0 引言
本文提出了一种基于协克里金技术的陆相地层反演低频模型构建方法,该方法以测井数据为主变量,地震速度为辅变量,将地震速度的横向连续性与测井数据的高纵向分辨率结合在一起,融合两者优势,得到了高精度的反演低频模型。实际应用证明了方法的有效性,在陆相地层少井区、低勘探程度区反演低频模型构建中具有较好的推广价值。
1 反演低频模型的重要作用
1.1 地震反演的基本原理
地震反演的原理为求式(1)的极小值:
式中:
式(1)由3部分组成,
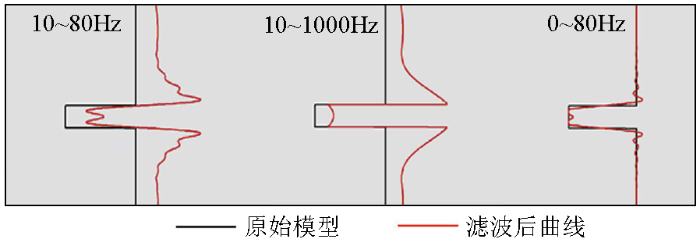
由于海上常规地震采集的限制,地震资料缺失6~8 Hz以下的低频分量,该部分分量蕴含了压实特性、沉积相变等重要信息,缺失低频分量显著降低了岩性、物性定量预测的准确性,充分合理地利用速度、属性等信息,构建准确合理的低频模型具有重要的实际意义。
1.2 低频模型的作用
图1
图1
模型经过不同频率范围滤波前后对比
Fig.1
Comparison of the model before and after filtering in different frequency ranges
2 基于协克里金技术的低频模型构建方法
基于协克里金技术的低频模型构建方法,以协克里金法为基础,综合变量的空间连续性和变量间的相关性,以纵向精度更高的测井数据为主变量,以空间连续分布的地震速度为辅变量,采用不同的空间变异函数,运用协克里金法实现二者的数据融合,以提高反演低频模型估计的精度。
2.1 方法原理
普通克里金是最基本和常见的克里金方法,它假设样本之间的空间相关性可以通过半变异函数来描述,并且不考虑任何外部因素的影响。在确定半变异函数模型和权重分配方法后,可以通过求解克里金矩阵来估计未知点的值。
普通克里金算法的公式如下:
式中:
普通克里金法是针对单变量的,未考虑区域化变量之间的相互关系,为了解决这一问题产生了多元地统计学。协克里金法是多元地统计学研究的基本方法之一,以协同区域变量理论为基础,利用多个区域化变量之间的互相关性,通过建立交叉协方差函数和交叉变异函数模型,用易于观测的变量对不易观测的变量进行局部估计,相较于普通克里金法,该方法能有效改进估计精度和采样效率。
本文拟采用协克里金算法整合测井数据与地震速度数据,以纵向分辨率高的测井数据作为主变量,以地震速度数据作为辅变量,协克里金估计值可表示成测井数据和地震速度数据的线性组合形式:
式中:
在协克里金中,辅助变量的权重系数之和为0,这个约束条件反映了辅助变量不能对预测结果产生偏移的特性,因此在计算权重系数时也需要考虑到这一点。同时,还需要求解出
式中:λ和β分别为权重系数向量;y1为主变量在已知位置处的观测值向量;C11、C12、C21及C22分别是主变量和辅变量的协方差矩阵。
主要变量和辅助变量之间的协方差矩阵描述了它们之间的相关性,这个协方差矩阵一般是由样本自相关系数和互相关系数估计得到的。
设有n个已知位置上的观测值,可以计算主变量和辅变量的样本协方差矩阵
式中:
需要注意的是,协克里金方法中的协方差矩阵是与空间距离相关的。为了准确地估算未知位置处主变量的值,需要根据实际数据对协方差函数进行合理的拟合和参数估计。
协克里金插值方法需要满足两个前提条件:
1)主变量和辅变量之间存在一定的空间相关性;
2)辅变量本身已知在未知位置处的值。
如果这两个条件都成立,那么协克里金方法可以更准确地估算未知位置上的主变量值。
2.2 主变量及辅变量特征分析
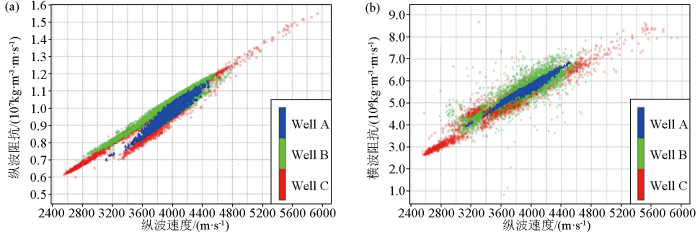
本文研究的反演低频模型,通常包括纵波阻抗、横波阻抗等弹性参数。实际数据分析表明,井上实测的纵波阻抗、横波阻抗等弹性参数,与地震勘探中通过层析反演获得的地震纵波速度具有非常好的相关性(图2),即主变量与辅变量之间存在空间相关性,满足协克里金插值的第一个前提条件。
图2
图2
纵波速度与纵波阻抗、横波阻抗交汇
a—纵波速度与纵波阻抗关系;b—纵波速度与横波阻抗关系
Fig.2
Crossplot of P-wave velocity with P-wave impedance and S-wave impedance
a—relationship between P-wave velocity and P-wave impedance;b—relationship between P-wave velocity and S-wave impedance
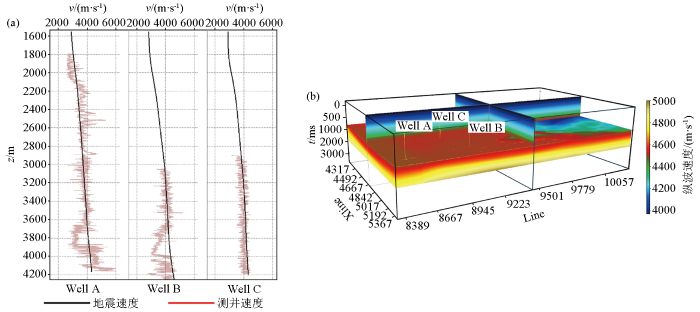
测井数据具有较高的纵向分辨率(0~1 000 Hz),地震速度数据纵向分辨率仅0~3 Hz左右,但具有较高的空间分辨率,且在待预测点处地震速度的值是已知的(图3),满足协克里金插值的第二个前提条件。
图3
图3
地震速度、测井速度特征
a—井点处测井速度与地震速度对比;b—地震速度空间分布特征
Fig.3
Characteristics of seismic velocity and logging velocity
a—comparison of logging velocity and seismic velocity at well points;b—spatial distribution characteristics of seismic velocity
以上分析表明,以测井数据为主变量,地震速度数据为辅变量进行插值,满足协克里金插值的两个前提条件,该方法可以用于构建地震反演低频模型,以提高空间插值精度,获得常规地震缺失的6~8 Hz以下的低频信息。
3 实际应用效果
图4
图5
图5
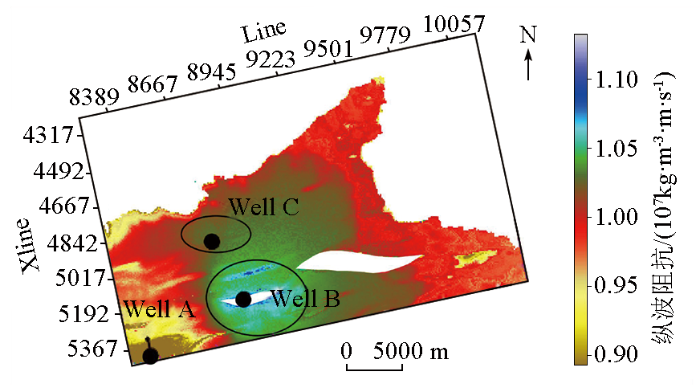
井插值法纵波阻抗模型沿目的层属性
Fig.5
Well interpolation method P-wave impedance model along target layer attributes
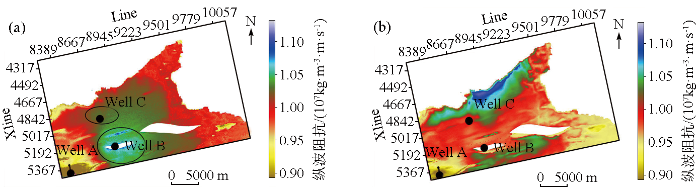
图6
图6
不同建模方法纵波阻抗沿目的层属性对比
a—反距离加权法;b—协克里金法
Fig.6
Comparison of P-wave impedance along target layer attributes using different modeling methods
a—inverse distance weighting method;b—co-kriging
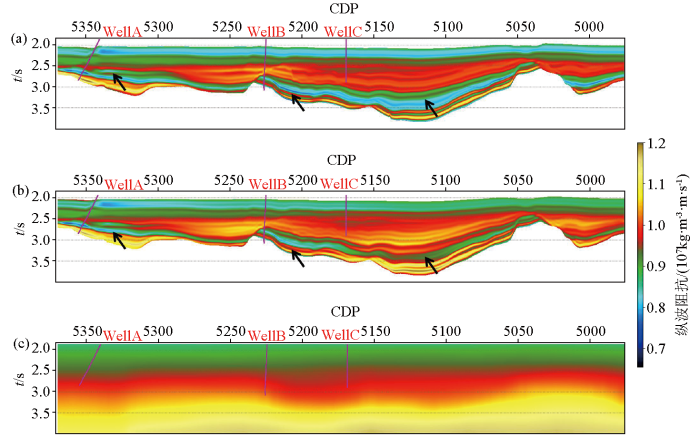
图7
图7
不同建模方法纵波阻抗剖面及地震速度剖面特征
a—反距离加权法;b—协克里金法;c—地震速度剖面
Fig.7
Characteristics of P-wave impedance profiles and seismic velocity profiles using different modeling methods
a—inverse distance weighting method;b—co-kriging;c—seismic velocity profile
采用本文研究的低频模型构建方法分别建立纵波阻抗、横波阻抗、密度低频模型,将以上模型作为初始输入,对研究区域进行叠前反演,可以得到纵波阻抗、横波阻抗、纵横波速度比、密度等三维弹性数据体。
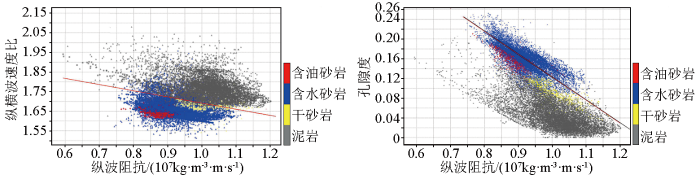
岩石物理交汇分析表明,纵横波速度比、纵波阻抗单一参数难以对不同岩性进行区分,不同岩性存在大范围重叠。纵横波速度比、纵波阻抗两个弹性参数联合,可以区分砂岩、泥岩;对于砂岩,纵波阻抗与孔隙度存在较好的线性关系(图8)。因此,可以基于叠前反演得到的纵波阻抗、纵横波速度比,预测目的层砂岩储层;然后,通过砂岩纵波阻抗与孔隙度的线性关系,预测储层孔隙度;最终实现对优质储层分布范围的预测,为古近系勘探部署提供指导。
图8
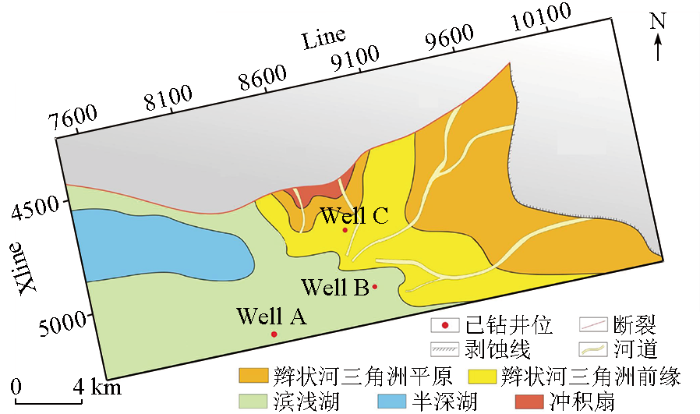
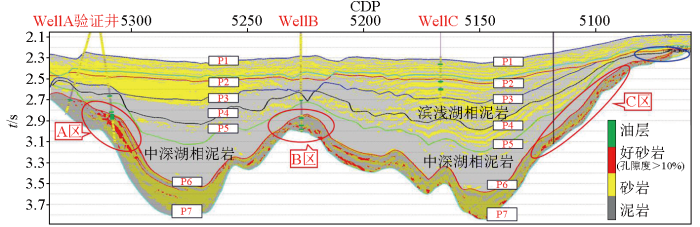
结合孔隙度预测结果对目的层段(P6~P7层位之间)孔隙度大于10%的优质砂岩进行了预测,在图中标识为红色。结果表明,研究范围内存在3个优质砂岩分布区,A区优质砂岩最厚,Well A井恰好位于A区,B区、C区厚度差别不大(图9),目前在A、B两区的钻井均已获得油气发现,预测结果与实钻吻合度较高。特别是在未参与反演的验证井处, 岩性及物性预测结果与钻井揭示的情况相吻合。结合以上预测结果,分析认为C区缓坡带是区域内下一个有利的勘探目标,该区钻井一旦成功,可发现新的油藏模式、实现满凹含油,具有重要的勘探意义。
图9
4 结论
1)基于协克里金技术的低频模型构建方法,以空间连续测量的地震速度数据为辅变量,以分辨率高的测井数据为主变量,将辅变量的信息整合到估计结果中,弥补了主变量数据不足的缺点,通过结合两者优势得到了代表地下情况的低频模型,为少井区建模提供了有效方法。
2)不同建模方法对比分析表明,基于协克里金技术的低频模型构建方法,可以有效整合甚低频信息,插值结果优于反距离加权法,避免了“牛眼”现象,保持了地震速度的低频趋势,可以较好反映陆相地层沉积相变化特征,提高了反演低频模型的精度,提高了储层预测的可靠性,具有广泛的应用前景。
随着定量储层预测技术的发展,低频模型构建、低频地震采集等技术将发挥更加重要的作用。
参考文献
波阻抗反演中低频分量构建的经验与技巧
[J].低频信息的构造是波阻抗反演中极为重要的技术环节,低频信息构造的准确与否,直接影响波阻抗反演结果的准确性。低频分量的构建要作好井资料本身的标准化、环境校正和深时转换等,还要以地质理论为指导,顺解释层位横向递推,特别要作好遇见断层、岩性突变等情况下的处理。针对不同的地质情况应当采用不同的构建方法。本文根据实践经验和生产中遇见的具体问题,提出了一套低频分量的构建方法与技巧。
Experience and skill of constructing low frequency components in impedance inversion
[J].The construction of low frequency information is an extremely important technical link in wave impedance inversion. The accuracy degree of low frequency information construction directly affects the impedance inversion results. To construct low frequency component, well data standardization, environment correction and depth time conversion need to be made. Moreover, horizontal recursion along the interpretation layer should be done with the guiding of geological theory. Different constructing mthods should be adopted according to different geologic circumstances such as fault and lithological mutation. This paper puts forward a set of low frequency component construction methods and techniques on the basis of the authors’ practical experiences.
Broadband seismic data:The importance of low frequencies
[J].
低频模型对波阻抗反演结果定量解释的影响
[J].
Impacts of low-frequency models on the quantitative interpretation of acoustic impedance inversion
[J].
Low frequency models for seismic inversions:Strategies for success
[C]//
低频信息对阻抗反演的影响分析
[J].
Effect analysis of low frequency on acoustic impedance inversion
[J].
Prestack 3D and 4D seismic inversion for reservoir static and dynamic properties
[J].
DOI:10.1190/tle35050415.1
URL
[本文引用: 1]

We present a successful case study in which prestack 3D and 4D simultaneous AVO inversion is used in conjunction with rock-physics analysis to estimate saturation and pressure changes in a West Africa brownfield using time-lapse (4D) seismic as input. We show that, in 4D seismic, there can be many competing production effects that can be difficult to disentangle using traditional 4D interpretation methods, such as amplitude differences between the base and monitors. This begs the need for a more sophisticated approach to decouple these competing effects, such as the use of prestack simultaneous 3D and 4D inversions. Multiple substack seismic data are used to estimate a variety of 3D and 4D petroelastic attributes for mapping static and dynamic reservoir properties with the primary objective of influencing the continuous infill drilling and the overall reservoir management strategy. Facies-specific low-frequency models were used as priors for the 3D inversion, while velocity changes from time-lapse time shifts were used as priors for the 4D inversion. We also demonstrate the use of rock-physics templates coupled with a lithology-specific Gassmann fluid-substitution method to establish a nonlinear regression-based rock-physics model that obeys bound theory from classical rock physics and honors single and multimineral fluid-substitution theory. The resulting templates, when integrated with the prestack AVO-inversion technique, produce a set of attributes that accurately explain the time-lapse production effects observed on seismic.
地震低频信息在反演中的作用
[J].
Low-frequency seismic information applied in inversion
[J].
不同地质条件下反演低频模型构建方法分析
[J].
Analysis on construction method of inversion low frequency model under different geological conditions
[J].
基于宽频资料的扩展弹性阻抗反演方法在陆丰22洼陷低勘探区古近系岩性预测中的应用
[J].
Application of broadband data-based extended elastic impedance inversion method in Paleogene lithology prediction of areas at a the low exploration level in Lufeng 22 subsag
[J].
Co-kriging of soil properties with limited data
[J].
A co-kriging method for high-dimensional spatial data interpolation and prediction
[J].DOI:10.1007/s00477-015-1169-3 URL [本文引用: 1]
Modeling and prediction of the spatiotemporal dynamics of Nitrogen dioxide concentrations using Landsat imagery and meteorological data in Beijing,China
[J].
DOI:10.3390/rs11182075
URL
[本文引用: 1]

Physiological maturity date is a critical parameter for the selection of breeding lines in soybean breeding programs. The conventional method to estimate the maturity dates of breeding lines uses visual ratings based on pod senescence by experts, which is subjective by human estimation, labor-intensive and time-consuming. Unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV)-based phenotyping systems provide a high-throughput and powerful tool of capturing crop traits using remote sensing, image processing and machine learning technologies. The goal of this study was to investigate the potential of predicting maturity dates of soybean breeding lines using UAV-based multispectral imagery. Maturity dates of 326 soybean breeding lines were taken using visual ratings from the beginning maturity stage (R7) to full maturity stage (R8), and the aerial multispectral images were taken during this period on 27 August, 14 September and 27 September, 2018. One hundred and thirty features were extracted from the five-band multispectral images. The maturity dates of the soybean lines were predicted and evaluated using partial least square regression (PLSR) models with 10-fold cross-validation. Twenty image features with importance to the estimation were selected and their changing rates between each two of the data collection days were calculated. The best prediction (R2 = 0.81, RMSE = 1.4 days) was made by the PLSR model using image features taken on 14 September and their changing rates between 14 September and 27 September with five components, leading to the conclusion that the UAV-based multispectral imagery is promising and practical in estimating maturity dates of soybean breeding lines.
Co-Kriging with non-stationary variance:A case study of surface ozone concentration over South Korea
[J].
喀斯特地区月均降水协克里金插值方法研究——以贵州省为例
[J].
On the association of co-kriging interpolation method research based on GIS:A case study in Karst area of Guizhou Province
[J].
基于协克里金的雨量雷达融合置信处理方法
[J].
A fusion-based confidence processing algorithm for regional rainfall radar based on Co-Kriging
[J].
基于协同克里金的大坝心墙渗流空间模型研究
[J].
Research on spatial model for core-wall seepage of dams based on cooperative Kriging
[J].
A statistical approach to some basic mine valuationproblems on the Witwatersrand
[J].
Geostatistics:Modeling spatial uncertainty
[J].DOI:10.2307/2669569 URL [本文引用: 1]