0 引言
地震和测井数据是油气勘探开发中最为常用的两类地球物理观测数据。地震数据对地质构造空间描述性强,但其信息频带有限,往往不能满足薄储层研究要求。测井数据具有频带宽、精度高及靶向性强等特点,可较好揭示井点处储层厚度、岩性、物性及流体等油藏特征,但测井数据是一维数据,难以表征地质储层三维空间连续变化。地震构造约束下构建测井模型能够直观表征地质储层空间变化,可直接用于油气勘探开发储层油藏描述[1⇓⇓⇓-5],还可用于地震反演约束,提高地震弹性参数反演精度,再进行储层油藏描述[6⇓⇓-9]。利用已知点数值估计未知点数值是测井插值建模的关键,常用的方法有反距离加权法、克里金插值、最近邻点插值等方法,建模方法众多,最终结果也不尽相同。因此,针对不同的数据需要根据其类型、分布特征及相关性等影响因素进行优选[9⇓⇓⇓⇓⇓⇓⇓-17]。
测井数据具有空间相关性,符合地理学第一定律:地理空间上的所有值均互相联系,且距离近的值联系更强[18]。因此,反距离加权作为描述数据距离相关性的方法在数据建模中得到广泛应用,其具有以下假设:2个物体相似性随距离增大而减小,以插值点与样本点的距离的倒数作为加权系数进行样本点数值加权平均,从而得到插值点数值。该方法中每个样本点均会对插值点有贡献,只是贡献大小会随距离远近而变化,离插值点越近的样本点贡献越大,越远的样本点贡献越小,如2个样本点与插值点相同,其贡献就完全相同。
最近邻点插值方法和克里金插值法中,只有靠近插值点的已知点有贡献,反距离加权方法所有未知点都会有贡献,贡献大小与距离相关[19-20]。克里金插值方法也是常用的一种数据建模方法,是由法国地理学家Matheron和南非矿山工程师Krige提出,用于矿山勘探。与反距离加权方法最大的不同在于加权系数的求取,克里金法加权系数是满足插值点估计值与期望值差最小目标条件的一套优化权系数,需要计算半方差函数(也称为变差函数或变异函数),利用观测数据两两计算距离和半方差数据对,然后利用球状、指数及高斯等理论模型拟合距离和半方差关系函数,一般距离近方差小,距离远方差大,方差随着距离变化到一定程度会相对稳定不再变化,称为基台值,此时对应的距离称为变程。利用变差函数可估算插值点到任意距离样本点的半方差,然后利用方差函数并优化目标函数得到权系数,其加权系数仍为与距离有关的函数,距离插值点越近的样本点贡献越大。克里金插值方法与反距离插值方法的不同在于,样本点对插值点贡献大小并非由距离倒数决定,而是取决于变差函数,同时当样本点与插值点距离超过统计变程就不会产生贡献。克里金方法用变程距离描述了空间数据不相关性,更匹配实际数据变化情况。
最近邻点插值、反距离加权和克里金插值等方法均只考虑了数据点空间相关性与距离关系。由于地质沉积具有连续性和方向特点,因此测井数值大小与地质构造和沉积物源方向密切相关,测井数据不仅具有强空间相关性,而且具有连续性和方向性。测井建模中除了要考虑距离因素,还应该考虑方位因素,距离预测点近的测井会对较远测井产生方位遮挡,常用测井插值建模方法只考虑距离而没考虑这种方位遮挡关系,影响测井建模精度。
针对常用插值方法存在的问题,笔者提出了一种测井方位遮挡反距离加权插值方法,在常规插值建模分析对比的基础上,构建了方位遮挡反距离加权插值公式,研究距离和方位双影响因素的权系数计算方法,并利用模型数据进行了数值对比试验,并且在实际资料中开展了应用。
1 方法原理
1.1 测井反距离加权建模
测井反距离加权插值是常用的测井建模方法,其插值建模公式通常表示为:
式中:
从式(1)中可以看出,测井样本点对插值点的影响除了样本点自身的属性大小外,只与2点间的距离远近有关系,距离越远的样本点对插值点贡献会越小,任一测井样本点会对任何位置和方向的点产生影响,但该方法只考虑了空间数据相关性,没有考虑地质沉积由于物源和构造控制造成的空间数据方向性。
1.2 测井方位遮挡反距离加权建模
针对地质沉积和测井数据具有空间相关性和方向性的特点,研究发展并形成测井方位遮挡反距离加权插值方法,其插值建模公式为:
相比式(1),式(2)中增加了综合非方位遮挡权系数
式中:
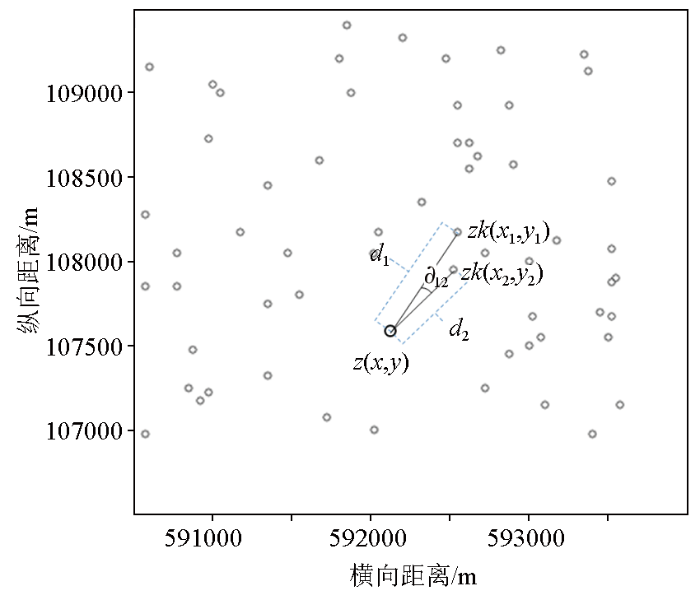
图1
图1
测井方位遮挡反距离插值原理示意
Fig.1
Schematic diagram of logging azimuth occlusion inverse distance interpolation
通过测井已知点两两组合可以得到测井点相互间的非方位遮挡权系数,然后将每个测井点与其他测井点计算得到非方位遮挡权系数相乘,就可以得到每个测井点对插值点的综合非方位遮挡权系数,计算公式为:
与距离倒数作用一样,综合非方位遮挡权系数的大小也会影响样本点对插值点的贡献,该值越大,测井点受其他测井点方向遮挡越小,与距离插值点相同测井点相比,对插值点的贡献越大,最后插值大小是由所有测井数值进行反距离加权系数和综合非方位遮挡权系数进行加权平均得到。通过理论方法对比可以看出,该方法考虑到地质数据空间的相关性和方向性,相比反距离加权建模方法更适合测井数据建模。
2 数值试验
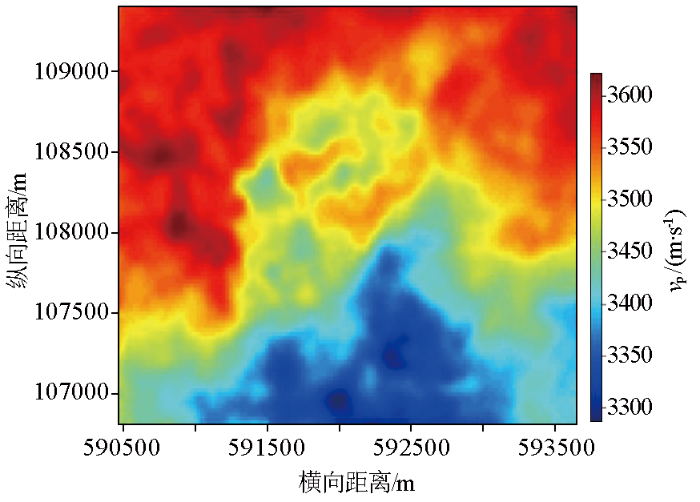
图2为从三维速度体提取的一平面切片。作为数值试验平面比对速度模型,模型纵、横向长均为3 000 m,是面积为9 km2的正方形,根据实际地震采集处理参数,设置网格为25 m×25 m。可以看出,提取模型属性中,速度宏观表现为北高南低,局部速度存在变化。从该平面比对速度模型中分别随机提取60个点和120个点速度值并记录坐标,用来模拟测井点某沉积时期的平均速度,然后分别利用测井方位遮挡反距离加权建模方法和测井反距离加权建模方法进行建模试验,并与平面比对速度模型进行对比分析。
图2
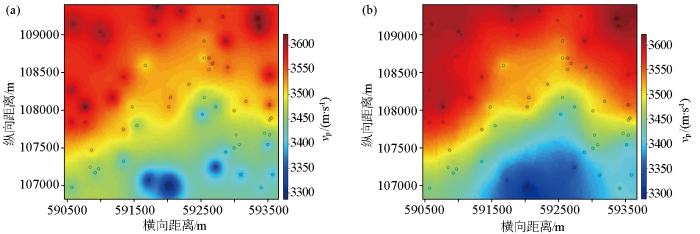
图3
图3
采用60个模拟测井点速度建模切片
a—测井反距离加权建模;b—测井方位遮挡反距离加权建模
Fig.3
Velocity modeling slice with 60 simulated logging points
a—inverse distance weighted modeling of logging;b—inverse distance weighting modeling under logging azimuth occlusion
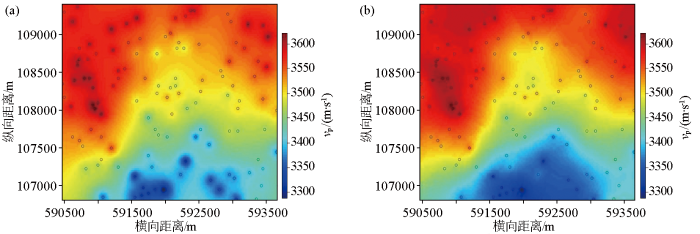
图4
图4
采用120个模拟测井点速度建模切片
a—测井反距离加权建模;b—测井方位遮挡反距离加权建模
Fig.4
Velocity modeling slice with 120 simulated logging points
a—inverse distance weighted modeling of logging;b—inverse distance weighting modeling under logging azimuth occlusion
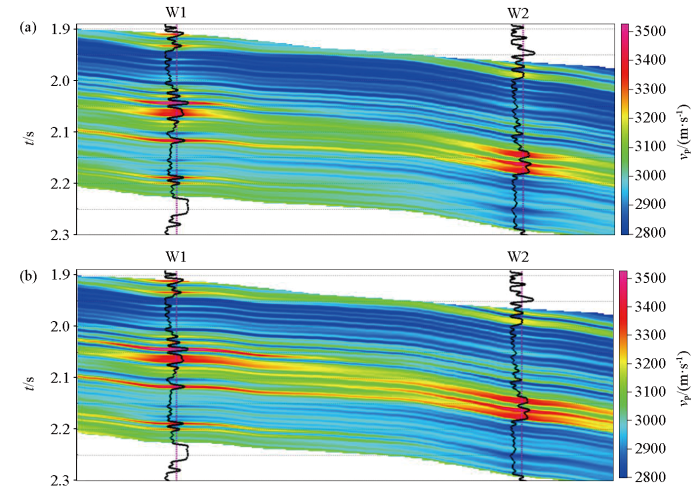
3 实际数据应用
在SL油田开展了实际资料测井速度建模应用,工区网格为25 m×25 m,面积约为55 km2,采用7口测井数据,井口分布密度相对较低,仅为0.13口/ km2,为匹配实际地震频带,将测井速度曲线进行了高截频滤波处理,高截频率120 Hz,然后开展了测井速度模型构建。
图5
图5
SL油田测井速度建模剖面
a—测井反距离加权建模;b—测井方位遮挡反距离加权建模
Fig.5
Velocity modeling profile of SL oil field
a—inverse distance weighted modeling of logging;b—inverse distance weighting modeling under logging
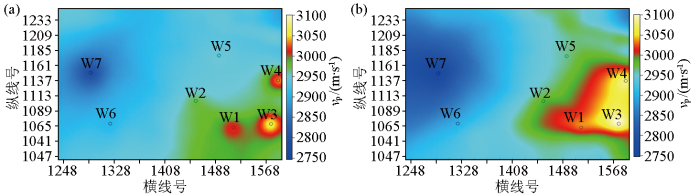
对速度建模提取的整个模型时窗平均速度平面属性进行分析(图6)可以看出,2种方法均能够反映区域速度宏观变化特征,整个建模工区为深湖相沉积,物源来自东南方向,西北部为沉积洼陷中心,主要为低速度泥岩沉积地层,东南部靠近物源,地层为深湖相泥岩夹浊积砂岩组合,砂泥比相对较高,因此地层速度整体偏高。2种方法对比显示,图6a为采用测井反距离加权建模方法得到速度平面属性,井点周围受井影响明显,有明显的“牛眼现象”,当井与其他钻井速度差异大时,这种现象会更明显;图6b为采用测井方位遮挡反距离加权方法速度建模剖面,速度变化更加自然,体现地质沉积空间方向性和连续性的特征,该速度模型提高了地质研究人员区域地质沉积认识,可为地震反演提供更可靠的初始速度模型。
图6
图6
SL油田速度建模切片
a—测井反距离加权建模;b—测井方位遮挡反距离加权建模
Fig.6
Velocity modeling slice of SL oil field
a—inverse distance weighted modeling of logging;b—inverse distance weighting modeling under logging
4 结论与认识
本文研究了测井方位遮挡反距离加权建模方法,利用反距离权系数和综合非方位遮挡权系数联合加权建模,并提供了非方位遮挡权系数的计算方法,该方法能够顾及测井距离和方位双重因素影响,更能够体现地质沉积岩性空间相关性和方向性特点。测井方位遮挡反距离加权建模方法能够提高建模精度,建模结果变化过渡自然,符合地质沉积变化,测井控制点越多,建模精度越高;在测井及其他非均匀离散数据建模中具有广阔的推广应用前景。
参考文献
Global cycles of relative changes of sea level
[J].
Sequence stratigraphy workbook,fundamentals of sequence stratigraphy
[J].
基于储层构造和沉积等时格架的储层静态建模实例而研究
[J].
A case study of reservoir static modeling based on reservoir structure and sedimentary isochronous framework
[J].
储层速度建模分析及域转换
[J].
Analysis of reservoir velocity modeling and domain conversion
[J].
储集层参数随机建模方法在扇三角洲储集层非均质性研究中的应用
[J].
Application of stochastic simulation of reservoir parameters on heterogeneity in fan delta reservoir
[J].
测井约束反演技术在建南地区南部储层预测中的应用
[J].
Application of logging constrained inversion technology in reservoir prediction in the south of Jiannan District
[J].
高分辨率地震反演技术及应用
[J].
High-resolution seismic inversion technology and its application
[J].
测井约束与神经网络联合反演储层预测技术
[J].
Reservoir prediction technology based on joint inversion of logging-constrained and neural network
[J].
测井模型约束全波形反演的应用
[J].
Application of the well logging model constraining the full waveform inversion
[J].
地球物理不规则分布数据的空间网格化法
[J].
Gridding methods of geophysical irregular data in space domain
[J].
散乱离散点数据的三角形网格化快速成图
[J].
Triangular grid-based rapid mapping of scattered data
[J].
地球物理数据网格化方法的选取
[J].
The choice of gridding methods for geophysical data
[J].
基于离散光滑插值的三维地质体构造网格模型
[J].
3D geological grid model based on discrete smooth interpolation
[J].DOI:10.3724/SP.J.1249.2014.06600 URL [本文引用: 1]
测井数据Matlab插值与地质旋会性分析应用
[J].
Application of interpolation of well logs based on Matlab to analysis of geological cyclicity
[J].
沿层微测井插值方法反演复杂地区近地表模型
[J].
Near-surface model inversion in complex terrain area by along-horizon interpolation method
[J].
水文资料插值计算方法探讨
[J].
Discussion on the interpolation calculation methods of hydrological data
[J].
不同插值方法对降水量空间不确定性的影响
[J].
Influence of different interpllation methods on spatial univertainty of rainfall
[J].Journal of University of Jinan:Sci.and Tech.
A computer movie simulating urban growth in the Detroit region
[J].DOI:10.2307/143141 URL [本文引用: 1]
克里金法在GPS数据内插中的应用
[J].
The application of keiging to GPS data interpolation
[J].
自适应的IDW插值方法及其在气温场中的应用
[J].
DOI:10.11821/dlyj201408003
[本文引用: 1]

反距离权重(Inverse Distance Weighting,IDW)插值通常采用距离搜索策略选择插值参考点,当采样点集分布不均匀时,距离搜索策略使得参考点聚集一侧影响插值精度。自然邻近关系具有良好的自适应分布特性,可有效地解决参考点分布不均匀问题。结合自然邻近关系,提出自适应的反距离权重(Adaptive-IDW,AIDW)插值方法。首先对采样数据构建初始Delaunay三角网,然后采用逐点插入法,将待插值点插入初始Delaunay三角网中,局部调整得到新的Delaunay三角网,以待插值点的一阶邻近点作为IDW插值的参考点,使参考点自适应均匀地分布在待插值点周围,再进行IDW插值计算。利用AIDW插值方法对Franke函数、全国气温观测数据进行插值实验,结果表明此方法具有较高的精度,且减少了“牛眼”现象。
Adaptive IDW interpolation method and its application in the temperature field
[J].
DOI:10.11821/dlyj201408003
[本文引用: 1]

The Inverse Distance Weighting (IDW) interpolation has the advantage of simpleness, convenience for calculation, and high compatibility with Tobler's first law. It is widely used in construction of DEM, weather analysis, hydrological analysis, and so on. Distance search strategy is usually adopted by the IDW interpolation to select referent points. However, referent points gathering in one side may cause the loss of interpolation accuracy when sampling points are unevenly distributed. The natural adjacency spatial relationship with good adaptive characteristics about choosing referent points can effectively solve the problem of reference points’ uneven distribution. Based on this, the adaptive inverse distance weighting (AIDW) interpolation method was proposed in this paper. Firstly, the initial Delaunay triangulation was built with the sampling data points. Secondly, interpolative points were inserted one by one, the purpose of which was making the referent points evenly distributed around the interpolative points by taking the first-order neighboring of interpolative points as referent points. At last, IDW was interpolated. In step two, when each point was inserted, the Delaunay triangulation should be reconstructed, which elapseded time a lot. To solve this problem, the patial grid index was built in order to raise the speed of Delaunay triangulation's reconstruction. Compared with ordinary IDW, there was no need to assign the number of referent points or search radius in the AIDW, because the referent points could be adaptively selected with the natural adjacency spatial relationship of interpolative points. Especially when referent points were too intensive, the problem of superfluous points being inserted could be avoided. Two experiments were conducted in this paper, which were the theoretical surface reconstruction of the Franke and the national surface air temperature field reconstruction respectively. The results were compared with IDW interpolation methods with different search strategies in ArcGIS 10.1, which verify that the proposed method have higher accuracy. Meanwhile, the results of the proposed method show that the 'buphthalmos' phenomenon is reduced. All the outcomes indicate that the proposed method can be applied in the interpolation of geographical phenomenon as a new method.