0 引言
华南火成岩发育区有着陆缘地带的复杂构造格局和活动状态,其中地热资源丰富,近地表主要以中低温和中温水热存储,深层富含高温、高压的地热储层,是地热勘探的有利探区[1⇓⇓-4]。对于深层地热勘探,研究地热储层的结构、边界和空间展布至关重要。大量证据表明,在地温梯度高、温度高的地区存在近垂直深断裂[5],即地热储层常伴有断裂发育。然而,具有高陡构造形态的伴生断裂热储刻画难度较大,常规重、磁、电等勘探方法难以取得较为理想的效果。相比较而言,地震勘探具有更高的成像分辨率,可以实现深层热储精细刻画。尽管三维地震勘探采集成本较高,但部分探区已开展油气勘探,可以利用其采集的三维地震资料进行高精度成像,实现深层热储的精细刻画。相比于油气勘探,地热勘探更加注重对热储分布及边界的刻画,两者处理目标和处理方式差异较大。针对深层火成岩热储实际地质条件,目前在地震资料处理方面,应该从保低频去噪、精细化速度建模、高精度成像3方面进行关键技术研发及应用,建立具有识别深层地热构造的流程,为后续地热储层的精细刻画提供高品质数据。
首先,保低频去噪是深层热储精确成像的数据基础。目前,地震资料去噪领域出现了诸多新技术、新方法,Saad等[6]基于自编码器原理,提出了一种基于深度自编码器(DDAE)的智能化去噪方法,在随机噪声压制方面效果突出,能保护有效信号频带不受损失。Shan等[7]根据Unet网络学习传统去噪方法,通过训练后的网络模型实现地震资料有效去噪,一定程度上解决了传统智能化算法泛化性的问题。石战战等[8]提出了一种在F-X域利用低秩矩阵近似的算法对共偏移距道集进行去噪,可以实现非平稳信号的去噪处理,并同时保持低频有效信号。崔亚彤等[9]提出了一种快速自适应的非局部均值滤波技术,通过自适应算法有效区分噪声与有效信号,采用非局部的均值滤波压制低频噪声。在实用化应用方面,杜耀斌等[10]将多域去噪的方式成功应用于塔里木盆地深层探区,有效压制了低频噪声,提高了深层目的层构造成像的精度。徐颖等[11]针对塔中奥陶系低信噪比的问题,利用“六分法”的多域组合去噪技术思路与处理流程实现了碳酸盐岩储层的保低频噪声压制,相比于常规处理流程,更加注重对低频信号的保护,使深层小尺度异常体清晰度明显提升。王立歆等[12]根据超深层碳酸盐岩断控缝洞体的特点,提出了一种保低频的弱信号恢复技术,有效恢复深层能量,为高精度成像提供了基础数据。相比于油气勘探,深层地热勘探更注重对大中尺度构造的精细刻画,因此针对深层热储成像,如何在去噪过程中保护低频有效信号、压制低频噪声是关键。
另外,精细化速度模型是深层热储成像的核心。层析反演是目前深度域速度建模中常用的方法,该方法通常利用走时信息,沿波传播路径进行速度反演,将成像空间映射到模型空间[13],得到地下层速度。目前,基于射线理论的层析反演方法已经较为成熟,并在地热勘探中进行了试验,有效提高了热储结构的识别能力[14-15]。然而,传统的层析反演只能得到低波数分量,不能很好地反演得到深层热储结构特征及伴生断裂的速度。为了解决该问题,提高深层复杂构造的反演精度,通常会采用模型正则化方法进行先验信息约束。张在金等[16]提出了一种井控与构造约束条件下的网格层析速度建模技术,对断层两侧的速度进行了准确刻画。郑浩等[17-18]针对复杂构造及断裂建模难题,分别提出了基于构造导向滤波及断裂属性约束的层析速度建模技术,有效提升了速度反演的分辨率,得到了更符合地质认识的高精度速度模型,改善了成像质量。对于深层热储边界、高陡构造及复杂断裂,常规层析速度建模方法难以满足精度要求,应当采用模型正则化技术,形成一套考虑结构特征及伴生断裂的构造约束速度建模技术流程,实现深层热储边界及内幕的精细速度反演。
最后,高效的高精度成像方法是关键。对于深层热储边界、基底及复杂断裂系统,逆时偏移技术(RTM)具有较为明显的理论优势,该方法对于高陡构造成像效果较好,但作为双程波波动方程偏移,计算量及存储量较大,规模化应用较难。针对该问题,刘守伟等[19]研发了可以应用于GPU集群的最佳匹配层边界条件逆时偏移技术。张慧宇等[20]针对海量地震数据,研发了基于GPU集群的大规模分布式逆时偏移技术,能够应用于高密度采集的地震三维数据成像,推进了该技术的实用化进程。刘立民等[21]根据起伏地表复杂构造成像中逆时偏移存在的问题,将有限元正演技术应用于逆时偏移中,进一步改善了复杂构造区逆时偏移的应用效果。目前,随着高性能硬件及并行算法的不断发展,高效RTM技术较为成熟,借助GPU加速算法,已基本实现规模化生产应用。对于华南火成岩深层热储高精度成像,应采用该算法实现高精度成像,改善热储边界及伴生断裂的成像效果。
针对上述华南火成岩深层地热地震资料处理三大关键问题,本文提出了以保低频多方法联合去噪、断控层析速度建模及高效解析波场逆时偏移技术组合的解决方案,形成了一套面向复杂岩性和构造条件下的深层地热地震资料处理技术流程。实际资料测试表明,该技术流程能够有效提升深层热储边界、基底和复杂断裂系统的成像精度,为后续地热开发有利目标优选和井位部署提供可靠的数据基础。
1 深层地热地震预处理关键技术
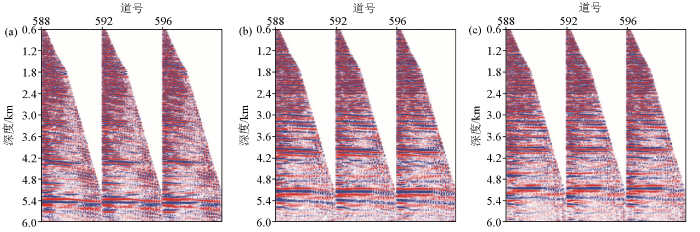
图1
图1
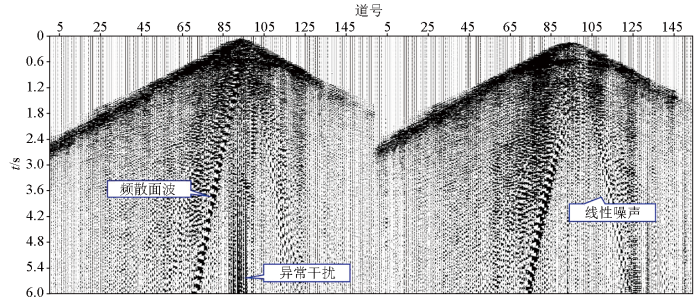
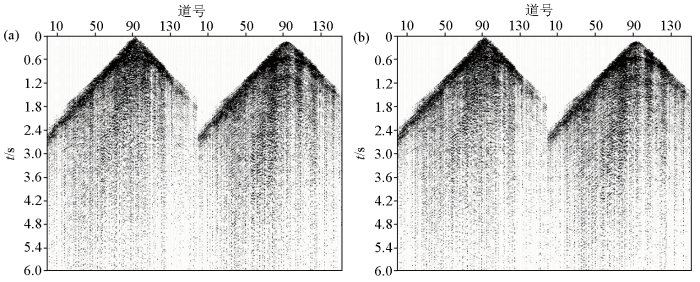
华南火成岩地区多类型噪声发育
Fig.1
Kinds of noises exist in seismic data of Southern China
图2
1.1 自适应频散面波压制技术
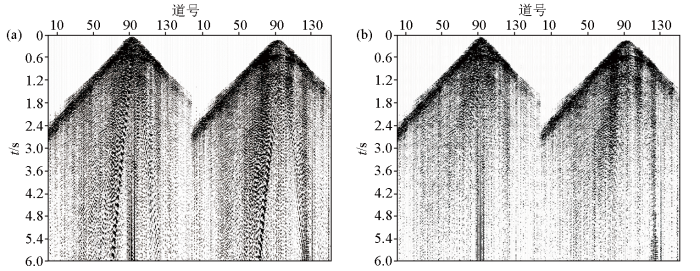
频散面波介于相干噪声与非相干噪声之间,能量强、频率低,且深度越深,影响范围越大,通常以扫把状形态分布于近偏移距。在频散面波压制方面,本文采用自适应频散面波压制技术,通过迭代计算的方式调整褶积因子,修改频散面波模型,使之接近真实面波,最后通过自适应相减的方式从单炮记录中减去模拟的频散面波,达到面波压制的效果。基于华南火成岩高精度数据,建立200 m×200 m的空间频散曲线场计算频散面波模型,通过自适应相减去除频散面波,去噪效果如图3所示,可以看出,该技术能够有效压制频散面波,同时最大限度地保护有效信号不受损失。相比于常规FK滤波方法,该方法对低频信号具有更好的保护作用,有利于深层热储基底高陡构造的精确成像。
图3
图3
频散面波压制前(a)与压制后(b)效果对比
Fig.3
Comparison of surface wave noise before(a) and after(b) suppression
1.2 异常振幅噪声压制技术
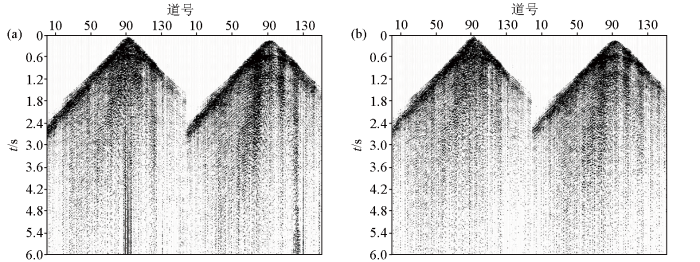
面波压制后,单炮记录中还存在有异常道、野值干扰等非相干噪声,对地震成像影响较大。根据不同数据域中有效信号与噪声的差异,本文采用频率域噪声压制技术分别将数据分选到炮域、检波点域及CMP域进行异常振幅去噪,有效压制非相干噪声,从而进一步提升去噪效果。该技术的关键是选取合理的时窗确定压噪阈值,从而保护有效信号,去除异常振幅类的非相干噪声,这里选取处理时窗为1 000 ms,门槛值为15,去噪效果如图4所示。显然,通过该技术处理后,异常振幅得到有效压制,信噪比显著提升。
图4
图4
异常振幅噪声压制前(a)与压制后(b)效果对比
Fig.4
Comparison of abnormal amplitude noise before(a) and after(b) suppression
1.3 非规则相干噪声压制技术
在进行面波、非相干噪声压制后,还会存在部分非均匀线性干扰,这里采用非均匀线性噪声压制技术进一步提高数据的信噪比,改善数据品质。该技术基于不规则的炮点/检波点采集数据驱动,设计抗假频F-X滤波器获取地震道对应的线性噪声模型,通过匹配相减从叠前记录中去除噪声,分频压制线性噪声。根据原始资料分析,这里选取的两组线性干扰速度区间分别为100~600 m/s及500~1 000 m/s,滤波频率为25 Hz,有效信号保护的速度区间为1 600~2 000 m/s,去噪效果如图5所示。可以看出,该技术能有效压制残余的部分非均匀线性噪声,进一步改善了叠前数据品质,为后续深层热储成像提供了高品质数据。
图5
图5
非规则相干噪声压制前(a)与压制后(b)效果对比
Fig.5
Comparison of irregular coherent noise before(a) and after(b) suppression
1.4 叠前五维规则化技术
地震采集受地形和地表因素影响,炮点和检波点变观严重,数据在空间上不规则,容易产生空间假频等现象。对数据进行五维规则化处理后,不规则观测系统的炮检点归位到理论设计点位,能够有效防止空间假频现象,进一步提升数据信噪比。叠前五维规则化技术基于防假频傅里叶变换,在线域、点域、时间域、炮检距域、方位角域五维空间进行插值,通过对每一个频率依据最小视速度确定出重构数据的带宽,然后从不规则地震数据的空间傅里叶系数中估计出重构数据的空间傅里叶系数,将估计的傅里叶系数进行非规则傅里叶反变换,重构出目标观测系统地震数据,达到规则化目的。该技术适用于深层热储复杂陡倾角数据,能够有效改善假频问题,解决变观引起的数据缺失,改善地震数据叠加及成像质量。在处理华南火成岩地震资料时,通过参数优选测试,最终确定时间方向插值时窗为100 ms,主测线和联络线方向插值时窗均为12 m,偏移距插值时窗为1 000 m,方位角插值时窗为180°。图6a、b分别为叠前五维规则化处理前后的叠加效果对比,可以看出,经过五维规则化处理后,信噪比进一步提升,高陡构造刻画更加清晰,叠加质量明显改善。
图6
图6
叠前五维规则化前(a)、后(b)效果对比
Fig.6
Comparison of matching pursuit Fourier interpolation before(a) and after(b) application
2 断控层析速度建模技术
针对华南火成岩局部高速异常及深层热储基底、断裂体速度建模难题,本文采用了断控层析速度建模技术,有效改善火成岩速度异常、热储基底及复杂断裂带的速度反演精度。
通常,深度域高斯束层析目标函数可以表示为:
式中:
首先,为进一步提高局部火成岩的反演精度,本文引入了不等式层析正则化技术,利用测井速度及地震相分布得到区域速度范围界限,实现对火山岩速度异常体的速度范围“软约束”,提高了局部火成岩速度建模精度:
式中:
该项通过压缩反演零空间,实现更加精细的速度约束反演。
在此基础上,为进一步提高深层热储边界、复杂断裂等高陡构造的速度建模精度,这里引入断控算子进行先验信息约束,那么目标函数可以表示为
式中:F表示断控正则化算子,该算子通过引入断裂、基底边界等构造信息实现模型更新量
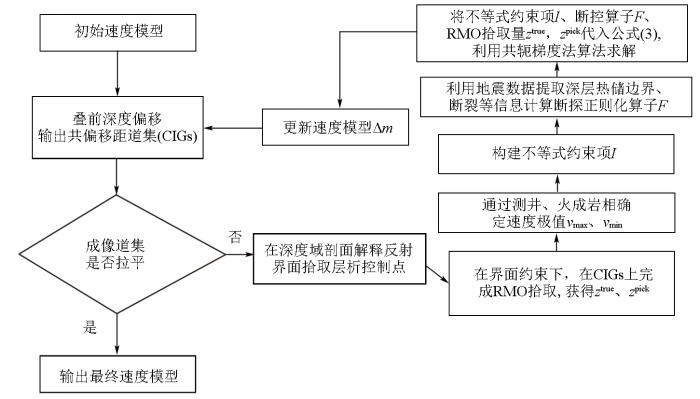
利用式(3)即可实现针对深层热储成像的精细速度建模,该技术与常规深度域偏移速度建模流程基本一致,通过输入CMP道集进行叠前深度偏移,输出偏移剖面和偏移距域成像道集进行层析反演。区别在于该技术通过在反演过程中加入测井速度范围及构造等先验信息约束实现更加精细的速度建模,具体流程如下图7所示。
图7
通过以上技术流程即可实现面向深层热储的高精度层析速度建模,该技术的关键在于准确地提取成像道集RMO,从而获得
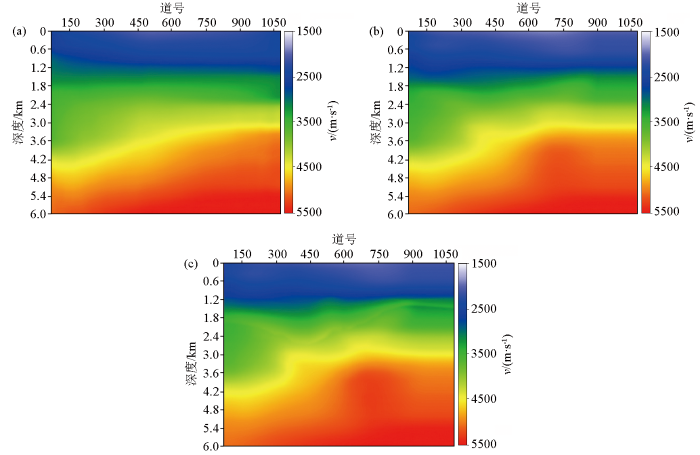
本文采用时间域RMS速度,通过DIX公式转换为层速度,利用时深转化结合大平滑操作建立初始速度模型,见图8a。通常初始速度准确性较差,成像结果相对不准确,构造信息不可靠,因此,第一轮层析反演(反演网格为400 m×400 m)使用常规无约束信息的速度反演;经过两轮反演可以得到相对准确的低频背景速度场,此时速度低波数信息较为可靠,但缺乏中波数信息,表现为反演结果整体较好,大尺度构造信息较为可靠,但细节不足,如图8b所示;因此,第三、四轮反演(反演网格为100 m×100 m)采用断控层析速度建模技术,通过引入大尺度层位、断裂等构造信息实施构造约束,对速度局部细节进行精细反演,得到精细速度模型,如图8c所示。本次建模采用无约束—大尺度构造约束—小尺度断控层析的建模策略,依据道集的拉平度判断每次更新的有效性与合理性,最终实现成像道集拉平(图9),得到高精度速度模型。图10a、b分别是初始速度模型(图8a)和最终速度模型(图8c)的成像效果对比,可以看出,通过多轮迭代后,图10b中成像结果反射层位同相轴更加连续,断裂刻画更加清晰,基底成像质量明显提升。
图8
图8
速度更新迭代结果对比
a—初始模型深度域速度;b—无约束大尺度层析速度;c—构造约束小尺度层析速度
Fig.8
Comparison of velocity iterative update
a—initial velocity model;b—large-scale velocity update without fault constraint;c—small-scale velocity update with fault constraint
图9
图9
迭代过程成像道集对比
a—初始模型深度域成像道集;b—无约束大尺度层析成像道集;c—构造约束小尺度层析成像道集
Fig.9
Comparison of CIGs corresponding to the iterative process
a—CIGs of initial velocity model;b—CIGs of large-scale velocity without fault constraint;c—CIGs of small-scale velocity with fault constraint
图10
图10
初始模型与更新后模型对应的PSDM剖面对比
a—
Fig.10
Comparison of PSDM sections corresponding to the initial velocity and the updated velocity
a—PSDM section of initial velocity model(
3 保低频逆时偏移技术
逆时偏移是一种可以适用于陡倾角构造成像的双程波波动方程偏移技术。该技术通过多年的发展和实用化打磨,目前已基本实现实际资料的规模化应用。为了兼顾计算效率与成像质量,本文就华南火成岩深层热储成像问题,开展实用化的保低频逆时偏移方法研究及应用测试,采用解析波场隐式分解的成像条件,形成了高效稳定的保低频逆时偏移成像技术及流程,达到了保低频成像效果,显著改善了成像质量。
解析波场隐式分解的逆时偏移成像条件通常可以表示为:
式中:
式中:
图11
图11
克希霍夫偏移(a)与保低频RTM偏移(b)效果对比
Fig.11
Comparison of Kirchhoff migration(a) and RTM migration(b)
4 华南火成岩区实际处理效果
实际资料选自中国华南某火成岩发育区,该区资料浅中层沉积环境相对稳定,速度变化较小;深层波场复杂,信噪比较低,受陡倾角构造的影响,纵、横向速度变化大,速度建模及成像困难。
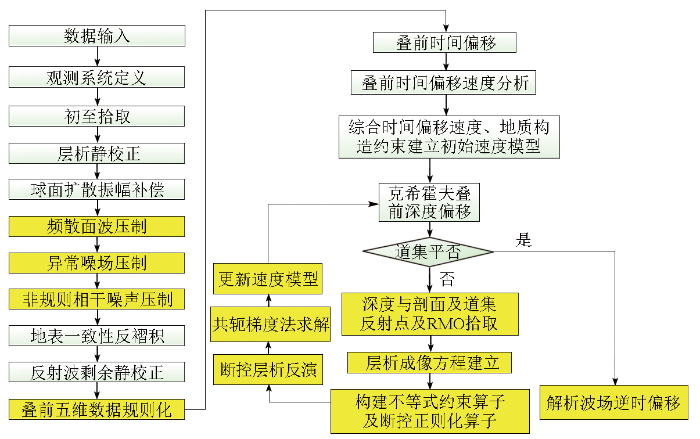
为解决火成岩区热储边界、断裂成像刻画难题,采用本文建立的地震成像技术流程(图12)进行应用测试。
图12
图12
面向复杂岩性和构造条件下的深层地热地震资料处理关键技术流程(图中黄色位置为关键性技术)
Fig.12
The key processing flow for deep geothermal imaging(the yellow position in the figure is the key technology)
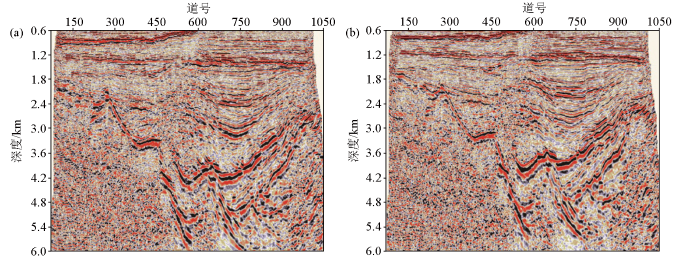
图13
图13
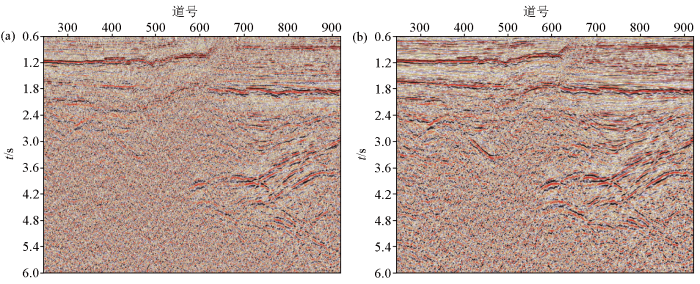
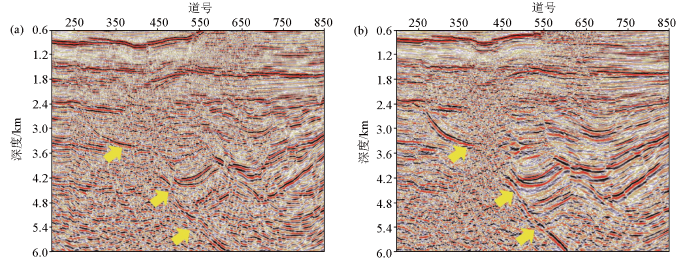
前期处理结果(a)与本期处理结果(b)基底边界成像效果对比
Fig.13
Boundary imaging comparison of previous imaging results(a) and current imaging results(b)
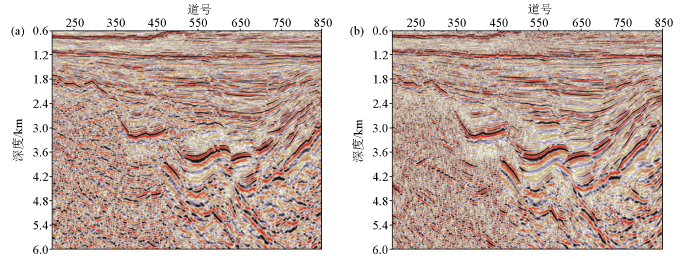
图14
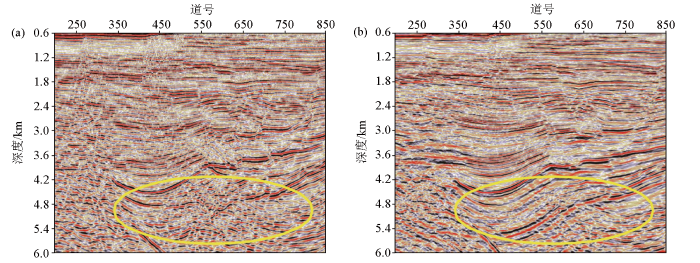
图14
前期处理结果(a)与本期处理结果(b)基底内幕成像效果对比
Fig.14
Basement insider imaging comparison of previous imaging results(a) and current imaging results(b)
5 结论
地震资料处理是一项复杂的系统工程。对于不同地质目标,应具体问题具体分析。面向华南火成岩深层地热勘探地震资料处理,本文围绕深层热储地震资料信噪比低、构造复杂、陡倾角发育几个关键问题,通过保低频联合去噪、断控速度建模及解析波场逆时偏移技术组合应用,建立了面向华南火成岩深层热储地震资料的针对性处理流程。实际处理效果显示了本文技术流程能够显著改善深层热储边界、内幕复杂断裂系统的成像质量,为后续热储刻画提供了高品质成像数据,具有较好的推广应用价值。
参考文献
福建陆缘壳幔异常结构与深部热储潜能分析
[J].
Abnormal structure of crust and mantle and analysis of deep thermal potential in Fujian continental margin
[J].
华南陆缘高热流区的壳幔温度结构与动力学背景
[J].
DOI:10.6038/cjg2018L0448
[本文引用: 1]

华南陆缘是我国重要的矿产、地热资源区.晚中生代以来,在太平洋板块西向俯冲,地幔热对流活动共同作用下,该区出现多期岩浆-热事件和大规模爆发式成矿作用.在前人研究基础上,本文利用地表热流观测资料、地震剪切波资料、重力位球谐系数,计算了壳-幔温度结构,分析了动力学背景.计算结果表明:华南陆缘东南沿海地带,地壳10 km以浅温度达200℃以上,居里点温度475℃,莫霍面平均温度550℃.地壳浅层较热,花岗岩中放射性元素衰变放热是地壳浅层地下水热活动的重要热源,但地壳总体温度不高,为"冷壳热幔"型热结构.地幔中,90 km深度,温度950~1250℃;120 km深度,温度1050~1400℃;150 km深度,温度1200~1450℃;220 km深度,温度1500~1700℃."热"岩石圈底界深度在110~150 km之间,西深东浅.岩石圈内,地幔应力场为挤压-伸展相间格局;岩石圈之下,地幔应力场为一个以南昌为中心、长轴NE-SW向的椭圆.分析认为,晚中生代以来,太平洋板块的西向俯冲,导致华南陆缘在区域性SE向地幔对流背景上叠加局域性不稳定热扰动,在175~85Ma期间,上地幔物质向上流动,形成不同的岩浆活动高峰期.同时,岩石圈地幔受俯冲洋壳流体的影响,含水量高,黏度小,在地幔流切向应力场作用下,岩石圈底界由西向东"波浪"状减薄.现今岩石圈之下仍具备地幔小尺度热对流温度条件,但除地表浅层外,地壳整体温度不高,岩石圈构造稳定.
Temperature structure and dynamic background of crust and mantle beneath the high heat flow area of the South China continental margin
[J].
音频大地电磁法在地热勘查中的应用——以福建省宁化县黄泥桥地区为例
[J].
The application of audio frequency magnetotelluric method to the geothermal exploration:A case study of Huangniqiao area,Ninghua County,Fujian Province
[J].
东南沿海黄沙洞地热田地应力与控热构造研究
[J].
Research on the in situ stress state and the geothermal-controlling structure of the Huangshadong Geothermal Field in the Southeast Coast of China
[J].
The relationship between the deep faults and the geothermal structures identified on the Moesian Platform territory
[C]//
Deep denoising autoencoder for seismic random noise attenuation
[J].
DOI:10.1190/geo2019-0468.1
URL
[本文引用: 1]

Attenuation of seismic random noise is considered an important processing step to enhance the signal-to-noise ratio of seismic data. A new approach is proposed to attenuate random noise based on a deep-denoising autoencoder (DDAE). In this approach, the time-series seismic data are used as an input for the DDAE. The DDAE encodes the input seismic data to multiple levels of abstraction, and then it decodes those levels to reconstruct the seismic signal without noise. The DDAE is pretrained in a supervised way using synthetic data; following this, the pretrained model is used to denoise the field data set in an unsupervised scheme using a new customized loss function. We have assessed the proposed algorithm based on four synthetic data sets and two field examples, and we compare the results with several benchmark algorithms, such as f- x deconvolution ( f- x deconv) and the f- x singular spectrum analysis ( f- x SSA). As a result, our algorithm succeeds in attenuating the random noise in an effective manner.
ECA-UNet:Denoise seismic data by learning from traditional method
[C]//
基于f-x域时频非凸正则化低秩矩阵近似的共偏移距道集去噪方法
[J].
Random noise attenuation of common offset gathers by f-x low-rank matrix approximation with nonconvex regularization
[J].
基于快速自适应非局部均值滤波的地震随机噪声压制方法
[J].
Seismic random noise attenuation method based on the fast adaptive non-local means filtering algorithm
[J].
塔里木盆地河南探区地震资料处理方法研究
[J].
Study of the methods for seismic data processing in Henan prospecting area in Tarim Basin
[J].
多域组合去噪技术在塔中奥陶系低信噪比资料处理中的应用
[J].
DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1000-1441.2015.02.008
[本文引用: 1]

塔中地区主要目的层是深层奥陶系碳酸盐岩储层,由于地表沙丘起伏大、沙层松散,地震波吸收衰减严重,干扰波复杂,导致目的层地震资料信噪比非常低。沙丘所产生的噪声不仅使有效波特征受到影响,而且使面波等相干噪声的规律性遭到破坏,从而增加了去噪处理的难度。为了在保真的前提下最大限度地压制干扰波、提高塔中奥陶系目的层资料信噪比,基于多年沙漠区地震资料处理所取得的经验与认识,通过对塔中地区地震资料干扰波成因、类型及其特点进行分析,提出了根据噪声类型、能量强弱、频带范围及其在不同域中所表现的特征,分类、分步、分频、分域、分时窗、分区的六分法多域组合去噪技术思路与处理流程。实际资料应用效果表明,多域组合去噪技术能明显提高奥陶系内幕反射的信噪比以及小断点、碳酸盐岩内部异常或“串珠”状反射的清晰度。
Application of multi-domain composite denoising technology for the processing of Ordovician low SNR seismic data in Tazhong Area
[J].
DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1000-1441.2015.02.008
[本文引用: 1]

Deep Ordovician carbonate reservoir is the main exploration target in Tazhong area.The undulate dunes,the loose surface sand bed and the serious absorption & attenuation effect leads to low SNR seismic data of the target layers.The noise caused by sand dunes affects the characteristics of the effective wave,and also breaks the law of the coherent noise,which increases the difficulty for seismic data denoising processing.In order to suppress interference wave and improve the SNR of Ordovician target layers with the premise of fidelity,based on the experience and recognition obtained from the desert seismic data processing in the last few years,in terms of noise type,energy strength,frequency bandwidth and their characteristics in different domain,we proposed multi-domain composite denoising technique and processing workflow,and the multi-domain includes scale,step,frequency,domain,time window,zone etc.Actual data application results indicate that mlti-domain composite denoising technique obviously improve the SNR of Ordovician insider reflections,the clearness of small fault points,inside abnormal of carbonate or moniliform reflection.
复杂地质条件下超深层碳酸盐岩断控缝洞体成像及预测技术
[J].
DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1000-1441.2022.05.011
[本文引用: 1]

复杂地质条件下的超深层碳酸盐岩断控油气藏是近年来油气勘探的热点之一,其所发育的超深层断控缝洞型储集体受走滑断裂控制。沙漠起伏地表造成地震波能量吸收衰减严重,储层的上覆地层的火成岩严重影响目的层成像,同时超深层储集体地震波有效信号弱、反射特征复杂,影响了预测精度。以塔里木盆地顺北油气田为例,对该地区储集体高精度成像及储层预测难点进行剖析,建立了针对性技术策略:采用以弱信号恢复为代表的地震资料预处理技术提升叠前道集品质,为速度建模及成像提供基础数据;将火成岩高斯束层析速度建模与宽频RTM成像技术相结合,有效提升火成岩及高陡构造的建模成像精度;建立了面向超深层断裂及储集体的多属性综合预测技术流程,通过模拟断控缝洞体的地震波场响应,分析不同类型储集体的地震响应特征,对断裂带边界及内幕的叠后多属性进行降维处理,实现对超深层碳酸盐岩断控缝洞体的有效预测,为塔里木盆地超深层碳酸盐岩油气勘探开发提供了技术支撑。
Imaging and prediction technology of fault-karst reservoirs in ultra-deep carbonate rocks under complex geological conditions
[J].
DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1000-1441.2022.05.011
[本文引用: 1]

Oil and gas reservoirs in fault-karst,ultra-deep carbonate rocks under complex geological conditions havebecome a popular exploration target in recent years.The fault-karst reservoirs are controlled by strike-slip faults.The undulating surface of the desert causes significant energy absorption and attenuation of seismic waves,the effectivesignal of seismic waves in ultra-deep reservoirs is weak and the reflection characteristics are complex,which affects the prediction accuracy.Simultaneously,the igneous rocks in the strata overlying the reservoirs affect the imaging of the target layer.The difficulties of high-precision reservoir imaging and prediction are analyzed using the Shunbei oil and gas field in the Tarim Basin as an example.The seismic data pre-processing technology represented by weak signal recovery is adopted as a targeted technical countermeasure to improve the quality of pre-stack gathers,thus providing basic data for velocity modeling and imaging.The modeling and imaging accuracy of igneous rocks and high and steep structures can be effectively improved using the combination of igneous rock Gaussian beam tomography velocity modeling and broadband reverse-time migration (RTM) imaging technology.A multi-attribute comprehensive prediction process which analyzes the seismic response characteristics of different types of reservoirs is established for ultra-deep fractures and reservoirs,through seismic wave field response simulation.This uses post-stack multi-attribute dimensionality reduction to process the fault zone and its boundaries and predict ultra-deep carbonate fault-karst reservoirs.This method provides improved technical support for the exploration of ultra-deep carbonate rocks in the Tarim Basin and the development of fault-karst reservoirs in the area.
Gaussian beam velocity tomography based on azimuth-opening angle domain common imaging gathers
[J].
DOI:10.1093/jge/gxz061
URL
[本文引用: 1]

Ray-based tomography in the imaging domain, implemented with seismic migration, is currently widely used in industrial applications. However, conventional ray-based tomography has some inherent problems, such as shadow area, multi-path problem and so on, which limit the inversion accuracy. To alleviate these problems, we proposed Gaussian beam velocity tomography (GBT) based on azimuth-opening angle domain common imaging gathers (ADCIGs). According to the first-order Born and Rytov approximations, we derived a linear relationship between travel-time perturbation and velocity perturbation in the imaging domain, by which we construct the explicit expression of the sensitivity kernel function and use a Gaussian beam operator to compute the kernel. Furthermore, by introducing the preconditioned model regularization, a method of GBT under the constraint of a structure-guided filter is derived. Iterative applications of migration and tomography, both based on a Gaussian beam propagator, embody the idea of integrating velocity inversion and imaging. Numerical tests on both synthetic data and field data demonstrate that Gaussian beam propagator-based travel-time tomography in the imaging domain is effective.
Deep structure investigations of the geothermal field of the North Euboean Gulf,Greece,using 3-D local earthquake tomography and Curie Point Depth analysis
[J].DOI:10.1016/j.jvolgeores.2011.06.008 URL [本文引用: 1]
Geothermal reservoir characterization using passive seismic tomography:A case history
[C]//
井控与构造约束条件下的网格层析速度建模技术及应用
[J].
DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1000-1441.2020.02.006
[本文引用: 1]

地震勘探的关键是速度分析,常用的叠前深度偏移速度建模技术为网格层析反演,但当研究区断层较为发育时,网格层析跨越断层进行,速度更新导致断层两侧速度描述不准确,从而产生断层阴影构造假象,对解释及井位部署产生影响。为此,从井震标定和精细构造解释入手,首先建立测井速度与地震层速度的关系,根据层位标定结果在时间域利用VSP速度及测井速度校正沿层层速度;然后将校正后的时间域层速度变换到深度域,将得到的结果作为叠前深度偏移的初始速度;再采用层控、断控高精度网格层析技术进行速度建模,利用深度域解释的层位和断层控制断层两侧速度的准确性;最后采用小网格层析技术提高垂向速度分析的精度,对断层两侧速度进行准确刻画。实际资料处理结果表明利用井控与构造约束条件下的网格层析速度建模技术建立的速度模型符合实际情况,叠前深度偏移结果可以较好地消除断层引起的下部构造假象。
Seismic wave velocity modelling through grid tomography inversion constrained by well logging and structural modeling
[J].
DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1000-1441.2020.02.006
[本文引用: 1]

<p>Seismic velocity analysis is important for geophysical exploration.Grid tomography inversion is a common technique to estimate the velocity of seismic waves in geological formations.If faults are abundant in the domain under investigation,and the tomography is carried out in a direction transverse to the faults,the seismic wave velocity on the two sides of the faults cannot be described with sufficient accuracy.This phenomenon is known as “fault shadowing” and can have a great impact on the interpretation,and ultimately on the locations chosen for well deployment.In this work,on the basis of seismic calibration of well logs and fine-structure interpretation,a relationship between well logging velocity and seismic interval velocity was established.Accordingly,VSP and logging velocities were used to correct the estimated velocities along the horizon in the time domain.Then,these velocities in the time domain were transformed into depth domain information,so as to serve as the initial velocity field in the pre-stack depth migration.Subsequently,high-precision grid tomography—entailing formation-controlled and fault-controlled techniques—was carried out to obtain the velocity.The information on the faults and that on the horizons obtained in the depth domain were used to invert the velocities on both sides of the faults.Meanwhile,the small-grid tomography technique was also used to improve the vertical accuracy of the velocity field.By this technique,the velocity on both sides of the faults could be accurately described.Results obtained by processing actual data showed that the velocity model obtained by the aforementioned technique was accurate,and the pre-stack depth migration can eliminate the fault shadowing phenomenon effectively.</p>
基于构造导向滤波的高斯束层析速度建模方法及其应用
[J].
Gaussian beam tomography with structure-filtering and its applications
[J].
基于断裂属性约束的深度域层析速度建模技术
[J].
DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1000-1441.2021.04.004
[本文引用: 1]

断裂发育地区地震速度建模困难,但其精度决定着成像结果的精度和可信度。将断裂属性作为先验信息应用于正则化约束中,针对人工解释断裂信息精度不高、重复工作量大的难题,以高斯束层析反演理论为基础,研究了基于断裂属性约束的高斯束层析速度建模技术。该方法通过引入基于最优路径寻优的断层特征提取技术,利用数据驱动得到高精度断裂信息,结合预条件正则化技术将断裂属性应用于层析反演迭代过程中,建立深度域断裂属性约束高斯束层析速度建模的地质框架,得到更为精确的速度模型,所得结果能够更加准确地刻画断裂两侧的地层速度,从而提高断裂的成像精度。理论模型数据及实际地震资料测试结果表明该技术反演得到的速度模型更加精细,相比于常规网格层析结果,断裂成像效果好,断面干脆,断点清晰,验证了方法的有效性与实用性。
Fault-constrained velocity tomography in the depth domain
[J].
DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1000-1441.2021.04.004
[本文引用: 1]

Fault-controlled reservoirs have attracted increasing attention as the main exploration targets.Fault-constrained velocity model building and seismic imaging are of great significance for exploration.To improve the accuracy of the velocity model in fault developed areas,fault information has been introduced into a velocity building model in the depth domain based on the Gaussian beam theory.Furthermore,fault-controlled Gaussian beam tomography has been deduced to improve model accuracy,which depends on the accuracy of the information on fault attributes.By introducing a fault detection algorithm based on optimal surface voting,high-accuracy fault information was obtained in a data-driven manner.By combining this algorithm with pre-condition regularization to constrain the Gaussian beam tomography,a fault-constrained velocity building model in the depth domain was established.The proposed model could improve the accuracy of velocity modeling in fault developed regions.Testing on synthetic and actual field data confirmed the validity and practicability of the proposed method.
三维逆时偏移GPU/CPU机群实现方案研究
[J].
Implementation strategy of 3D reverse time migration on GPU/CPU clusters
[J].
适于大规模数据的逆时偏移实现方案
[J].
The implementation scheme of reverse-time migration for mass seismic data
[J].
起伏地表谱元逆时偏移方法
[J].
DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1000-1441.2021.02.012
[本文引用: 1]

谱元法综合了有限元法边界适应性强和谱方法精度高、收敛快的优点。研发了一种基于谱元法的起伏地表逆时偏移方法,采用切比雪夫谱元法并结合隐式Newmark时间积分法求取波场传播算子,推导出波动方程切比雪夫谱元逆时偏移算法(CSE-RTM),该算法在空间上具有谱精度,在时间上达到二阶精度。同时,为了充分利用计算机集群资源,提高该方法的并行效率,基于自由度凝聚和局部松弛的思想,推导了切比雪夫谱元逆时偏移方法的多级并行算法(HEP-CSE-RTM),该算法具有并行效率不随处理器数目增多而下降的优点。二维加拿大起伏地表逆掩断层模型及三维SEAM起伏地表复杂构造模型测试结果表明:该方法在起伏地表复杂构造区成像精度明显高于常规有限差分法逆时偏移,由于该方法本身具有谱方法的稀疏网格快速收敛特性,结合自由度凝聚的多级并行计算,运行效率大幅度提高,达到了与常规有限差分法逆时偏移相当的计算效率。
Reverse time migration for irregular topography based on spectral element method
[J].