0 引言
常规油气储层的裂缝勘探常使用阵列声波测井方法,国内外专家学者对此展开过不同的研究[7⇓⇓⇓⇓⇓⇓⇓⇓⇓⇓⇓⇓-20]。综合前人的研究发现,在常规储层中,纵波对裂缝反映不敏感,横波及斯通利波受裂缝影响产生衰减[21⇓⇓-24]。帕尔哈提·祖努等[25]和齐兴华等[26]研究了煤层中不同裂缝宽度和不同裂缝条数下声波测井的响应特征。但目前鲜少有应用阵列声波测井方法开展花岗岩储层裂缝形态的研究,无法确定花岗岩储层中声波对裂缝的响应规律。因此,本文采用数值模拟阵列声波测井方法研究花岗岩储层裂缝的形态规律,即通过对花岗岩裂缝宽度、裂缝倾角、裂缝长度不同情况下的阵列声波测井数值模拟,来研究纵波、横波、斯通利波在不同裂缝情况下的声场响应规律,为采用阵列声波测井判断花岗岩储层中裂缝的发育状态提供依据。
1 模型建立
1.1 理论基础
式中:
式中:ρ为介质密度;u为振幅;S为第二类Piola-Kirchhoff应力张量;
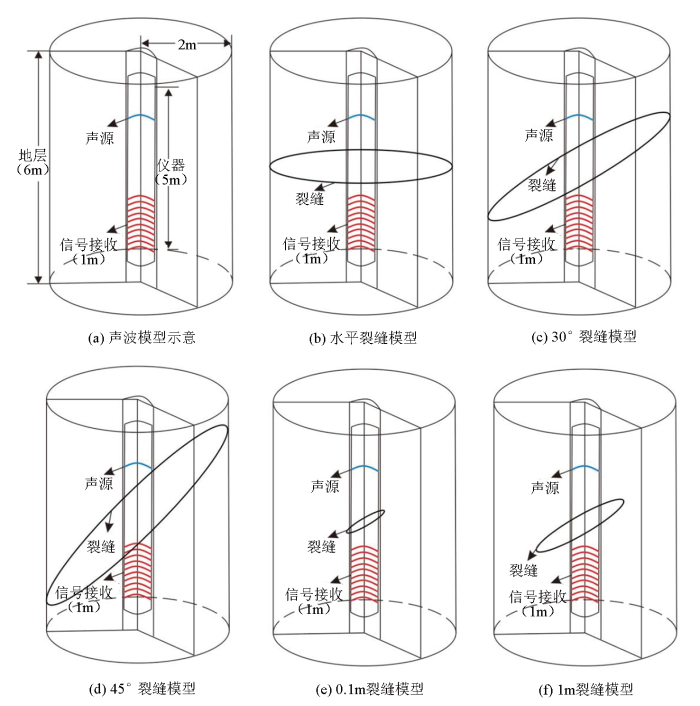
1.2 模型设置
图1
表1 模型各材料参数
Table 1
| 材料设置 | 密度/ (kg·m-3) | 声速/ (m·s-1) | 杨氏模 量/Pa | 泊松比 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 地层 井眼 裂缝 | 2600 1000 1000 | 5000 1500 1500 | 6×1010 0 0 | 0.5 0.25 0.25 |
发射探头所激发的波主频约为10 kHz。为了得到更精确的数值解,模型网格设置为极细化剖分,网格最大单元设置为0.02 m。模型中设置吸收边界,分别在花岗岩地层周围设置低反射边界,在井眼顶底设置平面波反射边界。
2 模拟结果
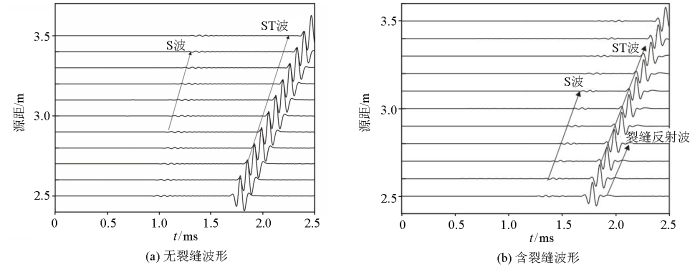
2.1 含裂缝模型模拟
图2
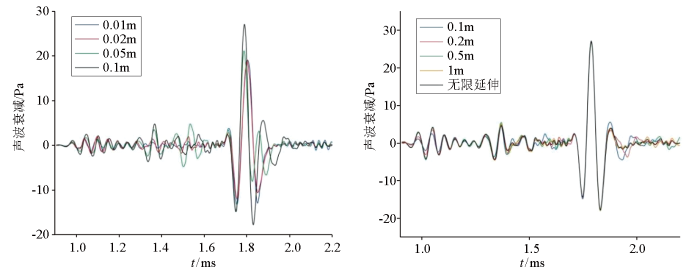
2.2 裂缝宽度变化模拟
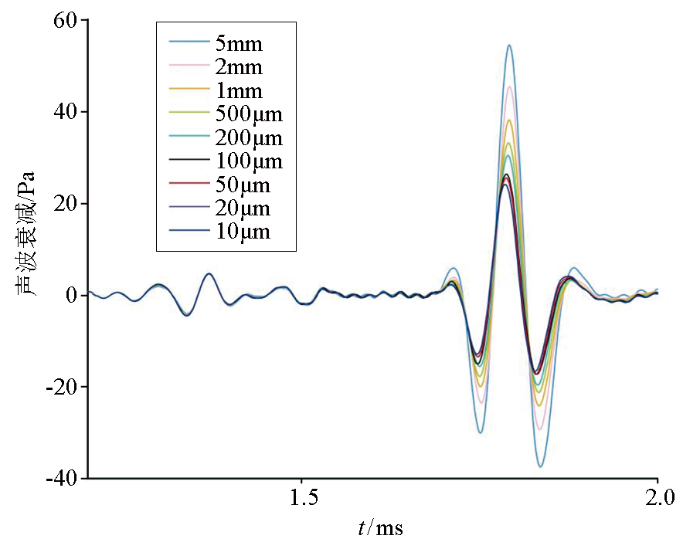
保持其他条件不变,当裂缝为30°贯穿缝,裂缝宽度分别为10 μm、20 μm、50 μm、100 μm、200 μm、500 μm、1 mm、2 mm、5 mm时,裂缝在源距2.5 m处对声波的衰减结果如图3所示。可以看出,裂缝宽度的增加与裂缝对声波的衰减程度呈正比,缝宽小于100 μm时,裂缝对声波的衰减程度影响变小,裂缝小于20 μm时,缝宽的减小对声波的衰减情况基本不再改变;纵波、横波对裂缝宽度的改变无明显影响;斯通利波的到时并未有明显改变,但斯通利波的响应幅度与裂缝宽度的增加呈反比关系。
图3
图3
裂缝宽度与声压衰减的关系曲线
Fig.3
Relationship between crack width and sound pressure attenuation
2.3 裂缝倾角变化模拟
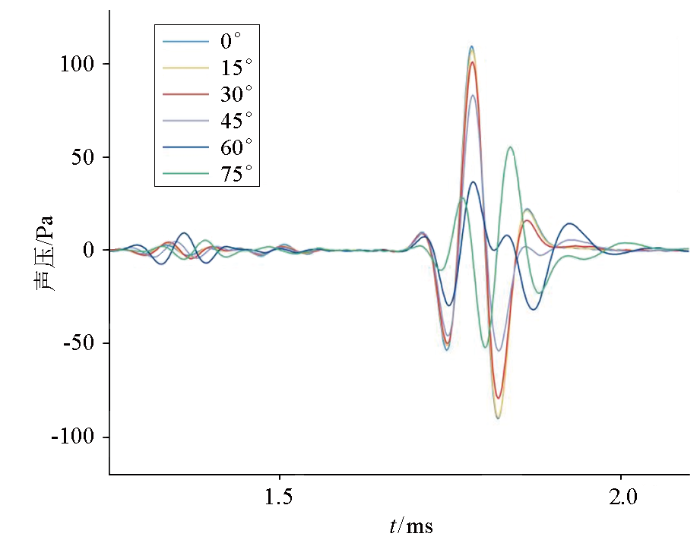
当裂缝宽度为100 μm,贯穿缝分别为0°、15°、30°、45°、60°、75°时裂缝在源距2.5 m处对声波的响应结果如图4所示。可以看出,当裂缝倾角为低角度(倾角<45°)时,声波响应值与裂缝倾角呈反比,声波衰减与裂缝倾角呈正比;当裂缝倾角为高角度(倾角>45°)时,声波衰减程度变大且相位发生变化;纵波对不同倾角裂缝的响应无明显变化。裂缝倾角在低角度范围时,裂缝倾角的增大和横波到时呈正比关系,与横波响应幅度呈正比关系。斯通利波到时未发现明显改变,斯通利波幅度值与裂缝倾角增加呈反比关系。裂缝倾角在高角度范围时,裂缝倾角的增大和横波到时呈正比关系,但由于相位发生改变且反射波发生叠加,与横波响应幅度关系无法确定;由于相位发生改变,斯通利波对高倾角裂缝的响应无明显规律。
图4
图4
裂缝倾角与声压的关系曲线
Fig.4
Relationship between crack inclination and sound pressure
2.4 裂缝长度变化模拟
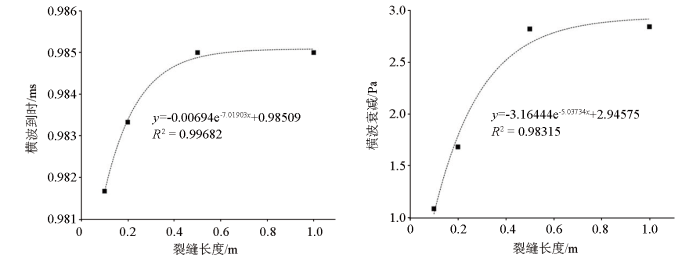
当裂缝宽度为100 μm、裂缝倾角为30°时,裂缝长度分别为0.01、0.02、0.05、0.1、0.2、0.5、1 m和无限延伸长度时裂缝在源距2.5 m处对声波的响应结果如图5所示。可以看出,当裂缝长度小于0.1 m时,即裂缝主要分布在井壁周围时,裂缝长度增加与声波衰减程度呈正比且声波相位发生改变;纵波对裂缝长度变化不敏感;横波到时与裂缝长度增加呈反比,横波响应幅度与裂缝长度呈反比;斯通利波到时与裂缝长度增加呈正比,斯通滤波响应幅度与裂缝长度增加呈反比。当裂缝长度大于0.1 m时,此时裂缝主要分布在地层中,裂缝长度的增加对声波衰减程度的影响不明显;纵波对裂缝长度变化不敏感;横波到时与裂缝长度增加呈反比,横波响应幅度与裂缝长度呈反比,横波衰减程度与裂缝长度增加呈正比;斯通利波对裂缝长度变化无明显响应。
图5
图5
裂缝长度与声压衰减的关系曲线
Fig.5
Relationship between crack length and sound pressure attenuation
3 结果分析
由于纵波对裂缝响应变化相对较小,因此本文主要分析横波与斯通利波对裂缝的响应。
3.1 裂缝宽度对声波的影响
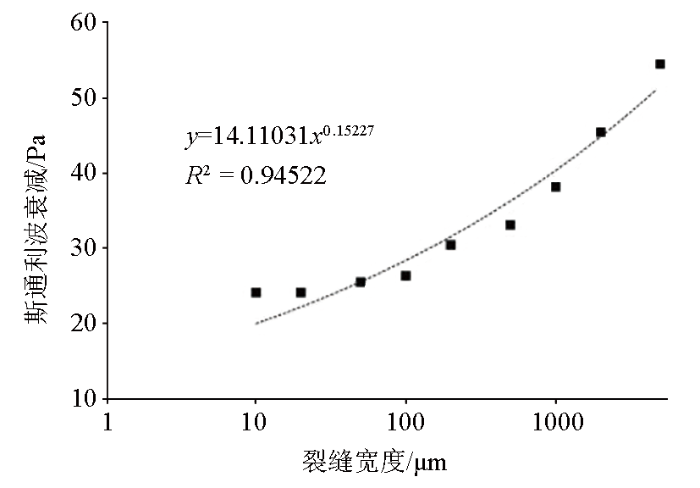
裂缝宽度变化对横波无明显影响,因此,此处主要分析裂缝宽度变化对斯通利波的影响。图6为裂缝宽度变化对斯通利波衰减的影响,其中声波衰减是指无裂缝模型的斯通利波声压值与含裂缝模型斯通利波声压值之差。从图中可以看出,裂缝宽度与斯通利波声压衰减具有很好的正相关性,且当裂缝宽度小于100 μm时,裂缝对斯通利波的衰减程度影响变小,裂缝小于20 μm时,裂缝宽度的减小不再对斯通利波的衰减程度造成影响。
图6
图6
裂缝宽度与斯通利波衰减的关系
Fig.6
Relationship between crack width and stoneley wave attenuation
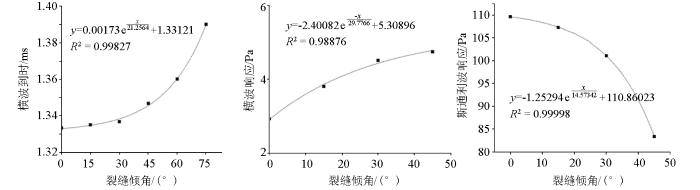
3.2 裂缝倾角对声波的影响
图7为裂缝倾角对横波与斯通利波的影响。从图中可看出,横波到时在裂缝倾角增大时出现明显滞后,且当裂缝倾角小于30°时,横波到时受裂缝倾角影响较小,当裂缝倾角大于30°时,横波到时受裂缝倾角影响出现显著变化。因高角度(倾角>45°)裂缝相位发生变化,反射波出现叠加,所以此处主要分析低角度裂缝下横波与斯通利波的响应。裂缝倾角在低角度范围内时,横波响应声压与裂缝倾角呈正相关关系,即裂缝倾角越小横波衰减越明显;而斯通利波响应声压与裂缝倾角呈负相关关系,表明裂缝倾角越大斯通利波衰减越明显。
图7
图7
裂缝倾角与横波、斯通利波的关系
Fig.7
Relationship between crack inclination and transverse and Stoneleigh waves
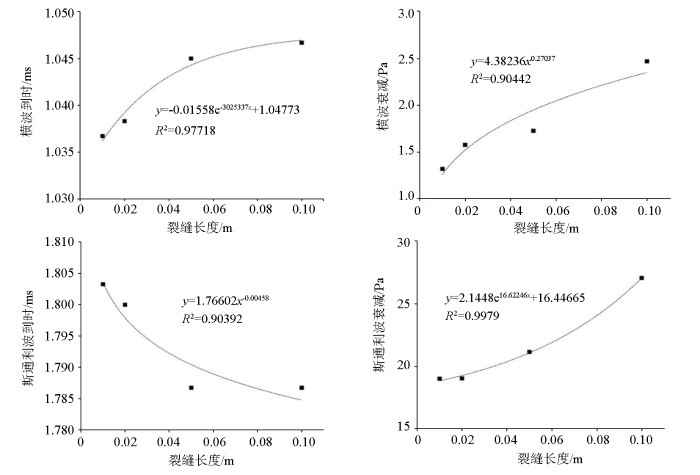
3.3 裂缝长度对声波的影响
长度小于0.1 m的裂缝主要为井旁诱导缝。图8为裂缝长度<0.1 m时对横波与斯通利波的影响,其中横波衰减程度是指无裂缝模型的横波声压值与含裂缝模型横波声压值之差。从图中可以看出:横波到时与裂缝长度呈正相关关系,横波衰减程度与裂缝长度呈正相关关系;斯通利波到时与裂缝长度呈负相关关系,斯通利波衰减程度与裂缝长度呈正相关关系。
图8
图8
裂缝长度<0.1m时与横波和斯通利波的关系
Fig.8
Relationship between crack length (<0.1m) and transverse and Stoney waves
长度大于0.1 m的裂缝主要存在于地层中。图9为裂缝长度>0.1 m时对横波到时、横波衰减的影响,从图中可以看出横波到时与裂缝长度呈正相关关系,横波衰减程度与裂缝长度呈正相关关系。
图9
图9
裂缝长度>0.1m时与横波的关系
Fig.9
Relationship between crack length (>0.1m) and transverse wave
4 结论
本文通过使用COMSOL Multiphysics有限元模拟软件对阵列声波测井探测裂缝性花岗岩储层进行模拟,得出以下结论:
1)裂缝性花岗岩地层中,横波受裂缝宽度变化影响不明显,横波衰减程度受裂缝倾角与裂缝长度变化影响,裂缝倾角越小,横波衰减程度越大;裂缝长度越长,横波衰减越大。
2)裂缝性花岗岩地层中,斯通利波对裂缝宽度、裂缝倾角、裂缝长度等变化均有明显响应,即裂缝宽度越大,斯通利波衰减程度越大;裂缝倾角越大,斯通利波衰减程度越大;在裂缝长度小于0.1 m时,裂缝长度越大斯通利波衰减程度越大,在裂缝长度大于0.1 m时,斯通利波对裂缝长度改变无明显响应。
参考文献
南海北部陆缘盆地形成的构造动力学背景
[J].
DOI:10.13745/j.esf.2015.03.003
[本文引用: 1]

南海北部陆缘盆地处于印度板块与太平洋及菲律宾海板块之间,但三大板块对南海北部陆缘盆地的影响是不同的。通过对三大板块及古南海演化的研究,可知南海北部陆缘地区应力环境于晚白垩世发生改变。早白垩世处于挤压环境,晚白垩世以来转变为伸展环境并且不同时期的成因不同。晚白垩世—始新世,华南陆缘早期造山带的应力松弛、古南海向南俯冲及太平洋俯冲板块的滚动后退导致其处于张应力环境。始新世时南海北部陆缘裂陷盆地开始产生,伸展环境没有变,但因其是由太平洋板块向西俯冲速率的持续降低及古南海向南俯冲引起的,南海北部陆缘盆地继续裂陷。渐新世—早中新世,地幔物质向南运动及古南海向南俯冲导致南海北部陆缘地区处于持续的张应力环境;渐新世早期南海海底扩张;中中新世开始,三大板块开始共同影响着南海北部陆缘盆地的发展演化。
Tectonic dynamics of northern continental margin basins in South China Sea
[J].
渤海西部曹妃甸1-6花岗岩潜山油藏的发现
[J].
Discovery of CFD1-6 granite buried-hill oil pool in western Bohai area
[J].
乍得Bongor盆地花岗质基岩潜山储层特征
[J].
DOI:10.7623/syxb201508001
[本文引用: 1]

乍得Bongor盆地基底是由早寒武世及更老的花岗岩、混合花岗岩和片麻岩等构成,经历了古生代—侏罗纪长期的风化剥蚀夷平作用。早白垩世受中非剪切带走滑-拉张作用影响形成拉分盆地,同时在基底形成大量的构造裂缝;晚白垩世强烈反转,古近纪发育成为统一的盆地。2007年以来实施多层系立体勘探,不仅在下白垩统沉积地层发现一系列大中型油气田,而且还在花岗质基岩潜山获得高产油气流,证实了5个潜山油藏带。根据储集空间的特征将基岩储层划分为孔隙型和裂缝型两类。综合地震、测井、地层成像、元素测井和岩心分析等资料,垂向自上而下将潜山的储层序列划分为风化淋滤带、缝洞发育带、半充填裂缝发育带和致密带。潜山所处的构造位置和埋藏深度决定了潜山储层序列发育的完整性和物性的好坏。基岩储层的垂向分带性为钻前储层的地震横向预测和评价提供了可能。
Characteristics of granitic basement rock buried-hill reservoir in Bongor Basin,Chad
[J].
琼东南盆地梅山组海底扇天然气成因类型及成藏模式
[J].
Genetic types and accumulation model of submarine fan gas in the Meishan Formation,Qiongdongnan Basin
[J].
渤海湾盆地花岗岩潜山油田裂缝发育特征厘定
[C]//
Determination of fracture development characteristics in granite buried hill oil fields in the Bohai Bay Basin
[C]//
Using compressional and shear acoustic amplitudes for the location of fractures
[J].
DOI:10.2118/723-PA
URL
[本文引用: 1]

Field results have shown that fractured zones may be located by their attendant reduction of acoustic amplitude. Laboratory and theoretical investigations confirm this technique, but interpretation of amplitude logs is complicated by the many variable factors encountered in actual logging operations. The acoustic amplitude investigations covered by this paper were made by continuous measurements of the peak amplitudes of single, and well defined compressional and shear-wave arrivals. A simultaneously recorded measurement of interval transit time or total travel time, in each case, indicated whether or not there had been continuous amplitude measurement of the same wave arrival. Investigations have shown that the angle at which a fracture plane crosses a borehole affects the attenuation of acoustic signals. Theoretically, horizontal fractures (those perpendicular to the axis of the borehole) should cause little or no attenuation of the compressional wave; this is confirmed by field examples. Shear-velocity waves, on the other hand, are significantly attenuated by horizontal fractures. While oblique fractures cause a reduction of compressional-wave amplitude, shear-wave amplitude measurements in such cases may not be as definitive. Since the early compressional arrivals are not subject to interference complications, as are shear arrivals, both measurements should be made and used to complement each other.
Acoustic propagation in the vicinity of fractures which intersect a fluid-filled borehole
[C]//
Physical modeling of the full acoustic waveform in a fractured,fluid-filled borehole
[J].
DOI:10.1190/1.1442562
URL
[本文引用: 1]

Three concrete models were constructed, one each with a fracture oriented at 90, 45, and 10 degrees to the axis of the borehole. These were used to simulate physically the propagation of the full acoustic waveform through a fluid‐filled borehole in crystalline rock and to ascertain the effects of fracture aperture and orientation of fluid‐filled fractures on the waveform. The tube‐wave mode of the waveform was most indicative of the magnitude of fracture aperture. Normalized tube‐wave amplitude decreased as a negative exponential function of aperture over the range of fracture apertures studied (closed to 0.66 cm). The 90 degree fracture orientation caused greater tube‐wave amplitude reduction than the 45 degree fracture. We hypothesize that this reduction can be attributed to the borehole wall’s guiding the wave across the 45 degree fracture. However, the 10 degree model gave ambiguous results, which are believed to be related to the low ratio of tube‐wave wavelength to aperture as measured parallel to the borehole axis, i.e., axial aperture.
裂缝性地层中的井孔声场模拟
[J].
Simulation of the fracture formation acoustic field in boreholes
[J].
贴井壁声波测井仪的有限差分模拟研究
[J].
Finite difference modeling of the acoustic field by sidewall logging devices
[J].
井旁裂缝的声场模拟及反射波提取方法
[J].
Sonic field simulation for borehole-side fracture and reflection wave extraction method
[J].
裂缝性致密砂岩储层声波测井数值模拟响应特性研究
[J].
Research on numerical simulation response characteristics of acoustic logging for fractured tight sandstone reservoirs
[J].
Frequency-domain finite-element simulations of 2D sonic wireline borehole measurements acquired in fractured and thinly bedded formations
[J].
含有倾斜薄裂缝孔隙地层中的井孔声场
[J].
DOI:10.6038/cjg20150128
[本文引用: 1]

应用三维交错网格应力-速度有限差分方法,数值模拟了含有倾斜裂缝孔隙介质地层中点声源所激发的井孔声场问题.为满足薄裂缝计算需求,开发了不均匀网格有限差分算法,提高了计算精度及计算速度.利用将孔隙介质方程参数取为流体极限的办法来处理裂缝中的流体,实现了流体-孔隙介质界面处的差分方程统一,使界面处的计算更加灵活方便.在验证了方法正确性的基础上,分别考察了单裂缝宽度、裂缝带宽度、裂缝倾斜角度以及孔隙介质渗透率等参数的变化对井轴上阵列波形的影响并进行了分析.结果表明,声波经过裂缝时可能产生反射横波及斯通利波,后者随裂缝宽度的减小而减小,而前者随裂缝宽度的改变,变化不大,在裂缝很小(20 μm)时依然存在;裂缝带的宽度、密度越大,反射斯通利波越强;当裂缝(裂缝带)倾斜时,反射横波消失,但反射斯通利波受裂缝倾斜角度的影响较小;渗透率的改变对斯通利波的衰减影响较为明显.
Borehole acoustic fields in porous formation with tilted thin fracture
[J].
基于反射声波测井有限元方法的井旁裂缝分布特征
[J].
Near wellbore fracture distribution characteristics based on acoustic reflection logging finite element method
[J].
裂缝对井眼声波的传播影响规律研究
[J].
Studies on the effec of crack on the propagation of acoustic waves in wellbore
[J].
基于线性滑动模型的裂缝性地层声波测井响应数值模拟
[J].
Numerical simulation of acoustic logging in fractured formation based on linear-slip model
[J].
多极子声波测井的裂缝识别与评价
[J].
Fracture identification and evaluation based on multi-pole acoustic logging
[J].
粗糙裂缝对井眼声波传播的影响
[J].
Data influence of rough crack on borehole acoustic wave propagation
[J].
三维声波测井探测特性分析与处理技术应用
[J].
Analysis of detecting characteristics and application of data processing technology for 3D array acoustic logging
[J].
裂缝模型声波衰减系数的数值模拟
[J].
Numerical simulation of the fractured model acoustic attenuation coefficient
[J].
用有限元法计算井中水平裂缝的反射斯通利波
[J].
Computation of reflected stoneley wave at a horizontal fractures using finite element method
[J].
裂缝性煤层声波测井响应的有限元模拟研究
[J].
Finite element simulation of acoustic logging response in fractured coal seams
[J].