0 引言
储层非均质性是指沉积环境、成岩作用和构造运动等活动在储层的形成过程中对其产生的影响,在空间和内部的不同性质上均存在变化,是影响地下油、气、水运移和油气运移的关键参数[1-2]。对于储层非均质性的分类,早在20世纪80年代就有研究。Pettijohn以及Weber分别提出了5类和7类划分方案[3];裘怿楠[4]根据油田开发情况,将储层非均质性划分为层间、平面、层内和孔隙非均质性四类。层间非均质性指层系的旋回性、砂砾层间的不均匀性、夹层分布等,其研究内容包括分层系数、垂直砂体密度、各砂层间渗透系数的不均匀程度、有效厚度系数及储层间非均质性评价方法。平面非均质性是指由于砂体中孔隙度、渗透率的平面变化所引起的储层规模和几何形态的不均匀性。层内非均质性主要表现为颗粒尺寸的规律性、层理构造序列及横纵向渗透率之比在岩性、物性和沉积相等方面都存在不同程度的差异,其形成具有内在的复杂性,与形成的地质过程及原因密切相关[5]。孔隙非均质性是指所含岩石的成分、包含的填隙物类型以及孔喉结构等方面存在不同[6]。
学者多采用岩心分析与测井解释结合评价储层非均质性,并利用渗透率变异系数、突进系数、极差等参数,从多个方面对储层非均质性进行表征[7]。边会媛等[8]通过孔渗、X衍射和薄片分析等方法得出柴达木盆地渐新统下干柴沟组储层有较强的非均质性,并通过广义神经网络实现全井段伪毛管压力曲线应用于储层类型预测;李海燕等[9]通过压汞测试、扫描电镜和铸体薄片等资料分析储层的微观孔隙结构,并应用聚类分析和Bayes判别分析方法确定研究区的优质储层;袁红旗等[10]利用洛伦兹曲线,提出综合定量表征储层非均质性的方法,比传统仅基于渗透率指标所构建的参数能更好地反映储层非均质性;杨少春[11]利用综合指数法对储层非均质性进行了定量刻划。相对于常规测井方法,电成像测井能够将采集到的数据转换成直观的图像,具有较高的垂直分辨率[12],可以较为准确地反映井周地层的岩性及物性变化[13]。Aghli等[14]利用电成像测井对孔隙度系统、渗透剖面和非均质性指数进行评价,认为电成像测井可用于评价储层非均质性;侯振学等[15]对井壁微电阻率数据进行统计,提出了电阻率谱技术和分选指数的计算方法并对储层非均质性进行定量评价;李昌等[16]利用岩心、成像测井资料,基于分形理论计算电成像测井图像的分形维数来定量描述储层非均质性;蔺敬旗等[17]利用电成像测井的孔隙度谱及电阻率谱计算方法,定量表征了砂砾岩储层非均质性。
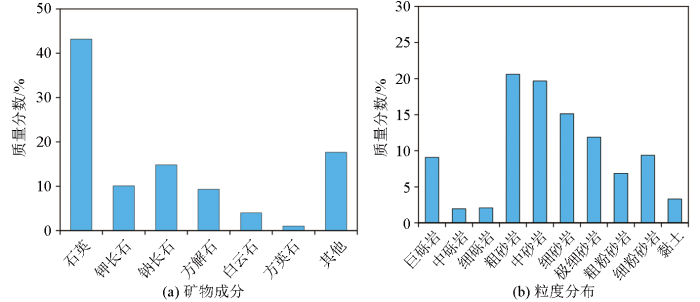
牛东地区侏罗纪储层岩性复杂,矿物成分多样,孔隙结构复杂,砂砾岩储层非均质性强,单一的表征参数无法对储层的非均质性进行全面评价。针对这一问题,本文将洛伦兹系数运用到电成像测井中,并引入集中程度函数,根据综合概率模型计算均值、方差、洛伦兹系数和集中程度函数,结合层次分析法,得到各个评价参数的权重,对储层非均质性进行定量评价,获得一种较为准确全面的层内非均质性评价标准。
1 研究区地质概况及储层特征
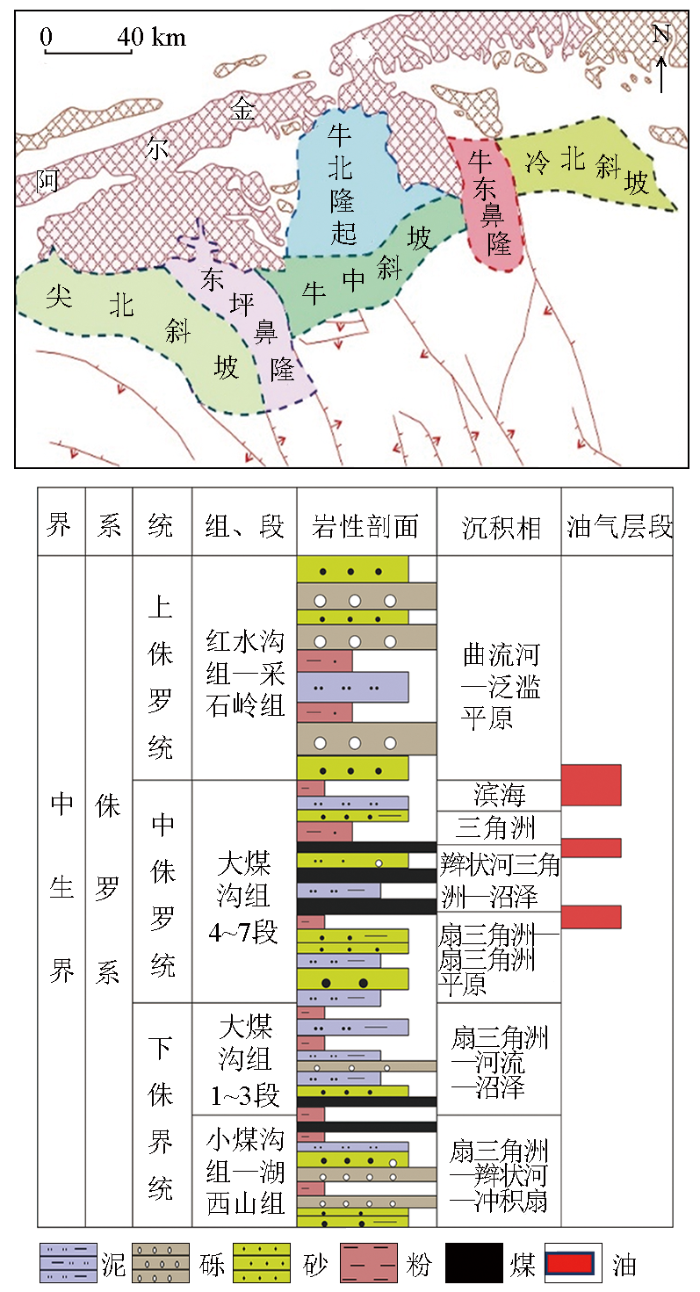
图1
图1
柴达木盆地牛东地区侏罗系构造位置及岩性柱状图
Fig.1
Structural location and lithologic histogram of Jurassic in Niudong Area, Qaidam Basin
图2
图3
图4
根据牛东地区毛管压力参数统计分析,砂砾岩储集层的排驱压力最低为0.042 MPa,最高为0.76 MPa;平均吼道半径最低为0.967 μm,最高为17.5 μm;最大进汞饱和度最低为58.9%,最高为80.1%;退汞效率最低为26.2%,最高为38.7%。毛管压力曲线参数变化较大,牛东地区砂砾岩储层孔隙结构非均质性强。
2 电成像测井孔隙度谱的计算方法
已有研究表明,电成像测井所测量的电阻率不是地层的真实电阻率。在电成像测井中,电流的流动方式、聚集以及探测深度与侧向测井相似,可选用浅侧向电阻率作为刻度标准[19]:
式中:Ri是在第i次钮扣电极刻度之后的电阻率;σi是对第i个钮扣电极进行预处理后的电导率;
电成像测井测量的电阻率反映储层冲洗带的信息,利用阿尔奇公式进行标定[20]:
式中:a、b为与岩性有关的系数;m为胶结指数;n为饱和度指数;φ为孔隙度;Sxo为冲洗带含水饱和度;Rxo为冲洗带电阻率;Rmf为泥浆溶液电阻率。再把刻度后的电阻率Ri代入计算,得到的孔隙度记作为φi,用常规浅侧向电阻率RLLS得到的孔隙度记作φ0,代入式(2)并整理得
再把式(1)代入式(3):
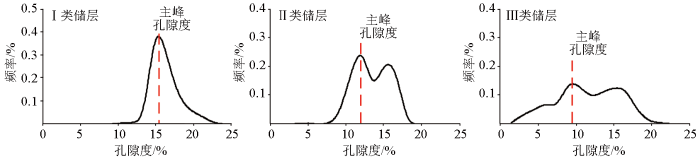
通常选取一个图像窗口,利用式(4)依次计算每个窗口中成像测井点的孔隙度,得到对应地层的孔隙度谱。应用此方法处理研究区的电成像资料,得到3种典型的孔隙度谱分布类型(图5):I类储层,孔隙度谱以单峰窄谱为主,谱峰靠前,储层较均一,主要为基质孔,物性偏差,非均质性弱;Ⅱ类储层,孔隙度谱以双峰为主,谱分布范围较宽,主峰相对靠前,相比次生孔隙,基质孔隙更为发育,非均质性一般;Ⅲ类储层,孔隙度谱以多峰宽谱为主,主峰相对靠后,相比基质孔隙,次生孔隙更为发育,非均质性强。
图5
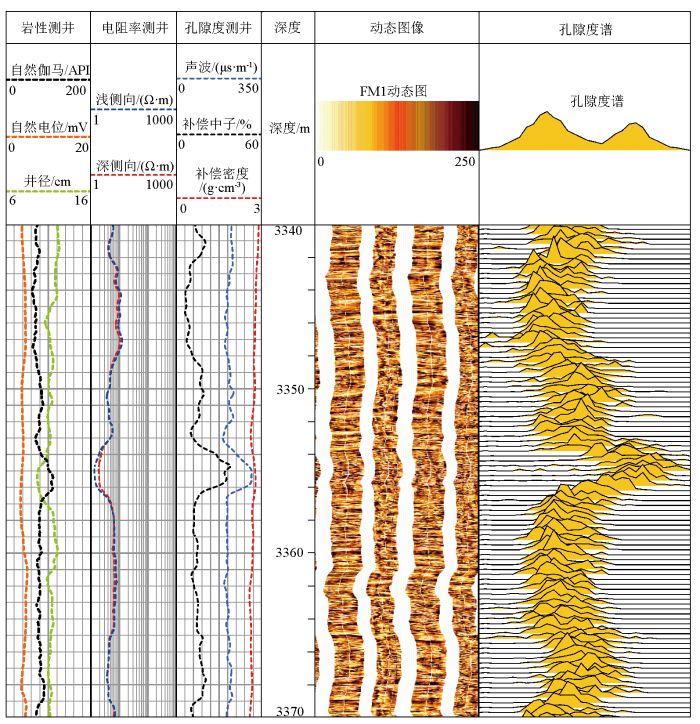
图6为牛东地区牛X井3 340~3 370 m井段储层孔隙度谱。牛X井孔隙度谱形态有单峰窄谱型、靠前的双峰宽谱型和靠后的多峰宽谱型。为了更精确评价砂砾岩复杂的孔隙结构和层内非均质性,对孔隙度谱做进一步分析。
图6
图6
牛东地区牛X井3340~3370 m砂砾岩孔隙度谱
Fig.6
Porosity spectrum of conglomerate 3340~3370 m from Niu X well in Niudong area
3 利用孔隙度谱评价储层层内非均质性
3.1 均值方差法评价储层层内非均质性
孔隙度谱均值(φa)指某一深度孔隙度的平均值,均值越大,储层特性越好;方差(
式中:φi是用电成像方法测量测井曲线的孔隙度;pi为其对应孔隙度的频数。
3.2 洛伦兹系数法评价层内非均质性
洛伦兹系数又叫基尼系数,最早是在经济学中使用,而后广泛用于评价储层的非均质性。洛伦兹系数法是利用储集层实测资料的真实孔隙度贡献曲线和理想储集层绝对均质曲线所围的区域,与储集层的绝对均质曲线和纵轴所围区域的面积之比来反映储集层的非均质性程度[22]。
将要计算的某深度段测井曲线的数值按一定顺序排列,得到y1,y2,…,yi,…,yn;它们的深度间隔为Δdi。令:
得到该深度段的洛伦兹曲线函数:
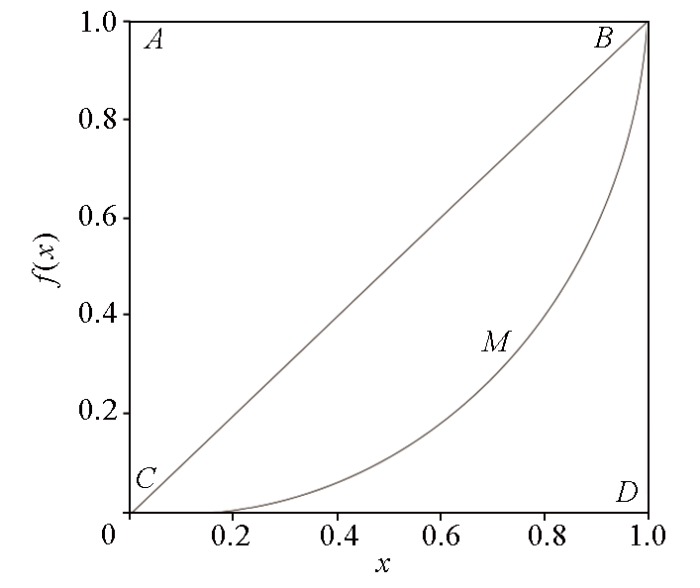
图7中,横轴x上的点代表测井值所在的深度间隔;纵坐标f(x)代表待求层段单条测井曲线上的测井值贡献;曲线BMC为洛伦兹曲线。洛伦兹曲线BMC和直线BC所围面积是反映储层非均质程度的重要指标,面积越大,非均质性也就越强。当曲线BMC与直线BC重合时,储层是完全均质的。洛伦兹系数值L可以表示为曲线BMC和直线BC的面积S1与三角形BCD的面积S2之比,即
图7
3.3 集中程度函数法评价储层层内非均质性
集中程度函数最初是在气象中表征云朵的分布情况,反映数据在一定程度上对平均态的偏离程度[23]:
式中:con(X)为集中程度函数;n为阶数,一般大于3;
4 综合概率法评价储层层内非均质性
综合概率法是通过对某一目标的多种不同评价方法进行综合评判,得出一种综合概率指标,从而对该储层进行分类。相对于单独的非均质性评价方法,综合概率法是一种更加准确全面的评价方法[24]。选择综合概率的方法,其关键在于选择综合概率函数的形式。本文选择的综合概率函数为
式中:K为综合概率指数;xi为孔隙度均值;yi为孔隙度的方差;zi为孔隙度的洛伦兹系数值;wi为孔隙度的集中程度函数值;a、b、m、n为各参数对应的权重。
4.1 利用层次分析法计算权重
表1 判断矩阵标度定义
Table 1
| 标度 | 含义 |
|---|---|
| 1 | 两个参数相比,具有相同重要性 |
| 3 | 两个参数相比,前者比后者稍重要 |
| 5 | 两个参数相比,前者比后者明显重要 |
| 7 | 两个参数相比,前者比后者强烈重要 |
| 9 | 两个参数相比,前者比后者极端重要 |
| 2,4,6,8 | 表示上述相邻标度的中间值 |
| 倒数 | 与上述情况相反 |
表2 参数权重的配对比较矩阵
Table 2
| 参数 | 均值 | 方差 | 洛伦兹 系数 | 集中程 度函数 | 权重 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 均值 | 1 | 1/3 | 1/8 | 1/7 | 0.0461 |
| 方差 | 3 | 1 | 1/7 | 1/5 | 0.0898 |
| 洛伦兹系数 | 8 | 7 | 1 | 2 | 0.5319 |
| 集中程度函数 | 7 | 5 | 1/2 | 1 | 0.3322 |
根据研究区地质特征,选取以上4个参数来融合非均质综合指数,以此来定量表征储层层内非均质性。由于所选取的参数具有不同的尺度,需要将其进行归一化处理:
式中:fi为归一化后的值;Xi为待处理值;Xmin为待处理参数组的最小值;Xmax为待处理参数组的最大值;p、q为常数,也就是处理后所需要的范围,这里取p=1,q=0。
4.2 利用综合概率法进行储层分类
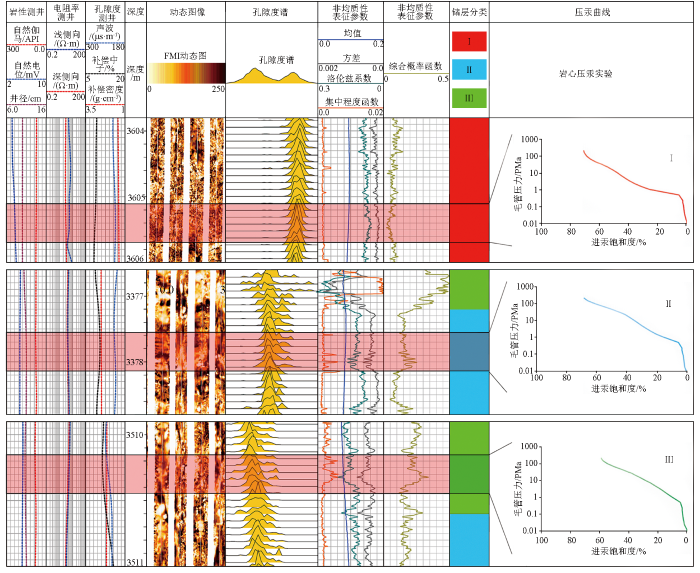
将储层孔隙度均值、方差、洛伦兹系数和集中程度函数归一化处理后,根据权重计算得到的综合概率K,当K≤0.07时为Ⅰ类储层,0.07<K≤0.2时为Ⅱ类储层,K>0.2时为Ⅲ类储层。对牛X井进行综合概率法层内非均质性评价,效果如图8所示。图中给出了均值、方差、洛伦兹系数和集中程度函数4种非均质性表征参数曲线,还给出了综合概率函数曲线、储层分类结果以及利用压汞实验的毛管压力曲线,用于对分类效果进行验证。根据解释结果,3 605.32 m为I类储层,排驱压力和中值压力均较小,毛管压力曲线较为平缓,非均质性弱;3 377.94 m为Ⅱ类储层,排驱压力较低,但中值压力缓升高,毛管压力曲线缓上升,非均质性一般;3 510.30 m为Ⅲ类储层,排驱压力和中值压力均偏高,毛管压力曲线平缓段变短,非均质性强。
图8
图8
牛X井侏罗纪储层非均质性评价结果
Fig.8
Results of Jurassic reservoir non-homogeneity evaluation in Niu X well
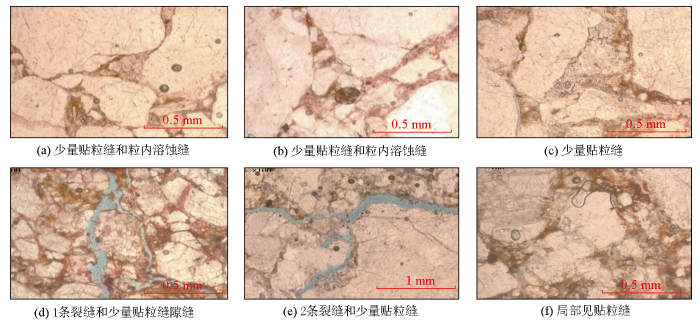
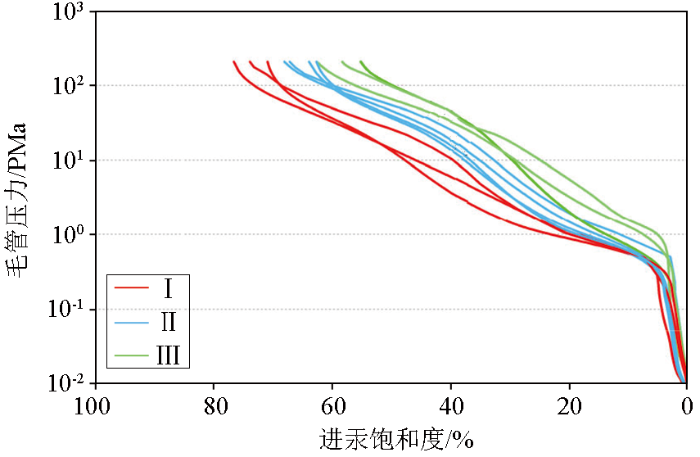
将牛X井的毛管压力曲线按照综合概率法解释结果进行分类(图9),并结合储层的粒度分析等资料对三类储层特征进行评价(表3)。I类储层综合概率值小于0.07,孔喉连通性较好,为粗歪度,分选性较好,孔喉半径较大,表明储层的孔隙结构和渗流能力好,是本地区最好的孔隙结构类型,非均质性弱;以长石岩屑砂岩为主,含少量砾石,填隙物为泥质和方解石,碎屑颗粒破碎,见少量贴粒缝和粒内溶蚀缝。Ⅱ类储层综合概率值在0.07~0.2之间,孔喉连通性一般,为中等歪度,分选性中等,表明储层的孔隙结构和渗流能力中等,是本地区主要的储层,非均质性一般;为泥质含砾不等粒长石岩屑砂岩,颗粒分选较差,填隙物为泥质和方解石,碎屑颗粒破碎,未见孔隙。Ⅲ类储层综合概率值大于0.2,孔喉连通性差,为细歪度,分选性较差,表明储层的孔隙结构和渗流能力差,非均质性强;以含泥砾质粗巨粒长石岩屑砂岩为主,填隙物为泥质和方解石,颗粒破碎剧烈,未见孔隙。
图9
图9
牛X井岩心压汞毛管压力曲线
Fig.9
Mercury capillary pressure curve of core injection in Niu X well
表3 综合概率值划分储层类型
Table 3
| 储层类型 | 岩性 | 洛伦兹系数 | 集中程度函数 | 综合概率函数 | 非均质性程度 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| I | 泥质长石岩屑砂岩 | ≤0.1 | ≤0.001 | ≤0.07 | 弱 | ||
| Ⅱ | 砾质长石岩屑砂岩 | 0.1~0.15 | 0.001~0.002 | 0.07~0.2 | 一般 | ||
| Ⅲ | 含泥砾不等粒砂岩 | >0.15 | >0.002 | >0.2 | 强 |
5 结论
1)研究区岩性复杂,矿物成分多样,储层孔隙发育裂缝、贴粒缝和粒内溶蚀缝等多种类型,物性发育中等,孔喉类型复杂,毛管压力曲线参数变化较大,均表现出强非均质性。
2)引入洛伦兹系数和集中程度函数,根据电成像测井资料得到孔隙度谱,结合层次分析法计算各指标权重,利用综合概率函数对储层进行分类。该方法在柴达木盆地牛X井侏罗系储层非均质性评价和综合定量表征中取得较好效果。
3)研究区储层按照非均质性程度可划分为3类:I类(K≤0.07),孔喉连通性较好,粗歪度,分选性较好,为弱非均质性储层;Ⅱ类(0.07<K≤0.2),孔喉连通性一般,中等歪度,分选性中等,为中等非均质性储层;Ⅲ类(K>0.2),孔喉连通性差,细歪度,分选性较差,为强非均质性储层。研究区储层主要发育强非均质性类型和中等非均质性类型。
参考文献
准噶尔盆地玛湖凹陷百口泉组砂砾岩非均质储层孔隙结构特征与成因
[J].
Pore structure characteristics and genesis of heterogeneous conglomerate reservoir of Baikouquan Formation in Mahu Sag,Junggar Basin
[J].
致密储层孔隙结构研究综述
[J].
Research into the pore structure of tight reservoirs:A review
[J].
Intra-layer heterogeneity of sandstone with different origins in deep-water environment and its causes
[J].DOI:10.1016/j.suscom.2018.11.003 URL [本文引用: 1]
微观非均质性对砂砾岩储层致密化的影响机理:以准噶尔盆地东道海子凹陷DN8井区上二叠统梧桐沟组为例
[J].
Influence mechanism of micro-heterogeneity on conglomerate reservoir densification:A case study of upper Permian Wutonggou formation in DN8 area of dongdaohaizi sag,Junggar Basin
[J].
储层宏观非均质性定量表征研究
[J].
DOI:10.7623/syxb200806015
[本文引用: 1]

针对当前储层宏观非均质性定量表征参数计算数值无界、表征角度各异、表征方法定量化程度不高等问题,提出了基于储层物性参数累积分布特征的宏观非均质定量表征新参数。通过对任意一组空间分布相对均匀的渗透率数据降序排列,计算出渗透率贡献百分数及其对应的序数百分数,并在直角坐标系中绘制出渗透率累积分布曲线。通过倒数坐标变换,将不同形态的渗透率累积分布曲线转换成斜率为0~1的直线,将直线斜率值定义为储层非均质程度系数。该值与储层非均质程度成反比。应用结果表明,非均质程度系数可应用于各种级次储层宏观非均质程度的定量评价。
Research on quantitative characterization of macroscopic heterogeneity of reservoir
[J].
DOI:10.7623/syxb200806015
[本文引用: 1]

There are some defects in the existing evaluation systems of macroscopic heterogeneity such as its unbounded parameters, fussy characterization and low degree of quantification. Based on the cumulative distribution of reservoir property, a new parameter named as coefficient of heterogeneity degree was proposed to quantitatively characterize the macroscopic heterogeneity degree. The homogeneous spatial distribution of a group of permeability data was arranged in descending order. The percentage of permeability contribution and the corresponding ordinal number were obtained and used to draw the cumulative distribution curve of permeability in Cartesian coordinate system. By means of coordinate conversion and regression, the different forms of cumulative distribution curves were converted into straight lines with bounded slope value from 0 to 1. The slope value was defined as coefficient of heterogeneity degree. The slope value is inverse proportion to the heterogeneity degree of reservoir. The coefficient of heterogeneity degree is favorable for the quantitative evaluation of macroscopic heterogeneity degree in different heterogeneity hierarchy.
柴北缘牛东地区砂砾岩储层特征及分类评价
[J].
Characteristics and classification of glutenite reservoirs in Niudong area,north margin of Qaidam Basin
[J].
苏里格气田低渗透储层微观孔隙结构特征及其分类评价方法
[J].以苏里格气田盒8段和山1段为例,开展了低渗透储集层微观孔隙结构特征的研究工作。以取心井压汞测试、扫描电镜、铸体薄片等分析化验资料为基础,通过分析储层的孔隙结构和孔隙类型,将储层微观孔隙结构分为4类,分析了各类微观孔隙结构的特征。沉积环境和成岩作用的双重影响使得盒8段和山1段的储层孔隙结构非常复杂,造成本区储层特低渗透率的主要成因机制为成岩期强烈的压实作用及各种自生矿物的充填和胶结作用。主要的储集空间为次生孔隙,孔喉组合主要为低孔小喉型。应用聚类分析和Bayes判别分析方法,选取7种宏观和微观非均质参数,在建立4类微观孔隙结构判别函数的基础上,对苏里格气田进行了微观孔隙结构识别,绘制了主力小层储层综合评价图。分析表明:Ⅰ类、Ⅱ类储层为研究区的优质储层,是今后低渗透盒8段和山1段的主要勘探开发目标。
Characteristics of pore structure and reservoir evaluation of low permeability reservoir in Sulige gas field
[J].
柳江盆地二叠系山西组露头致密砂岩储层非均质性表征方法
[J].
Characterizing the heterogeneity of tight sandstone in outcropped Permian Shanxi Formation,Liujiang Basin
[J].
储层非均质性定量研究的新方法
[J].
A new method for quantitatively studying reservoir heterogeneity
[J].
碳酸盐岩缝洞型储层测井评价方法
[J].
The logging evaluation methods for fractured-vuggy carbonate reservoirs
[J].
基于斯通利波及电成像测井数据对火成岩裂缝地层的特征分析
[J].
Analysis of fracture formation characteristics of igneous rock based on stoneley wave and electrical imaging logging
[J].
Reservoir heterogeneity and fracture parameter determination using electrical image logs and petrophysical data:A case study,carbonate Asmari Formation,Zagros Basin,SW Iran
[J].
DOI:10.1007/s12182-019-00413-0
[本文引用: 1]

Assessment of reservoir and fracture parameters is necessary to optimize oil production, especially in heterogeneous reservoirs. Core and image logs are regarded as two of the best methods for this aim. However, due to core limitations, using image log is considered as the best method. This study aims to use electrical image logs in the carbonate Asmari Formation reservoir in Zagros Basin, SW Iran, in order to evaluate natural fractures, porosity system, permeability profile and heterogeneity index and accordingly compare the results with core and well data. The results indicated that the electrical image logs are reliable for evaluating fracture and reservoir parameters, when there is no core available for a well. Based on the results from formation micro-imager (FMI) and electrical micro-imager (EMI), Asmari was recognized as a completely fractured reservoir in studied field and the reservoir parameters are mainly controlled by fractures. Furthermore, core and image logs indicated that the secondary porosity varies from 0% to 10%. The permeability indicator indicates that zones 3 and 5 have higher permeability index. Image log permeability index shows a very reasonable permeability profile after scaling against core and modular dynamics tester mobility, mud loss and production index which vary between 1 and 1000 md. In addition, no relationship was observed between core porosity and permeability, while the permeability relied heavily on fracture aperture. Therefore, fracture aperture was considered as the most important parameter for the determination of permeability. Sudden changes were also observed at zones 1-1 and 5 in the permeability trend, due to the high fracture aperture. It can be concluded that the electrical image logs (FMI and EMI) are usable for evaluating both reservoir and fracture parameters in wells with no core data in the Zagros Basin, SW Iran.
电成像测井处理新技术在储层评价方面的应用
[J].
Application of new processing technology of electrical imaging logging in reservoir evaluation
[J].
电成像测井储层非均质性评价方法在川东北G地区FC段地层的应用
[J].
The application of the reservoir heterogeneity evaluate method with microresistivity image log in FC formation of G region in northeastern Sichuan
[J].
砾岩储层电成像测井表征方法及应用——以准噶尔盆地玛湖凹陷砾岩油藏为例
[J].
Characterization method and application of electrical imaging logging in conglomerate reservoir:A case study in Mahu Sag of Junggar Basin
[J].
柴达木盆地油气聚集规律及勘探前景
[J].
DOI:10.7623/syxb200304001
[本文引用: 1]

柴达木盆地位于青藏高原北部,是中国7个大型内陆含油气盆地之一.发育有石炭系、侏罗系、第三系和第四系4个大含油气系统,形成了北缘、西部和中部3个勘探领域,共有油气资源量42×10<sup>8</sup>t(油当量),油气聚集受烃源岩、构造叠加及储集层性质的控制.该盆地勘探程度较低,具有较大的勘探潜力和广阔的勘探前景,是中国最有油气勘探潜力的盆地之一.根据盆地内不同地区的油气藏控制因素,盆地的西部南区、西北缘的阿尔金山前、北缘的冷湖三号等地区是碎屑岩油藏勘探的重要领域,西部北区是非常规储层油藏的重点勘探区,中部、西部第三系和北缘深层是天然气新的勘探领域.
Hydrocarbon accumulation and exploration potential in Qaidam Basin
[J].
基于电成像测井孔隙度分析技术的火山岩孔隙径向非均质性研究
[J].
DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1000-1441.2016.03.016
[本文引用: 1]

火山岩储集层孔隙结构复杂,孔隙发育类型多,产能预测困难。为此,根据电成像测井的方法原理,结合Archie公式和常规测井资料,将火山岩层的电成像数据转换为核磁区间孔隙度类似的形式,通过与核磁区间孔隙度对比,得到火山岩储层的孔隙区间特征。在此基础上,针对火山岩复杂的孔隙类型,对孔隙区间展开进一步分析,得到不同孔隙区间所占的比例,结合计算的孔隙度变异系数,得到火山岩储集层的孔隙区间特征及孔隙径向非均质性特征,进而发现影响火山岩储层产能的隔挡层的存在,为火山岩次生孔隙发育情况及火山岩储集层产能预测提供了参考依据。
The radial pore heterogeneity of volcanic reservoir based on the porosity analysis of micro-electric imaging logging
[J].
DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1000-1441.2016.03.016
[本文引用: 1]

The volcanic reservoir is characterized by complex pore structures and various pore types; therefore,the productivity forecast is difficult.In terms of the principles of micro-electric imaging logging,combining with the Archie formula and conventional logging data,the micro-electric imaging data of volcanic formations is transformed into the form similar to the nuclear magnetic interval porosity.The porosity interval characteristics of volcanic reservoir are obtained by comparing with nuclear magnetic interval porosity.On this basis,aiming at the complex pore types existing in volcanic reservoir,we carry out further analysis on porosity intervals and achieve the proportion of different porosity intervals.Integrating with the calculated porosity variation coefficient,the characteristics of porosity intervals and radial pore heterogeneity are achieved.As a result,the interlayers in volcanic reservoir are identified.The research results provide reference for the development of secondary pores in volcanics and productivity forecast of volcanic reservoirs.
致密砂岩储层的相渗特征与岩电参数的关系研究
[J].
Relationship between relative permeability and electrical parameters of tight sandstone reservoirs
[J].
电成像孔隙度谱在砂砾岩有效储层识别的应用
[J].
Application of electrical imaging logging porosity spectrum in identification of effective reservoir in sandy conglomeratic reservoirs
[J].
利用测井曲线的洛伦兹系数评价地层的非均质性
[J].
Evaluation of formation heterogeneity using Lorentz coefficient of logging curves
[J].
集中程度函数及其初步应用
[J].
Concentrative function and its primary application
[J].