0 引言
裂缝型储层是非常规油气勘探开发的重要对象,含裂缝储层以及缝隙流体反演也已成为研究的重点。准确高效识别含裂缝储层的缝隙流体并评估其反演不确定性具有重要应用价值,对非常规油气勘探开发提供一定指示作用。
对于含裂缝储层流体识别,其关键是构建一个合理且敏感的流体指示因子。对于各向同性岩石,基于Gassmann[1]的孔隙弹性理论,从地震数据直接估算各种流体敏感参数已实现含油气储层流体识别。其中Russell等[2-3]提出了基于纵波阻抗与横波阻抗差值的流体因子,业界将其定义为Russell流体因子并广泛应用。Yin等[4]根据一个严格的经验关系式将Russell流体因子解耦并定义了新的流体指示因子。对于各向异性含裂缝岩石,由于地震波对含裂缝岩石中传播方向的依赖性会导致各向异性现象,含裂缝储层表现出的较强各向异性引起其地震响应对地震波入射角以及方位角的变化更为敏感,提高了各向异性流体因子反演的可行性。Schoenberg和Douma[5]确定了两个裂缝弱度参数的比值为流体指示因子,该各向异性流体指示因子已被广泛应用。Shaw和Sen[6]基于垂直裂缝介质假设,实现流体指示因子地震AVOA预测。van der Neut等[7]将储层AVO梯度项与各向异性缝隙流体联系起来,引入了各向异性流体指示因子的反演理论。陈怀震等[8]综合分析了各向同性介质下的流体识别方法,从岩石物理模型出发预测获得各向异性介质流体因子。陈怀震等[9]建立了各向异性的岩石物理模型,并通过岩石物理分析了缝隙流体与储层微观物性参数之间的关系,最终结合AVAZ反演得到了缝隙流体因子。谢春辉等[10]认为利用Ruger提出的各向异性方程反演得到的各向异性梯度参数,与各向同性梯度参数的比值对储层流体敏感并将其定义为流体指示因子。孙炜等[11]在直角坐标系考虑各向异性参数与Russell流体因子的理论,并定义了一种新的流体指示因子。Pan等[12]提出了拟法向弱度以及拟切向弱度的概念,并基于EIVOA反演得到流体模量。印兴耀等[13]弹性参数以及各向异性参数的组合定义了一个各向异性流体因子,并应用五维地震数据实现流体因子的反演。
目前,各向异性参数反演方法主要有确定性反演以及概率化反演两种。确定性反演虽然可以通过各种全局优化算法预测最优反演参数,但难以满足复杂地下介质的综合识别[14]。尤其是随着裂缝介质复杂程度的提高,待反演参数不断增加,增加了地震反演的不稳定性与不确定性,亟需结合概率化反演算法在准确预测模型参数的同时,分析反问题的解的不确定性[15]。统计学反演主要是基于贝叶斯理论获得反演参数的最优解和置信区间,用于参数不确定性分析[16-17]。最大后验概率(MAP)解是统计学反演中最常用的算法,其引入待估计参数的先验分布信息,对最大似然估计解进行了改进,有效地缓解了地震反演的不适定性[18]。然而,MAP解只适用于后验概率密度分布为显式,即后验概率密度分布可以用具体的方程表征的情况,因此很难解决非线性反演问题[19]。与MAP解不同,MCMC算法不仅可以解决非线性反演问题,还适用于隐式解的反演,其应用较为广泛。理论上,MCMC算法可以获得模型参数的全局最优解,但存在的问题是算法启动缓慢,优化过程缓慢,即使得到最优解也会继续搜索,计算效率较低[20]。
本文以线性滑动模型为基础,基于准裂缝法向弱度以及准裂缝切向弱度定义了一个新的缝隙流体指示因子,结合散射理论和Born近似方程推导了包含准裂缝法向弱度以及准裂缝切向弱度的各向异性反射系数方程,应用改进的全局自适应MCMC反演算法实现缝隙流体指示因子叠前地震反演。
1 缝隙流体指示因子预测方法原理
在均匀各向同性背景夹杂一组对称轴为水平方向的裂缝可看作等效HTI(horizontal transversely isotropy)介质。基于线性滑动理论模型[21],HTI刚度系数矩阵可表示为:
式中:
Schoenberg 和 Sayers认为
根据方程(2)和方程(3),并参照Schoenberg 和 Sayers的理论,定义新的缝隙流体指示因子为:
式中:
式中:
式中:
将方程(1),方程(2),方程(4),方程(6),方程(7)代入方程(5)即可得到缝隙流体指示因子各向异性反射系数方程具体表达形式:
式中:
表1 双层模型参数
Table 1
| 层1 | 58 | 18 | 2.6 | 0 | 0 |
| 层2 | 78 | 23 | 2.5 | 1.15 | 1.07 |
图1
2 缝隙流体指示因子贝叶斯反演方法
本文的反问题可以写成:
式中:
反问题的解由模型参数的后验分布给出,该后验分布与贝叶斯框架下的先验分布和似然函数的乘积成正比。后验分布可表示为
在本研究中,我们假设噪声满足高斯分布,似然函数可表示为
待反演参数的先验信息,可从测井资料、岩心资料和其他地质资料中获得[24]。本文假设待反演的五个参数满足高斯分布,参数之间相互独立,因此先验函数可表示为
基于统计学经典的贝叶斯理论,本文在一般的MCMC反演算法的基础上引入全局自适应Metropolis算法,全局自适应策略的目的是用所有已经接受的建议修改提议分布,实现全局最优解的寻找与判别。改进的全局自适应MCMC反演算法总结如下:
我们假设总迭代次数
式中:
假设马尔可夫链在第
接受概率由Metropolis-Hasting算法给出:
一般来说,马尔可夫链的收敛效率取决于建议分布与目标分布的匹配程度。相较于一般的MCMC反演算法采用固定的提议分布,全局自适应策略能够根据已生成的样本点有效调整建议分布,使其能够有效拟合到目标分布,以得到全局最优解。
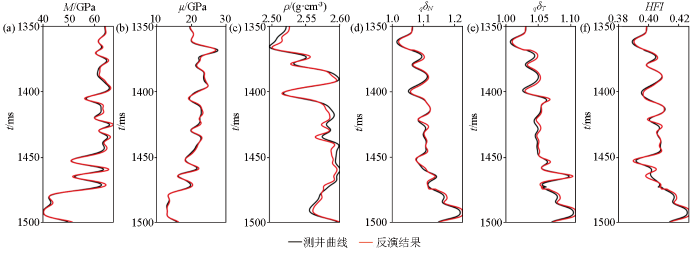
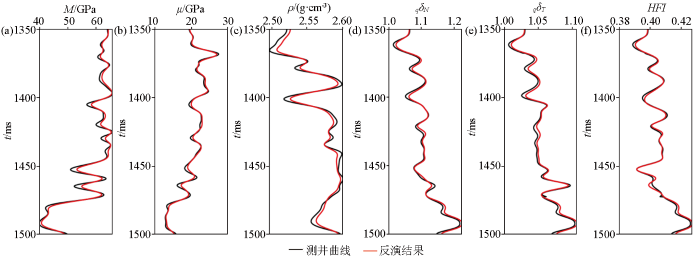
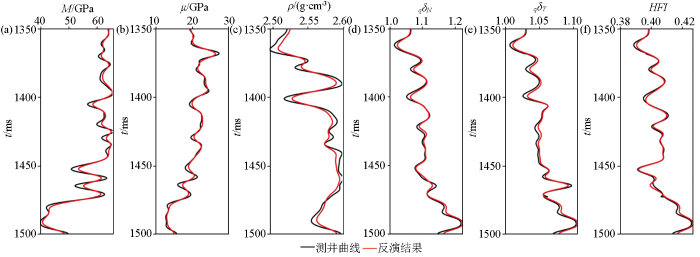
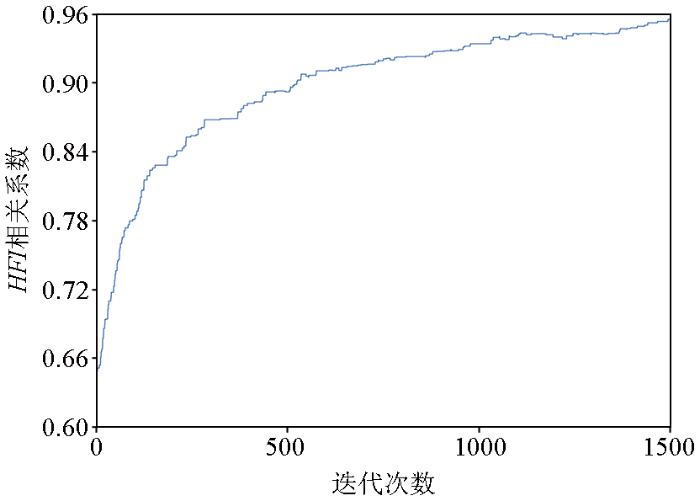
图2,图3,图4分别展示了不同信噪比情况下的纵波模量、剪切模量、密度、准裂缝法向弱度、准裂缝切向弱度以及流体指示因子HFI的反演结果。图2是无噪情况下5个待反演参数的反演结果,其中黑色曲线代表待反演参数的实际测井曲线,红色曲线代表模型参数反演结果。为了验证反演结果的鲁棒性,不断加入高斯噪声,图3,图4分别表示信噪比为5∶1和2∶1时的反演结果。从3个图中我们可以看出,在无噪时纵波模量、剪切模量、准裂缝法向弱度、准裂缝切向弱度以及HFI的反演结果曲线与实际井数据吻合程度较高,均达到了90%以上,密度的反演结果与其他参数相比较差,但也实现了85%的吻合度,我们认为密度参数的反演结果稍差是因为其在上下界面处变化较小,在反射系数方程中贡献度较低,导致了反演结果存在一定偏差。即使信噪比为2∶1时,纵波模量、剪切模量、准裂缝法向弱度、准裂缝切向弱度以及HFI的反演结果与井曲线的误差也能控制在20%以内,这也验证了本文所提出的反演方法的适用性与抗噪性。以缝隙流体因子HFI为例,将HFI参数的收敛过程展示如图5所示,纵坐标是反演结果与井曲线的相关系数,横坐标为迭代次数,可以看出迭代次数为1 300次时,反演结果就已实现收敛。
图2
图2
无噪情况下纵波模量(a)、剪切模量(b)、密度(c)、准裂缝法向弱度(d)、准裂缝切向弱度(e)以及流体指示因子HFI(f)的反演结果
Fig.2
Inversion results of P-wave modulus(a),shear modulus(b),density(c),normal weakness of quasi-fracture(d),tangential weakness of quasi-fracture(e),and fluid indicator factor HFI(f) without noise
图3
图3
信噪比为5∶1情况下纵波模量(a)、剪切模量(b)、密度(c)、准裂缝法向弱度(d)、准裂缝切向弱度(e)以及流体指示因子HFI(f)的反演结果
Fig.3
Inversion results of P-wave modulus(a),shear modulus(b),density(c),normal weakness of quasi-fracture(d),tangential weakness of quasi-fracture(e) and fluid indicator factor HFI(f) when the signal-to-noise ratio is 5∶1
图4
图4
信噪比为2∶1情况下纵波模量(a)、剪切模量(b)、密度(c)、准裂缝法向弱度(d)、准裂缝切向弱度(e)以及流体指示因子HFI(f)的反演结果
Fig.4
Inversion results of P-wave modulus(a),shear modulus(b),density(c),normal weakness of quasi-fracture(d),tangential weakness of quasi-fracture(e) and fluid indicator factor HFI(f) when the signal-to-noise ratio is 2∶1
图5
3 实际资料及应用
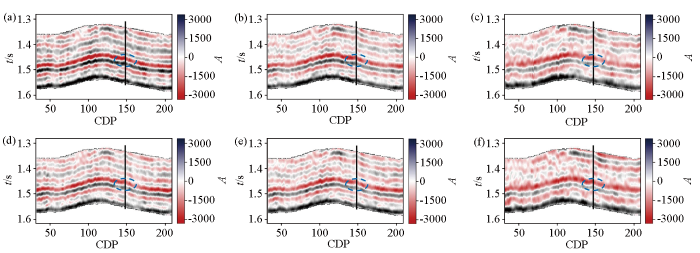
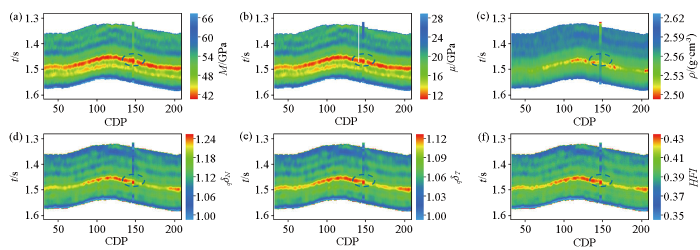
选取中国四川盆地某地区的方位地震资料来验证本文所提出的反演方法的实用性。该地区优质页岩分布面积广、成藏条件较好、储层质量好,极具勘探开发前景,且本研究应用的井钻遇油气层。选择不同方位角的叠前地震实测数据进行应用,叠前地震数据在反演前已经过处理,我们假设处理后的地震数据可以忽略层间多次波以及波形转换效应。此外,我们根据井数据计算得到的纵波模量、剪切模量、密度、准裂缝法向弱度、准裂缝切向弱度以及缝隙流体指示因子HFI建立低频模型,作为反演的约束并计算模型参数先验分布的均值以及方差。本文应用的方位地震数据45°以及135°,入射角为6°、18°以及30°,叠加地震剖面如图6所示,其中黑色实线表示井位置,蓝色虚线为目标层段。图7显示了纵波模量、剪切模量、密度、准裂缝法向弱度、准裂缝切向弱度以及缝隙流体指示因子HFI的实际资料反演结果。我们发现,目标层的纵波、剪切体积模量显示出较低的值,准裂缝法向弱度、准裂缝切向弱度以及HFI显示出较高的值,法向和切向裂缝弱度的反演结果表明该层的裂缝发育,HFI的反演结果表明该层裂缝中充填有流体,综合分析后我们可以得到在目的层发育有裂缝,且裂缝内充填有缝隙流体,成像测井解释结果为该目的层发育有大量裂缝,钻井结果表明在目的层钻遇油气层,反演结果与测井解释结果较为符合,验证了反演方法的准确性与适用性。
图6
图6
方位地震数据
a—入射角6°、方位角45°;b—入射角18°、方位角45°;c—入射角30°、方位角45°;d—入射角6°、方位角135°;e—入射角18°、方位角135°;f—入射角30°、方位角135°
Fig.6
Azimuth seismic data
a—angle of incidence 6°,azimuth 45°;b—angle of incidence 18°,azimuth 45°;c—angle of incidence 30°,azimuth 45°;d—angle of incidence 6°,azimuth 135°;e—angle of incidence 18°,azimuth 135°;f—angle of incidence 30°,azimuth 135°
图7
图7
纵波模量(a)、剪切模量(b)、密度(c)、准裂缝法向弱度(d)、准裂缝切向弱度(e)以及流体指示因子HFI(f)的反演结果
Fig.7
Inversion results of P-wave modulus(a),shear modulus(b),density(c),normal weakness of quasi-fracture(d), tangential weakness of quasi-fracture(e),and fluid indicator factor HFI(f)
4 结论
随着油气勘探开发技术的进步,非常规资源勘探前景优越,裂缝型储层作为重点开发对象受到广泛关注。如何构建一个合理的流体因子,以精确识别裂缝性储层缝隙流体至关重要,本文对此做出一定的研究与深入,结论总结如下:
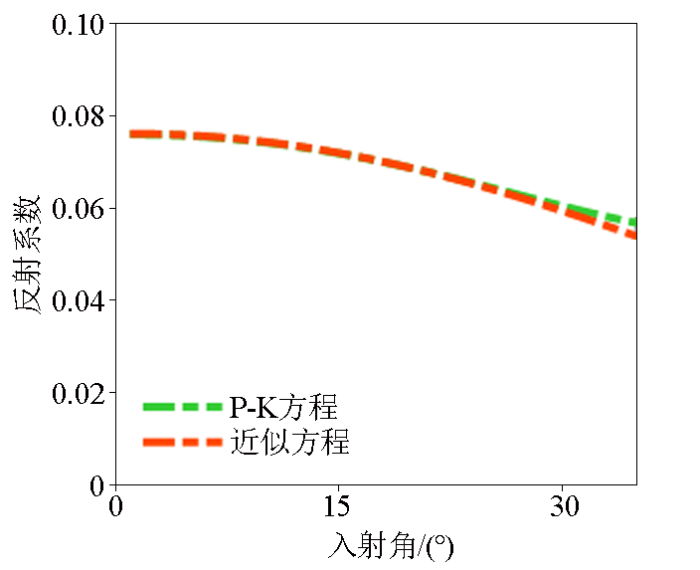
1)定义了新的缝隙流体指示因子,推导了包含缝隙流体因子的各向异性反射系数近似方程,在入射角为0°~30°范围内与P-K方程吻合较好。
2)应用改进的全局自适应MCMC反演算法反演,虽然效率上有一定提升,但仍有很大的优化空间。
3)成像测井解释结果表明目的层发育有大量裂缝,且钻井结果表明目的层钻遇油气,与反演结果认识相同,验证了本文提出的缝隙流体指示因子能够有效指示储层流体分布情况以及本文所提出的反演方法的准确性以及适用性。
参考文献
Elastic waves through a packing of spheres
[J].
DOI:10.1190/1.1437718
URL
[本文引用: 1]

Based on a theory of porous solids previously developed by the author, the elasticity of a hexagonal close packing of equal spheres is treated. The packing is anisotropic and because of the weight of the spheres, also inhomogeneous. The velocities of propagation of elastic waves have been calculated for evacuated interspaces and for interspaces filled with a liquid or gas. In the case of evacuated or air‐filled interspaces, the wave rays and travel times have been computed. The packing which has been treated may be of use as a model for a dry or wet loose material such as gravel or sand. Though the model is very simplified, the results obtained show some typical effects such as anisotropy, in homogeneity, and a 90° angle of emergence.
Fluid-property discrimination with AVO:A Biot-Gassmann perspective
[J].
DOI:10.1190/1.1543192
URL
[本文引用: 1]

This analysis draws together basic rock physics, amplitude variations with offset (AVO), and seismic amplitude inversion to discuss how fluid‐factor discrimination can be performed using prestack seismic data. From both Biot and Gassmann theories for porous, fluid‐saturated rocks, a general formula is first derived for fluid‐factor discrimination given that both the P and S impedances are available. In essence, the two impedances are transformed so that they better differentiate between the fluid and rock matrix of the porous medium. This formula provides a more sensitive discriminator of the pore‐fluid saturant than the acoustic impedance and is especially applicable in hard‐rock environments. The formulation can be expressed with either the Lamé constants and density, or the bulk and shear moduli and density. Numerical and well‐log examples illustrate the applicability of this approach. AVO inversion results are then incorporated to show how this method can be implemented using prestack seismic data. Finally, a shallow gas‐sand example from Alberta and a well‐log example from eastern Canada are shown to illustrate the technique.
Linearized AVO and poroelasticity
[J].
DOI:10.1190/1.3555082
URL
[本文引用: 1]

The technique of amplitude variation with offset (AVO) allows geoscientists to extract fluid and lithology information from the analysis of prestack seismic amplitudes. Various AVO parameterizations exist, all of which involve the sum of three weighted elastic-constant terms. In present-day AVO approaches, the weighting terms involve either knowledge of the incidence angle only, or knowledge of both the incidence angle and the in situ VP/VS ratio. We have used the theory of poroelasticity to derive a generalized AVO approximation that provides the estimation of fluid, rigidity, and density parameters. We have combined two previously independent AVO formulations, thus reducing, instead of adding to, the total number of formulations. This new approach requires knowledge of a third parameter to compute the weights: the dry-rock VP/VS ratio. We have derived a new equation and applied it to model and real data sets. The new formulation has allowed us to estimate fluid properties of the reservoir in a more direct manner than previous formulations.
Bayesian inversion for effective pore-fluid bulk modulus based on fluid-matrix decoupled amplitude variation with offset approximation
[J].
DOI:10.1190/geo2013-0372.1
URL
[本文引用: 1]

Fluid indicators estimated from seismic data play important roles in reservoir characterization and prospect identification. Traditionally, there are a variety of fluid indicators proposed, but they are very likely to provide ambiguous results for fluid identification due to the fact that their sensitivity is dependent upon the mixed effect of pore fluid and rock porosity. To raise the sensitivity of fluid indication, we used the effective pore-fluid bulk modulus as a fluid indicator. Starting with the poroelastic amplitude variation with offset (AVO) theory and the corresponding rock-physics model with the homogeneous sorting trend, we derived a new AVO approximation that allowed us to estimate the effective pore-fluid bulk modulus in a direct fashion. The inversion for the fluid indicator is formulated in Bayesian framework with the Cauchy distribution as a prior constraint. We tested the method on synthetic data and analyzed the feasibility and stability of the inversion. A field data example shows that the effective pore-fluid bulk modulus can reduce the ambiguity caused by the rock porosity and improve the quality of fluid discrimination in a clastic reservoir. Further research needs to be done on the reservoirs that do not fit the rock-physics model without a sorting trend.
Elastic wave propagation in media with parallel fractures and aligned cracks
[J].DOI:10.1111/gpr.1988.36.issue-6 URL [本文引用: 1]
Born integral,stationary phase and linearized reflection coefficients in weak anisotropic media
[J].DOI:10.1111/gji.2004.158.issue-1 URL [本文引用: 1]
Estimation of the fluid indicator from azimuthal AVO gradient variations at a fractured reservoir
[C]//
基于方位各向异性弹性阻抗的裂缝岩石物理参数反演方法研究
[J].
DOI:10.6038/cjg20141029
[本文引用: 1]

裂缝储层岩石物理参数的准确获得对地下裂缝预测具有重要意义,而叠前地震反演是获得裂缝岩石物理参数的有效手段.本文从裂缝岩石物理等效模型的构建出发,从测井数据上估测了裂缝岩石物理参数,通过推导含裂缝岩石物理参数的方位各向异性弹性阻抗公式,探讨了基于方位各向异性弹性阻抗的裂缝岩石物理参数地震反演方法.实际工区地震数据应用表明,基于方位各向异性弹性阻抗的裂缝岩石物理参数反演方法合理、可靠,可以降低裂缝岩石物理参数估测的不确定性,为地下裂缝预测提供有力的依据.
Seismic inversion for fracture rock physics parameters using azimuthally anisotropic elastic impedance
[J].
基于各向异性岩石物理的缝隙流体因子AVAZ反演
[J].
AVAZ inversion for fluid factor based on fracture anisotropic rock physics theory
[J].
裂缝型储层流体识别方法
[J].
DOI:10.6038/cjg20150527
[本文引用: 1]

裂缝型储层的描述包括预测裂缝分布特征和识别裂隙充填物.依据等效介质理论计算的纵波速度随裂缝密度的增大而减小.正演地震记录显示,裂缝介质含气时反射振幅最大,且变化程度比含油或含水时大.叠前方位AVO反演所得的各向异性梯度B<sup>ani</sup>与裂缝密度成正比,可用于描述有效裂缝发育强度.对于不同的裂缝密度,各向异性梯度B<sup>ani</sup>与各向同性梯度B<sup>iso</sup>的比值I<sub>fluid</sub><sup>(1)</sup>近似为常数,且对流体敏感.经裂缝纵横比和背景介质拉梅常数修正后,流体因子I<sub>fluid</sub>既不随纵横比变化,又不受背景介质的影响,是裂缝型储层敏感的流体识别因子.在塔里木盆地塔北哈拉哈塘地区热瓦普区块碳酸盐岩储层裂缝发育区域,运用该参数在井点处的流体识别效果与钻井结果一致.
The method for identification of fluid in fractured reservoirs
[J].
一种裂缝流体因子的提出及应用
[J].
DOI:10.6038/cjg20150728
[本文引用: 1]

为了解决各向异性下的流体识别问题,将纵波各向异性裂缝预测以及Russell的流体因子融合到直角坐标系中,提出了一种能够同时检测裂缝发育情况以及流体性质的新的裂缝流体因子(Factor of Fluid-filled Fracture,FFF),并通过一组岩性参数检验了裂缝流体因子在裂缝预测及流体识别中的有效性.在理论研究的基础上,选取松辽盆地某地区的火成岩裂缝及流体识别研究为应用实例.通过与测井流体及裂缝信息的对比验证,裂缝流体因子能够较为准确地预测研究区裂缝和流体的分布情况,且裂缝流体因子在单井上的计算结果与单井含气饱和度吻合度较高.此外,根据实际应用效果,指出裂缝流体因子在应用中的局限性:裂缝流体因子在平面成图时受地层厚度影响较大,且无法预测裂缝方向.
A new factor of fluid-filled fractures and its application
[J].
Elastic impedance parameterization and inversion for fluid modulus and dry fracture quasi-weaknesses in a gas-saturated reservoir
[J].DOI:10.1016/j.jngse.2017.10.020 URL [本文引用: 1]
五维地震油气识别方法
[J].
Seismic fluid identification based on 5D seismic data
[J].
确定性反演协同约束的叠后随机地震反演方法
[J].
The methodology of a post-stack stochastic seismic inversion with the co-constraint of deterministic inversion
[J].
基于量子退火Metropolis-Hastings算法的叠前随机反演
[J].
Prestack stochastic inversion based on the quantum annealing Metropolis-Hastings algorithm
[J].
Bayesian linearized AVO inversion
[J].
DOI:10.1190/1.1543206
URL
[本文引用: 1]

A new linearized AVO inversion technique is developed in a Bayesian framework. The objective is to obtain posterior distributions for P‐wave velocity, S‐wave velocity, and density. Distributions for other elastic parameters can also be assessed—for example, acoustic impedance, shear impedance, and P‐wave to S‐wave velocity ratio. The inversion algorithm is based on the convolutional model and a linearized weak contrast approximation of the Zoeppritz equation. The solution is represented by a Gaussian posterior distribution with explicit expressions for the posterior expectation and covariance; hence, exact prediction intervals for the inverted parameters can be computed under the specified model. The explicit analytical form of the posterior distribution provides a computationally fast inversion method. Tests on synthetic data show that all inverted parameters were almost perfectly retrieved when the noise approached zero. With realistic noise levels, acoustic impedance was the best determined parameter, while the inversion provided practically no information about the density. The inversion algorithm has also been tested on a real 3‐D data set from the Sleipner field. The results show good agreement with well logs, but the uncertainty is high.
基于Metropolis抽样的弹性阻抗随机反演
[J].
Stochastic inversion of elastic impedance based on Metropolis sampling algorithm
[J].
地震数据约束下的贝叶斯随机反演
[J].
Bayesian stochastic inversion constrained by seismic data
[J].
基于APSO-MCMC的叠前三参数同步随机反演方法研究
[J].
DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1000-1441.2022.04.010
[本文引用: 1]

针对确定性叠前三参数反演存在的精度低、稳定性差、抗噪性差以及过度依赖初始模型的问题,虽然利用随机反演方法实现叠前三参数同步反演有助于解决这些问题,但此类方法反演效率较低。为此,提出了利用自适应粒子群优化马尔科夫链蒙特卡洛(APSO-MCMC)算法以提高叠前三参数反演的计算效率。结合纵波速度、横波速度以及密度的变化统计扰动关系,建立模型扰动的高斯分布,根据三参数扰动先验分布抽样获取初始粒子群。在每一步迭代过程中,利用跃迁矩阵改变粒子的演化,根据粒子之间的距离计算演化因子,判定粒子群的收敛状态。此外,利用精英策略,帮助粒子实现跳出局部极小值的困境。由于传统叠前近似公式在宽角度区域与非近似公式误差较大,故利用Zoeppritz公式来保证叠前三参数反演在各个角度的精度。NS地区二维海洋实际数据应用表明,该方法估算纵波速度、横波速度和密度有效,稳定收敛,计算效率高于传统的随机方法,具有较好的精度和抗噪性。
Stochastically simultaneous inversion of prestack data using APSO-MCMC method
[J].
DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1000-1441.2022.04.010
[本文引用: 1]

Deterministic inversion of prestack data has problems concerning inaccuracy,instability,poor noise resistance,and excessive dependence on the initial model.Therefore,a stochastic inversion method was previously proposed to determine the prestack three-parameter simultaneous inversion;however,the efficiency of conventional stochastic inversion is low.In this study,the APSO-MCMC method was developed to improve the computational efficiency of the prestack simultaneous inversion.According to the statistical perturbation relationship of the P-wave velocity,S-wave velocity,and density,the Gaussian distribution of the model perturbation is constructed.Based on the acceptance-rejection method,an initial swarm is generated as an input for the inversion process.During the iteration,a transition matrix is employed to change the evolution of the particles.Additionally,the evolution factor was calculated based on the distance between the particles to determine the convergence state of the particle swarm.In each iteration,an elite learning strategy was employed to determine the jump-out of the local minimum.Because the conventional forward modeling algorithm is not accurate in wide-angle regions,this study employed the Zoeppritz equations to ensure the accuracy of the prestack three-parameter inversion.The field data test of the NS area shows that the method correctly estimates the P-wave velocity,S-wave velocity,and density,and has a stability of convergence,high resistance to noise,and better efficiency than conventional stochastic approaches.
多道随机稀疏反射系数反演
[J].
DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1000-1441.2020.06.009
[本文引用: 1]

常规随机稀疏反射系数反演方法采用单道反演策略,实现过程中需要依据经验预设非零反射系数个数,不恰当的预设参数会引起诸多问题,另外,方法的收敛准则从本质上放大了以振幅较大为特征的异常值的影响。为此,引入相邻地震道数据作为约束条件,提出了一种多道的随机稀疏反射系数反演方法。通过对目标地震道数据的非零反射系数的位置和倾角进行同时非线性搜索,有效提升了反演预设参数的选择稳定性,同时减轻了异常值对反演结果的影响。作为单道随机稀疏反射系数反演方法的拓展,该方法保留了可以对反演结果进行不确定性分析的优势,可以提高地震数据高分辨率处理结果的可信性。利用该方法获得的高分辨率反射系数和地震剖面能够得到更多的构造和界面信息,有利于后续的解释工作。
Multi-trace stochastic sparse-spike inversion for reflectivity
[J].
Seismic anisotropy of fractured rock
[J].
DOI:10.1190/1.1443748
URL
[本文引用: 1]

A simple method for including the effects of geologically realistic fractures on the seismic propagation through fractured rocks can be obtained by writing the effective compliance tensor of the fractured rock as the sum of the compliance tensor of the unfractured background rock and the compliance tensors for each set of parallel fractures or aligned fractures. The compliance tensor of each fracture set is derivable from a second rank fracture compliance tensor. For a rotationally symmetric set of fractures, the fracture compliance tensor depends on only two fracture compliances, one controlling fracture compliance normal, the other, tangential, to the plane of the fractures. The stiffness tensor, which is more useful in the consideration of elastic wave propagation through rocks, can then be obtained by inversion. The components of the excess fracture compliance tensor represent the maximum amount of information that can be obtained from seismic data. If the background rock is isotropic and the normal and shear compliance of each fracture are equal, although different from those of other fractures, the effective elastic behavior of the fractured rock is orthorhombic for any orientation distribution of fractures. A comparison of the theory with recent ultrasonic experiments on a simulated fractured medium shows near equality of the normal and shear compliance for the case of air‐filled fractures.
Use of AVOA data to estimate fluid indicator in a vertically fractured medium
[J].
DOI:10.1190/1.2194896
URL
[本文引用: 1]

Microstructural attributes of cracks and fractures, such as crack density, aspect ratio, and fluid infill, determine the elastic properties of a medium containing a set of parallel, vertical fractures. Although the tangential weakness [Formula: see text] of the fractures does not vary with the fluid content, the normal weakness [Formula: see text] exhibits significant dependence on fluid infill. Based on linear-slip theory, we used the ratio [Formula: see text] — termed the fluid indicator — as a quantitative measure of the fluid content in the fractures, with g representing the square of the ratio of S- and P-wave velocity in the unfractured medium. We used a Born formalism to derive the sensitivity to fracture weakness of PP- and PS-reflection coefficients for an interface separating an unfractured medium from a vertically fractured medium. Our formulae reveal that the PP-reflection coefficient does not depend on the 2D microcorrugation/surface roughness with ridges and valleys parallel to the fracture strike, whereas the PS-reflection coefficient is sensitive to this microstructural property of the fractures. Based on this formulation, we developed a method to compute the fluid indicator from wide-azimuth PP-AVOA data. Inversion of synthetic data corrupted with 10% random noise reliably estimates the normal and tangential fracture weaknesses and hence the fluid indicator can be determined accurately when the fractures are liquid-filled or partially saturated. As the gas saturation in the fractures increases, the quality of inversion becomes poorer. Errors of 15%–20% in g do not affect the estimation of fluid indicator significantly in case of liquid infill or partial saturation. However, for gas-saturated fractures, incorrect values of g may have a significant effect on fluid-indicator estimates.
Properties of weak contrast PP reflection/transmission coefficients for weakly anisotropic elastic media
[J].DOI:10.1023/A:1021868328668 URL [本文引用: 1]
A Bayes tour of inversion:A tutorial
[J].
DOI:10.1190/1.1444923
URL
[本文引用: 1]

It is unclear whether one can (or should) write a tutorial about Bayes. It is a little like writing a tutorial about the sense of humor. However, this tutorial is about the Bayesian approach to the solution of the ubiquitous inverse problem. Inasmuch as it is a tutorial, it has its own special ingredients. The first is that it is an overview; details are omitted for the sake of the grand picture. In fractal language, it is the progenitor of the complex pattern. As such, it is a vision of the whole. The second is that it does, of necessity, assume some ill‐defined knowledge on the part of the reader. Finally, this tutorial presents our view. It may not appeal to, let alone be agreed to, by all.
High-resolution three-term AVO inversion by means of a Trivariate Cauchy probability distribution
[J].
DOI:10.1190/1.3554627
URL
[本文引用: 1]

Three-term AVO inversion can be used to estimate P-wave velocity, S-wave velocity, and density perturbations from reflection seismic data. The density term, however, exhibits little sensitivity to amplitudes and, therefore, its inversion is unstable. One way to stabilize the density term is by including a scale matrix that provides correlation information between the three unknown AVO parameters. We investigate a Bayesian procedure to include sparsity and a scale matrix in the three-term AVO inversion problem. To this end, we model the prior distribution of the AVO parameters via a Trivariate Cauchy distribution. We found an iterative algorithm to solve the Bayesian inversion and, in addition, comparisons are provided with the classical inversion approach that uses a Multivariate Gaussian prior. It is important to point out that the Multivariate Gaussian prior allows us to include the correlation of the AVO parameters in the solution of the inverse problem. The Trivariate Cauchy prior not only permits us to incorporate correlation but also leads to high-resolution (broadband) P-wave velocity, S-wave velocity, and density perturbations.
Elastic impedance parameterization and inversion with Young’s modulus and Poisson’s ratio
[J].
DOI:10.1190/geo2012-0529.1
URL
[本文引用: 1]

Young’s modulus and Poisson’s ratio are related to quantitative reservoir properties such as porosity, rock strength, mineral and total organic carbon content, and they can be used to infer preferential drilling locations or sweet spots. Conventionally, they are computed and estimated with a rock physics law in terms of P-wave, S-wave impedances/velocities, and density which may be directly inverted with prestack seismic data. However, the density term imbedded in Young’s modulus is difficult to estimate because it is less sensitive to seismic-amplitude variations, and the indirect way can create more uncertainty for the estimation of Young’s modulus and Poisson’s ratio. This study combines the elastic impedance equation in terms of Young’s modulus and Poisson’s ratio and elastic impedance variation with incident angle inversion to produce a stable and direct way to estimate the Young’s modulus and Poisson’s ratio, with no need for density information from prestack seismic data. We initially derive a novel elastic impedance equation in terms of Young’s modulus and Poisson’s ratio. And then, to enhance the estimation stability, we develop the elastic impedance varying with incident angle inversion with damping singular value decomposition (EVA-DSVD) method to estimate the Young’s modulus and Poisson’s ratio. This method is implemented in a two-step inversion: Elastic impedance inversion and parameter estimation. The introduction of a model constraint and DSVD algorithm in parameter estimation renders the EVA-DSVD inversion more stable. Tests on synthetic data show that the Young’s modulus and Poisson’s ratio are still estimated reasonable with moderate noise. A test on a real data set shows that the estimated results are in good agreement with the results of well interpretation.