0 引言
分布式声波传感(distributed acoustic sensing,DAS)技术引入我国以来发展十分迅速,与之配套的光纤系统也因为低廉与便捷的优势,让各学科的学者将这种全新的数据采集方式应用在多种不同条件的环境中。在近期发表的相关文献中,利用中国本土的测量数据进行处理和解释文章的出现,证实了DAS技术正在地球物理领域中蓬勃发展。目前DAS技术配合光纤系统的勘探方法不仅被利用于收集自然条件下的地质数据,还因为能够测量人类活动创造的各种建筑体内部的相关结构的特点,被应用于多种需要测量结构和采集数据的场景中,采集环境包括但不限于山区、河床、隧道、坝体、桥梁等情景。
DAS技术在地球物理勘探领域的应用呈现出了广阔的前景。本研究旨在探讨当前DAS在地球物理勘探领域包括油气地球物理、海洋地球物理和环境工程地球物理等方面的应用和研究进展,通过综合分析相关文献,评估DAS在不同工作条件下的优势和局限性;同时,进一步在物探方法、智慧平台、环境安全等方面探讨DAS在地球物理勘探领域的未来发展方向,为未来的相关研究提供建议和参考。
1 文献检索分析
图1
图2
图2
国家或地区发表的文献数量(数据来源:Web of Science)
Fig.2
Number of publications by country or region (data from: Web of Science)
图3
图3
主要文献类型及同类型文献数量对比
Fig.3
Comparison of the main literature types and the number of the same types
图4
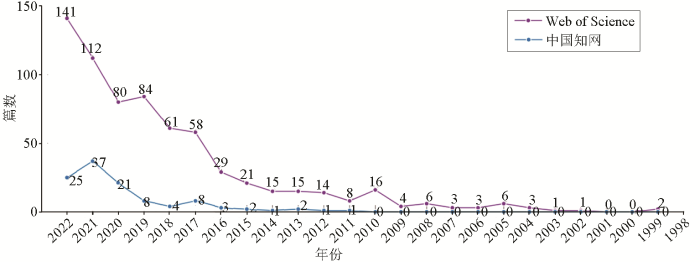
图1对比了Web of Science与中国知网两个文献数据库自1998年以来的文献发表数量。在Web of Science的数据中,DAS的相关文献的发表数量在逐年增长,并且在2019年有明显的增加,2022年和2023年发表的文献总数更是比之前所有文章的总数都多;在中国知网的数据中,DAS的相关中文文献自2011年开始稳步增长,自2019年起数量快速增长,2020年虽然有所减少,但发表数量仍多于学科发展前期。上述情况表明,DAS技术近年来受到的关注越来越多,我国对DAS技术的研究虽然起步与世界范围内相比较晚,但近年来取得了极大的进展,相关文献的数量也在稳步提升。DAS技术在新背景下的地质学中有极高的发展潜力和蓬勃的发展前景,能够面向国家“三深一系统”国家战略[1],为未来地球物理的发展提供更高效的勘探方法。
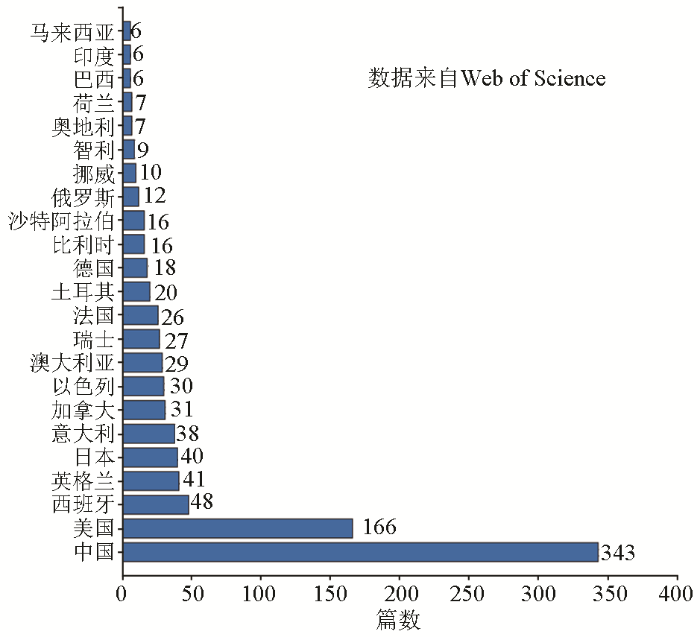
图2是由Web of Science所统计的关于DAS主题所发表文章的国家或地区及其发表的文献数量,图中数据仅使用了自2013年起至今发表文献数量大于5篇的记录。中国与美国发表的文献数量最多,其中收录的中国学者所发表的文献达到了343篇,说明近年来DAS在我国的发展较为迅速,我国学者也积极将DAS这一方法应用在各个学科中,并取得了一定的成果。
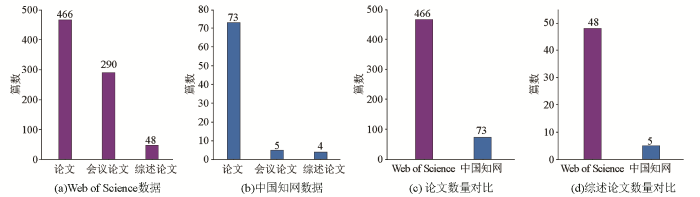
Web of Science提供了更多的文献类型,但中国知网目前只有论文、会议论文和综述论文3种,因此图3展示的是两个网站中与DAS技术相关的主要文献类型及同一类型文献的数量对比。根据两个网站所提供的数据能够明显发现:首先,与DAS技术相关的中文论文明显少于国际相关论文,这一方面是由于国内引入DAS技术和开展DAS技术研究的时间较晚,另一方面是因为目前相关学科的理论研究尚不完善,不足以支撑DAS技术的大规模、多学科应用;其次,综述论文较另外两种文献类型在数量上更少,这种情况在国内与国际范围内都相同,国内与国外在综述文献方面相差多于10倍。造成这种情况的原因可能是DAS技术虽然被应用于多种场景,但各个学者只根据自己的需要对获得的数据进行特定处理,在其熟悉的领域进行应用。DAS技术发展迅速,如果缺乏整体系统的认识,将会对后期的发展造成一定的影响。
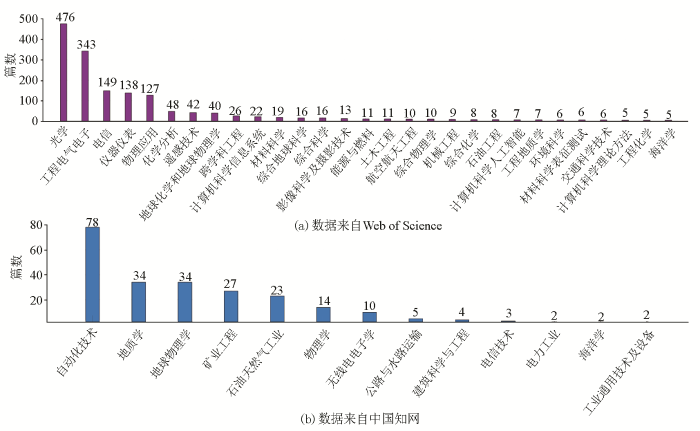
图4展示了国内外DAS在各个研究方向中的文献数量。Web of Science网站收录的相关研究方向有38种,而中国知网收录的相关研究方向目前只有13种。图中只展示了部分研究方向的文献数量。从数据来看,DAS技术在国内的研究方向远少于国外,大概率是由于国内引入DAS技术的时间较晚,应用尚不成熟造成的;从文献数量来看,国内自动化技术方向的文献较多,国外工程方向的文献较多,不难看出国内在DAS技术方面更趋向于数据处理,而国外更趋向于实际应用。由于Web of Science将地球化学和地球物理的相关文献归为了一类,而中国知网中有地球物理类别但没有地球化学类别,因此不能进行同学科论文数量对比。
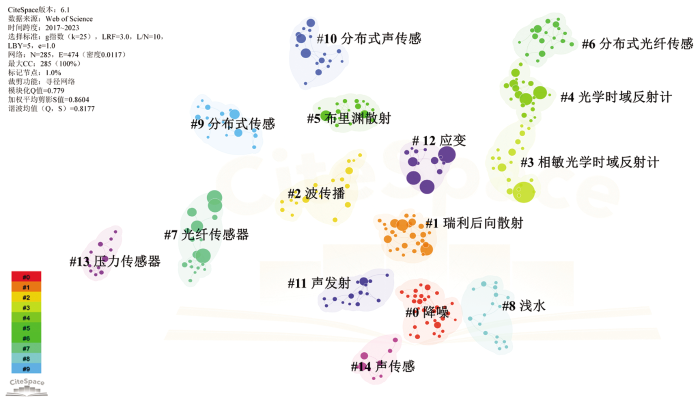
图5
图5
数据库文献聚类图谱(数据来源:Web of Science)
Fig.5
Database literature clustering map (data from: Web of Science)
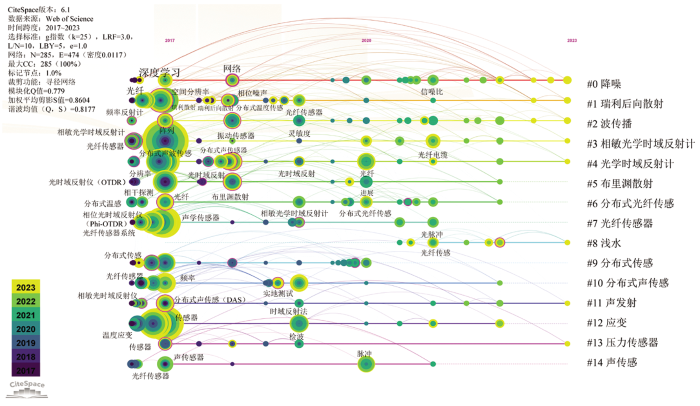
图6
图6
数据库文献时间图谱(数据来源:Web of Science)
Fig.6
Database document time map (data from: Web of Science)
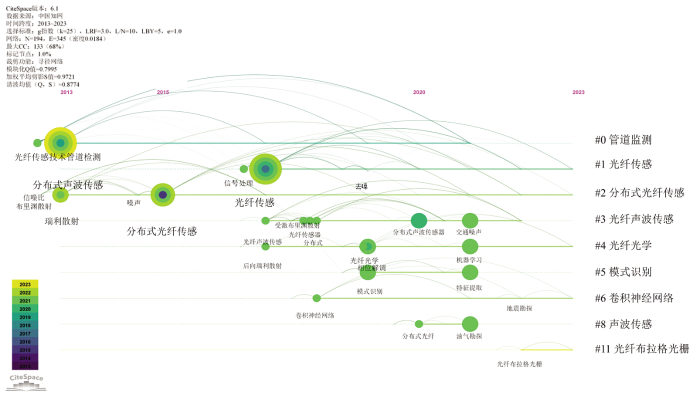
图7
图8
图8
数据库文献聚类图谱(数据来源:中国知网)
Fig.8
Database Literature Clustering Map (data from: CNKI)
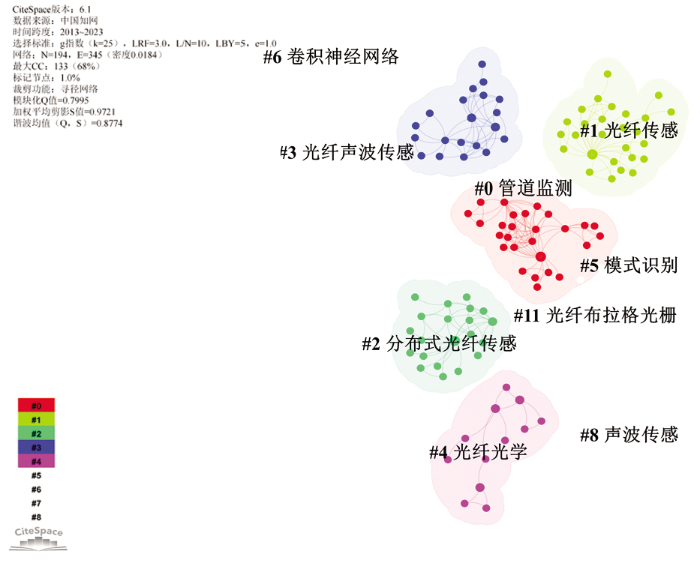
相较于Web of Science数据库中的内容,中国知网的内容明显较少,但近年来的数量较多,这也侧面验证了虽然国内引入分布式声学传感技术的时间晚,但呈现出快速发展的特点。
综上所述,DAS技术不仅发展空间大,研究方向多,而且近年来发展速度快,应用范围广。在引入时间较晚的背景下,DAS技术在国内进展快,已经被应用于多个领域,出现了多个研究方向的成果。由于目前的研究成果较为发散,缺乏较为系统的认识,因此,对DAS技术方面的发展概况进行总结,综合各个发展方向撰写相关综述文献是十分必要的。
2 光纤声学传感系统的原理和技术发展
2.1 技术简介
DAS技术作为最先进的声场检测技术之一,其中的光纤勘探系统工作原理主要是基于光纤对声音或振动敏感的特性,对与光纤相互作用的环境振动与声场信息进行分布式、长距离、高精度的实时检测[2⇓-4]。正因为光纤材料具有抗电磁干扰、体积小、复用性高且价格低廉的特殊性,因此DAS检波器在地震勘探工作中可以进行长期、大规模的布设,并进行长时间、多次数的测量,从根源上解决了常规仪器成本高、布设难度大等问题。相比于常规检波器,DAS检波器更适合开展地震勘测工作[5]。而布设在光缆上的检波器无需在测量后期移动,测量结束后也不需要逐个回收,使勘探效率大幅提高,对开展高效的井中地震勘探工作有极大的助益[6-7]。在地震勘探的分布式光纤传感系统中,不同井段的缆线可以通过桥接的方式进行连接,从而实现测区测井的全井覆盖,十分适用于测量区域大或深井及超深井地震勘探工作;DAS检波器间距能够灵活调整,通过选择较小的采样间距获取具有较高空间分辨率的地震信息,减小空间假频对勘探数据的影响[8]。
目前,DAS技术已经成为了世界范围内采集方法的研究热点,相关配套设施也逐渐趋于成熟,能够用于补充或代替传统检波器阵列进行地震勘探工作,以获取质量更好的钻孔地震数据;同时,DAS技术配套的光纤系统的便捷性使得该方法能够应用于更多地质工作场景。DAS技术具有广阔的发展前景。
2.2 基本原理
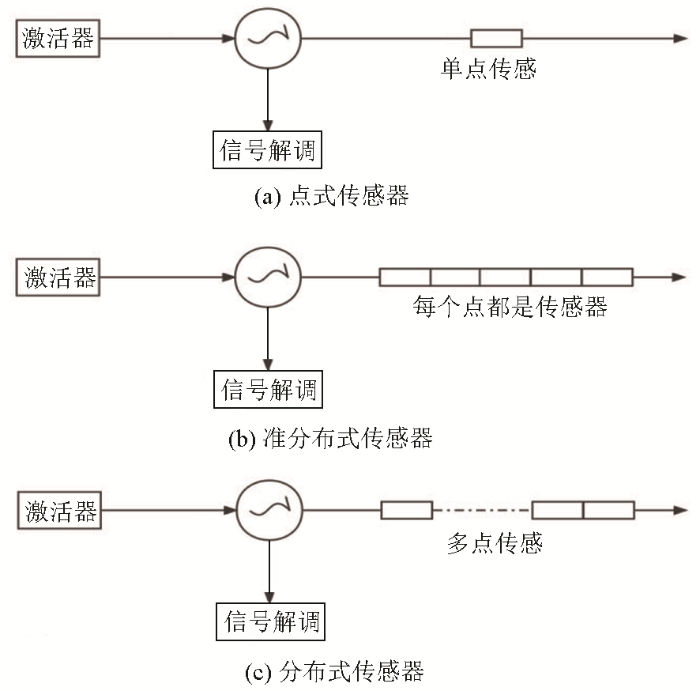
分布式光纤传感器是地震监测传感器中光纤传感技术的一个分支,与其同类别的传感器还有点式传感器、准分布式传感器两种(图9)。
图9
DAS技术中的光纤勘探系统以光纤的弹光效应[13]为基本原理,是一种可以实现振动和声场连续分布式探测的新型传感技术[14]。光纤介质的介电常数或光折射率因介质中应力波的存在发生改变,从而影响光在介质中的传播特性,而介质存在的不均匀性会导致光通过介质时向各个方向散射[15]。基于DAS技术的光纤勘探系统可以通过检测激光脉冲在光纤中散射引起的相位变化来测量光纤的轴向应变。系统主要由两方面构成:光纤(即传输介质)和地表仪器(即发射脉冲与探测瑞利散射信号的仪器),其中每一小段光纤都相当于一个单分量应变仪。该系统的工作原理是:通过在特定的路径上铺设光纤,地表仪器系统与光纤相连;对主动源模拟或被动源产生的地震波进行探测,光纤接收振动信号并将信号反传回地表仪器;地表仪器分析振动信号并将其转换为地震信号,以便于进行后期数据解释[9]。
目前,主流DAS相关仪器的原理是结合相干瑞利散射对应变化高度敏感的特性(窄线宽单频激光在光纤中激发产生)与反射计原理,对与光纤相互作用的环境振动与声场信息进行长距离、高时空精度的感知[14]。
2.3 技术发展
在DAS数据处理方面,时旸[20]提出了基于低秩矩阵近似(ILMA)和基于张量鲁棒主成分分析(T-RPCA)两种DAS数据降噪方法。ILMA算法能够有效压制噪声,T-RPCA算法能得到预期目标;但ILMA算法中的秩是一固定的常量,目前没有实现自适应选择合适大小的秩进行处理,T-RPCA算法由于DAS数据计算量本身较大等问题,计算效率较低,需要进一步改进。邢桐[21]提出了一种多尺度渐进融合算法(MFPF),MFPF在去噪性能、信号泄露、定量分析等多个层面都有更出色的表现。虽然上述算法基于的理论各有不同,但主要目标都是为了解决DAS数据的高噪声问题,而上述去噪方法也为DAS数据处理提供了新的研究思路和去噪方式,深度学习在去噪中的应用有望成为DAS大数据量特点的又一解决方式。
3 DAS在油气地球物理中的应用
DAS技术最早应用于油气地球物理中,在经过与常规检波器对比并验证了其可行后,立刻投入了生产。而DAS技术所带来的施工优势和数据优势也为油气地球物理勘探工作做出了贡献。
3.1 垂直地震剖面法中的应用
垂直地震剖面(VSP)技术是一种地表震源激发,在沿井孔不同深度布置的一些检波点上进行观测的地震观测方法[27]。由于VSP数据具有包含信息丰富、波结构特征清晰明显的优点,被广泛应用于全波勘探领域。但复杂的地震勘探目标预示着常规仪器的布设难度,DAS检波器更适合开展井中VSP地震勘测工作。
图10
DAS-VSP技术作为新技术与旧方法的融合,目前已经得到了可观的成果,尤其是该方法在目前的热点问题——碳封存(CCUS)中的应用及相关成果十分显著。不难预测,与热点问题联系后的DAS技术一定能在短时间内获得广泛关注。
3.2 油藏监测中的应用
图11
油气地球物理方面的研究主要集中在地下油藏勘探与油气运输管道监测两个方面,其中油气管道监测方面的文章较多,推测是由于已经建成的油气管道较多较长,且传统检波器不能满足长期有效监测油气管道的要求,而DAS系统的高覆盖率与便携性解决了这一难题;同时DAS系统所使用的光纤材料在实际工程作业中的成本更低,也让DAS系统在长期监测油气管道这一工作中得到了广泛推广。
3.3 矿产资源勘探中的应用
常规勘探技术在效率低下的同时还受极端环境的限制,无法满足勘探需求,而DAS技术因其传感距离大、时空分辨率高和适应复杂环境的特性更加适合于进行地面探测和井内探测,为矿产资源勘探技术提供了新的思路。
图12
在地下油藏勘探方面,目前以验证可行性的研究为主,其中对DAS系统测量得到的数据中的相关参数与数据处理方面的研究较多。通过对DAS数据与传统检波器测量得到的数据进行对比,在验证DAS系统在油气领域可行性的同时,可利用DAS数据完善已有的数据材料,为同一地点的后期工作打下较好基础,同时也为将来的发展提供方向。
4 DAS在海洋地球物理中的应用
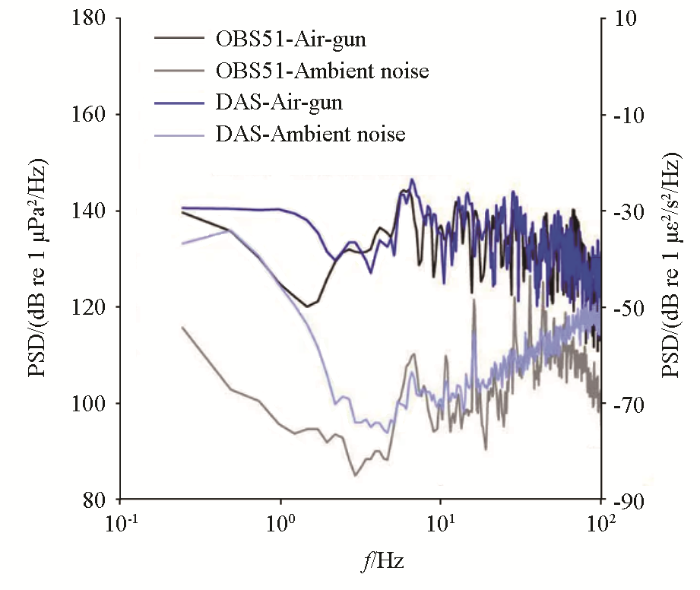
陈同彦等[64]开发并研究了新型海底管道分布式光纤传感器的和安装工艺,成功在埕岛油田实现了分布式光纤传感器新建海底管道的布设。Matsumoto等[65]为了调查日本四国岛附近地震结构,利用OptaSense有限公司制造的远程DAS Plexus系统进行了一次舰载地震调查,图13展示了水听器OBS51(黑线)和DAS仪器(蓝线)在相同入射信号下的功率谱密度(PSD)。由于两种仪器所得信号的换算方式不同,左侧PSD轴表示水听器所接收到气枪震源与背景噪声的信号值,右侧PSD轴表示DAS仪器所接收到气枪震源与背景噪声的信号值,结果证明DAS仪器检测到的短持续时间和宽带水声信号具有与共定位水听器非常相似的特征。如果选择相应的海底电缆路线,DAS能够探测海底火山的水声信号,为海底火山的远程监测提供了可能。
图13
在海洋地球物理方面,目前国内将DAS系统用于相关研究的文章较少。根据海洋地球物理的特点,目前相关研究中使用分布式光纤系统中的DTS系统的学者较多。同时,为了分布式光纤这一优势较多的方法能够更加适应海洋环境,并顺利进行海洋地球物理的相关工作,有不少文章提出新的方法或研发新仪器。DAS系统在海洋地球物理中的应用主要集中在监测海底油气管道和海洋背景音,以及海底地质水声信号测定等方面。根据目前文献方向来看,后期可能会将DAS系统与DTS系统结合,应用在海底油气管道的长期监测方面;在DAS系统测定水声信号方面,未来有望将海底电缆用于DAS系统,并对海底火山等地质体进行远程监控。
5 DAS在环境工程地球物理中的应用
5.1 地质灾害监测
不少学者已经利用DAS技术进行了相关实验。2018年12月和2019年12月,Wang等[71]利用中国移动提供的标准单模光纤,在云南省宾川县城区进行了两次观测实验,成功验证了城市通信光缆用于地震预警和地下结构观测的可能性,为DAS研究和地震监测研究提供了新的方向。
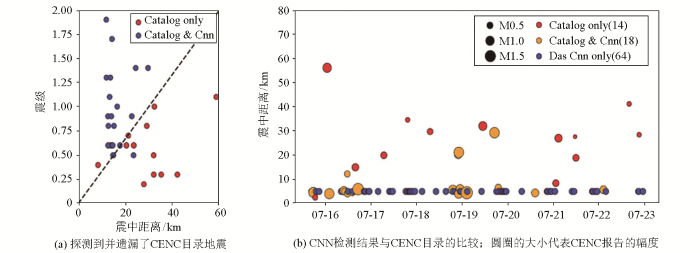
Hudson等[72]提出了一种能够准确表征各向异性冰结构引起的横波劈裂的二维DAS阵列多分量传感器。Nayak等[73]证明DAS技术在局部和区域小地震事件检测方面具有显著的潜力。余双勇[74]基于DAS机理的地震检波器总体结构设计光电探测模块,选择光缆外部材料以及脉冲宽度,证明传统地震检波器与DAS平台单点探测输出信号相符,但DAS平台在微弱信号的探测上更为灵敏。Lyu等[75]提出了一种小样本集的DAS海量数据事件检测算法,就结果来看该方法检测出的地震事件数量明显多于CENC所检测到的地震数量(图14)。同时,该方法为DAS相关的海量数据事件监测提供了新的思路,但检测能力受信噪比限制,检测下限在2 dB左右。
图14
5.2 城市建设
分布式光纤声波传感系统(DAS)是一种以光纤电缆进行声波信号采集的新兴技术。光纤电缆价格低廉、可代替性高,更加适用于对城市建设过程中可能出现的公路裂隙、隧道坍塌、桥梁坍塌等问题的日常监测。而DAS具有可便捷调节标距的特点,能够通过在目标一侧布设长距离的光纤进行实时监测的同时,避免对关键位置的监测偏差, 大幅提升了工作效率。
在环境工程地球物理方面,DAS系统在地质灾害监测、矿产资源勘探和城市建设中都有一定的应用。其中在城市建设方面应用较多,推测原因可能是城市建设与人民生活息息相关,其中坝体、桥梁、隧道等大型人类活动工程建筑物如果不能及时维护或修缮,极有可能存在坍塌危险,因此对相关建筑物的定期监测或长期监测是必不可少的。同时,由于建筑物较地质灾害和矿产资源两种目标更为常见和稳定,通过对监测数据在时间和空间上的差异进行分析,能够获知目标体是否需要进一步完善,这一特点也使得这部分的研究广受相关学者的青睐。
6 DAS的发展前景
根据目前DAS在各个领域的发展,不难推断出DAS的发展将集中在以下几个方面。
图15
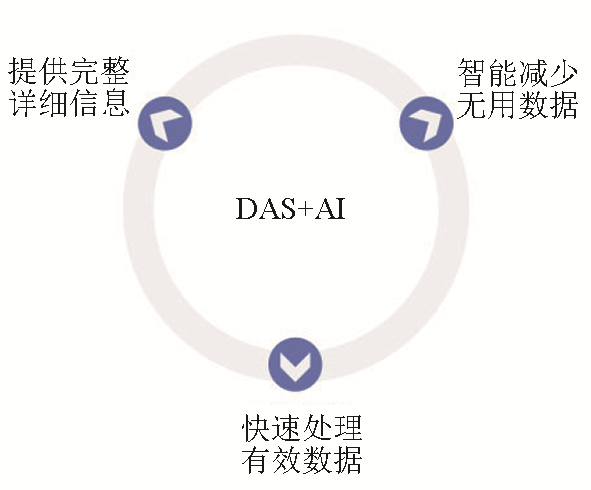
2)在智慧勘探平台的建设中发挥重要作用。光纤传感技术具备井中地震、压裂监测、产剖监测、智能注采监测等“动静结合”的优势,或将成为智慧勘探平台建设的必选项[13]。由于利用DAS技术获得和相关工作所需的数据量变得非常庞大,仅依靠该领域的专家提供完整和详细的分析并在整个过程中做出决策是不现实的。基于上述原因,使用先进的人工智能(AI)和机器学习方法,可以帮助减少数据大小并提取事件的有用数据,甚至可以代表专家做出决定,在一定程度上削减问题的难度(图16)。此外,考虑到勘探行业中许多不同的传感和测量系统当前和未来的应用,采用基于云的平台将是一个有前途的解决方案,可以解决安全可靠的数据传输、管理、存储、分析、可视化和下载问题。
图16
图16
人工智能为DAS技术带来的改变
Fig.16
Changes to DAS technology brought about by artificial intelligence
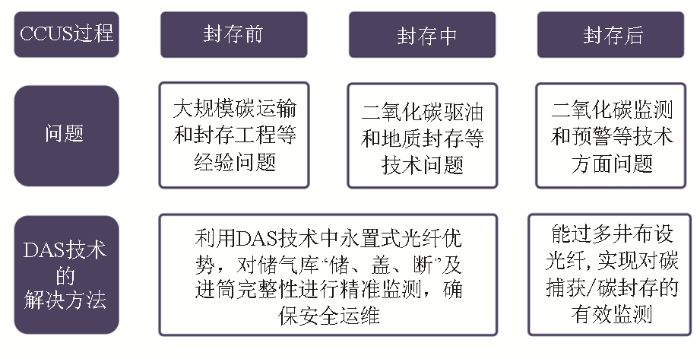
3)在储气库监测和CCUS领域广泛应用。我国在CCUS技术链各环节已经具备一定的研发基础,在开发出多种具有自主知识产权的计算基础上,同时具备大规模全流程系统的设计能力,目前已取得不错的研究成果。但相比国际先进水平依然存在一定的差距,主要集中在以下三个方面:大规模碳运输和封存工程经验;二氧化碳驱油、地质封存等理论和核心技术;封存后的二氧化碳监测、预警等技术[91]。基于上述种种问题,可以利用目标位置或在目标位置布设对应光纤,利用DAS技术中永置式光纤优势,对储气库“储、盖、断”及井筒完整性进行精准监测,确保安全运维。通过多井布设光纤实现对碳捕获/碳封存的有效监测,为新能源业务发展提供有效评价手段(图17)。
图17
图18
图18
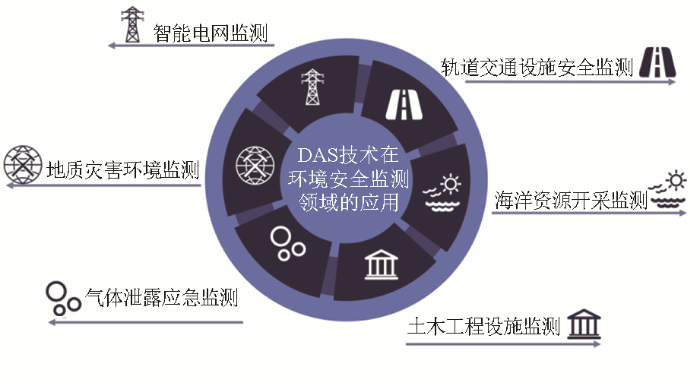
DAS技术在环境安全监测领域的应用
Fig.18
Application of DAS technology in the field of environmental safety monitoring
7 结论
DAS技术凭借自身优势在地球物理领域中应用广泛。本文介绍了DAS技术的主要概念,对DAS技术在地球物理学中的应用进行了分类介绍,最后讨论了DAS技术的未来发展趋势。DAS技术已经在油气地球物理,海洋地球物理,环境与工程地球物理中有了重大突破,但目前技术还不够成熟,实际应用的事件识别率较低,与传统点传感器相比,在灵敏度等方面还有相当大的差距。
DAS技术在地球物理领域创造了更多可能的同时,也带来了更多的挑战。随着DAS技术在检测距离、灵敏度、多参数监测、多维监测等方面的突破,加上与深度学习、神经网络的结合,DAS技术的独特优势将在众多领域发挥重要作用。
参考文献
实验地球科学的前沿与发展战略
[J].
Frontiers and development strategies of experimental geoscience
[J].
Validation of DAS data integrity against standard geophones—DAS field test at Aquistore site
[J].
DOI:10.1190/tle36120981.1
URL
[本文引用: 1]

Distributed acoustic sensing (DAS) using fiber-optic cables is a recent addition to seismic acquisition methods. However, a DAS “sensor” differs significantly from conventional, discrete sensing devices such as geophones or accelerometers. For one, DAS measures something akin to strain instead of particle velocity or acceleration. Other properties of the DAS system also aren't obvious at first. What is its instrument response, noise performance, and repeatability? How are DAS channels properly positioned, e.g., in case of a borehole deployment: depth calibrated? To better understand these issues and their impact on the DAS seismic method's application space, a field test was conducted in which three DAS vendors recorded the same survey using a borehole-installed fiber while recording simultaneously with a conventional downhole array. The results show that all DAS systems achieved good, repeatable signal integrity while exhibiting different noise characteristics. DAS noise can be addressed with well-established processing algorithms, but further benefits can be gained from DAS-specific algorithms. Where required, DAS seismic data can be processed to closely match the vector response of conventional geophones. DAS data converted in this way can assist in the up/down separation step without the need for dip filters. DAS VSP data can also be merged with conventional 3D and 4D seismic, adding value in situations such as undershooting of surface facilities in marine settings.
Downhole sand-ingress detection with fiber-optic distributed acoustic sensors
[J].
DOI:10.2118/1017-0099-JPT
URL
[本文引用: 1]

This article, written by JPT Technology Editor Chris Carpenter, contains highlights of paper SPE 183329, “Downhole Sand-Ingress Detection With Fiber-Optic Distributed Acoustic Sensors,” by Pradyumna Thiruvenkatanathan, Tommy Langnes, Paul Beaumont, Daniel White, and Michael Webster, BP, prepared for the 2016 Abu Dhabi International Petroleum Exhibition and Conference, Abu Dhabi, 7–10 November. The paper has not been peer reviewed.
High-fidelity distributed fiber-optic acoustic sensor with fading noise suppressed and sub-meter spatial resolution
[J].
DOI:10.1364/OE.26.016138
PMID:30119450
[本文引用: 1]

In order to solve fading problem and realize sub-meter spatial resolution in DAS, this paper proposes a novel configuration of time-gated digital optical frequency domain reflectometry (TGD-OFDR) based on optical intensity modulator (IM). IM has a large modulation bandwidth and the positive and negative harmonics can be fully used to suppress fading while the spatial resolution remains unchanged. In experiments, with fading suppressed, the spatial resolution of DAS is 0.8 m and the strain resolution is about 245.6 pε√Hz along the total 9.8-km sensing fiber. The response bandwidth of vibration is 5 kHz, only/limited by the fiber length.
Comparison of geophone and surface-deployed distributed acoustic sensing seismic data
[J].
分布式声传感井中地震信号检测数值模拟方法
[J].
Numerical simulation of detecting seismic signals in DAS wells
[J].
Surface orbital vibrator (SOV) and fiber-optic DAS:Field demonstration of economical,continuous-land seismic time-lapse monitoring from the Australian CO2CRC Otway site
[C]//
分布式光纤传感器原理及在地震监测中的应用研究现状
[J].
Principles and application research status of distributed optical fiber sensor
[J].
DFB fiber laser static strain sensor based on beat frequency interrogation with a reference fiber laser locked to a FBG resonator
[J].
DOI:10.1364/OE.24.012321
PMID:27410147
[本文引用: 1]

We report on a high-resolution static strain sensor developed with distributed feedback (DFB) fiber laser. A reference FBG resonator is used for temperature compensation. Locking another independent fiber laser to the resonator using the Pound-Drever-Hall technique results in a strain power spectral density better than S<sub>ε</sub>(f) = (4.6 × 10<sup>-21</sup>) ε<sup>2</sup>/Hz in the frequency range from 1 Hz to 1 kHz, corresponding to a minimum dynamic strain resolution of 67.8 pε/√Hz. This frequency stabilized fiber laser is proposed to interrogate the sensing DFB fiber laser by the beat frequency principle. As a reasonable DFB fiber laser setup is realized, a narrow beat frequency line-width of 3.23 kHz and a high beat frequency stability of 0.036 MHz in 15 minutes are obtained in the laboratory test, corresponding to a minimum static strain resolution of 270 pε. This is the first time that a sub-0.5 nε level for static strain measurement using DFB fiber laser is demonstrated.
Rockburst characteristics and microseismic monitoring of deep-buried tunnels for Jinping II Hydropower Station
[J].DOI:10.1016/j.tust.2015.04.016 URL [本文引用: 1]
光纤技术在地震勘探领域的应用
[J].由于光纤技术的不断发展及其在地震勘探领域的推广应用,光缆的种类也越来越多。为了使用者能在地震勘探中更好地了解和应用光缆,本文从光纤的结构、工作原理出发,全面介绍了在地震勘探领域当前各种仪器应用的光缆类型、使用方式以及在应用中的注意事项。
Application of optical fiber technology in seismic exploration
[J].With the developing of optical fiber technology and its popularization in seismic exploration,there are more and more types of fiber optic cable now.From the fiber structure and working principle,this paper made a comprehensive introduction to a variety of optical fiber cable types and patterns adopting for most used seismic instruments,and the matters needing attention in application.
Application of optical fiber sensing real-time monitoring technology using in Ripley landslide
[J].DOI:10.4028/www.scientific.net/AMM.610 URL [本文引用: 3]
光纤传感推动油藏地球物理技术智能创新发展
[J].
Optical sensing promotes intelligence,innovation and development of reservoir geophysical technology
[J].
艾白布·阿不力米提.DAS与DTS光纤测试技术在水平井中的应用
[J].
Abeib Abulmiti.Application of DAS and DTS optical fiber testing technology in horizontal wells
[J].
光纤布拉格光栅(FBG)和分布式声波传感器(DAS)在地学中的应用进展及发展方向
[J].
Recent advances in geoscience using Fiber Bragg Grating(FBG)and Distrusted Acoustic Sensing(DAS)and the road ahead
[J].
分布式光纤声波传感技术研究进展
[J].
Progress in research of distributed fiber acoustic sensing techniques
[J].
分布式光纤声波传感系统的研究与工程应用
[J].
Research and application of distributed optical fiber acoustic sensor system
[J].
分布式光纤声波传感系统在近地表成像中的应用Ⅰ:主动源高频面波
[J].
DOI:10.6038/cjg2020N0184
[本文引用: 1]

近年来发展的新型地震观测系统——分布式光纤声波传感器(DAS,Distributed Acoustic Sensing)可以实现低成本高密度观测,有望提高浅层结构成像的精度以及分辨率.最近国内研发了一系列具有自主知识产权的DAS设备,为验证国产设备在浅层结构研究中的可行性以及应用效果,2018年7月我们开展了一次DAS观测实验.实验采集了50 kg落锤震源激发的地震信号,并采用多道面波分析方法提取了8~20 Hz频段的主动源Rayleigh波相速度频散曲线,得到了实验区浅层30 m的S波速度结构.获得的主动源面波频散曲线与共址检波器的结果吻合,也与背景噪声提取的结果具有较好的一致性,表明国产设备的可靠性和DAS在浅层结构主动源面波成像研究中的可行性.
Distributed Acoustic Sensing for imaging shallow structureⅠ:Active source survey
[J].
分布式光纤声波传感系统在近地表成像中的应用Ⅱ:背景噪声成像
[J].
DOI:10.6038/cjg2020N0272
[本文引用: 1]

随着城市化的发展,城市地球物理日益成为地球物理研究的重要方向,地震成像是构建城市地下空间三维/四维图像的重要手段,但面临观测成本高的困难.近年来国际上新发展的分布式光纤声波传感器作为高密度地震观测系统已经在地震层析成像方面得到了应用,在提高成像分辨率的同时,又降低了观测成本.本研究使用国产分布式光纤声波传感器开展了观测实验,利用480 m埋地光缆记录了13 h背景噪声,计算得到噪声互相关函数,获得了高频Rayleigh面波信号.采用多道面波分析方法提取相速度频散曲线,其结果与传统检波器记录和主动源结果较为一致.采用遗传算法反演得到了研究区内二维S波速度剖面,获得了下方沉积物横向变化特征.通过本次实验,初步验证了国产设备开展地震背景噪声成像研究、构建地下浅层结构模型的可行性.
Distributed acoustic sensing for imaging shallow structure Ⅱ:Ambient noise tomography
[J].
基于MF-J变换的DAS观测高阶面波提取和浅地表结构成像
[J].
Shallow structure imaging using higher-mode Rayleigh waves based on F-J transform in DAS observation
[J].
光缆布设方式对DAS主、被动源记录的影响
[J].
The influence of cable installment on DAS active and passive source records
[J].
基于Simulink的分布式光纤声波传感系统仿真实验
[J].
Simulation experiment of distributed fiber acoustic sensing system based on Simulink
[J].
垂直地震剖面法
[J].
Vertical seismic profiling method
[J].
Simultaneous Multiwell VSP using Distributed Acoustic Sensing
[C]//
基于光纤分布式声波传感的井下多相流测试研究
[J].
Study on down-hole multiphase flow measurement system based on fiber distributed acoustic sense
[J].
High-resolution Carina distributed acoustic fibreoptic sensor for permanent reservoir monitoring and extending the reach into subsea fields
[J].
Distributed acoustic sensing for reservoir monitoring with VSP
[J].
DOI:10.1190/tle32101278.1
URL
[本文引用: 1]

3D VSP has long been viewed as conceptually attractive for illuminating targets under complex overburden, both for exploration purposes and for time-lapse monitoring of reservoirs. However, the widespread use of 3D VSP has been hindered by the cost and risk of deploying geophones in a borehole, and by the limited availability of accessible wells. These hurdles are largely removed when acquiring downhole seismic with a new measurement called distributed acoustic sensing (DAS).
DAS-VSP interferometric imaging:CO2CRC Otway Project feasibility study
[J].
Borehole seismic survey using multimode optical fibers in a hybrid wireline
[J].DOI:10.1016/j.measurement.2018.04.058 URL [本文引用: 3]
DAS-VSP采集技术在四川盆地的应用
[J].
Application of DAS-VSP acquisition to Sichuan Basin
[J].
DAS-VSP采集处理方法研究及应用
[J].
DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1000-1441.2022.01.011
[本文引用: 1]

分布式光纤声波传感技术(DAS)是通过解调光信号背向瑞利散射相位变化表征地震信号的一种新型信号采集技术,其在井中采集具有一次性覆盖全井段和测量高密度的特点,施工效率和数据的一致性大幅提高,因此受到广泛关注。以光纤在井中地震的实际应用为例,讨论了影响DAS采集资料信噪比和分辨率的光信号解调因素和采集因素,提出了一种在无检波器定位情况下校正DAS深度位置的解决思路,利用时间方向求导和反演耦合干扰减去法提高了DAS-VSP采集资料的上行波信噪比和全波场高频成分。基于预处理后的高密度DAS-VSP数据,提取了层速度、各向异性参数用于深度域井控各向异性偏移,通过井控各向异性叠前深度偏移,使偏移成像频带拓宽约20Hz,主要目的层井震误差小于0.15%,展现了高密度DAS数据在井中地震中良好的应用前景。
Research and application of the DAS-VSP acquisition and processing method
[J].
DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1000-1441.2022.01.011
[本文引用: 1]

<p>Distributed optical-fiber acoustic sensing (DAS) is a new type of acquisition technology that uses backward Rayleigh scattering to demodulate the phase change of optical signals to characterize seismic signals.DAS is characterized by logging-scale density;as such,a single VSP acquisition can cover the entire distance from the surface wellhead to the end of the deployed fiber in the well.Because of its advantages,DAS has received widespread attention,leading to great improvements in construction efficiency and data consistency.In this work,a case in which DAS was applied for borehole acquisition is presented.The optical signal demodulation and acquisition factors that affect the SNR and resolution of the DAS data are discussed,and a method to calibrate DAS-VSP data without simultaneous geophone acquisition is developed.The SNR of the upward wave and the high frequency part of the full wave field can be improved by subtracting the inverse DAS coupling noises and estimating the time derivative.From the pre-processed high-density DAS-VSP data,the layer velocity and anisotropy parameters are extracted and used for well-controlled pre-stack anisotropic depth migration,which has broadened the frequency band by approximately 20Hz,and resulted in a borehole seismic error of the main target layer of less than 0.15%.These results show that high density DAS has good application prospects in borehole seismic studies. </p>
Denoising and wavefield separation method for DAS VSP via deep learning
[J].DOI:10.1016/j.jappgeo.2023.104946 URL [本文引用: 1]
DAS技术在油气地球物理中的应用综述
[J].
Application review of DAS technology in oil and gas geophysics
[J].
Distributed acoustic sensing:A new way of listening to your well/reservoir
[C]//
Fiber optic sensing for improved wellbore production surveillance
[C]//
Distributed acoustic sensing for downhole production and injection profiling
[J].
Fluid production profile monitoring of marine shale reservoir using fiber sensing within the coiled tubing
[C]//
油气井分布式光纤生产监测技术研究
[C]//
Research on distributed fiber optic production monitoring technology for oil and gas wells
[C]//
DAS井地联合勘探实例分析——以长庆油田环县三维井地联采为例
[J].
DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1000-1441.2022.01.012
[本文引用: 1]

光纤分布式声波传感(DAS)技术因其耐高温高压和高密度全井段采集等技术优势使得井地联合勘探技术更加高效,在井驱参数提取及井旁成像等方面具有广泛的应用前景,但目前该技术面临记录数据的信噪比偏低、单分量数据波场分离困难、地面激发点稀疏造成照明不均匀和成像质量欠佳等技术难题。为此,系统分析了长庆油田珠60井的套管外DAS-VSP井地联采数据的采集质量及对处理结果的影响、DAS单分量波场特征及反射波分离、井驱参数提取、井地联合多次波分析、3D-VSP成像的技术优势和不足等,形成了高效初至拾取及井驱参数提取、单分量保真波场分离、扩展面元VSP CDP成像等一系列技术成果,提出了下一步的研究重点是将高密度优势转化为高信噪比,进一步提高波场分离保真度,并在处理中尽可能克服激发点稀疏的影响,以实现3D-VSP的精确成像,最终实现井地联合成像,这些结果对于今后的DAS井地联合勘探具有非常积极的指导意义。
DAS joint VSP and 3D surface seismic:A case study on HX3D in the Changqing oilfield
[J].
DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1000-1441.2022.01.012
[本文引用: 1]

Optical fiber distributed acoustic sensing (DAS) technology makes downhole-surface joint exploration more efficient because of its high temperature,high pressure resistance,and high-density whole-wellbore acquisition.It has been widely used in well-driven parameter estimation and near-well imaging,but it currently faces technical problems such as low signal-to-noise ratio,difficult wavefield separation due to one-component (1C) data,inhomogeneous illumination,and unsatisfactory imaging caused by sparse shot points.In this study,many issues were investigated,such as the acquisition quality and its influence on the processing of DAS VSP data with cemented fiber,separation of DAS 1C wavefield,well-driven parameter extraction,multiple reflection analysis,and technical advantages and weakness of 3D-VSP imaging.A series of technical achievements were presented,such as efficient first break picking,refined well-driven parameter extraction,high-fidelity 1C wavefield separation,and extended bin VSPCDP imaging.It has been pointed out that the emphases would achieve high S/N data from high-density raw data,further improving the wavefield separation fidelity,and overcoming the effect of shot point sparsity as much as possible in the processing,realizing 3D-VSP precision imaging,and finally achieving joint borehole and surface imaging.This understanding has very positive guidance for DAS joint VSP and surface seismic exploration in the future.
分布式光纤声波传感系统在西部已开发气田井下断层活动性监测中的试验研究与应用
[J].
Fault stability analysis and evaluation by long-term micro-seismic monitoring with distributed optical fiber acoustic sensing system in a gas field West China
[J].
用于石油物探的分布式光纤声波地震检波器
[J].
Distributed fiber-optic acoustic seismic geophone for petroleum geology exploration
[J].
Full distributed fiber optical sensor for intrusion detection in application to buried pipelines
[J].
油气管道安全分布式光纤预警系统研究
[J].
Study on the distributed optical fiber pre-warning system for the safety of oil and gas pipeline
[J].
OTDR型分布式光纤传感器在油气管道监测中的应用
[J].
OTDR-type distributed optical fiber sensors and application of oil and gas pipelines online monitoring
[J].
Detection of leak-induced pipeline vibrations using fiber-optic distributed acoustic sensing
[J].
DOI:10.3390/s18092841
URL
[本文引用: 1]

In the presented work, the potential of fiber-optic distributed acoustic sensing (DAS) for detection of small gas pipeline leaks (<1%) is investigated. Helical wrapping of the sensing fiber directly around the pipeline is used to increase the system sensitivity for detection of weak leak-induced vibrations. DAS measurements are supplemented with reference accelerometer data to facilitate analysis and interpretation of recorded vibration signals. The results reveal that a DAS system using direct fiber application approach is capable of detecting pipeline natural vibrations excited by the broadband noise generated by the leaking medium. In the performed experiment, pipeline vibration modes with acceleration magnitudes down to single μg were detected. Simple leak detection approach based on spectral integration of time-averaged DAS signals in frequency domain was proposed. Potential benefits and limitations of the presented monitoring approach were discussed with respect to its practical applicability. We demonstrated that the approached is potentially capable of detection and localization of gas pipeline leaks with leak rates down to 0.1% of the pipeline flow volume and might be of interest for monitoring of short- and medium-length gas pipelines.
Distributed fiber sensor and machine learning data analytics for pipeline protection against extrinsic intrusions and intrinsic corrosions
[J].
DOI:10.1364/OE.397509
PMID:32988024
[本文引用: 2]

This paper presents an integrated technical framework to protect pipelines against both malicious intrusions and piping degradation using a distributed fiber sensing technology and artificial intelligence. A distributed acoustic sensing (DAS) system based on phase-sensitive optical time-domain reflectometry (φ-OTDR) was used to detect acoustic wave propagation and scattering along pipeline structures consisting of straight piping and sharp bend elbow. Signal to noise ratio of the DAS system was enhanced by femtosecond induced artificial Rayleigh scattering centers. Data harnessed by the DAS system were analyzed by neural network-based machine learning algorithms. The system identified with over 85% accuracy in various external impact events, and over 94% accuracy for defect identification through supervised learning and 71% accuracy through unsupervised learning.
Lateral positioning of vibration source for underground pipeline monitoring based on ultra-weak fiber Bragg grating sensing array
[J].DOI:10.1016/j.measurement.2020.108892 URL [本文引用: 1]
Nonintrusive distributed flow rate sensing system based on flow-induced vibrations detection
[J].
分布式光纤声波传感的管道泄漏监测指标分析
[J].
Analysis of pipeline leakage monitoring index based on distributed optical fiber acoustic sensing system
[J].
基于分布式光纤声波传感的管道泄漏监测
[J].
Monitoring pipeline leakage using fiber-optic distributed acoustic sensor
[J].
集输管道分布式光纤声波泄漏监测系统的设计与试验
[J].
Design and experimental study of distributed optical fiber acoustic leakage detection system for gathering and transportation pipeline
[J].
基于分布式光纤声波传感技术的管道侵入识别与定位
[J].
Detection and localization of pipeline intrusion with distributed optical fiber acoustic sensing technology
[J].
Experimental study on distributed optical fiber sensing monitoring for ground surface deformation in extra-thick coal seam mining under ultra-thick conglomerate
[J].DOI:10.1016/j.yofte.2019.102006 URL [本文引用: 1]
分布式光纤声波地震波勘探技术
[J].
DOI:10.3976/j.issn.1002-4026.2021.04.001
[本文引用: 1]

随着常规和易采油气资源日渐减少,勘探开发复杂地质油气资源,对降低我国油气对外依存度,保障国家能源安全发挥着越来越重要的作用。复杂地质油气藏具有储层更薄、更深,非均质性更强等特性,现有地震波检测技术难以实现有效勘探。设计了一种用于油气地震波勘探开发的分布式光纤声波监测系统,使用光缆作为传感器来检测声音信号,采用基于背向瑞利散射的相位调制解调技术,实现了10 m的空间分辨率、-145.35 dB的声压灵敏度的测试,并进行了地震弹炮实地勘探,完成了地震波信号采集处理,获得了清晰的地层反演信息。
Distributed optical fiber acoustic seismic wave exploration technology
[J].
Deep neural networks for detection and location of microseismic events and velocity model inversion from microseismic data acquired by distributed acoustic sensing array
[J].
DOI:10.3390/s21196627
URL
[本文引用: 3]

Fiber-optic cables have recently gained popularity for use as Distributed Acoustic Sensing (DAS) arrays for borehole microseismic monitoring due to their physical robustness as well as high spatial and temporal resolutions. As a result, the sensors record large amounts of data, making it very difficult to process in real-/semi-real-time using the conventional processing routines. We present a novel approach, based on deep learning, for handling the large amounts of DAS data in real-/semi-real-time. The proposed neural network was trained on synthetic microseismic data contaminated with real-ambient noise from field data and was validated using field DAS microseismic data obtained from a hydraulic fracturing operation. The results indicate that the trained network is capable of detecting and locating microseismic events from DAS data and simultaneously update the velocity model to a high degree of precision. The mean absolute errors in the event locations and the velocity model parameters are 2.04, 0.72, 2.76, 4.19 and 0.97 percent for distance (x), depth (z), P-wave velocity, S-wave velocity and density, respectively. In addition to automation and computational efficiency, deep learning reduces human expert data handling during processing, thus preserving data integrity leading to more accurate and reproducible results.
基于应变率的分布式光纤声波传感全波形反演研究
[J].
Study of distributed acoustic sensing data waveform inversion based on strain rate
[J].
海洋地球物理综合探测法在海底管线探测的应用研究
[J].
Study on the application of marine geophysical comprehensive detection method in submarine pipeline detection
[J].
海洋地球物理探测技术及其在近海工程中的应用
[J].
Marine geophysical survey techniques and their applications to offshore engineering
[J].
海底管道分布式光纤传感器安装工艺研究
[J].
Research on installation technology of distributed fiber optic sensor in submarine pipeline
[J].
Detection of hydroacoustic signals on a fiber-optic submarine cable
[J].
DOI:10.1038/s41598-021-82093-8
PMID:33531541
[本文引用: 3]

A ship-based seismic survey was conducted close to a fiber-optic submarine cable, and 50 km-long distributed acoustic sensing (DAS) recordings with air-gun shots were obtained for the first time. We examine the acquired DAS dataset together with the co-located hydrophones to investigate the detection capability of underwater acoustic (hydroacoustic) signals. Here, we show the hydroacoustic signals identified by the DAS measurement characterizing in frequency-time space. The DAS measurement can be sensitive for hydroacoustic signals in a frequency range from [Formula: see text] to a few tens of Hz which is similar to the hydrophones. The observed phases of hydroacoustic signals are coherent within a few kilometers along the submarine cable, suggesting the DAS is suitable for applying correlation analysis using hydroacoustic signals. Although our study suggests that virtual sensor's self-noise of the present DAS measurement is relatively high compared to the conventional in-situ hydroacoustic sensors above a few Hz, the DAS identifies the ocean microseismic background noise along the entire submarine cable except for some cable sections de-coupled from the seafloor.
海底电缆运行状态监测技术研究
[J].
Research on monitoring technology of submarine cable operation state
[J].
基于分布式光纤声波传感的海洋环境噪声监测技术
[J].
Marine environmental noise monitoring technology based on distributed optical fiber acoustic sensing
[J].
基于分布式光纤传感的海底管线横向屈曲识别方法
[J].
Recognition method of lateral buckling of submarine pipeline based on distributed optical fiber sensing
[J].
Earthquake emergency response framework on campus based on multi-source data monitoring
[J].DOI:10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.117965 URL [本文引用: 1]
A study of the geophysical response of distributed fibre optic acoustic sensors through laboratory-scale experiments
[J].DOI:10.1111/gpr.2017.65.issue-5 URL [本文引用: 1]
Seismic observation and subsurface imaging using an urban telecommunication optic-fiber cable
[J].
Distributed acoustic sensing (DAS) for natural microseismicity studies:A case study from Antarctica
[J].
Distributed acoustic sensing using dark fiber for array detection of regional earthquakes
[J].
DOI:10.1785/0220200416
URL
[本文引用: 1]

The intrinsic array nature of distributed acoustic sensing (DAS) makes it suitable for applying beamforming techniques commonly used in traditional seismometer arrays for enhancing weak and coherent seismic phases from distant seismic events. We test the capacity of a dark-fiber DAS array in the Sacramento basin, northern California, to detect small earthquakes at The Geysers geothermal field, at a distance of ∼100 km from the DAS array, using beamforming. We use a slowness range appropriate for ∼0.5–1.0 Hz surface waves that are well recorded by the DAS array. To take advantage of the large aperture, we divide the ∼20 km DAS cable into eight subarrays of aperture ∼1.5–2.0 km each, and apply beamforming independently to each subarray using phase-weighted stacking. The presence of subarrays of different orientations provides some sensitivity to back azimuth. We apply a short-term average/long-term average detector to the beam at each subarray. Simultaneous detections over multiple subarrays, evaluated using a voting scheme, are inferred to be caused by the same earthquake, whereas false detections caused by anthropogenic noise are expected to be localized to one or two subarrays. Analyzing 45 days of continuous DAS data, we were able to detect all earthquakes with M≥2.4, while missing most of the smaller magnitude earthquakes, with no false detections due to seismic noise. In comparison, a single broadband seismometer co-located with the DAS array was unable to detect any earthquake of M&lt;2.4, many of which were detected successfully by the DAS array. The seismometer also experienced a large number of false detections caused by spatially localized noise. We demonstrate that DAS has significant potential for local and regional detection of small seismic events using beamforming. The ubiquitous presence of dark fiber provides opportunities to extend remote earthquake monitoring to sparsely instrumented and urban areas.
ADE-net:A deep neural network for DAS earthquake detection trained with a limited number of positive samples
[J].
Fiber optic train monitoring with distributed acoustic sensing:Conventional and neural network data analysis
[J].
DOI:10.3390/s20020450
URL
[本文引用: 1]

Distributed acoustic sensing (DAS) over tens of kilometers of fiber optic cables is well-suited for monitoring extended railway infrastructures. As DAS produces large, noisy datasets, it is important to optimize algorithms for precise tracking of train position, speed, and the number of train cars. The purpose of this study is to compare different data analysis strategies and the resulting parameter uncertainties. We present data of an ICE 4 train of the Deutsche Bahn AG, which was recorded with a commercial DAS system. We localize the train signal in the data either along the temporal or spatial direction, and a similar velocity standard deviation of less than 5 km/h for a train moving at 160 km/h is found for both analysis methods. The data can be further enhanced by peak finding as well as faster and more flexible neural network algorithms. Then, individual noise peaks due to bogie clusters become visible and individual train cars can be counted. From the time between bogie signals, the velocity can also be determined with a lower standard deviation of 0.8 km/h. The analysis methods presented here will help to establish routines for near real-time train tracking and train integrity analysis.
Real-time train tracking from distributed acoustic sensing data
[J].
DOI:10.3390/app10020448
URL
[本文引用: 1]

In the context of railway safety, it is crucial to know the positions of all trains moving along the infrastructure. In this contribution, we present an algorithm that extracts the positions of moving trains for a given point in time from Distributed Acoustic Sensing (DAS) signals. These signals are obtained by injecting light pulses into an optical fiber close to the railway tracks and measuring the Rayleigh backscatter. We show that the vibrations of moving objects can be identified and tracked in real-time yielding train positions every second. To speed up the algorithm, we describe how the calculations can partly be based on graphical processing units. The tracking quality is assessed by counting the inaccurate and lost train tracks for two different types of cable installations.
Research on application of deep convolutional network in high-speed railway track inspection based on distributed fiber acoustic sensing
[J].DOI:10.1016/j.optcom.2021.126981 URL [本文引用: 1]
用于铁路基础设施综合监测的分布式光纤传感器
[J].
Distributed fiber optic sensors for comprehensive monitoring of railway infrastructure
[J].
Interferometric interpolation of missing seismic data
[C]//
Interferometry by deconvolution:Part 1—Theory for acoustic waves and numerical examples
[J].
Space and Time Spectra of Stationary Stochastic Waves,with Special Reference to Microtremors
[J].
分布式光纤声波传感系统记录的交通噪声的干涉处理分析
[J].
DOI:10.6038/cjg2021O0513
[本文引用: 1]

分布式光纤声波传感系统(DAS)是近年来迅速发展的高密度、低成本的地震观测设备,已经在基于面波的速度层析反演、反射成像、微地震监测等多个领域显示巨大潜力.本文基于美国加利福尼亚州Garner Valley实验中DAS记录的交通噪声数据,分析交通噪声数据特点,并利用地震干涉方法从交通噪声记录提取出近地表传播的面波信息.结果显示,利用记录时长6 s的DAS记录的车辆噪声数据,可以提取与主动源数据信号信噪比略高、特征一致的面波记录.同时,分析比较了互相关干涉、反褶积干涉和互相干干涉三种方法.结果显示三种方法均能从Garner Valley实验中DAS系统记录的公路噪声中有效提取面波信息,其中的互相干干涉和互相关干涉结果具有较高的高信噪比,互相干干涉和反褶积干涉结果有更优的频带宽度.
Seismic interferometry for traffic noise recorded by a distributed acoustic sensing system
[J].
基于分布式光纤的沥青道面振动状态感知技术
[J].
Vibration monitoring of asphalt runway using distributed optical fiber sensor
[J].
分布式光纤声波传感技术在PCCP管道监测中的应用
[J].
Application of distributed optical fiber acoustic wave sensing technology in PCCP pipeline monitoring
[J].
基于分布式光纤传感技术的边坡岩土体变形智能监测
[J].
Intelligent monitoring of slope rock and soil deformation based on distributed optical fiber sensing technology
[J].
基于新型分布式传感器的桥梁监测技术研究
[C]//
Research on bridge monitoring technology based on new distributed sensor
[C]//
光纤地球物理技术的发展现状与展望
[J].
DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1000-1441.2022.01.002
[本文引用: 1]

近年来,光纤传感技术已经应用于地面地震数据、海洋地震数据、井中地震数据和井地联合地震数据的采集,推动了光纤传感技术在地球物理特别是地震数据采集领域的应用。对国内外应用于陆地、海洋和井中的光纤地震数据采集系统进行了简要介绍,重点关注了分布式光纤声波传感(DAS)技术在井中地震数据和井地联合地震数据的采集、处理和综合解释中的应用。光纤传感技术是一项革命性的新技术,光纤因体积小、不带电、分布式、高密度、多参量、耐高温、高压、全段接收和低成本等特征,必将带来井下、海洋和陆地地球物理技术的一场革命。井中分布式光纤声波传感技术已广泛应用于井中VSP数据采集、水力压裂微地震监测和精准工程监测,可实现油气井全生命周期监测、管理和使用。分布式光纤传感技术在油气资源勘探开发领域的规模化推广应用,已经从井中延伸到陆地和海洋;从井下单分量测量拓展到井下和陆地三分量测量(螺旋形绕制的铠装光缆);从单井单参数测量发展到了多井多参数同步测量,调制解调仪器也从单通道单参数发展到了多通道多参数复合调制解调系统。光纤传感技术应用已经由地震勘探领域延伸至油气藏开发领域,围绕光纤应用的地球物理技术对地下结构的静态刻画和动态永久监测逐步形成光纤油藏地球物理技术的基础。展望未来,分布式三分量光纤声波传感技术将在井中、陆地(沙漠)和海洋中用来替代常规三分量检波器采集高密度全波场三分量地震数据,可实现陆地、海洋和井下的高效率、低成本、高密度三分量地震数据采集。此外,研制开发集分布式光纤声波、温度、应变传感于一体的多分量、多参数、多通道复合调制解调仪器;开展耐高温、高瑞利散射系数、抗氢损和弯曲不敏感特种光纤的研制与批量生产;三分量分布式光纤声波(地震波)传感数据采集系统的研制;高密度分布式三分量光纤地震数据处理软件的开发;井地三分量联采地震数据的联合偏移成像方法研究;套管外铠装光缆定位定向技术与设备研发和与之配套的定向射孔光缆避射技术的发展;人工智能技术在光纤传感领域的推广应用等,必将推动光纤地球物理技术的创新性发展,实现对整个油气田储层的光纤智能油藏感知、描述、模拟和监测,智能优化开发方案和生产制度,在未来智慧油气田的建设中发挥重要的技术支撑作用。
Optical fiber geophysics:Development status and future prospects
[J].
DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1000-1441.2022.01.002
[本文引用: 1]

In recent years,optical fiber sensing systems have been applied to the acquisition of land 3C seismic,marine 4C seismic,borehole seismic,and borehole-surface joint seismic data,which has promoted the application of optical fiber sensing techniques in geophysics,especially in the field of seismic data acquisition.This paper briefly introduces optical fiber seismic data acquisition systems applied in land,marine,and boreholes around the world,and focuses on the application of the distributed acoustic sensing (DAS) technique in the acquisition,processing,and comprehensive interpretation of borehole seismic data and borehole-surface jointly acquired seismic data.Optical fiber sensing is a novel and revolutionary technique.Because of their small size,non-electrical nature,distribution,high density,multi-parameter nature,high-temperature and high-pressure resistance,full cable sensing capability,and low cost,optical fibers will bring a revolution in borehole,marine,and terrestrial geophysical data acquisition.The downhole distributed acoustic sensing (DAS) technique has been widely used in VSP data acquisition,hydraulic fracturing microseismic monitoring,and precision engineering monitoring.It can thus achieve the entire life cycle monitoring,management,and use of oil and gas wells.The large-scale application of distributed optical fiber sensing techniques in the exploration and development of oil and gas resources has extended from well to land and marine environments,from downhole 1C measurements to downhole and terrestrial 3C measurements,and from single well single parameter measurements to multi-well multi-parameter simultaneous measurements.The capability of the demodulation instrument also has been enhanced,from a single channel and single parameter system to multi-channel and multi-parameter composite demodulation systems.The application of optical fiber sensing techniques has extended from the field of seismic exploration to oil and gas reservoir development and production.The static characterization and dynamic permanent monitoring of subsurface structures based on optical fiber application gradually form the basis of optical fiber reservoir geophysical technology.In the future,the distributed three-component optical fiber acoustic sensing technology will be used to replace the conventional three-component geophone to collect high-density full-wave field three-component seismic data in the well,land (desert),and sea,which can realize high-efficiency,low-cost,and high-density three-component seismic data acquisition on land,sea,and underground.In addition,a multi-component,multi parameter and multi-channel composite modulation and demodulation instrument integrating distributed optical fiber acoustic wave,temperature,and strain sensing needs to be developed.Future directions of research include the development and mass production of special optical fibers with high temperature resistance,high Rayleigh scattering coefficient,hydrogen loss resistance and bending insensitiveness;the development of a three component distributed optical fiber acoustic wave (seismic wave) sensing data acquisition system;the development of a high-density distributed three component optical fiber seismic data processing software;research on a joint migration imaging method of well ground three component combined mining seismic data;research and development of a positioning and orientation technology,as well as development of an armored optical cable outside the casing and a supporting directional perforation optical cable anti shooting technology.In addition,with vigorous promotion and application of artificial intelligence technology in the field of optical fiber sensing,all the developments will promote the implementation of the optical fiber geophysical technology,which will achieve the optical fiber-based intelligent reservoir sensing,description,simulation and monitoring of the whole oil and gas field reservoir.Finally,these developments will lead to an intelligent optimization of development schemes and production systems,and will play an important technical support role in the construction of smart oil and gas fields in the future.
我国碳捕获、利用与封存(CCUS)技术的发展现状与展望
[J].
Development status and prospect of carbon capture,utilization and storage(CCUS) technology in China
[J].