0 引言
陆相、湖相、海相等连续沉积岩心被公认是重建多样地理环境地质以及历史时期的自然和人文信息、勘探矿产资源储层情况的良好载体[1⇓-3]。20世纪90年代兴起的XRF岩心扫描(XRF Core Scanning,XRF-CS)技术[4]由于其快速、连续、无损且高分辨率等特点,极大提升了沉积岩心地球化学元素组成和变化特征分析精度,为识别短时间尺度的气候变化及地质事件、快速检测和推断各类矿产资源丰度提供了可能[5⇓⇓-8]。但是,XRF-CS技术获得的元素信号强度除受控于元素绝对含量外,也受仪器设置、扫描时间、沉积岩心物理属性等影响,可能会产生如下问题:①生成无效值(负值或0)或削弱的元素信号强度[9⇓⇓⇓-13];②过度或错误解释岩心记录[11,14];③错失关键矿藏储层和重大地质事件层理[8,15-16]。
正确分析XRF-CS元素信号强度的影响因素,并通过合理校正得到其“真实”的元素信号,是基于沉积岩心元素分布解译古环境记录和勘探矿藏储层情况的首要工作。因此,本文对近20余年XRF-CS技术手段及应用的最新研究成果进行系统性梳理和归纳,详细分析XRF-CS相较于传统XRF技术的优缺点,综合评述XRF-CS技术在扫描过程中对元素信号的影响因素及国际上较为前沿的3种校正方法,为精确鉴别基于XRF-CS的元素信号值“真实”的高分辨率分布和准确解释沉积岩心的地球化学记录奠定科学基础。
1 前人研究现状及存在的问题
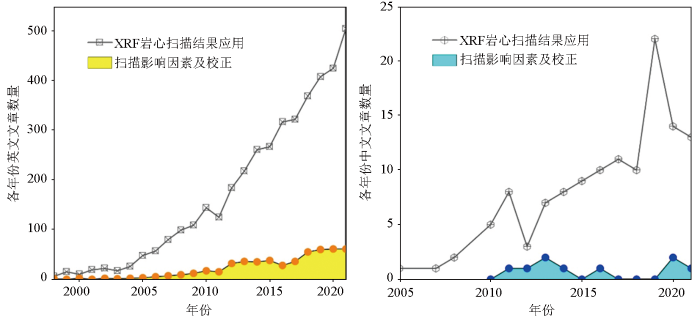
XRF-CS技术发展于20世纪90年代荷兰海洋研究所设计的CORTEX扫描仪[4]。经过20余年的发展,市面上的XRF-CS仪器主要有5种类型,分别为Avaatech[12]、Itrax[13]、Eagele III BKA[17]、Tatscan-F2[18]和Geotek[19],其中,Avaatech和Itrax XRF-CS仪器在国内外被广泛应用[20]。当前,XRF-CS技术广泛用于海洋[9,14,21⇓⇓⇓⇓⇓-27]、湖泊[10,28⇓⇓⇓⇓-33]、地表硬岩[8,34]、黄土[35⇓⇓⇓⇓⇓-41]、石笋[42⇓⇓⇓⇓-47]、泥炭[48⇓⇓⇓⇓-53]、河流沉积[54⇓⇓⇓⇓⇓-60]等岩心沉积序列分析,也用于环境调查取证[61⇓⇓⇓-65]、土壤重金属污染分析[66]、金属矿藏探测[15]等方面的研究。XRF-CS通过对沉积岩心光滑表面原位测量,可获取Al(13)~U(92)的半定量元素信号强度,其结果单位通常为counts per second(cps)[11]。图1展示了1998~2021年XRF-CS技术应用的中、英文论文数量变化情况,总体上呈现出以下特点:①国际上自2005年以来相关应用成果显著增长,国内于2010年开始逐步应用。②分析扫描信号值影响因素及校正的研究相对较少,特别是国内极为少见。例如,张玉枝等[10]基于XRF-CS扫描和传统X射线荧光光谱(XRF)技术分析青藏高原西部阿翁错沉积岩心的元素含量,对比发现岩心的含水量显著影响Al、Si、K的元素信号强度,经现有模型校正后Al的元素信号强度与真实含量的相关系数(r2)由0.03提高到0.48,Si的相关系数由0.04提高到0.57,K的相关系数由0.35提高到0.65。然而,大多类似研究仅分析单一因素(如含水量[10-11]、粒度[67-68]等)的影响程度,也仅利用某一校正方法进行分析和解释[25,69⇓-71]。整体性地审视XRF-CS扫描结果综合影响因素的相关研究较为少见,且仍未见全面性归纳国际上最新数据校正方法等方面的报道,限制了XRF-CS这一先进技术手段的独特优势和应用潜力的深度挖掘及广泛应用。
图1
图1
1998~2021年XRF-CS扫描应用的中英文论文数量统计(源自Google Scholar)
Fig.1
Statistics of the number of Chinese and English papers on XRF-CS scanning applications from 1998 to 2021 (source Google Scholar)
2 XRF-CS与传统XRF分析技术的比较
沉积物元素组成及含量主要通过XRF技术手段测定,其基本原理为利用高能量的X射线驱逐特定样品原子的内层电子,高能量的外层电子跃迁到低能量状态,多余的能量以辐射形式释放,形成该样品的特征X射线荧光,利用其强度预估样品的不同元素丰度[20]。传统XRF分析方法主要包括波长色散X射线荧光(WD-XRF)、能量色散X射线荧光(ED-XRF)、电感耦合等离子体质谱法(ICP-MS)和电感耦合等离子体发射光谱法(ICP-OES)等[72-73]。上述传统方法均需将干燥散样(分辨率≥0.5 cm)研磨压片或融为液态珠状,从而生成一个平整且均一的表面进行元素含量的精确测定[74-75],但是样品前处理复杂,所需散样量大,耗时且测试价格昂贵,更重要的是较低的分辨率或许会错失一些极端地质事件[20,72,76]。因此,需同步发展快速、连续且高分辨率的沉积岩心地球化学元素分析仪器,便携式X射线荧光光谱仪(pXRF)和XRF-CS在此背景下应运而生。
不同于上述两种元素分析技术,XRF-CS技术可直接作用于沉积岩心表层进行原位扫描并获取Al(13)~U(92)元素的信号值分布,还可通过加载多类型传感器(如高清照相机、磁化率仪等)获得高精度光学图像、色度和磁化率等数据,为高分辨率地识别沉积岩心记录提供了极大的便利[32-33,48,85-86]。Croudace等[13]以地中海中部1 m长沉积岩心为载体,率先在55 kV电压、50 mA电流、40 s曝光时间、0.5 mm扫描间隔下利用Itrax XRF-CS获取其元素分布;随后,以5 mm间隔分样并冷冻干燥,研磨至200目以下通过压片后利用WD-XRF光谱仪测定元素含量;在此基础上,全面对比了两种方法的仪器要求、样品准备、数据分辨率及所需时间等(表1)。结果表明:①XRF-CS技术分析呈现出样品前处理简单、无损、分辨率高、测试速度快等优势;②XRF-CS测试的元素范围较少,特别是所获取的半定量元素信号值精确度不高,易受多种仪器和岩心的因素影响。因此,为了正确解读XRF-CS扫描数据和科学应用,需全面梳理影响元素信号的因素和校正方法。
| 参数 | Itrax XRF-CS | WD-XRF |
|---|---|---|
| 仪器要求 | 三相电源、液态水 冷却 | 一相或三相电源、 液态水冷却 |
| X-ray光管 | Mo、Cr、Cu | Rh |
| 高分辨率X光照相 | 是 | 否 |
| 高精度光学图像 | 是 | 否 |
| X光照相分辨率 | ≥0.1mm | 否 |
| 可添加传感器 | 是 | 否 |
| X光照相和光学图像 的获取时间# | 0.5h | 否 |
| 样品处理和准备 要求 | 无损坏、平坦和光 滑的表面,并覆盖 4μm聚乙烯薄膜 | 分离样品烘干、研 磨、压片或融化, 约需5g左右 |
| 真空系统要求 | 可选 | 是 |
| 对挥发或研磨样品 的He气系统要求 | 否 | 是 |
| 样品扫描分辨率 | ≥0.02mm | ≥5mm |
| 测量元素 | Al-U | Na-U |
| 获取数据所需时间 (K、Ca、Fe) | 2h# | 10个工作日§ |
| 获取数据所需时间 (Si、Al、K、Ca、Ti、 Fe、Mn、Zn、Sr、Zr) | 15h# | 10个工作日§ |
| 获取数据所需时间 (Si、Al、S、Cl、K、Ca、 Fe、As、Pb、Zn、Br、 Rb、Sr、Zr) | 48h# | 10个工作日§ |
| 分析数据质量 | 较好 | 高精度 |
注:“#”表示0.2 mm分辨率扫描1 m岩心;“§”表示1 cm分辨率分析1 m岩心。
3 XRF-CS元素信号值的影响因素
3.1 仪器设置方面的影响因素
3.1.1 X射线光管限定扫描元素范围
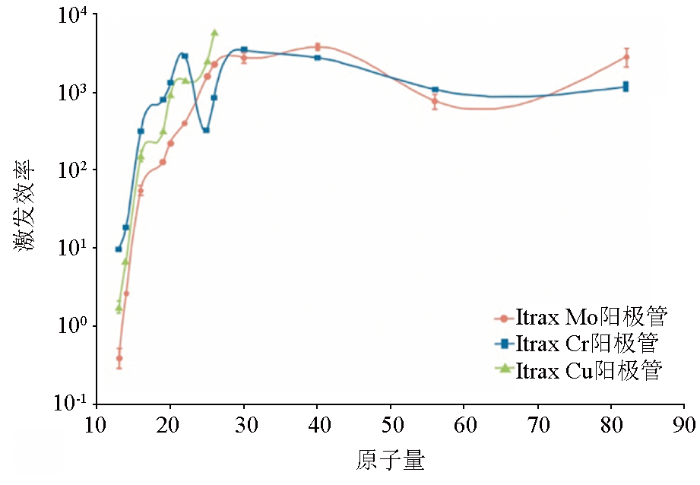
Avaatech和Itrax XRF-CS仪器均提供了多种X射线光管和过滤片类型,用于测定不同元素的信号强度。Avaatech XRF-CS仪器仅利用铑(Rh)射线管,采用锘(No)过滤片测定Al、Si、S、Cl、K、Ca、Ti、Mn和Fe等元素,采用铅(Pd)过滤片测定Cu、Zn、Ga、Br、Rb、Sr、Y、Zr等元素,采用铜(Cu)过滤片测定Ba、Pb和U等元素[12],因此无需考虑Avaatech XRF-CS仪器X射线光管的影响。相较而言,Itrax XRF-CS仪器分别采用铬(Cr)、钼(Mo)和铜(Cu)射线管获取不同元素的信号值[13,87](图2)。根据各类射线管对应的不同元素的激发效率[87],通常推荐采用Cr阳极管获取原子量小于Cr(Z=24)的元素的信号强度值,采用Mo阳极管获取原子量大于Cr(Z=24)的元素的信号强度值[13,87],国际上少见专用Cu阳极管获取激发效率最高的Mn和Fe的元素信号值。
图2
X射线光管的使用寿命也是影响沉积岩心元素信号强度的一个因素。使用不同寿命的X射线光管扫描同一岩心的不同岩心段,会导致获得的元素信号值无法在时间轴上进行比较,从而错误地解释岩心的连续沉积过程及其记录的古环境信息。因此,为解决以上问题并获取同一岩心可靠的元素信号值分布,建议在较短时间内一次性完成所有岩心段的扫描工作。
3.1.2 电压和电流强度决定扫描元素信号强度
Avaatech XRF-CS仪器只使用一个X射线光管。因此在利用其获取岩心元素信号值时,通常使用10 kV电压测定Al、Si、S、Cl、K、Ca、Ti、Mn和Fe等元素,用30 kV测定Cu、Zn、Ga、Br、Rb、Sr、Y、Zr等元素,用50 kV测定Ba、Pb和U等元素[12]。这是Avaatech仪器公司推荐且国际公认的电压要求。
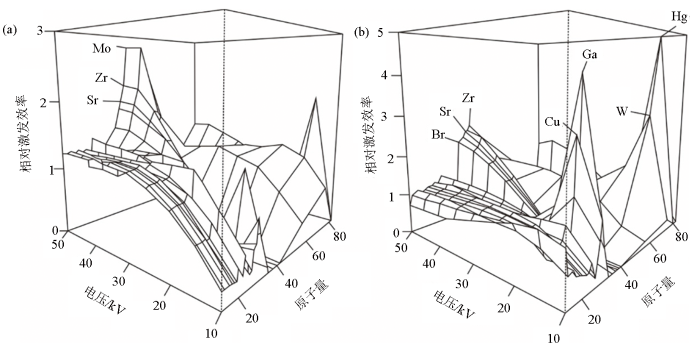
Itrax XRF-CS仪器采用3个X射线光管获取不同元素的信号值。因此,不同的光管要选取合适的电压来获取最佳的元素信号强度。图3显示了标准样品中的各个元素在不同电压强度(10~50 kV)下采用Cr阳极管和Mo阳极管扫描的相对激发效率。采用Cr阳极管扫描标准样品时(图3a),大多数元素(特别是原子量相对较小的元素(如Z≤24))在高于30 kV的电压下的激发效率基本保持稳定,而Sr、Zr和Mo的激发效率在电压50 kV条件下达到最大。因此,30 kV的电压是Cr阳极管扫描较轻元素(Z≤24)信号强度的理想电压。采用Mo阳极管扫描标准样品时(图3b),元素(Z≤24)信号强度在低于30 kV时有明显的韧致辐射。一些重金属元素(如Cu、Ga、W、Hg等)在15 kV电压下同样存在显著的韧致辐射,但在30 kV电压下这些元素的激发效率基本保持稳定。对于Br、Sr和Zr元素,在50 kV的电压下元素激发效率达到最大值。因此,30 kV是Mo阳极管扫描较轻元素(Z≥24)信号强度的理想电压,而50 kV是获取Br、Sr和Zr元素信号强度的理想电压[87]。
图3
除电压外,XRF-CS测得的元素峰域面积与X光管电流也成正比,电流越强,元素信号强度越高,而一些较轻的元素(如Al)在低电流条件下由于较低的电子辐射和空气吸收使得元素信号强度较低[25]。但是持续较高的电流强度也会大大缩短X光管的使用寿命。Avaatech XRF-CS仪器常使用的电流强度为1~2 mA,Itrax XRF-CS仪器建议的可靠电流强度为30~50 mA。综上所述,为了获得目标元素足够的信号强度并延长光管的使用寿命,在XRF-CS测试过程中要选择适当的电压和电流强度。
3.1.3 扫描间隔和曝光时间共同控制实验耗时
对于单个岩心段,XRF-CS扫描所需总时间主要取决于两个方面:扫描间隔和曝光时间[12-13,90]。扫描间隔需根据岩心沉积相特征、颗粒组成等进行设置,特别是高分辨率鉴定岩心的年纹层理和“关键层”需更小间隔才能实现。XRF-CS的扫描间隔最小可达200 μm[13],但要大于沉积岩心颗粒的最大粒径。然而,扫描间隔越小,完成扫描所需的时间越长。为了缩短扫描时间并减少经济花费,最佳办法是选择尽可能短且合适的曝光时间。曝光时间是每个测试点在扫描过程中暴露于X射线下的时间,其长短显著影响不同元素的扫描计数。理论上,曝光时间越长,扫描信号强度越高。因此,扫描间隔和曝光时间之间的平衡在很大程度上影响了扫描花费的总时间和费用,并影响元素的高分辨率分布和关键层理的鉴定。然而,过长的曝光时间不仅影响X光管的使用寿命,还延长了岩心段的扫描时间并提高了实验费用。因此,在确保扫描间隔的条件下,需分析和选择最佳的曝光时间。
3.1.4 塑料薄膜确保扫描样品无污染
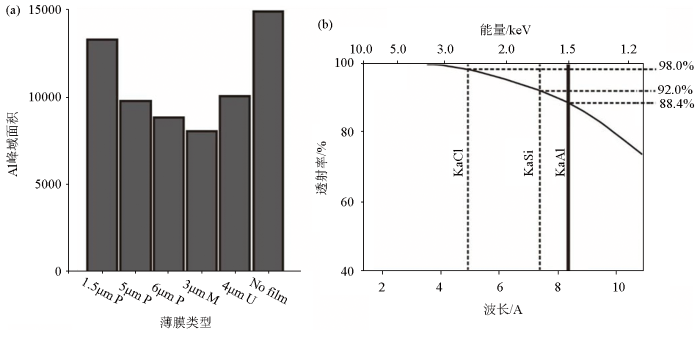
图4
图4
塑料薄膜对XRF峰域面积的影响
a—使用一系列可用的 XRF薄膜和无薄膜记录的Al峰域面积的比较(使用Mo阳极管在30 kV和30 mA下扫描,计数时间为100 s,引自文献[87]);b—用于XRF岩心扫描仪分析的Ultralene薄膜的透射特性,以及元素 Al、Si 和 Cl 的Kα荧光能量,引自文献[11]
Fig.4
Effect of plastic film on XRF peak areas
a—a comparison of recorded Al peak areas using a range of available XRF films and no film (scanned with Mo anode tube at 30 kV and 30 mA, with 100 s count time,cited in [87]);b—transmission properties of the Ultralene foil used for the XRF core scanner analyses, and the Kα fluorescence energies of elements Al, Si, and Cl,cited in [11]
3.2 岩心物理属性的影响
3.2.1 含水量和薄膜下水汽吸收X射线光谱
式中:Ix为剩余X光强度;I0为初始X光强度;α为质量衰减系数。
研究表明,沉积岩心的含水量显著影响原子量较低元素(如Al(13)和Si(14))的信号强度,而对K(19)、Ca(20)、Ti(22)和 Fe(26)的元素信号强度的影响可忽略不计[11]。因此,为了合理解释这些受影响元素的信号分布,需利用含水量校正相关元素的原始扫描值。在海相和咸水湖相沉积岩心中,Cl是孔隙水的指标性元素,二者间成正比[11]。雷国良等[91]基于XRF-CS扫描典型咸水湖泊兹格塘错沉积岩心,证实Cl的扫描信号强度与含水量的变化趋势相一致。因此,Cl的扫描强度变化被用作沉积物岩心含水量变化的代用指标。而对于其他淡水湖或陆源沉积岩心,Cl信号强度作为含水量代用指标的可行性需进一步评估。
3.2.2 粒度分布和表面平整度增加X射线散射
在传统的XRF荧光分析中,通常将沉积物样品均匀研磨进而最大程度削弱粒度的影响。然而,XRF-CS扫描对象为原状沉积岩心,岩心粒度分布被认为会对XRF-CS的元素信号强度产生影响[13-14,67]。XRF-CS早期主要用于海相和湖相沉积物的扫描,岩心粒度变化较小,粗颗粒的影响仅体现在薄膜下水汽的富集,通过含水量校正后可消失其误差,故颗粒组成的影响通常会被忽略[14]。然而,该仪器在广泛应用于陆相沉积的扫描分析后发现,粒径范围为10~20 μm的颗粒组成影响可忽略不计[67];而对粗颗粒(>63 μm)的含量高于25%的岩心段,粒度变化会增加X射线的散射程度,进而削弱了获得的元素信号强度[68]。因此,XRF-CS仪器更加适用于主要由细颗粒(黏土和粉砂)组成的沉积岩心扫描。
3.2.3 岩心裂隙和基质产生无效信号值
不同相沉积岩心在垂直分样过程中,岩心表面可能会出现裂隙,特别是一些含水量较低且松散的陆相沉积,如黄土、古河道沉积等。这些裂隙通常在岩心表面肉眼可见,XRF-CS扫描的结果均表现为一致的低值或无效值,在后期数据处理时较易识别和排除。需指出的是,在前期处理岩心表面时,需将可见裂隙保留下来,从而确保岩心的完整性[40]。
综上所述,基于XRF-CS技术获取的不同类岩心元素信号值分布受仪器(X射线光管类型、电压和电流强度、扫描间隔和曝光时间、塑料薄膜)和岩心(含水量和薄膜下水汽、粒度分布和表面平整度、岩心裂隙和基质)的多种因素影响,难以直接用于古环境研究、矿产资源的评估勘探、土壤污染防治修复等。因此,亟需探求能广泛应用的校正方法消除岩心扫描数据的不确定性,从而激发高分辨率XRF-CS的全部潜力并基于扫描数据正确解译其元素地球化学信息。
4 XRF-CS元素信号值的校正方法
在XRF-CS扫描过程中,通用操作是先后扫描标准样品和对照标准光谱,判别仪器设置的稳定程度[92]。目前,判读扫描数据准确性的常见方法是XRF-CS数据和传统XRF数据的线性相关分析,进而选取影响较小的扫描元素分布解释其意义。但是,对影响较大的元素却难以利用和分析,限制了XRF-CS技术优势的发挥。此外,XRF-CS扫描元素信号值的误差是上述多种因素共同作用的结果,单一因素影响结果的校正难以排除其他因素的影响。因此,国际上广泛使用的校正模型均是对多种因素综合作用下的扫描元素信号值进行校正,以期准确解读扫描数据。
4.1 Normalized Median-Scaled(NMS)模型
为了消除半定量的XRF扫描信号值差异,需要在校正前将所有信号值归一化,使XRF峰域面积测量范围与扫描元素的峰域面积范围相匹配,Lyle等[25]提出了扫描信号值缩减方法,即Normalized Median-Scaled(NMS)模型。
在理想情况下,如果所有沉积组分都被测定,则元素比例总和应是100%。然而,在岩心因素的影响下,XRF扫描数据缩放后的总和常低于100%[25]。而扫描数据归一化可消除上述误差,具体公式为:
式中:NMSc是元素的归一化标准值;raw sum为原始测定值;C是元素的中值比例。在此基础上,基于各元素组分的WD-XRF浓度校正其归一化标准值,进而生成沉积物中各元素成分的校正浓度[25]。
4.2 Log-ratio Calibration Equation(LRCE)和Multivariate Log-ratio Calibration(MLC)模型
在常规XRF定量分析中,元素的净强度与质量比例换算的一般方程[69]如下:
式中:Wij表示元素j在样品i中的浓度;Kj表示仪器对元素j的检测效率;Iij代表样品i中元素j的净强度;Mij是样品中其他元素对Iij的基质效应;Si是样品均质效应[69]。
然而,由于XRF-CS扫描数据受仪器和岩心的多重因素影响,难以直接利用上述理想模型预测各元素的净强度。Weltje等[69]结合了XRF光谱理论、数据分析原理和经验,提出了Log-ratio Calibration Equation(LRCE)对数校正模型,强调利用元素扫描强度和真实浓度的对数比校正二者间的非线性关系。在合并简化等多个步骤后,无量纲的标准对数校正方程为:
式中:系数α和β分别是X射线荧光光谱法中单一元素分析的基质效应和检测效率的对数比值常数;D为元素j的绝对含量;变量I和W以无量纲对数比的形式考虑。LRCE与组分数据分析原理保持着一致性,且不考虑分析前的数据归一化,故该模型没有单位和非负性的约束[69]。
4.3 Normalized Polynomial-Scaled Calibration(NPS)和Polynomial-Corrected Multivariate Log-ratio Calibration(P-MLC)模型
相较于上述介绍的NMS模型,NPS改进的地方主要体现在:①拟合的二次多项式替代了NMS模型中的元素中值;②元素信号强度归一为该元素的绝对含量;③使用线性回归方程将校正的组分浓度转化为元素绝对含量。
在P-MLC校正中,最主要的改进即为对所有可能的对数比率组合执行多项式校正,从而选择最佳对数比的元素用作公共分母,以获得最准确的校正。最后使用XELERATE软件对多项式校正强度执行标准MLC校正[71]。
5 结论与展望
XRF-CS技术因其样品前处理简单、分辨率高、无损、测试速度快、可同步获得高精度光学图像和色度数据等优势和特点,在近20余年的沉积岩心地球化学元素分析中得到了广泛使用,并取得了富有成效的研究进展。随着该技术研究和应用进入“深水区”,对XRF-CS岩心扫描的影响因素及元素信号值校正等方面的关注逐步提升。本文归纳分析了XRF-CS技术的“仪器”和“岩心”两大类因素产生的影响效果,并简要介绍了国际上通用的校正模型,得出了以下结论:①沉积岩心在稳定且最佳的仪器设置下应一次性完成XRF岩心扫描,尽可能消除仪器因素对元素信号值的影响。②扫描海洋、湖泊、河流等含水量高的岩心时,需通过适当晾干降低水汽的削弱作用;扫描黄土、泥炭、岩石等颗粒分布不均的岩心时需尽可能平整表面减弱粗颗粒的散射作用。③对沉积岩心的XRF元素信号值分析时,基于多重因素的综合考虑选择最佳模型对其进行校正,以此获取各元素的真实分布。
下一步可以在以下方面开展深入研究,获取新的进展或认识:①深入分析单一影响因素对XRF-CS元素信号值的影响效果,揭示各因素的影响机制和过程;开展Avaatech和Itrax等多类型XRF-CS仪器间同一因素影响效果的异同,以期实现不同类型仪器元素信号的横向对比。②针对不同理化特征的多类型沉积岩心,优化当前使用的XRF-CS元素信号校正模型,提高扫描数据的准确性;开发能够搭载在Python或R等计算机语言上的通用且可视化的软件包,简化数据校正的过程。③探讨在XRF-CS设备上搭载多类型传感器(如含水量、颗粒组成、孔隙度等)的可能性,实现对沉积岩心的高分辨率“一体化”分析。④对比分析XRF-CS与pXRF技术快速测试岩石等地质样品元素分布的优缺点,探寻野外和室内测试相结合的矿藏地球化学元素的最优分析手段,全面探索XRF-CS在岩矿勘探和测试中的应用前景。
致谢
感谢中国科学院青藏高原研究所高少鹏高级工程师对Itrax XRF Core Scanner仪器使用的指导;感谢兰州大学西部环境与气候变化研究院潘燕辉老师对Avaatech XRF Core Scanner扫描岩心的帮助。特此感谢编辑和审稿专家提出的建设性意见。
参考文献
Millennial and centennial CO2 release from the Southern Ocean during the last deglaciation
[J].DOI:10.1038/s41561-022-00910-9 [本文引用: 1]
Impact of warmer climate periods on flood hazard in the European Alps
[J].DOI:10.1038/s41561-021-00878-y [本文引用: 1]
基于便携式X射线荧光光谱(PXRF)分析的西南印度洋脊龙角区沉积物地球化学找矿研究
[J].
Application of PXRF in sediment analysis for geochemical prospecting in Dragon Horn area on the southwestern Indian Ridge
[J].
CORTEX,a shipboard XRF-scanner for element analyses in split sediment cores
[J].DOI:10.1016/S0025-3227(98)00074-7 URL [本文引用: 3]
Geochronology and geochemical properties of Mid-Pleistocene sediments on the Caiwei Guyot in the Northwest Pacific imply a surface-to-deep linkage
[J].
DOI:10.3390/jmse9030253
URL
[本文引用: 1]

Seamounts are ubiquitous topographic units in the global ocean, and their effects on local circulation have attracted great research attention in physical oceanography; however, fewer relevant efforts were made on geological timescales in previous studies. The Caiwei (Pako) Guyot in the Magellan Seamounts of the western Pacific is a typical seamount and oceanographic characteristics have been well documented. In this study, we investigate a sediment core by geochronological and geochemical studies to reveal a topography-induce surface-to-bottom linkage. The principal results are as follows: (1) Two magnetozones are recognized in core MABC–11, which can be correlated to the Brunhes and Matuyama chrons; (2) Elements Ca, Si, Cl, K, Mn, Ti, and Fe are seven elements with high intensities by geochemical scanning; (3) Ca intensity can be tuned to global ice volume to refine the age model on glacial-interglacial timescales; (4) The averaged sediment accumulation rate is ~0.73 mm/kyr, agreeing with the estimate of the excess 230Th data in the upper part. Based on these results, a proxy of element Mn is derived, whose variability can be correlated with changes in global ice volume and deep-water masses on glacial-interglacial timescales. This record is also characterized by an evident 23-kyr cycle, highlighting a direct influence of solar insolation on deep-sea sedimentary processes. Overall, sedimentary archives of the Caiwei Guyot not only record an intensified abyssal ventilation during interglaciations in the western Pacific, but also provide a unique window for investigating the topography-induced linkage between the upper and bottom ocean on orbital timescales.
The impact of cyclical,multi-decadal to centennial climate variability on arsenic sequestration in lacustrine sediments
[J].DOI:10.1016/j.palaeo.2020.110189 URL [本文引用: 1]
Monsoon variations inferred from high-resolution geochemical records of the Linxia loess/paleosol sequence,western Chinese Loess Plateau
[J].DOI:10.1016/j.catena.2020.105019 URL [本文引用: 1]
The role of detrital anhydrite in diagenesis of aeolian sandstones (upper Rotliegend,the Netherlands):Implications for reservoir-quality prediction
[J].DOI:10.1016/j.sedgeo.2014.10.001 URL [本文引用: 3]
XRF岩心扫描估算海洋沉积物有机碳含量的适用性
[J].
DOI:10.11978/2021041
[本文引用: 2]

X射线荧光光谱仪(XRF)的沉积物岩芯扫描技术可以无损、快速获得高分辨率的溴(Br)计数信息, 可用来估算海洋沉积物中有机碳含量, 但是其准确性及各种校正方法的效果还需要深入研究。文章选择两根在有机质来源构成上有明显差异的阿拉伯海和南海的沉积柱, 系统开展了沉积物有机碳(total organic carbon, TOC)含量与Br计数的相关性分析, 深入剖析了沉积物含水量、Br计数校正方法等对利用Br计数估算沉积物TOC含量的影响及评估该方法的适用性。对于有机质含量较高的海洋沉积物而言, Br计数与TOC含量之间存在较好的相关性, 且其相关性与是否校正Br计数没有显著关系。在陆源有机质输入量比较大的沉积物样品中, 则需谨慎采用Br计数来估算沉积物的总有机碳含量。
The estimation of organic contents in marine sediments based on bromine intensity by the XRF scanner
[J].
DOI:10.11978/2021041
[本文引用: 2]

The Bromine (Br) intensity collected by the non-destructive X-ray fluorescence (XRF) core scanner has been used to estimate the content of organic carbon in marine sediment in high speeds. However, the accuracy of this estimation and the effectiveness of various calibration methods need to be carefully evaluated. In this study, two gravity cores from the Arabian Sea and South China Sea, where the organic contents and their source components are different in sediment, are selected to investigate the correlation between the total organic carbon (TOC) content and the Br intensity by the core scanner. This study also analyzes the influence of water content and evaluates the effectiveness of different calibration methods used to estimate the TOC content according to the Br intensity. A good correlation is found between the Br intensity and the TOC in marine sediment with high organic carbon contents, no matter whether the Br intensity is calibrated or not. However, the estimation of sedimentary TOC content should be cautiously used when terrigenous organic matter is high.
湖泊沉积物含水量和结构对XRF扫描结果影响的评估及校正──以西藏阿翁错为例
[J].
Accuracy assessment and calibration of the impact of water content and structure of lake sediments on the XRF scanning data—A case study of Aweng Co in the Tibetan Plateau
[J].
Influence of the water content on X-ray fluorescence core-scanning measurements in soft marine sediments
[J].
The Avaatech XRF core scanner:Technical description and applications to NE Atlantic sediments
[J].DOI:10.1144/GSL.SP.2006.267.01.03 URL [本文引用: 5]
ITRAX:Description and evaluation of a new multi-function X-ray core scanner
[J].DOI:10.1144/GSL.SP.2006.267.01.04 URL [本文引用: 11]
X-ray fluorescence core scanning of wet marine sediments:Methods to improve quality and reproducibility of high-resolution paleoenvironmental records
[J].DOI:10.4319/lom.2012.10.991 URL [本文引用: 8]
ITRAX:A potential tool to explore the physical and chemical properties of mineralized rocks in mineral resource exploration
[J].DOI:10.1016/j.gexplo.2013.06.010 URL [本文引用: 2]
A Hylogger-Itrax core-scanner comparison for multi-scale high-resolution petrophysical characterisation workflow
[J].DOI:10.1016/j.apgeochem.2021.104956 URL [本文引用: 1]
The Eagle III BKA system,a novel sediment core X-ray fluorescence analyser with very high spatial resolution
[J].DOI:10.1144/GSL.SP.2006.267.01.02 URL [本文引用: 1]
Non-destructive X-Ray fluorescence (XRF) core-imaging scanner,TATSCAN-F2
[J].DOI:10.5194/sd-2-37-2006 URL [本文引用: 1]
Approaches to water content correction and calibration for μXRF core scanning:Comparing X-ray scattering with simple regression of elemental concentrations
[G]//Croudace I W,Rothwell R G.Micro-XRF studies of sediment cores:Applications of a non-destructive tool for the environmental sciences.Dordrecht,Netherlands:Springer,
XRF岩心扫描在第四纪沉积物研究中的应用
[J].
The application of XRF core scanning to Quaternary sediments
[J].
Investigation of adequate calibration methods for X-ray fluorescence core scanning element count data:A case study of a marine sediment piston core from the Gulf of Alaska
[J].
DOI:10.3390/jmse9050540
URL
[本文引用: 1]

X-ray fluorescence (XRF) core scanner elemental count data are useful for high-resolution paleoceanographic studies. However, because several factors, such as changes in physical core properties, significantly affect element count intensities, the appropriate calibration of the count data is required. Besides, the existing approaches for calibration were not widely employed and require rigorous testing based on sediment variety. In this study, we analyzed high-resolution element intensity (cps) using a wet muddy marine sediment piston core that was collected from the northeast Gulf of Alaska and tested several approaches with ratio and log-ratio methods, and the reliability was evaluated by comparison with the concentrations that were measured by WD-XRF and an elemental analyzer. The results show that the lighter elements (Ti and K) exhibited a significantly weak relationship between raw counts measured by ITRAX and concentrations that were measured by the WD-XRF, indicating that some factors artificially influence ITRAX intensity data. The Cl intensity that is expressed as the water content in marine sediment increased significantly in the upper 202 cm by 42% and the top 25 cm by 73% as compared to the down-core (below 202 cm), which deviates the X-ray scattering and element-counts. The calibration of raw data through coherent/incoherent X-ray scattering ratio (CIR) and additive- and centered-log ratio reduces the offsets. The calibration by CIR performed best for Sr, Fe, Mn, Ti, Ca, K, and Br (0.56 < R2 < 0.91), and the correlation with concentration significantly increased for Ti and K of 100% and 56%, respectively. Therefore, the study suggests that the correction of raw counts through CIR is an effective approach for wet marine sediment when core physical properties have greater variability.
A high-resolution paleosecular variation record for marine isotope stage 6 from Southeastern Black Sea sediments
[J].
Characterization of organic matter in marine sediments to estimate age offset of bulk radiocarbon dating
[J].DOI:10.1016/j.quageo.2021.101242 URL [本文引用: 1]
Isolating detrital and diagenetic signals in magnetic susceptibility records from methane-bearing marine sediments
[J].
Data report:Raw and normalized elemental data along the Site U1338 splice from X-ray fluorescence scanning
[J].
X射线岩心扫描系统对海洋沉积物成分测定质量的综合评价和校正
[J].
The calibration and quality evaluation of elemental analysis results of marine sediment measured by an X-ray fluorescence core scanner
[J].
Data report:Raw and normalized elemental data along the Site U1335,U1336,and U1337 splices from X-ray fluorescence scanning
[J].
Climate-driven fluxes of organic-bound uranium to an alpine lake over the Holocene
[J].DOI:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.146878 URL [本文引用: 1]
Patterns of alluvial deposition in Andean lake consistent with ENSO trigger
[J].DOI:10.1016/j.quascirev.2021.106900 URL [本文引用: 1]
Late Pleistocene hydroclimatic variabilities in arid north-west China:Geochemical evidence from Balikun Lake,eastern Tienshan,China
[J].DOI:10.1002/jqs.v36.3 URL [本文引用: 1]
Late Holocene periods of copper mining in the Eisenerz Alps (Austria) deduced from calcareous lake deposits
[J].DOI:10.1016/j.ancene.2020.100273 URL [本文引用: 1]
基于XRF岩芯扫描的Rb/Sr比值的古气候意义探讨──以青藏高原东部若尔盖盆地为例
[J].
Paleoclimatic indication of X-ray fluorescence core-scanned Rb/Sr ratios:A case study in the Zoige Basin in the eastern Tibetan Plateau
[J].
大兴安岭阿尔山天池湖泊沉积物记录的全新世气候突变
[J].
Climatic abrupt events implied by lacustrine sediments of Arxan Crater Lake,in the central Great Khingan Mountains,NE China during Holocene
[J].
XRF半定量分析技术在矿石光片鉴定中的作用
[J].
Application of XRF semi-quantitative analysis technology in identifying ore on polished section
[J].
Soil erosion fluxes on the central Chinese Loess Plateau during CE 1811 to 1996 and the roles of monsoon storms and human activities
[J].DOI:10.1016/j.catena.2021.105148 URL [本文引用: 1]
High-sedimentation-rate loess records:A new window into understanding orbital- and millennial-scale monsoon variability
[J].DOI:10.1016/j.earscirev.2021.103731 URL [本文引用: 1]
New insights into dating the sediment sequence within a landslide-dammed reservoir on the Chinese Loess Plateau
[J].
DOI:10.1177/0959683619831426
URL
[本文引用: 1]

The deposition couplets within the check dams and landslide-dammed reservoirs on the Chinese Loess Plateau (CLP) document the processes and histories of watershed soil erosion, transportation and deposition, related to floods, eco-environment and land use changes, and human activities. Previously, dating the couplets was dominantly dependent on multiple intercomparisons among specific sediment yields of visible couplets, 137Cs activities distributions and erosive rainfall events by meteorological records. However, inter-annual division of the deposition couplets and dating historical sequence beyond meteorological records in the landslide-dammed reservoir are little known. Based on high-resolution XRF core scanning on a 22.75 m sediment sequence in Jingbian (JB) landslide-dammed reservoir on the central hilly-gully area of the CLP, and cross checking of multiple dating methods, this study tried to propose a new method to build the accurate chronology sequence based on inter-annual division by annual freeze-thaw layer and to further date the sediment without rainfall records. The results showed that a total of 126 deposition couplets and 78 annual freeze-thaw layers were identified in the JB sequence. Multimethod cross-dating, including 137Cs activities, annual freeze-thaw layers, couplet specific sediment yield and modern rainfall records, was the most accurate method of dating the JB sediment sequences since 1960s with detail meteorological records. Furthermore, the correspondence between annual freeze-thaw layers and the historical grades of flood index from literature was the valid method to date the JB historical sequences without rainfall records. Consequently, the JB sequence was deposited during the period between 1855 and 2014. High-resolution dating of the JB sequence provides the chronology for recovering natural and anthropogenic information on the central hilly-gully area of CLP since 1850s. The proposed methods will also shed new light on the accurate dating of the sediment sequences within other check dams and landslide-dammed reservoirs on the central and northern CLP.
High-resolution scanning XRF investigation of Chinese loess and its implications for millennial-scale monsoon variability
[J].DOI:10.1002/jqs.v31.3 URL [本文引用: 1]
High-resolution geochemical records of deposition couplets in a palaeolandslide-dammed reservoir on the Chinese Loess Plateau and its implication for rainstorm erosion
[J].DOI:10.1007/s11368-017-1888-9 URL [本文引用: 1]
High-resolution X-ray fluorescence core scanning of landslide-dammed reservoir sediment sequences on the Chinese Loess Plateau:New insights into the information and geochemical processes of annual freeze-thaw layers
[J].DOI:10.1016/j.geoderma.2016.06.008 URL [本文引用: 2]
Evaluation of high-resolution elemental analyses of Chinese loess deposits measured by X-ray fluorescence core scanner
[J].DOI:10.1016/j.catena.2011.11.010 URL [本文引用: 1]
Speleothem-based hydroclimate reconstructions during the penultimate deglaciation in Northern China
[J].
Centennial- to millennial-scale monsoon changes since the last deglaciation linked to solar activities and North Atlantic cooling
[J].
DOI:10.5194/cp-16-315-2020
URL
[本文引用: 1]

. Rapid monsoon changes since the last deglaciation remain poorly constrained\ndue to the scarcity of geological archives. Here we present a high-resolution scanning X-ray fluorescence (XRF) analysis of a 13.5 m\nterrace succession on the western Chinese Loess Plateau (CLP) to infer rapid\nmonsoon changes since the last deglaciation.\nOur results indicate that Rb∕Sr and Zr∕Rb are sensitive indicators of chemical weathering and wind sorting, respectively, which are further linked to the strength of the East Asian summer monsoon (EASM) and the East Asian winter monsoon (EAWM). During the last deglaciation, two cold intervals of the Heinrich event 1 and Younger Dryas were characterized by intensified winter monsoon and weakened summer monsoon.\nThe EAWM gradually weakened at the beginning of the Holocene, while the EASM remained steady till 9.9 ka and then grew stronger.\nBoth the EASM and EAWM intensities were relatively weak during the Middle Holocene, indicating a mid-Holocene climatic optimum. Rb∕Sr and Zr∕Rb exhibit an antiphase relationship between the summer and winter monsoon changes on a centennial timescale during 16–1 ka. Comparison of these monsoon changes with solar activity and North Atlantic cooling events reveals that both factors can lead to abrupt changes on a centennial timescale in the Early Holocene. During the Late Holocene, North Atlantic cooling became the major forcing of centennial monsoon events.\n
Centennial- to decadal-scale monsoon precipitation variations in the upper Hanjiang River region,China over the past 6650 years
[J].DOI:10.1016/j.epsl.2017.11.044 URL [本文引用: 1]
Avvatech XRF岩芯扫描分析方法在石笋Sr/Ca测试中的应用
[J].
Application of Avaatech X-ray fluorescence core-scanning in Sr/Ca analysis of speleothems
[J].
Can XRF scanning of speleothems be used as a non-destructive method to identify paleoflood events in caves?
[J].DOI:10.5038/1827-806X URL [本文引用: 1]
石笋氧同位素和微量元素记录的陕南地区4200-2000 a B.P.高分辨率季风降雨变化
[J].
High-resolution monsoon precipitation variations in southern Shaanxi,Central China during 4200-2000 a B.P.as revealed by speleothem δ18O and Sr/Ca records
[J].
基于XRF岩芯扫描的贵州喀斯特地区晚全新世泥炭古环境研究
[J].
Application of XRF core scanning method in Late Holocene environment change study derived from a peat core from southwestern Guizhou,Southwestern China
[J].
Persistent,multi-sourced lead contamination in Central Europe since the Bronze Age recorded in the Füramoos peat bog,Germany
[J].DOI:10.1016/j.ancene.2021.100310 URL [本文引用: 1]
Utilisation of XRF core scanning on peat and other highly organic sediments
[J].
DOI:10.1016/j.quaint.2018.10.015
[本文引用: 1]

XRF core scanning (XRF-CS) is a valuable tool, which allows for the rapid, non-destructive geochemical analysis of sediment cores at extremely high (sub-millimetre) resolution. Peat sediments, due to their near-worldwide distribution, high organic content allowing for reliable radiocarbon chronology development, and typically autochthonous nature, have long been used for palaeoenvironmental reconstructions. However, XRF-CS methods have been utilised on peat sediments relatively rarely. This is due in part to analytical uncertainty relating to high water content, uneven sediment surfaces and high organic matter contents negatively impacting the ability of the approach to reliably reproduce elemental compositions. Here we provide evidence from Mohos peat bog record in central Romania, and, by comparing to ICP measurements, indicate the ability of XRF-CS to consistently investigate the elemental geochemistry of peat sediments for major elements such as Fe and Ti. However, trace element (Cu, Ni and Sc) measurements appear to be unreliable, due in part to measurements approaching detection limits, and the diluting nature of the peat. Further, we investigate the usefulness of the Incoherent/Coherent (inc/coh) scattering ratio as a proxy for organic matter content, concluding that within high-organic sediment such as peat, the ratio does not pick up small shifts (< 5%) in organic content. Finally, we present a review of approaches applied to investigating peat sediments via XRF-CS to date, with a number of suggestions for future avenues of research.
XRF core scanning yields reliable semiquantitative data on the elemental composition of highly organic-rich sediments:Evidence from the Füramoos peat bog (Southern Germany)
[J].DOI:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.134110 URL [本文引用: 1]
Testing commonly used X-ray fluorescence core scanning-based proxies for organic-rich lake sediments and peat
[J].DOI:10.1111/bor.12145 URL [本文引用: 1]
Cross calibration between XRF and ICP-MS for high spatial resolution analysis of ombrotrophic peat cores for palaeoclimatic studies
[J].
DOI:10.1007/s00216-014-8289-3
PMID:25404165
[本文引用: 1]

Ombrotrophic peatlands are remarkable repositories of high-quality climatic signals because their only source of nutrients is precipitation. Although several analytical techniques are available for analysing inorganic components in peat samples, they generally provide only low-resolution data sets. Here we present a new analytical approach for producing high-resolution data on main and trace elements from ombrotrophic peat cores. Analyses were carried out on a 7-m-long peat core collected from Danta di Cadore, North-Eastern Italy (46° 34' 16″ N, 12° 29' 58″ E). Ca, Ti, Cr, Fe, Cu, Zn, Ga, Sr, Y, Cd, Ba and Pb were detected at a resolution of 2.5 mm with a non-destructive X-ray fluorescence core scanner (XRF-CS). Calibration and quantification of the XRF-CS intensities was obtained using collision reaction cell inductively coupled plasma quadruple mass spectrometry (CRC-ICP-QMS). CRC-ICP-QMS measurements were carried out on discrete samples at a resolution of 1 cm, after dissolution of 150-mg aliquots with 9 ml HNO3 and 1 ml HF at 220 °C in a microwave system. We compare qualitative XRF-CS and quantitative CRC-ICP-MS data and, however the several sources of variability of the data, develop a robust statistical approach to determine the R (2) and the coefficient of a simple regression model together with confidence intervals. Perfect positive correlations were estimated for Cd, Cr, Pb, Sr, Ti and Zn; high positive correlations for Ba (0.8954), Y (0.7378), Fe (0.7349) and Cu (0.7028); while moderate positive correlations for Ga (0.5951) and Ca (0.5435). With our results, we demonstrate that XRF scanning techniques can be used, together with other well-established geochemical techniques (such as ICP-MS), to produce high-resolution (up to 2.5 mm) quantitative data from ombrotrophic peat bog cores.
Long-term environmental changes in the Geum Estuary (South Korea):Implications of river impoundments
[J].DOI:10.1016/j.marpolbul.2021.112383 URL [本文引用: 1]
Extreme floods of the Changjiang River over the past two millennia:Contributions of climate change and human activity
[J].DOI:10.1016/j.margeo.2020.106418 URL [本文引用: 1]
Last millennium intensification of decadal and interannual river discharge cycles into the Southwestern Atlantic Ocean increases shelf productivity
[J].DOI:10.1016/j.gloplacha.2020.103367 URL [本文引用: 1]
Holocene fluvial landscape evolution driven by sea level and tectonic controls in the Gangkou River,Hengchun Peninsula
[J].DOI:10.3319/TAO.2021.04.08.01 URL [本文引用: 1]
近百年来长江水下三角洲高分辨率洪水沉积记录及其控制机理
[J].
High resolution flood records in the Yangtze subaqueous delta during the past century and control mechanism
[J].
Micro-XRF applications in fluvial sedimentary environments of Britain and Ireland:Progress and prospects
[G]//Croudace I W,Rothwell R G.Micro-XRF studies of sediment cores:Applications of a non-destructive tool for the environmental sciences.Dordrecht,Netherlands:Springer,
河流沉积物原位XRF岩芯扫描结果定量估算的初步研究
[J].
Preliminary study on calibration of X-ray fluorescence core scanner for quantitative element records in the yellow river sediments
[J].
Historical and post-ban releases of organochlorine pesticides recorded in sediment deposits in an agricultural watershed,France
[J].
Calibrating high resolution XRF core scanner data to obtain absolute metal concentrations in highly polluted marine deposits after two case studies off Portmán Bay and Barcelona,Spain
[J].DOI:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.134778 URL [本文引用: 1]
200-year industrial archaeological record preserved in an Isle of Man saltmarsh sediment sequence:Geochemical and radiochronological evidence
[J].
DOI:10.1016/j.quaint.2018.09.045
[本文引用: 1]

The Isle of Man, situated in the central Irish Sea, was a significant centre for Pb and Zn mineral extraction during the Industrial Revolution. Comminuted mining debris from the East Snaefell and North Laxey mining areas was transported, through hydrological action, from upland catchments to the coast. This study focuses on an eastern coastal sediment sink and a salt marsh sediment sequence from Port Cornaa. A sediment monolith was excavated, sub-sampled and geochemically investigated using Itrax scanning, WD-XRF analysis and radionuclide methods. Since the island is only 55 km from one of the world's major nuclear reprocessing sites (Sellafield), it was anticipated that a record of these radionuclide discharges (1951-present) would be identifiable and contribute clear chronological markers. The Cs-137 profile shows a Sellafield discharge component and also a larger component that is attributed to the 1986 Chernobyl airborne plume. This contribution in the salt-marsh sediment would be derived from the erosion and transport of Chernobyl-labelled upland soils into the marsh. Sediment depth was converted to age using natural (Pb-210) and anthropogenic radionuclides (Cs-137 and (239), Pu-240) and a compelling age vs depth relationship was obtained. The ability to reliably date the overall sediment section shows that sediment accumulation is uniform for the top 25 cm (5 mm/y) and from -25 to -70 cm (3.2 mm/y). The robust age-depth model allows features in the geochemical profiles for S, As, Pb, Zn and Cu to be dated and used to infer events at the East Snaefell and North Laxey mines. These include start-up of mining, introduction of more-efficient mining practises (i.e. water-wheel technology), change in the intensity of mining and final mine closure. The study provides a 200-year industrial archaeological record for the east coast of the Isle of Man. It demonstrates the benefits offered by a combined study involving non-destructive, high resolution Itrax scanning, conventional WDXRF and radionuclide dating.
X-ray core scanners as an environmental forensics tool:A case study of polluted harbour sediment (Augusta Bay,Sicily)
[G]//Croudace I W,Rothwell R G.Micro-XRF studies of sediment cores:Applications of a non-destructive tool for the environmental sciences.Dordrecht,Netherlands:Springer,
Modern pollution signals in sediments from Windermere,NW England,determined by Micro-XRF and lead isotope analysis
[G]//Croudace I W,Rothwell R G.Micro-XRF studies of sediment cores:Applications of a non-destructive tool for the environmental sciences.Dordrecht,Netherlands:Springer,
Tracking the legacy of early industrial activity in sediments of Lake Zurich,Switzerland:Using a novel multi-proxy approach to find the source of extensive metal contamination
[J].
DOI:10.1007/s11356-022-21288-6
[本文引用: 1]

Historical industrial activities at the Horn Richterwil, on the shore of Lake Zurich (Switzerland), caused widespread metal contamination on land and in the adjacent lake sediments. This study provides an estimation of the age and source of the contamination by using XRF core scanning, ICP-OES, and Hg-AFS for quantitative measurements of trace metals and MC-ICP-MS for the stable isotope analysis of mercury. Radiometric dating ($$^{137}$$\n \n \n 137\n \n Cs, $$^{210}$$\n \n \n 210\n \n Pb, and Pu dating) of two proximal cores and varve chronology in a distal core suggest two different contaminations, one stemming from around 1960 (Zn, Cd) and an earlier one from 1880 (Cr, Cu, Hg, Pb, Sn). The XRF data suggest two different contamination pathways: one by landfill of contaminated soil and another one by industrial wastewater effluents. Maximum concentrations found within all samples are in the range of per mil (dry weight) for Cr, Cu, Hg, Pb, Sn, and Zn and lie within the top 10 cm of the sediment cores. The analysis of the mercury isotopic composition ($$\\delta ^{202}$$\n \n δ\n 202\n \n Hg and $$\\Delta ^{199}$$\n \n Δ\n 199\n \n Hg) shows a significantly different signature for one of the cores, indicating a second mercury source. We could not identify the exact source or process leading to the isotopic fractionation of mercury, but the isotopic data confirm two different sources.
Limited influence of sediment grain size on elemental XRF core scanner measurements
[G]//Croudace I W,Rothwell R G.Micro-XRF studies of sediment cores:Applications of a non-destructive tool for the environmental sciences.Dordrecht,Netherlands:Springer,
An empirical assessment of variable water content and grain-size on X-ray fluorescence core-scanning measurements of deep sea sediments
[G]//Croudace I W,Rothwell R G.Micro-XRF studies of sediment cores:Applications of a non-destructive tool for the environmental sciences.Dordrecht,Netherlands:Springer,
Calibration of XRF core scanners for quantitative geochemical logging of sediment cores:Theory and application
[J].DOI:10.1016/j.epsl.2008.07.054 URL [本文引用: 5]
Prediction of geochemical composition from XRF core scanner data:A new multivariate approach including automatic selection of calibration samples and quantification of uncertainties
[G]//Croudace I W,Rothwell R G.Micro-XRF studies of sediment cores:Applications of a non-destructive tool for the environmental sciences.Dordrecht,Netherlands:Springer,
Correction of interstitial water changes in calibration methods applied to XRF core-scanning major elements in long sediment cores:Case study from the South China Sea
[J].DOI:10.1002/2016GC006320 URL [本文引用: 5]
Comparison and calibration of elemental measurements in sediments using X-ray fluorescence core scanning with ICP methods:A case study of the South China Sea deep basin
[J].
WDXRF光谱仪与EDXRF光谱仪之异同
[J].
Comparison of WDXRF and EDXRF spectrometry
[J].
粉末压片—X射线荧光光谱法分析富硒土壤样品中的硒及主次量元素
[J].
Determination of selenium,major and minor elements in selenium-rich soil samples by X-ray fluorescence spectrometry with powder pellet preparation
[J].
熔融制样—X射线荧光光谱法测定稀土矿石中的主量元素和稀土元素
[J].
Determination of major and rare earth elements in rare earth ores by X-ray fluorescence spectrometry with fusion sample preparation
[J].
长江三角洲平原湖沼沉积物XRF岩芯扫描结果的可靠性分析
[J].
Reliability analysis of X-ray fluorescence core-scanning in the Yangtze River delta limnetic sediments
[J].
便携式X荧光分析仪在萤石矿勘查中的应用
[J].
The application of portable X-ray fluorescence analyzer to fluorite prospecting
[J].
手持式X射线荧光光谱分析仪在斑岩铜矿快速勘查中的应用
[J].
Practicality of hand-held XRF analyzer in rapid exploration of porphyry copper deposit
[J].
便携式X荧光仪在多金属矿区的应用
[J].
The application of portable X-ray fluorescence instrument to the polymetallic ore district
[J].
基于pXRF原位分析的内蒙古兴和曹四夭钼矿床深部岩石地球化学特征
[J].
Lithogeochemistry characterization based on the in-Situ pXRF analyses of rocks in depth of the Caosiyao molybdenum deposit,Inner Mongolia,China
[J].
手持式X荧光分析仪在空气颗粒物分析中的应用
[J].
Application of handheld X-ray fluorescence in the analysis of air particulate matter
[J].
手持式XRF分析仪快速检测大气颗粒物中Cu、Zn、Pb含量
[J].
Pb in atmospheric particulate matter by the handheld X-ray fluorescence analyzer
[J].
便携式XRF仪在土壤重金属检测中的应用
[J].
Application of portable X-ray fluorescence spectrometer analyzer in field detection of heavy metal
[J].DOI:10.1021/es034515c URL [本文引用: 1]
便携式X射线荧光光谱仪快速监测重金属土壤环境质量
[J].
Fast monitoring soil environmental qualities of heavy metal by portable X-ray fluorescence spectrometer
[J].Portable X-ray fluorescence (PXRF) spectrometer as a new type of equipment for quick test has a prominent prospect, but there are also shortcomings of detection range and limition, therefore this paper studied the suitability of PXRF spectrometer in monitoring soil environmental qualities of heavy metals included Cr, Ni, Cu, Zn, Pb, Cd, As and Hg, the aim of this paper is to screen elements which can be detected by this kind of instrument and evaluate the accuracy of test results. The research method is to test heavy metals contaminated soil samples by PXRF spectrometer, evaluate the accuracy of test results of PXRF compared with inductively coupled plasma mass(ICP-MS), then establish linear regression relationship between analysis results of PXRF and ICP-MS method. The results show that, (1) When measuring the soil environmental quality, PXRF spectrometer is appropriate to measure the content of Pb, Zn, Cr and Cu, except Ni, Cd, As and Hg. (2) Compared with the test value of ICP-MS, the test value of Pb and Zn is lower, the test value of Cu is higher, the test value of Cr is too high, all the results of PXRF spectrometer should be linear corrected according to standard analysis method. In conclusion, PXRF spectrometer is suitable for monitoring environmental quality of soil which is polluted by heavy metal such as Pb, Zn, Cr and Cu, it is an analysis means with characteristics of simple and rapid, accurate and reliable. The innovation of this article is that reasonable avoiding the shortcomings of PXRF spectrometer as using the instrument to monitor soil environmental quality, at last improved the application value of test results.
Paleoenvironmental evolution and human activities at the Hejia Site on the Ningshao coastal plain in Eastern China
[J].
DOI:10.3389/feart.2020.609912
URL
[本文引用: 1]

The eastern China coastal plain is an ideal area for studying the human–environment interaction during the Neolithic period as there are multiple Neolithic sites in this area. Located in the Ningshao Coastal Plain of the south bank of Hangzhou Bay in eastern China, the Hejia Site is part of the late Hemudu Culture sites and includes the late Hemudu Culture, the Liangzhu Culture, and the Qianshanyang Culture. Based on palynology, charcoal, X-ray fluorescence (XRF), and magnetic susceptibility (χ), combined with accelerator mass spectrometry 14C dating and analysis of the archaeological cultural layers, we explored the paleoenvironmental evolution and human activities at the Hejia Site. 1) Pollen records suggest that the vegetation type was evergreen and deciduous broad-leaved mixed forest during the Middle Holocene. Cr/Cu and low-frequency magnetic susceptibility (χlf) reveal that the climate underwent through warm and wet (Hemudu Culture Period IV)–cool and dry (Liangzhu Culture Period)–warm and wet (Qianshanyang Culture Period) periods. 2) During the Middle Holocene, the intensity of human activities, related to the transformation of the natural environment, increased obviously. The increasing Poaceae pollen (&gt;37 μm) indicates that the ability of prehistoric humans in managing crop fields gradually increased from the late Hemudu Culture Period to the Liangzhu Culture Period. The charcoal concentration results suggest that the occurrence of high-intensity fire events during the late Hemudu Culture Period might be caused by the slash-and-burn operation, while those that occurred during the middle Liangzhu Culture Period might be caused by the increasing fire demand owing to the greater ancestors’ lives and production activities in the Liangzhu Culture Period.
Recognition of Milankovitch cycles in XRF core-scanning records of the Late Cretaceous Nenjiang Formation from the Songliao Basin (northeastern China) and their paleoclimate implications
[J].DOI:10.1016/j.jseaes.2019.104183 URL [本文引用: 1]
Parameter optimisation for the ITRAX core scanner
[G]//Croudace I W,Rothwell R G.Micro-XRF studies of sediment cores:Applications of a non-destructive tool for the environmental sciences.Dordrecht,Netherlands:Springer,
X-ray fluorescence (XRF) set-up with a low power X-ray tube
[J].
DOI:10.1016/j.apradiso.2010.05.001
PMID:20570160
[本文引用: 1]

The X-ray fluorescence set-up with a 100 W X-ray tube comprises a computer controlled system developed for remote operation and monitoring of tube and an adjustable stable 3D arrangement to procure variable excitation energies with low scattered background. The system was tested at different filament currents/anode voltages. The MDL of the set-up at 0.05-1.00 mA/4-12 kV is found approximately (1-100)ppm for K and L excitations and approximately (200-700)ppm for M excitations of elements and improves with filament current and anode voltage. Moreover, L measurements for Sm and Eu at five K X-ray energies of elements(Z=29-40) and analytical determination in some synthetic samples were undertaken.Copyright 2010 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Enhancing the ratio of fluorescence to bremsstrahlung radiation in X-ray tube spectra
[J].This paper describes techniques that can be used to improve the ratio of fluorescence to bremsstrahlung radiation (F/B) in X-ray tube spectra. Firstly, an extension of the EGS4 code system is used to evaluate the impact of the substrate in thin target applications, in terms of the yield of bremsstrahlung photons produced. The choice of materials to filter X-ray tube spectra, and its effect in the F/B and the tube efficiency is discussed. The characteristics of spectra produced in transmission tubes with different target thicknesses, substrates and tube voltages are also presented.
Choosing optimal exposure times for XRF core-scanning:Suggestions based on the analysis of geological reference materials
[J].DOI:10.1002/2016GC006256 URL [本文引用: 2]
湖泊沉积物XRF元素连续扫描与常规ICP-OES分析结果的对比及校正——以兹格塘错为例
[J].
Comparison and correction of element measurements in lacustrine sediments using X-ray fluorescence core-scanning with ICP-OES method:A case study of Zigetang Co
[J].DOI:10.18307/2011.0220 URL [本文引用: 2]
同步辐射X射线荧光光谱法测定沉积物中元素含量的归一方法研究——以四海龙湾纹层沉积物为例
[J].
Research on normalization method for element analysis of sediment with Synchrotron Radiation X-Ray Fluorescence(SRXRF)——An example of varved sediment in Lake Sihailongwan,Northeast China
[J].