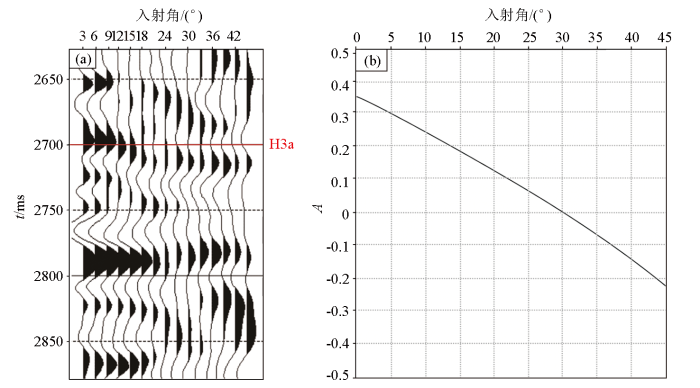
图7
图7
研究区H3a层的地震道集(a)和AVO曲线特征(b)
Fig.7
Seismic gathers (a)and AVO curve characteristics(b) of layer H3a
3.3 优势角度的选取及叠加
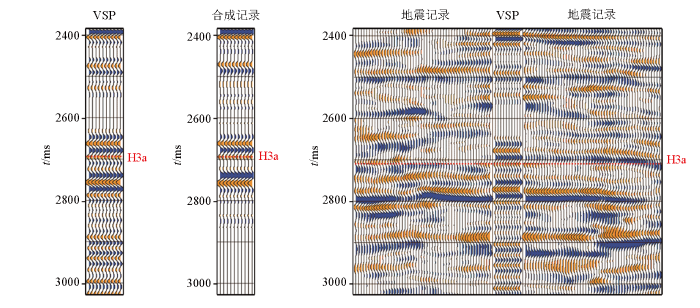
优势角度的选取需要对不同角度角道集进行全面分析。依据目的层的AVO特征和不同角度道集特征,优选优势道集叠加,放大目的层有效信号,使叠加效果既能保证分辨率高,又能兼顾阻抗界面真实性。采用VSP和合成记录标定综合优选优势道。合成记录作为地震标定的依据,是通过声波测井和密度测井计算反射系数,然后再与合适的子波褶积得到的。测井曲线质量及子波选取的合适度对合成记录的质量有重要影响。VSP 走廊叠加数据具有波形一致性好、信噪比高和波组多解性少的特点,更有利于优势角度的选择。
研究区地震资料基本情况为:CRP 道集最大覆盖次数为60 次,有效偏移距范围75~6 000 m,最大入射角45°。通过对比VSP 走廊叠加道和合成地震记录,发现3°~15°角道集叠加数据体波峰反射较稳定,与VSP 走廊叠加道同相轴相似性好(图8),能提高H3a砂体分辨能力。因此,选取3°~15°角道集进行叠加,得到了优势道处理后的地震数据。
图8
图8
VSP走廊叠加道、合成记录与地震剖面对比
Fig.8
Comparison of VSP corridor stacking traces, synthetic records, and seismic profiles
研究区H3a砂岩纵波速度为3 500 m/s,地震主频为23 Hz;计算得到的主波长λm≈152 m,视波长λs=0.78×λm≈30 m,λs/4 ≈ 30 m,λs/2 ≈ 60 m;H3a层砂体厚度40~60 m,处于地震可准确分辨范围内(λs/4~λs/2)。因此,为了实现反射界面到岩性体的转换,将3°~15°部分叠加数据体进行-90°相移即可表征H3a岩性信息。通过精细标定(图3),可以看出相比于常规全叠加地震,合成记录与近道叠加地震对应关系更好。
4 应用效果分析
图9
图9
连井常规叠加剖面(a)与优势道叠加剖面(b)对比
Fig.9
Comparison between post stacked profile (a) and advantage trace stacking profile (b)
图10
图11
图11
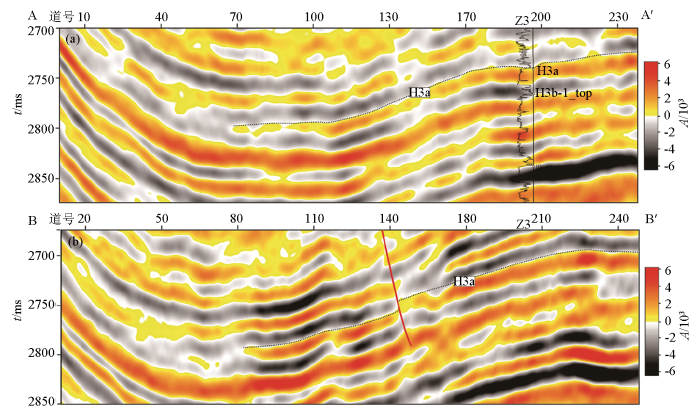
H3a层西南角储集层尖灭减薄的2条典型地震剖面
Fig.11
Typical seismic profile for pinch out of H3a layer
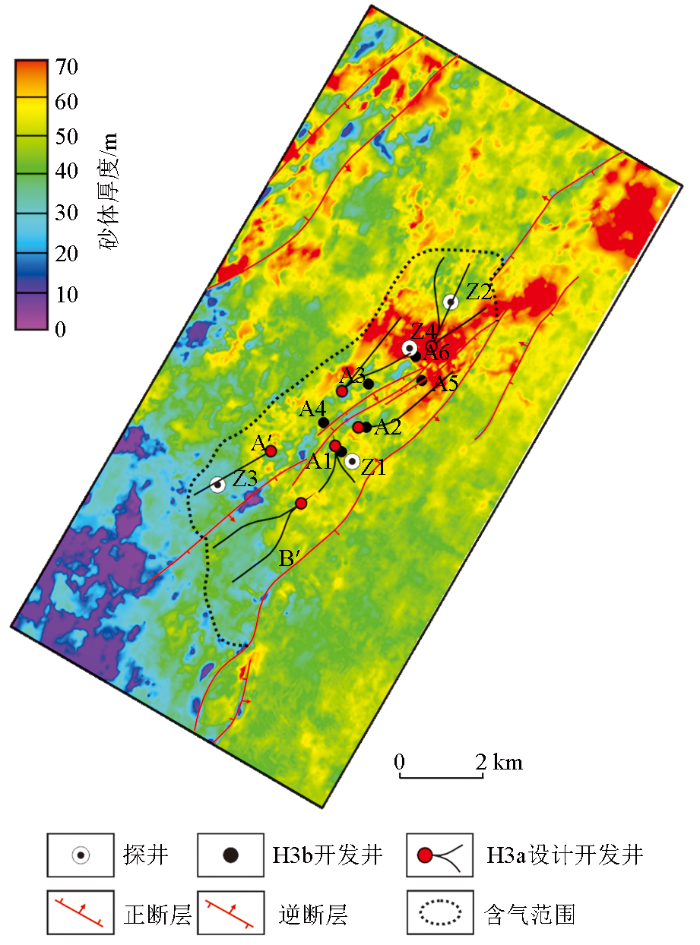
在储层平面刻画的基础上,开展了井位方案的设计。考虑到H3a为低渗储层,采用大斜度长水平井和分支井开发。由于H3a北部储层优于南部,北部设计4口开发井,同时采用两分支井和三分支井;南部由于储层减薄,储量丰度降低,仅设计2口开发井。整体上,采用近道叠加-90°相移地震资料,实现了H3a储集层的精细刻画,为研究区开发方案设计提供了储集层认识依据。
5 结论
1)基于地震正演分析Z气田H3a储集层的地震响应特征,明确物性差是“暗点”储集层形成的主要因素。研究区H3a为中高阻气砂,表现为Ⅱa类AVO特征,其近道为中强波峰反射,远道逐渐相变为波谷反射,叠加后形成“暗点”反射。
2)在东海Z 气田首次采用优势道集叠加技术,刻画H3a储集层展布。H3a储层北部厚,设计4口开发井,井型采用两分支井和三分支井;南部由于储层减薄,储量丰度降低,仅设计2口开发井。整体上,采用近道叠加-90°相移地震资料,实现了H3a储集层的精细刻画,为研究区开发方案设计提供了储集层认识依据。该方法对其他相似地区的储集层预测工作也具有一定的参考意义。
参考文献
川西致密砂岩气藏“暗点” 型河道砂岩识别方法
[J].
Dim spot channel sandstone identification for tight sandstone gas reservoir in western Sichuan
[J].
莺歌海盆地乐东区深层暗点型目标敏感属性优化方法
[J].
Optimization method for sensitive attributes of Dim spot targets in Ledong area,Yinggehai Basin
[J].
地震沉积学在东海陆架盆地西湖凹陷河流—三角洲相储集层刻画中的应用
[J].
DOI:10.11698/PED.20220204
[本文引用: 2]

针对东海陆架盆地西湖凹陷渐新统花港组河流-三角洲相储集层横向变化快、常规切片属性形态差、储集层预测难度大、难以满足岩性油气藏的后续勘探开发的问题应用分频解释、反演-常规-90°相移联合构建地震岩性体、非线性切片、古地貌恢复、多属性融合等特色技术对传统地震沉积学方法进行优化。研究发现花港组发育辫状河、曲流河和浅水三角洲3类沉积体,垂向沉积演化受中期基准面旋回和古地貌联合控制。在中期基准面旋回上升阶段的早—中期以辫状河道沉积为主,发育垂向叠置型砂体;在上升半旋回晚期和下降半旋回的早期以曲流河沉积为主,发育孤立型砂体;在中期基准面下降半旋回的中—晚期以浅水三角洲沉积为主,发育迁移型中—厚层砂体。限定性古地貌对砂体展布具有控制作用,非限定性古地貌对砂体展布影响较小。在储集层刻画的基础上,提出断层封堵型和储集层上倾尖灭型构造岩性圈闭是西湖凹陷下一步滚动挖潜的主力方向。
Application of seismic sedimentology in characterization of fluvial-deltaic reservoirs in Xihu Sag,East China Sea shelf basin
[J].
河流相储层刻画与垂向非均质性分析——以西湖凹陷C油田柳浪组为例
[J].
Fluvial reservoir characterization and vertical heterogeneity analysis:Taking Liulang Formation of C Oilfield in Xihu Depression as example
[J].
河流—三角洲相不同厚度储层的地震沉积学研究
[J].
Application of seismic sedimentology to the prediction of fluvial-delta facies reservoirs with different thickness
[J].
叠前有色反演技术在地震岩性学研究中的应用
[J].
DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1000-1441.2013.02.009
[本文引用: 1]

地震岩性学是将地震数据通过特殊处理转化为具有明确岩性意义的岩性体,为地震地貌表征服务。该地震岩性体需要满足3个方面的要求:①数据体的幅值与岩性相关;②数据体的横向振幅相对保持;③数据体的值最好为相对值。叠前射线弹性阻抗有色反演技术,既使反演体数值与井资料靠近,又保持了反演振幅的横向相对关系,可以作为实现地震岩性体的一个关键技术。该技术在冀中坳陷饶阳凹陷蠡县斜坡实际应用中取得了很好的效果,预测结果符合研究区的地质背景和沉积规律,为地震地貌刻画提供了有利工具。
Application of prestack colored inversion technology in seismic lithology
[J].
DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1000-1441.2013.02.009
[本文引用: 1]

<div style="line-height: 150%">Seismic lithology and seismic geomorphology are subdisciplines of seismic sedimentology.Seismic geomorphology</div><div style="line-height: 150%">focuses on plane sedimentary imaging by stratal slice.Seismic lithology serves seismic geomorphology by</div><div style="line-height: 150%">interpreting the seismic data into a lithologic data with a clear sense of lithology cube.The seismic lithologic cube</div><div style="line-height: 150%">should satisfy three demands.Firstly,the amplitude of the data volume is related to lithology.Secondly,the horizontal</div><div style="line-height: 150%">amplitude preserved relatively.Thirdly,the value of data should be relative.The result of Ray-path elastic impedance</div><div style="line-height: 150%">colored inversion can be regarded as an attribute volume with lithology cube meaning for its value is close to well</div><div style="line-height: 150%">and horizontal amplitude is preserved relatively.This technology obtained good result in practical application of</div><div style="line-height: 150%">seismic lithology research at Lixian slope of Raoyang Sag in Jizhong Depression.</div>
中国石化地球物理勘探实践与展望
[J].
DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1000-1441.2022.01.001
[本文引用: 1]

中国石化资源禀赋相对较差,围绕东部老区小规模隐蔽圈闭精细描述难、西部深层超深层碳酸盐岩孔缝洞储层成像刻画精度低、非常规领域一体化程度不高等重点领域的油气勘探开发难题,形成了单点高密度地震采集、以叠前逆时偏移成像(RTM)为核心的高精度成像、地震多属性分析以及叠前叠后储层反演等技术系列,有效提高了地震资料品质,助力稳油增气降本。东部老区主要目的层沙三段优势频带扩宽了20Hz以上,有效提高了隐蔽圈闭识别精度;四川盆地超深层生物礁储层预测结果与实钻吻合率达到93%;塔里木盆地顺北超深层断控储集体实现了量化描述,有效支撑了SHB4X、SHB8X等日产千吨井的部署;初步形成非常规领域地质物探工程一体化技术,中国石化率先探明了国内首个千亿方常压页岩气田。在取得勘探新成果的同时,中国石化地球物理勘探当前还面临着物探技术对勘探领域拓展和勘探部署支撑的力度不够;物探精度尚不能满足复杂地质目标识别的要求;装备软件“卡脖子”问题依然存在;技术集成和攻关合力不够等4个方面的挑战。展望未来,针对中国石化东部断陷盆地、深层超深层海相碳酸盐岩、中西部致密碎屑岩、山前带、非常规、海域、火成岩七大重点领域的油气勘探开发难题及物探技术需求,需要提升完善6项核心技术,支撑当前勘探开发;攻关研究5项关键技术,突破技术发展瓶颈;探索储备2项前沿技术,引领未来技术发展。
Geophysical exploration practices and perspectives at Sinopec
[J].
DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1000-1441.2022.01.001
[本文引用: 1]

Sinopec's resource endowment is relatively poor.Various technologies have recently been proposed to improve the quality of seismic data,thereby addressing oil and gas exploration and exploitation issues in key fields,such as the challenging fine description of small-scale subtle traps in the eastern old oilfields,low imaging accuracy of deep and ultra-deep carbonate porous-fractured and cavernous reservoirs in the western oilfields,and low degree of integration in unconventional fields.These technologies include the single-sensor-based high-density seismic acquisition,high-precision imaging of prestack reverse time migration imaging,multi-attribute analysis,and prestack and poststack reservoir inversion.The dominant frequency band of the third member of the Shahejie Formation,that is,the main target layer in the old exploration area of the eastern oilfields,could be widened by more than 20Hz,leading to a significant improvement in the identification accuracy of subtle traps.Thus,the coincidence rate between predictions and drilling results for ultra-deep reef reservoirs in the Sichuan Basin reached 93%.The ultra-deep fault-controlled reservoirs in the Shunbei Tarim Basin were quantitatively analyzed,supporting the deployment of 1000 ton/day wells such as SHB4X and SHB8X.A technology integrating geological,geophysical,and engineering exploration methods for unconventional fields was established at Sinopec.Thus,Sinopec took the lead in exploring the first 1011 m3 of normal-pressure shale gas fields in China.Despite the exploration achievements,geophysical exploration activities at Sinopec are still facing four challenges:Ⅰ) technical support for expanding the exploration areas and subsequent well deployment are insufficient;Ⅱ) accuracy of current technologies is insufficient for identifying complex geological targets;Ⅲ) equipments and softwares are strangling the development;Ⅳ) integration among technologies is insufficient.Considering the aforementioned issues that condition the activities in seven key areas (namely the eastern rift basin,deep-ultra deep marine carbonate rock formations,dense clastic rock formations in central and western China,the piedmont belt,unconventional resources,the maritime space,and igneous rock formations),six core technologies should be improved in the future to support the exploration and exploitation;five key technologies should be studied to overcome the bottleneck in technological development;and two cutting-edge technologies should be developed to lead the future technological development.
从勘探领域变化看地震储层预测技术现状和发展趋势
[J].
Current status and development trends of seismic reservoir prediction viewed from the exploration industry
[J].
地震反演储层描述精度影响因素分析
[J].
Analysis of influencing factors in reservoir description accuracy by seismic inversion
[J].
AVO梯度谱蓝化在中深层薄砂岩刻画中的应用
[J].
Application of the AVO gradient-based spectral bluing technique in the characterization of thin sandstones in moderately deep strata
[J].
分频AVO技术在安岳气田须二段储层含气性分析中的应用
[J].
Application of frequency division AVO in the gas-bearing analysis of reservoir in the Xu-2 Member of the Anyue gas field
[J].
AVO attribute analysis and seismic reservoir characterization
[J].
AVO技术进展
[J].
Advances in AVO technique
[J].
叠前AVO属性的地震岩性学探索与实践研究
[J].
DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1000-1441.2013.03.004
[本文引用: 1]

自地震沉积学诞生以来,国内众多学者主要的研究方向集中在地震地貌学上,而对于地震岩性学却鲜有研究。以往对于地震岩性的表征技术主要为90°相位化和叠后反演,但在复杂地区这两种方法都存在一定的缺陷。为此,在前期研究中提出了地震岩性体概念:将地震数据转化为有明确岩性意义的地震属性体,来表征地震地貌。重新推导了AVO属性表达式,选择其中新的G属性作为地震岩性体,并在四川盆地中部某研究区取得了较好的应用效果。
Exploration and practice of seismic petrology on pre-stack AVO attribute
[J].
东海致密气藏AVO反射特征及其在储层预测中的应用
[J].
AVO reflection characteristics of the tight gas reservoir and its application in the reservoir prediction of the East China Sea
[J].
Analysing sand-dominated channel systems for potential gas-hydrate-reservoirs using an AVO seismic inversion technique on the Southern Hikurangi Margin,New Zealand
[J].
多分量地震资料在识别隐蔽河道砂岩中的应用
[J].
Identification of concealed channel sandstone based on multi-component seismic data
[J].
优势道叠加技术在岩性油气藏识别中的应用
[J].
Application of advantage trace stacking technique for lithologic reservoirs prospecting
[J].
琼东南盆地LS区近道地震反射性质研究及意义
[J].
The nature and significance of shortcut seismic reflection in the LS area in Qiongdongnan Basin
[J].
隐蔽河道砂体地震识别关键技术——以四川盆地中江气田中侏罗统沙溪庙组为例
[J].
Key technologies for seismic identification of hidden channel sandbodies:A case study of Middle Jurassic Shaximiao Formation in the Zhongjiang Gas Field of the Sichuan Basin
[J].
赤道几内亚湾深水海域基于部分叠加角道集的地震烃类检测
[J].
DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1000-1441.2017.06.010
[本文引用: 1]

直接利用地震资料进行含油气性检测在海洋深水油气勘探中尤为重要,但是利用单一属性或参数进行油气检测存在多解性和不确定性。以赤道几内亚深水沉积目标为例,基于部分叠加角道集,利用振幅属性、频率属性、分频技术、波形分类技术以及远道叠加数据与近道叠加数据交会分析等技术手段进行综合油气检测,预测了油气分布范围,预测结果与钻井结果以及已知的油气水分布吻合较好,有效排除了“假亮点”等非含气目标,提高了烃类检测的精度和可靠程度,取得了良好的应用效果,同时形成了一套适合海洋深水沉积储层烃类检测的方法和流程。
Seismic hydrocarbon detection based on partial stack angle gathers in offshore deep-water of the Equatorial Guinea Bay
[J].
DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1000-1441.2017.06.010
[本文引用: 1]

<p> Exploration of hydrocarbons in offshore deep-water reservoirs using seismic data is a highly relevant task.However,detection by a single attribute or parameter of seismic data leads to a high level of uncertainty.Here we use an example of the deep-water sedimentary hydrocarbon reservoir of the Gulf of Equatorial Guinea to detect hydrocarbons based on partial stack angle gathers.We used five techniques for hydrocarbon exploration,namely,seismic amplitude and frequency attribute,spectrum decomposition,waveform classification and crossplot analysis of far offset stack and near offset stack data.The distribution of hydrocarbons in the study area was detected using the abovementioned techniques,and the predicted results agreed with the drilling data and the known reservoir fluid distribution.Moreover,we discovered that the proposed method can effectively eliminate false bright spot anomalies and other non-gas bearing prospects,thus improving the accuracy and reliability of hydrocarbon detection,which can support seismic hydrocarbon exploration in offshore deep-water sedimentary hydrocarbon reservoirs.</p>
基于部分叠加角道集属性的含油薄层砂体预测
[J].
DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1000-1441.2014.06.015
[本文引用: 1]

针对在调谐背景下直接利用叠后属性识别预测薄层砂体多解性强的问题,研究并提出了塔中北坡S1井区目标储层基于部分叠加角道集属性的含油薄层砂体预测方法。首先,以现有井资料为基础,开展薄层地震反射波随入射角变化规律的正演分析,认为研究区含油薄层反射的视AVA效应是敏感且可检测的;其次,在对原始CRP道集资料提高储层成像精度预处理的基础上,利用部分道集叠加的方式进一步增强薄层反射视AVA效应的规律性;然后,结合正演模拟取得的认识和实钻井目的层油气显示结果,进行基于部分叠加角道集数据的属性随入射角变化规律分析,认为在调谐背景下目的层最大波峰振幅和最大波峰主频属性是检测薄层砂体含流体性质的敏感地震属性,据此提出了相应的油气检测因子,预测了研究区目的层含油薄层砂岩有利分布区。
Sandstone prediction of the oil-bearing thin-layers based on seismic attributes from partial stack angle gathers
[J].
DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1000-1441.2014.06.015
[本文引用: 1]

In the target reservoirs of S1 well area at the north slope of Tazhong Uplift,the tuning effect will cause multi-solution in the thin-layer sandstone prediction.Therefore,we studied and proposed an oil-bearing thin-layer sandstone prediction method based on seismic attributes from partial stack angle gathers.Firstly,the seismic reflection variation versus incident angle is studied by forward modeling,which indicates that the apparent AVA effect of the reflection from the oil-bearing thin-layers is sensitive and detectable.Secondly,on the basis of preprocessing on the CRP gathers for improving the reservoir imaging precision,partial stack angle gathers are used to enhance the regularity for apparent AVA effect of the reflection from the oil-bearing thin-layers.Thirdly,the achievements from forward modeling and the drilling results are jointed to analyze the variation of seismic attributes versus accident angle for the intervals based on partial stack angle gathers,which demonstrates that the maximum peak amplitude and maximum peak dominant frequency are sensitive to the fluid properties.Based on the recognition,we proposed corresponding hydrocarbon detection factor,which is used to successfully predict the potential zone for oil-bearing sandstone in the area.
Seismic-fluid detection-a review
[J].
Seismic attribute for hydrocarbon expressions in stack section
[J].