0 引言
大气沉降分为干沉降和湿沉降两种方式,干沉降是指大气中的颗粒物在重力或与其他物体碰撞后发生沉降,湿沉降是指通过降雨、降雪等方式使颗粒物从大气中去除的过程[1]。气源重金属颗粒是造成土壤重金属侵袭、累积或污染的重要途径之一[2],更有研究显示在许多工业发达国家,大气沉降对土壤系统中重金属累计贡献率在各种外源输入因子中排在首位[3⇓-5]。随着对环境质量的日益关注,国内开展了较多关于大气沉降中重金属对土壤重金属富集影响的相关研究。熊秋林等[6]对北京市表层土壤重金属污染分布及大气贡献的研究表明,北京表层土壤中重金属Cd、Cr、Cu、Ni、Zn和Pb的大气沉降平均贡献率分别为17.4%、21.2%、14.6%、12.2%、16.0%和 20.0%。大气沉降中重金属的来源也是近年来研究的热点问题,多项基于大中型城市、工业型城市、燃煤城市以及平原大田区的研究认为,Cd多来源于燃煤冶金、化学工业、交通以及矿产开采,Zn、Pb多来源于道路源、铅锌矿开采、燃煤、冶金,Cr多来源于燃煤、电镀、皮革业,Ni多来源于化石燃料燃烧、钢铁冶炼,Hg多来源于汞矿开采、废物焚烧[7⇓⇓⇓⇓⇓⇓⇓⇓⇓⇓-18]。现有研究认为,影响大气沉降通量和沉降速率的因素主要有排放源、距排放源的距离和采样点的气象条件等[6-7],较少地关注地形、地貌条件对大气沉降重金属的影响。本次研究针对重庆市秀山县北部地区开展,研究区位于著名的锰三角区,东部湖南省花垣县也是著名的铅锌矿产区。本文通过为期1年的监测,研究秀山县北部大气干湿沉降中7种重金属的沉降总量及分布特征,结合地形、地貌特点对重金属来源进行分析,并对沉降超标区土壤及农产品的安全性进行初步评估,期望对山区大气沉降重金属来源的分析,为有效防治环境污染提供参考,并对秀山县北部地区环境污染防治和农田土壤安全利用提供依据。
1 研究方法
1.1 研究区概况
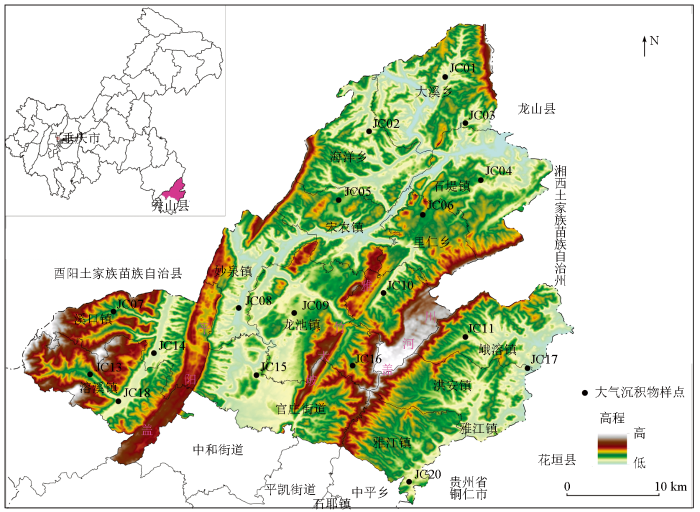
研究区位于重庆市秀山县北部,东经108°42'36″~109°18'53″,北纬28°27'21″~28°53'11″,属武陵山二级隆起带南段,地形、地貌受地质构造控制明显,山脉多呈NE—SW向展布,整体呈“三山夹三槽”的格局,最高海拔1 663 m,最低点海拔245.7 m。年平均气温16.5 ℃,主导风向为东南风,土壤类型以黄壤为主。研究区内地层出露齐全,多为沉积岩,有少量浅变质岩。研究区位于渝湘黔锰矿集中产区,东部湖南省花垣县为著名的铅锌矿产区(图1)。
图1
图1
研究区范围及大气沉降采样点位分布
Fig.1
Study area and distribution of atmospheric dust sampling sites
1.2 样品采集
按照1个点/69 km2的密度布设接沉缸,接沉缸选择放置在周围无更高建筑的民房房顶,一般距离地面约11 m,将其垫高1.5 m防止扬尘进入并固定,记录每个接沉缸质量。接沉时间为2019年4月1日至2020年4月1日,共布设18个大气干湿沉降采样点。
收样前,先称取装有干湿沉降物的接沉缸的总质量,测量接沉缸缸口直径。随后用玻璃棒充分搅拌均匀,取1 000 mL装入塑料瓶,分别称取装水前后塑料瓶的质量。记录样品编号,装箱送检。
1.3 分析测试
分析测试Cd、Hg、Pb、Cr、Cu、Zn、Ni等7种重金属元素,测试工作由重庆市地质矿产测试中心负责。用虹吸法将经过沉淀的上清液、悬浮物及沉淀物进行分离并测量质量及体积,悬浮物及沉淀物用0.45 μm的聚酯纤维滤膜全部过滤,记录滤液质量及体积。固体物中Pb、Zn采用X射线荧光光谱法,Cd、Cu、Ni、Cr采用等离子体质谱法,Hg采用氢化物发生—原子荧光光谱法进行分析,分析插入准确度控制的国家一级标准物质2件。上清液中Cd、Cu、Ni、Cr、Pb、Zn采用电感耦合等离子体质谱法,Hg采用原子荧光法进行分析,分析插入准确度控制的国家一级标准物质2件。国家一级标准物质测定值准确度合格率均为100%,重复性检验合格率100%。样品皆采取100%重复样分析,双样结果的相对偏差RE/%均小于30%。
2 结果及分析
2.1 大气干湿沉降重金属分布及含量特征
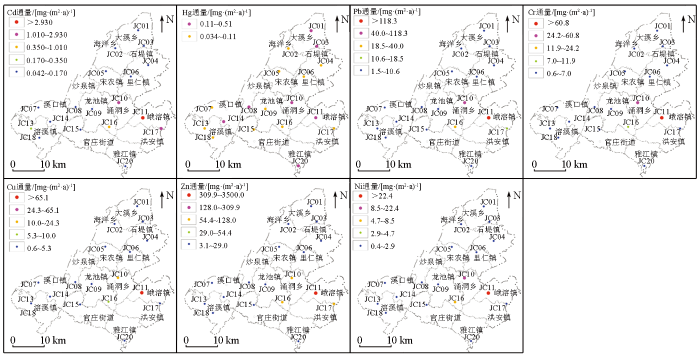
图2
图2
各样点重金属元素沉降通量点位符号
注:蓝色点表示低于25%百分位;绿色点表示位于25%~50%百分位;橙色点表示位于50%~75%百分位;玫色点表示位于75%~90%百分位;红色点表示高于90%百分位
Fig.2
Symbol diagram of heavy metal element deposition flux at various points
Note:blue points are below 25% percentile;green points are in 25%~50% percentile;orange points are in 50%~75% percentile;rose points are in 75%~90% percentile;red points are above 90% percentile
表1 各样点大气干湿沉降中重金属元素沉降通量
Table 1
| 分区 | 样品编号 | Cd | Cr | Cu | Ni | Pb | Zn | Hg |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 一般区 | JC01 | 0.077 | 0.935 | 1.150 | 0.550 | 2.014 | 4.765 | 0.155 |
| JC02 | 0.059 | 0.948 | 0.909 | 1.597 | 1.506 | 3.664 | 0.040 | |
| JC03 | 0.042 | 1.067 | 1.091 | 1.179 | 1.528 | 4.723 | 0.129 | |
| JC04 | 0.113 | 2.505 | 1.046 | 0.628 | 1.762 | 5.096 | 0.048 | |
| JC05 | 0.058 | 0.679 | 0.617 | 0.441 | 1.459 | 3.689 | 0.042 | |
| JC06 | 0.053 | 0.656 | 0.649 | 0.492 | 1.532 | 3.131 | 0.065 | |
| JC07 | 0.120 | 0.766 | 1.053 | 0.433 | 2.432 | 5.658 | 0.059 | |
| JC08 | 0.071 | 1.371 | 1.141 | 0.788 | 5.550 | 5.516 | 0.173 | |
| JC09 | 0.061 | 1.353 | 1.024 | 1.653 | 1.695 | 3.753 | 0.083 | |
| JC13 | 0.213 | 2.043 | 3.109 | 1.558 | 4.678 | 13.765 | 0.063 | |
| JC14 | 0.138 | 0.784 | 1.209 | 0.459 | 2.853 | 6.769 | 0.162 | |
| JC15 | 0.082 | 3.491 | 1.478 | 1.041 | 3.199 | 6.476 | 0.079 | |
| JC18 | 0.115 | 0.837 | 1.065 | 0.341 | 3.393 | 4.935 | 0.102 | |
| JC20 | 0.162 | 0.643 | 0.655 | 0.352 | 2.647 | 8.851 | 0.176 | |
| 平均值 | 0.097 | 1.291 | 1.157 | 0.822 | 2.589 | 5.771 | 0.098 | |
| 川河盖两翼沉 降量高值区 | JC10 | 2.500 | 40.500 | 17.200 | 14.500 | 65.400 | 108.000 | 0.138 |
| JC11 | 76.100 | 388.800 | 298.400 | 237.900 | 1395.600 | 3482.200 | 0.146 | |
| JC16 | 0.737 | 9.689 | 8.284 | 5.076 | 21.439 | 66.948 | 0.101 | |
| JC17 | 1.250 | 3.530 | 3.542 | 1.621 | 15.753 | 93.506 | 0.078 | |
| 平均值 | 20.981 | 117.633 | 85.052 | 64.271 | 376.904 | 960.891 | 0.097 | |
| 全区 | 最大值 | 76.100 | 388.8 | 298.400 | 237.900 | 1395.6 | 3482.2 | 0.176 |
| 最小值 | 0.042 | 0.643 | 0.617 | 0.341 | 1.459 | 3.131 | 0.024 | |
| 平均值 | 4.554 | 25.585 | 19.087 | 15.032 | 85.246 | 212.859 | 0.102 | |
| 标准差 | 17.31 | 88.54 | 67.85 | 54.14 | 318.15 | 793.58 | 0.05 | |
| 变异系数 | 3.81 | 3.46 | 3.55 | 3.60 | 3.73 | 3.73 | 0.45 | |
| 全国[19] | 平均值 | 0.71 | 18.21 | 15.55 | 7.57 | 36.72 | 147.85 | 0.07 |
| 重庆主城区降水[20] | 平均值 | 0.44 | 2.9 | 13 | 2.22 | 30.25 | 76.26 |
川河盖两翼高值区包含了JC10、JC11、JC16、JC17共4个观测点,该区Hg沉降通量与一般沉降区较为接近,平均值略高于全国平均值,其余6种重金属元素沉降通量平均值远高于全国平均值及重庆主城降水中的平均值。其中,Cd沉降通量平均值高达20.981 mg/(m2·a),是全国平均值的30倍,重庆主城区平均值的48倍;Cr沉降通量平均值高达117.633 mg/(m2·a),是全国平均值的6倍,重庆主城区平均值的41倍;Cu沉降通量平均值高达85.052 mg/(m2·a),是全国平均值的5倍,重庆主城区平均值的7倍;Ni沉降通量平均值高达64.271 mg/(m2·a),是全国平均值的8倍,重庆主城区平均值的29倍;Pb沉降通量平均值高达376.904 mg/(m2·a),是全国平均值的10倍,重庆主城区平均值的12倍;Zn沉降通量平均值高达960.891 mg/(m2·a),是全国平均值的6倍,重庆主城区平均值的13倍。
表2为大气干湿沉降样点周边1 km范围内土壤中7种重金属元素含量的平均值。对比发现,大气干湿沉降物中重金属元素的含量与周围土壤中重金属元素的含量并不呈简单的线型相关。在一般沉降区,地质背景相同、人类活动程度相近的样点,土壤与大气干湿沉降物中重金属元素含量接近,例如同位于志留系泥页岩分布区,以农林业为主的JC01和JC03样点;同位于溶溪槽谷,以寒武系碳酸盐岩为主,工农业活动程度较强的JC14和JC18样点,其土壤和大气干湿沉降物中重金属元素含量均较为接近。位于锰矿产区的JC13样点,土壤中重金属元素含量与区域平均值接近,但大气干湿沉降物中重金属元素含量较一般沉降区偏高。在沉降高值区,大气干湿沉降物中重金属元素含量与周围土壤中重金属元素含量差异较大。这说明大气干湿沉降物中重金属元素的含量除受周围土壤中重金属元素含量的影响外,更受人类活动的影响。
表2 大气干湿沉降样点周围土壤中重金属元素含量
Table 2
| 样品编号 | Cd | Cr | Cu | Hg | Ni | Pb | Zn | 样品编号 | Cd | Cr | Cu | Hg | Ni | Pb | Zn | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| JC01 | 0.20 | 68.0 | 27.8 | 0.08 | 34.4 | 32.6 | 84.1 | JC13 | 0.40 | 81.2 | 32.4 | 0.24 | 33.6 | 33.9 | 99.1 | |
| JC02 | 0.21 | 71.1 | 28.5 | 0.06 | 34.4 | 32.1 | 89.5 | JC14 | 0.34 | 72.9 | 28.3 | 0.57 | 34.5 | 42.8 | 95.1 | |
| JC03 | 0.19 | 68.6 | 25.3 | 0.07 | 33.0 | 29.8 | 86.4 | JC15 | 0.36 | 86.7 | 26.0 | 0.21 | 33.5 | 40.7 | 95.8 | |
| JC04 | 0.16 | 59.2 | 19.0 | 0.07 | 25.8 | 26.3 | 69.5 | JC18 | 0.43 | 77.9 | 29.2 | 0.55 | 32.9 | 39.9 | 102.6 | |
| JC05 | 0.33 | 82.3 | 29.5 | 0.17 | 34.1 | 46.9 | 88.6 | JC20 | 0.39 | 77.6 | 32.6 | 0.17 | 39.0 | 44.0 | 104.0 | |
| JC06 | 0.46 | 69.5 | 27.0 | 0.30 | 30.2 | 47.6 | 90.2 | JC10 | 0.28 | 75.2 | 28.2 | 0.09 | 34.2 | 33.7 | 85.9 | |
| JC07 | 0.94 | 98.1 | 50.2 | 1.46 | 49.9 | 29.1 | 122.2 | JC11 | 0.32 | 74.0 | 47.7 | 0.07 | 34.5 | 35.7 | 87.9 | |
| JC08 | 0.26 | 76.1 | 28.6 | 0.35 | 35.5 | 31.1 | 84.3 | JC16 | 0.33 | 74.5 | 46.7 | 0.07 | 39.3 | 34.9 | 89.8 | |
| JC09 | 0.39 | 83.0 | 26.8 | 0.23 | 32.9 | 46.0 | 94.9 | JC17 | 0.53 | 71.4 | 32.1 | 0.22 | 34.4 | 48.8 | 94.2 |
2.2 大气干湿沉降重金属来源分析
研究区内一般沉降区重金属元素沉降通量显著低于全国和重庆市主城区,而川河盖两翼重金属沉降通量远高于全国和重庆市主城区,故本次对大气沉降重金属来源分析只针对川河盖两翼的沉降高值区。
川河盖及其东部的洪安镇是秀山县重点发展的旅游区,峨溶镇是重要的农业镇,上述区域工矿企业分布少,而本次观测接收的重金属沉降量却最多。
2019~2020年度,川河盖顶部有川河盖景区配套工程施工,相对集中在川河盖中部道路沿线。将川河盖两翼JC10、JC11、JC16、JC17点沉降重金属中各元素占比与川河盖顶部采集的表层土壤样品中相应重金属占比进行比对发现,大气干湿沉降物中Cd、Pb、Zn等3种元素占比远高于川河盖顶部土壤样品的占比,Hg占比基本与土壤样品持平,其余元素占比明显低于土壤样品(表3)。川河盖海拔较高,景区配套工程工期集中在春、夏、秋3个季节,风向以东风及东南风为主。JC11点距川河盖东缘约3.2 km,JC10点距川河盖西缘约3.3 km,两点大气干湿沉降总量差别很大,前者7种重金属的沉降总量约为后者的23.7倍。有研究表明,建筑主体建设降尘中Zn、Cr、Pb、Ni的高值区出现在主体建设中心附近,并有沿场地中心向四周扩散的趋势[25]。因此,上述4个观测点大气干湿沉降量的异常高值来源于川河盖顶部的可能性小。
表3 JC10、JC11、JC16、JC17与川河盖顶部土壤样品中重金属占比对比
Table 3
| 样品编号 | 占比/% | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cd | Cr | Cu | Ni | Pb | Zn | Hg | |
| JC10 | 1.01 | 16.30 | 6.93 | 5.84 | 26.35 | 43.51 | 0.06 |
| JC11 | 1.29 | 6.61 | 5.08 | 4.05 | 23.74 | 59.23 | <0.01 |
| JC16 | 0.66 | 8.63 | 7.38 | 4.52 | 19.09 | 59.63 | 0.09 |
| JC17 | 1.05 | 2.96 | 2.97 | 1.36 | 13.21 | 78.39 | 0.07 |
| 川河盖顶土壤 | 0.26 | 30.73 | 9.91 | 12.77 | 12.37 | 33.90 | 0.06 |
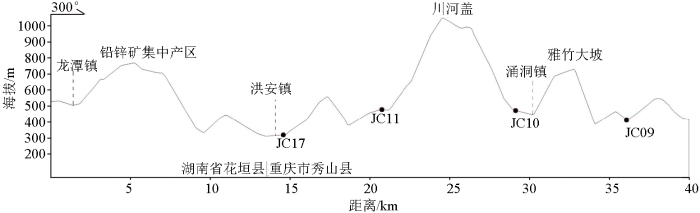
连接JC10和JC11,向东经JC17附近延伸至湖南省花垣县龙潭镇,向西经过一般沉降区的JC19附近横切地形剖面。如图3所示,以川河盖为界,JC17位于东部浅丘区域,地势相对平坦,地形起伏较小,7种重金属年度沉降总量为119.3 mg/(m2·a),是一般沉降区均值的10倍;JC11位于川河盖东翼第一级沟谷内,7种重金属年度沉降总量为5 879.0 mg/(m2·a),是一般沉降区均值的497倍;JC10位于川河盖西翼与雅竹大坡之间的沟谷内,7种重金属年度沉降总量为248.2 mg/(m2·a),是一般沉降区均值的21倍;JC09为一般沉降区观测点,位于雅竹大坡西部的浅丘区域,7种重金属年度沉降总量为9.6 mg/(m2·a),与一般沉降区均值相当。秀山县属亚热带温润季风气候区,冬季盛行西北风,夏季盛行东南风。根据上述4个点位7种重金属沉降总量分布来看,川河盖两翼大气沉降重金属来源于东南部。研究区东南部湖南省花垣县为著名的花垣铅锌矿产区,并拥有多家冶炼加工企业。在东南风的影响下,来自东南方携带Zn、Pb、Cd等多种重金属元素的空气在下风向沉降,遇到海拔陡增的川河盖时,受山体阻挡及山谷风等作用的影响下,在川河盖东翼沟谷富集沉降,少数翻越川河盖后,在川河盖和雅竹大坡之间的沟谷沉降[1,26]。
图3
地形、地貌通过影响水汽、热量循环从而对大气干湿沉降产生影响,JC11位于JC17观测点西北方向6.9 km,在不考虑与污染源距离远近的条件下,认为JC11相对于JC17的高沉降是由于地形引起,前者7种重金属沉降总通量是后者的49倍。因此,建议加强对污染源下风向该类型地貌区大气沉降重金属的监测及环境安全性评估工作。
2.3 大气沉降高值区沉降物污染程度及环境地球化学等级评价
Igeo=log2[Cn/(1.5×Bn)],
式中:Igeo为地累积指数;Cn为大气沉降中重金属元素n的含量;Bn为土壤中重金属元素n的地球化学背景值。Igeo≤0表示无污染,0<Igeo≤1表示轻度污染,1<Igeo≤2表示中度污染,2<Igeo≤3表示中度至严重污染,3<Igeo≤4表示严重污染,4<Igeo<5表示严重至极度污染,Igeo>5表示极度污染。
如表4所示,Cr、Ni无污染,Cu为无污染—轻度污染,Hg为无污染—中度污染,Cd为中度污染—严重至极度污染,Pb轻度污染—中度污染,Zn为轻度污染—中度至严重污染。从单元素看,可能对土壤造成中度以上污染的元素为Cd、Zn。从位置看,位于川河盖东翼的JC11、JC17大气沉降Cd、Zn污染程度明显较西翼JC10、JC16严重,其中污染最严重的是JC11点。
表4 川河盖两翼大气沉降重金属地累积指数
Table 4
| 项目 | 地累积指数 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cd | Cr | Cu | Hg | Ni | Pb | Zn | |
| JC10 | 3.6 | -0.2 | -0.1 | 0.7 | -0.6 | 1.5 | 0.9 |
| JC11 | 4.6 | -0.8 | 0.2 | -3.1 | -0.4 | 2.0 | 2.0 |
| JC16 | 2.5 | -1.6 | -0.4 | 1.0 | -1.4 | 0.6 | 0.9 |
| JC17 | 4.2 | -2.1 | -0.7 | 1.5 | -2.1 | 1.1 | 2.3 |
《土地质量地球化学评价规范》(DZ/T 0295—2016)中规定,Cd年沉降通量密度大于3 mg/(m2·a)的观测点大气干湿沉降物环境地球化学综合等级为二等,表示大气干湿沉降物沉降对土壤环境质量影响较大。JC11观测点Cd的沉降通量高达76.1 mg/(m2·a),远高于二等划分标准,该点具有较高的环境风险。此外,JC11观测点Zn的年沉降通量已接近《土地质量地球化学评价规范》(DZ/T 0295—2016)附表F2中所列10年后达到GB 15618—2018标准中土壤限定值大气干湿沉降物中Zn的最小年沉降通量密度。其余观测点的大气干湿沉降物环境地球化学等级皆为一等。
2.4 大气沉降高值区重金属生态效应评价
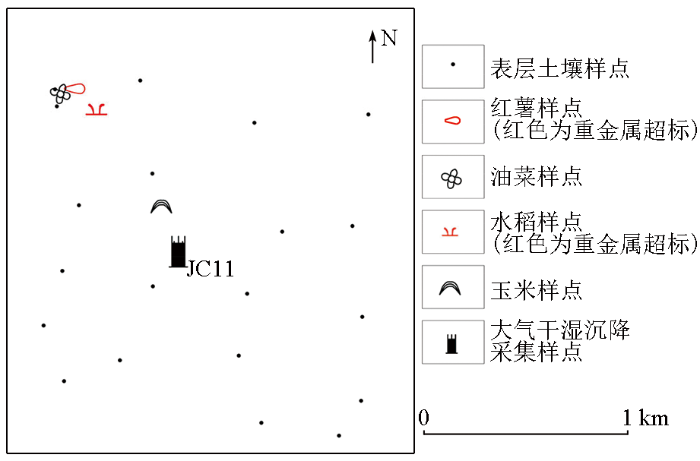
图4
图4
JC11观测点及周围1 km范围内表层土壤及农作物样点分布
Fig 4
Surface soil and crop sample points around JC11 within 1 km
该点周围1 km范围内采集的20件土壤样品(图4)中,Cd、Cr、Cu、Hg、Ni、Pb、Zn含量的平均值分别为0.33×10-6、74.5×10-6、46.7×10-6、0.07×10-6、39.3×10-6、34.9×10-6、89.8×10-6。其中,有6件土壤样品Cd含量超过《农用地土壤污染风险管控标准》(GB 15618—2018)的筛选值,最大值为0.83×10-6;Cu有7件超过筛选值,最大为98.98×10-6。按照《土地质量地球化学评价规范》(DZ/T 0295—2016)评价规范,土壤环境质量类别为清洁—轻微污染。说明JC11点处,较大量的大气重金属沉降暂未改变土壤环境质量等级,但已影响农产品安全。
3 结论
1)通过对秀山县北部大气干湿沉降物进行为期一年的采集测试,发现不同区域大气干湿沉降量差异较大,一般沉降区Cd、Cr、Cu、Ni、Pb、Zn等6种重金属元素年沉降通量较全国和重庆市主城区低。川河盖两翼的异常高值区,除Hg以外的上述6种重金属元素的沉降通量远高于全国及重庆市平均值。区内Hg沉降分布较为均匀,略高于全国平均值,推测与秀山县Hg地质背景值较高相关。
2)秀山北部川河盖两翼较高的大气干湿沉降受东部花垣县铅锌矿开采及特殊地形、地貌的综合影响。经本次估算,下风向陡增的地形使得大气干湿沉降物中7种重金属通量增加49倍,应加强该类型地貌区环境安全的监测与评估工作。
3)经地累积指数法估算,川河盖两翼大气干湿沉降物中Cr、Ni无污染,Cu为无污染—轻度污染,Hg为无污染—中度污染,Cd为中度污染—严重4至极度污染,Pb为轻度污染—中度污染,Zn为轻度污染—中度至严重污染。
4)沉降通量最大的JC11点处,Cd的沉降通量高达76.1 mg/(m2·a),远高于《土地质量地球化学评价规范》(DZ/T 0295—2016)二级标准,该点具有较高的环境风险;现阶段该重金属尚未改变土壤环境质量等级,但对农作物安全造成了一定影响。
参考文献
大气沉降对土壤重金属累积的影响
[J].
Effects of air settlement on heavy metal accumulation in soil
[J].
Particle size distribution and atmospheric metals measurements in a rural area in the South Eastern USA
[J].DOI:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2005.03.017 URL [本文引用: 1]
北京表层土壤重金属污染分布及大气沉降贡献
[J].
DOI:10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2021.04.018
[本文引用: 2]

可下载PDF全文。
A pollution distribution of topsoil heavy metals in Beijing and its atmospheric deposition contribution
[J].
我国主要城市大气重金属的污染水平及分布特征
[J].
Concentrations and distribution characteristic of atmospheric heavy metals in urban areas of China
[J].
大气沉降重金属污染特征及生态风险研究进展
[J].
Progress in research on heavy metals in atmospheric deposition:Pollution characteristics and ecological risk assessment
[J].
Seasonal variability and source apportionment of metals in the atmospheric deposi-tion in Belgrade
[J].DOI:10.1016/j.atmosenv.2010.06.045 URL [本文引用: 1]
太原盆地农田区大气降尘对土壤重金属元素累积的影响及其来源探讨
[J].
Effects of atmospheric fallouts on heavy metal elements accumulation in soils in farmland areas in the Taiyuan basin,Shanxi,China and sources of fallouts
[J].
北京平原区元素的大气干湿沉降通量
[J].
Dry and wet atmospheric deposition fluxes of elements in the plain area of Beijing municipality,China
[J].
哈尔滨市城区大气重金属沉降特征和来源研究
[J].
Multivariate analysis of heavy metal element concentrations in atmospheric deposition in Harbin City,northeast China
[J].In order to understand the characteristics of atmospheric heavy metal deposition in Harbin City, 46 deposition samples were collected which were taken using bulk deposition samplers during the period of 2008-2009 (about 365 days). The samples were analyzed for heavy metal concentration by atomic fluorescence spectrometry (AFS) and inductively coupled plasma-atomic spectrometry (ICP-AES). The deposition flux was calculated. Sources analysis was made by the method of principal component analysis (PCA), Pearsons and enrichment factor (EF). The following points can be gained through multivariate analysis. Mn and Co are mostly from natural sources while the others may be brought by coal dust, vehicle emissions and metal smelting.
南京市大气沉降中重金属特征及对土壤环境的影响
[J].
Atmospheric deposition of heavy metals and their impacts on soil environmentin in typical urban areas of Nanjing
[J].
兰州市大气降尘重金属污染评价及健康风险评价
[J].
pollution evaluation and health risk assessment of heavy metal from atmospheric deposition in Lanzhou
[J].
新疆准东煤田土壤重金属来源分析及风险评价
[J].
Soil heavy metal sources analysis and risk evaluation of Zhundong coal mine in Xinjiang
[J].
河北典型农田大气重金属干沉降通量及来源解析
[J].
Dry deposition flux of atmospheric heavy metals and its source apportionment in a typical farmland of Hebei Province
[J].
我国大气PM2.5中砷的污染特征、来源及控制
[J].
Pollution characteristics,sources and contral of arsenic in PM2.5 in China
[J].
鲁西南平原区大气干湿沉降元素输入通量及来源浅析:以巨野县为例
[J].
An analysis of the input flux and source of elements in dry and wet atmospheric deposition of southwest plain of Shandong:A case study of Juye County
[J].
我国大气重金属干湿沉降特征及时空变化规律
[J].
Characteristics and spatial temporal variation of heavy metals in atmospheric dry and wet deposition of China
[J].
重庆主城区降水中重金属的分布特征及其沉降量
[J].
Concentrations and deposition fluxes of heavy metals in precipition in core urban areas,Chongqing
[J].
重庆主城大气降尘中重金属污染特征及评价
[J].
Pollution characteristics and assessment of heavy metals in atmospheric deposition in core urban areas,Chongqing
[J].
汞的环境地球化学研究进展
[J].
Progresses on environmental geochemistry of mercury
[J].
秀山汞矿开采对当地土水环境的影响
[J].
Effects of mercury mine exploitation on local soil and water environment in Xiushan
[J].
不同类型施工降尘中重金属污染特征及健康风险评价
[J].
Heavy metal pollution characteristics and associated healthrisk assessment in different types of construction dust
[J].
复杂地形多尺度气流对城市大气污染影响的研究进展
[J].
Research of the influences of the air flows on multiple scales on the transport and diffusion mechanisms of urban air pollution over the complex terrains
[J].
济南市近地表大气降尘元素地球化学特征及污染评价
[J].
Geochemical characteristics and pollution assessment of near-surface atmospheric dust in Jinan
[J].
银川市大气降尘重金属污染状况评价
[J].
Contamination status assessment of heavy metals from atmospheric dust falls in Yinchuan
[J].
大气沉降及土壤扬尘对天津城郊蔬菜重金属含量的影响
[J].
Effects of atmospheric and dust depostion on content of heavy metals in vegetables in suburbs of Tianjin
[J].
铅锌矿区附近大气沉降对蔬菜中重金属累积的影响
[J].
Effect of atmospheric deposition on heavy metal accumulation in vegetable crop near a lead-zinc smelt mine
[J].