0 引言
四川中部须家河组油气储量广泛分布,其中安岳气田区域其构造位于上三叠统须家河组,地层受造山运动影响,受到了长期的挤压与压实作用,其构造格局介于挤压构造与挤压走滑构造之间,少数逆断层发育,变形较弱,存在众多小型圈闭,是典型的丘陵地貌。该构造带中的低缓短轴背斜非常有利于油气成藏。
本文研究目的层段为川中须家河组二段,其分布较为广泛,为一套砂泥岩互层完整的生储盖组合[1-2]。须二段为以灰色中—细粒砂岩为主的大规模辫状河三角洲沉积,是须家河组含油气层的主要储集层系,表现为典型的“厚砂薄储”的特点[3]。储层强烈的压实作用和广泛的胶结作用使须二段储层受到很强压实作用,具有非均质性特征[4-5],导致使用一种参数模型无法评价所有探井。同时,储层孔隙度平均8.36%,主要分布在4%~12%;渗透率平均为0.25×10-3μm2,主要为(0.05~0.55)×10-3μm2,属于典型的低孔、低渗致密砂岩储层。因此,须二段储集层在沉积作用、成岩作用和构造作用等多种因素控制下,具有非均质性显著、埋藏深、成岩改造强烈的特点[6]。储层的强非均质性使得利用常规测井、地震等手段对含气性参数的计算变得更为复杂,给储层预测带来了新的挑战。
为进一步提升须家河组的储层含气性预测精度,关旭等[8]采用近道、远道反射特征对比与AVO主振幅主频率技术相结合的方法,对须二段含气有利区分布进行预测。Lu等[9]则利用气藏中“低频阴影”和“高频衰减”的特征,将气藏与水藏区分开。以上基于地震信号的时频分析已被用来区分徐家河组的气藏和含水层。来自地下的地震反射波信息通常是多层介质的综合响应,每一个薄层产生的地震信号在频率域都有一个与之对应的特定频率,在有效地震频率范围内(10~60 Hz),通常这种频率成分在频率域是唯一的[10⇓-12]。由于受地层厚度、地震波反射频率耦合等不确定因素的影响,导致在实际应用中AVO反演的效果存在较大差异,增加了预测结果的不确定性。地震分频AVO技术作为一种基于频谱分析的地震成像解释新方法,更为全面的涵盖到了地层分界面两侧的弹性参数和频率因素[10]。许多学者在叠前AVO分析及地震属性计算中采用了时频分析工具进行分频研究。路慎强[13]和宁媛丽等[14]利用叠前分频AVO方法消除薄层调谐效应对AVO的影响,以解决薄互层储层AVO识别问题。孔栓栓等[15]研究分频振幅检测浅层“亮点”型气层的方法。然而致密气储盖组合空间差异大,层间物性差异小等特点决定了其预测技术要求更加精细,因此分频AVO技术应用于致密气储层预测还需进一步研究。
本文以安岳气田须家河二段储层地质特征为指导,引入分频AVO分析方法来对气层和水层进行区分,并对该地区须二段的含气储层进行综合预测。通过分频AVO分析技术在须家河组储层中的实际应用,较好地解决了气水分异难题,提高了须二段的气藏预测精度。
1 AVO正演模拟分析
1.1 不同流体地震频谱特征
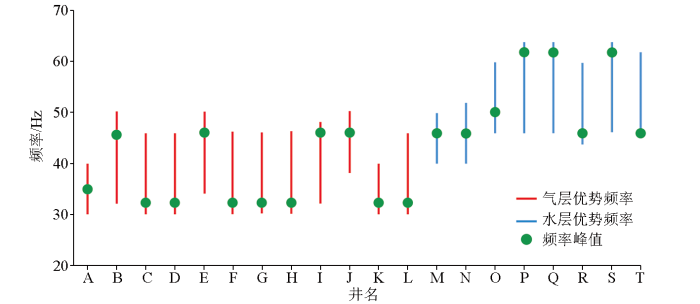
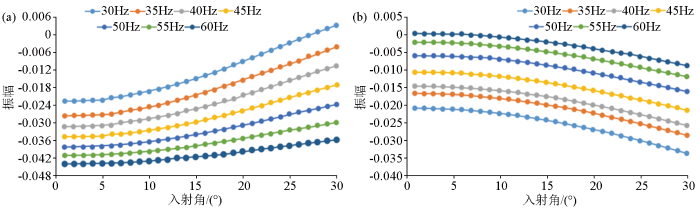
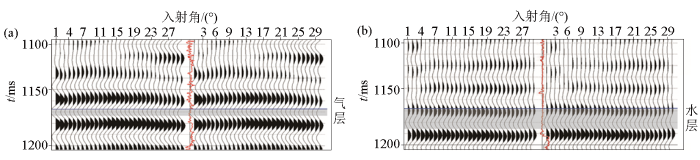
图1
图1
不同流体类型储层井旁道频谱差异
Fig.1
Spectrum difference diagram of sidetrack in reservoir with different fluid types
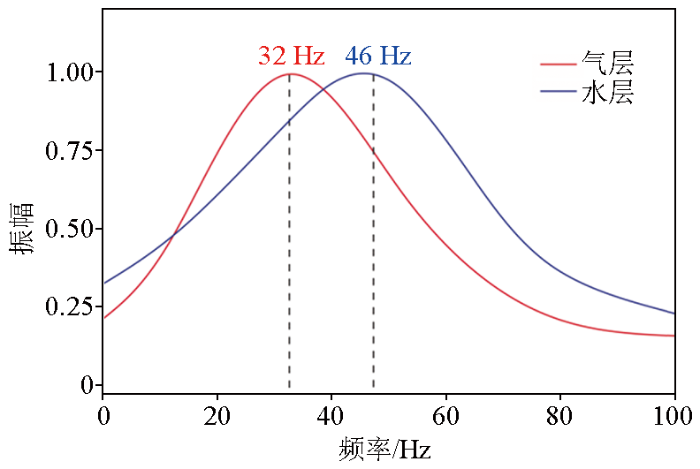
图2
图2
典型气、水层地震频谱特征
Fig.2
Seismic spectrum characteristics of typical gas and water layers
1.2 气层AVO响应特征
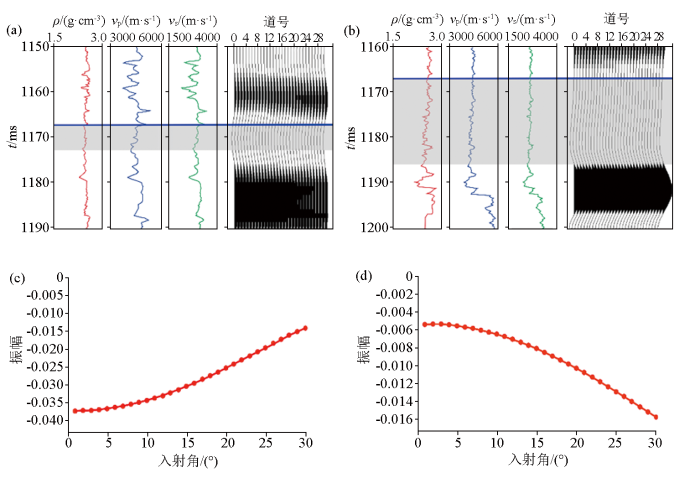
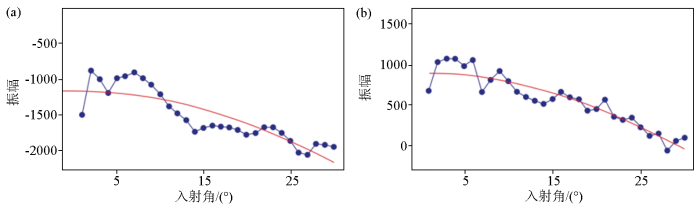
图3
图3
A井及B井正演模拟
a—A井测井曲线与正演道集;b—B井测井曲线与正演道集;c—A井AVO曲线;d—B井AVO曲线
Fig.3
Forward modeling of well A and well B
a—logging curve and forward trace gather of well A;b—logging curve and forward trace gather of well B;c—AVO curve of well A;d—AVO curve of well B
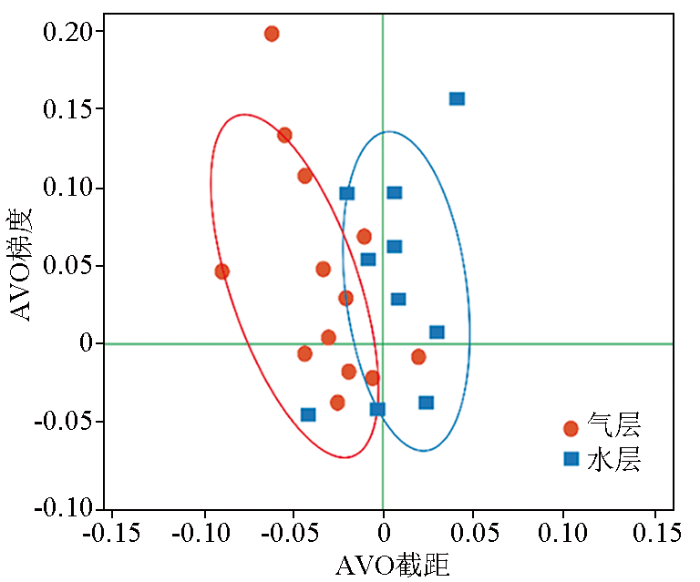
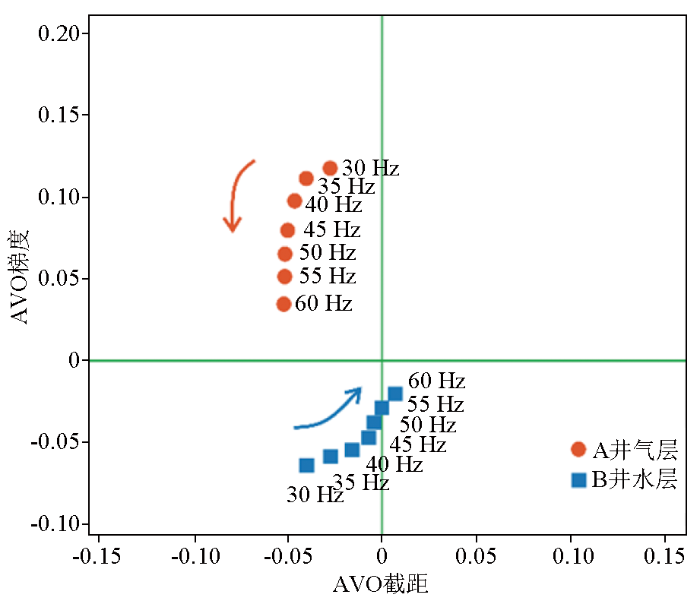
图4
图4
研究区多井气、水层P-G交会
Fig.4
P-G cross plot of multi well gas and water layer in the study area
图5
图5
A井及B井分频AVO曲线
a—A井气层;b—B井水层
Fig.5
Frequency division AVO curve of well A and well B
a—gas layer of well A;b—water layer of well B
图6
图6
A井气层及B井水层分频P-G交会
Fig.6
Frequency division P-G cross plot of gas layer of well a and water layer of well B
2 分频处理分析
2.1 基于小波变换的分频处理技术
1984年Morlet等[24]提出了连续小波变换,其核函数是Morlet小波。小波变换是一种利用偏移缩放的模式获取有效信息的时频分析方法,其出现时间较早,发展时间较长,研究体系已相对成熟。地震信号往往是以非平稳信号的形式表现的,在已知非平稳信号
其中:
较于傅里叶变换而言,由于其时窗可以自适应调节,被誉为“数学显微镜”,因此在一定程度上使得时间与频率在分辨率方面的矛盾有所缓解,其局部特征描述也较细致。基于以上特点,利用在应用范围上相对广泛的小波变换分频技术进行分频AVO分析。
2.2 叠前道集分频处理
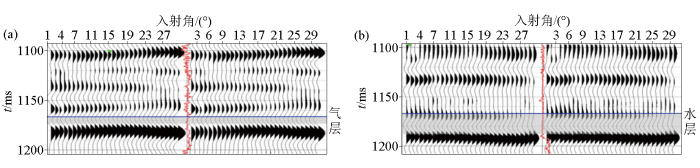
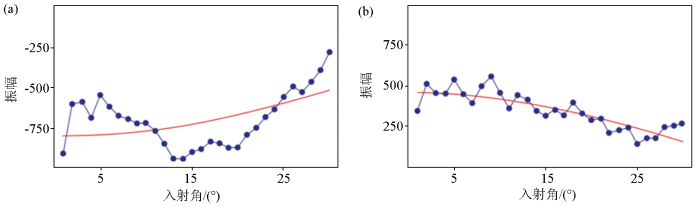
为了进一步增加分频结果的准确性,在AVO分析的基础上,需对CPR道集进行加工处理,如剩余时差微校正、超道集、角道集等。在叠前反演之前先进行AVO目标处理,相较于共中心点道集,叠前地震角道集(图7)可以通过对比振幅在不同地层界面上相同角度内的变化趋势,进而对地层流体和岩性的特征进行识别[25⇓-27]。从提取的A井和B井的实际井旁原始道集的振幅响应曲线可以看出,A井气层的原始叠前道集的AVO响应曲线与B井水层的响应特征一致(图8),其井旁道集振幅响应均随角度的增大而减小。上述结论与两口井的正演模型结果不同,并且A井的模型正演响应特征与地震响应特征明显相反(图3c、图8a)。由于测井资料真实可信,而常规地震处理方法在低频保护、分辨率提高、AVO 特征的道集保护等方面针对性不强,地震道集资料较差,AVO 响应特征分析受到影响较大[28],因此需对叠前道集进行分频处理。
图7
图7
A井气层(a)及B井水层(b)的叠前地震道集
Fig.7
Prestack seismic gathers passing through gas layer of well A(a) and water layer of well B(b)
图8
图8
A井气层(a)及B井水层(b)的原始叠前道集振幅响应特征
Fig.8
Amplitude response characteristics of original prestack gathers of gas layer in well A(a) and water layer in well B(b)
图9
图9
A井气层(a)及B井水层(b)的35~45 Hz角道集
Fig.9
35~45 Hz angle gathering through gas layer of well A(a) and water layer of well B(b)
图10
图10
35~45 Hz分频数据体在A井气层(a)及B井水层(b)的井旁的振幅响应曲线
Fig.10
Amplitude response curve of 35~45 Hz frequency divided data volume at the well side of gas layer of well A(a) and water layer of well B(b)
3 分频AVO属性分析
3.1 分频AVO敏感属性优选
Zoeppritz方程主要表达入射波、反射波及折射波的振幅与角度的关系。由于该方程的变量复杂,因此前人对其进行简化。而AVO 反演方法的理论基础是由 Zoeppritz 方程简化后的 shuey 近似方程[29],其三参数近似方程可表示为
式(3)中:R(θ)为界面反射系数; θ为入射角; A、B、C分别为AVO截距、斜率和曲率,是 AVO 的3个基本属性参数。式(4)中:Rpp为垂直入射P波反射系数;G为反射振幅随偏移距变化率。P和G为方程截距和梯度,是AVO双属性参数。对于不同的角度道集,通过角度道反射系数与角度的拟合关系可求取得到以上的基本属性,再依据属性之间的关系就能得到其他属性参数[17]。
基于角度道集资料进行AVO属性反演,提取相对密度(DDN)、相对横波速度(DVS)、流体因子(FF)、相对泊松比(PR)、相对泊松比差(PRR)、相对横波反射率(RVS)和相对横波速度差异(VSR)等常见的AVO属性。常见的AVO属性的物理意义及计算公式见表1。
表1 AVO属性物理意义及公式
Table 1
| AVO属性 | 物理意义 | 计算公式 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 差异横波速度 | 反映出横波速度的 变化率特征 | ||
| 差异密度 | 反映密度的变化 率特征 | ||
| 差异纵波速度 | 反映出纵波速度的 变化率特征 | ||
| 流体因子 | 显示与Castagna方 程不符的含油气区 | ||
| 泊松比 | 反映岩层泊松比 的变化特征 | ||
| 横波反射系数 | 反映横波阻抗 的特征 |
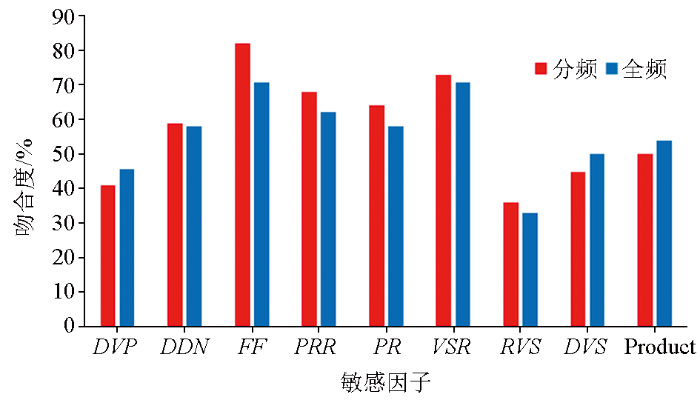
通过对工区10口井气层及水层的AVO属性剖面观察,相同位置剖面上,气层显示为负异常,水层显示为正异常。测井响应与属性图中负异常指示区域一致。对多井AVO属性与含气性响应吻合度对比(图11)可知,相对横波速度差异VSR、相对泊松比差PRR和流体因子FF的井震油气显示吻合度最高,可将其优选为含气性敏感属性,用于研究区的含气性预测。
图11
图11
多井AVO属性与含气性响应吻合度对比
Fig.11
Comparison of coincidence between AVO attribute and gas bearing response of multiple wells
3.2 含气性预测
从分频叠前道集中提取优势频段的流体因子(FF)、相对横波速度差异(VSR)、相对泊松比差(PRR)3个含气性敏感属性,构建优势频段流体指示因子,进行含气性分布预测。对上述3种相关性较高的属性赋予不同的权值,权值的计算为
最后将含气敏感参数组合叠加求得到烃类指示因子DHI,即
式中:Ci分别为流体因子(FF)、相对横波速度差异(VSR)、相对泊松比差(PRR)的权重,单位%;Ri分别为流体因子(FF)、相对横波速度差异(VSR)、相对泊松比差(PRR)的定量化贡献度。主要是将流体因子属性、相对泊松比差及相对横波速度差异的值置于同一个数量级上,DHI的累计负异常可指示含气性分布情况。
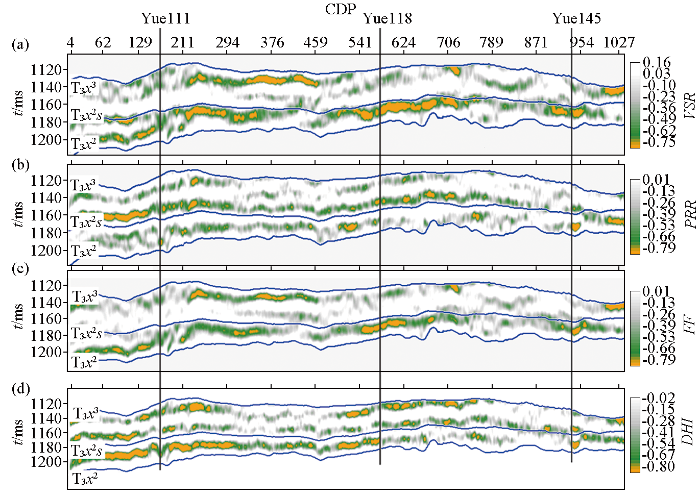
图12
图12
Yue111—Yue118—Yue145井连线的35~45 Hz优势频段属性预测剖面
Fig.12
Prediction profile of dominant frequency band with 35~45 Hz attribute of well Yue111—Yue118—Yue145 well
图13
图13
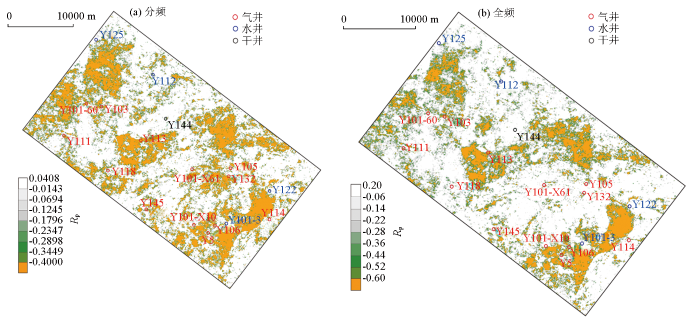
须二段上亚段DHI含气性预测平面对比
Fig.13
Plane comparison of DHI gas content prediction of upper sub member of Xujiahe formation 2
表2 AVO含气性异常响应对比
Table 2
| 井名 | 气测 结果 | AVO 响应 | 全频井震对比 | 分频井震对比 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 含气 响应 | 吻合 情况 | 含气 响应 | 吻合 情况 | |||
| Yue103 | 气井 | 负异常 | 有 | 吻合 | 有 | 吻合 |
| Yue111 | 气井 | 负异常 | 有 | 较吻合 | 有 | 吻合 |
| Yue113 | 气井 | 负异常 | 有 | 吻合 | 有 | 吻合 |
| Yue114 | 气井 | 正异常 | 无 | 不吻合 | 无 | 不吻合 |
| Yue118 | 气井 | 负异常 | 无 | 不吻合 | 有 | 较吻合 |
| Yue122 | 水井 | 负异常 | 无 | 吻合 | 无 | 吻合 |
| Yue145 | 气井 | 负异常 | 无 | 不吻合 | 有 | 吻合 |
| Yue101-3 | 水井 | 正异常 | 无 | 吻合 | 无 | 吻合 |
| Yue112 | 水井 | 正异常 | 无 | 吻合 | 无 | 吻合 |
| Yue125 | 水井 | 正异常 | 无 | 吻合 | 无 | 吻合 |
4 结论
1)川中地区须二段气层和水层的主频存在差异,气层地震反射主频在32 Hz左右,有效频带在32~46 Hz;水层地震反射主频在46 Hz左右,有效频带在46~62 Hz。在优势频段35~45 Hz范围内,气层AVO响应从Ⅳ类向Ⅲ类进行逆时针偏转;水层则从Ⅲ类向第一象限偏转。
2)通过对川中地区须二段气层及水层的研究,在优势频段35~45 Hz范围内,AVO 响应特征更好,差异性更大,更易突出含气响应特征,且分频道集的叠前数据响应特征与原始地震是一致的。
3)优选相对横波速度差、相对泊松比差PRR和流体因子为含气性敏感属性,将其叠加后得到的烃类指示因子DHI的负异常指示含气有利分布区。基于分频AVO的预测比全频段的预测效果较好,能有效提高了川中地区须二段气藏富集区地震预测的精确度。
参考文献
四川盆地须家河组气藏成藏特点及勘探前景
[J].
Exploration prospect and gas reservoir characteristics of Xujiahe Formation in Sichuan Basin
[J].
川中地区须家河组致密砂岩气藏气水分布模式及影响因素分析
[J].
Gas water distributed pattern in Xujiahe Formation tight gas sandstone reservoir and influential factor in central Sichuan Basin
[J].
川中地区上三叠统须家河组气源分析
[J].
An analysis of the gas source in the Upper Triassic Xujiahe Formation,central Sichuan Basin
[J].
四川盆地北部陆相大气田形成与高产主控因素
[J].
Key controls on accumulation and high production of large non-marine gas fields in northern Sichuan Basin
[J].DOI:10.1016/S1876-3804(13)60017-8 URL [本文引用: 1]
Impacts of lithologic characteristics and diagenesis on reservoir quality of the 4th member of the Upper Triassic Xujiahe Formation tight gas sandstones in the western Sichuan Basin,southwest China
[J].
DOI:10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2019.04.040
[本文引用: 1]

The 4th member of the Upper Triassic Xujiahe Formation has become a primary target for tight gas exploitation in the western Sichuan Basin in past decades. Finding relatively high porosity reservoirs in tight sandstones is significant for successful tight gas exploration. In this study, the Xu4 sandstone was studied by a variety of experimental methods, including core observation, thin-section and cathodoluminescence observation, porosity and permeability measurement, mercury intrusion, scanning electron microscopy, X-ray diffraction, electron probe micro-analyzer and fluid inclusion, to determine the reservoir characteristics and also diagenesis evolution and to discuss their impacts on the reservoirs. The Xu4 sandstones are mainly litharenites, feldspathic litharenites and sublitharenites. Among these, calcarenaceous sandstone (CS sandstone) and sandstone with a high kaolinite content (KS sandstone) are classified by their special compositions. The reservoir quality of the Xu4 sandstone is poor, and among the five types of sandstone, the reservoir quality of the KS sandstone is generally better than that of the other types. The diagenetic variations of the Xu4 sandstone are complicated by compaction, kaolinite and quartz cementation, two stages of carbonate cementation, and two stages of dissolution of feldspar and some unstable rock fragments. The KS sandstone is the product of feldspathic litharenite that underwent early-stage dissolution of feldspar during eodiagenesis because of the acidic fluids in the sandstone. This process resulted in a low K+/H+ ratio of the pore fluids, i.e., acidic fluids derived from atmospheric fresh water and fluids of adjacent strata bearing coal seams. The determination of the diagenetic evolution indicated that the poor reservoir quality can be attributed to strong compaction or extensive cementation (mainly calcite cementation). However, the occurrence of relatively high porosity reservoirs varies among the sandstones. For CS sandstone, weak early carbonate cementation is essential. For sublitharenite, feldspathic litharenite, and litharenite, late dissolution of feldspar and less cement are necessary for the formation of relatively high-quality reservoirs. Due to their high porosity, almost all of the KS sandstones are relatively high-quality reservoirs.
Data-driven diagenetic facies classification and well-logging identification based on machine learning methods:A case study on Xujiahe tight sandstone in Sichuan Basin
[J].
四川类前陆盆地须家河组序—岩相古地理特征
[J].
Sequence based lithofacies and paleogeographic characteristics of Upper Triassic Xujahe Formation in Sichuan Basin
[J].
川中地区须家河组岩性气藏特征与含气有利区预测——以安岳—磨溪地区须家河组二段为例
[J].
Lithologic gas reservoir characteristics and prediction of gas-bearing favorable zone ofthe Xujiahe Formation in central Sichuan Basin:Case study of the 2nd member of Xujiahe Formation in Anyue-Moxi areas
[J].
Gas and water reservoir differentiation by time-frequency analysis:a case study in southwest China
[J].DOI:10.1007/s40328-013-0031-7 URL [本文引用: 1]
地震分频AVO方法研究现状与展望
[J].
Research progressing on frequency dependent AVO analysis
[J].
基于叠前同时反演的致密砂岩储层预测及含气性识别——以苏里格S区块为例
[J].
Prediction and identification of gas-bearing gas-bearing properties of tight sandstone reservoirs through simultaneous pre-stack inversion:A case study of block S in Sulige gas field
[J].
广义S变换与薄互层地震响应分析
[J].
Generalized S transform and seismic response analysis of thin interbeds
[J].DOI:10.1002/cjg2.v46.3 URL [本文引用: 1]
叠前分频AVO分析方法在罗家地区的应用研究
[J].
DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1000-1441.2013.02.006
[本文引用: 1]

传统AVO理论只考虑单界面两侧地层的岩石物理特征,没有考虑地层厚度、地震波衰减及速度频散问题。采用考虑了层厚及地震波主频影响的层状介质Brekhovski方程进行岩石物理正演,并将其作为AVO分析的理论指导;利用小波分频技术与AVO分析相结合,分析不同频带范围内目的层地震反射振幅的AVO梯度变化,以解决薄互层储层的AVO识别预测问题。通过在罗家地区的应用研究,总结出了叠前分频AVO分析方法的实用流程,有效预测了沙河街组一段生物灰岩薄互层储层的分布范围。
Application of prestack frequency-division AVO analysis method in Luojia area
[J].
DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1000-1441.2013.02.006
[本文引用: 1]

<div style="line-height: 150%">The traditional AVO theory only considers the petrophysical characteristics of strata on both sides of the single</div><div style="line-height: 150%">interface,without considering the layer thickness,seismic wave attenuation and velocity dispersion.Here,we utilize</div><div style="line-height: 150%">layered media Brekhovski equation for rock physical forward modeling which takes layer thickness and the impact of</div><div style="line-height: 150%">seismic wave domain-frequency into account,and regards it as the theoretical guide for AVO analysis.By combining</div><div style="line-height: 150%">wavelet frequenct-division technique with AVO analysis,we study the AVO gradient variation of reflection amplitude</div><div style="line-height: 150%">of seismic wave in different frequency band to solve the AVO identification and prediction problem for thin-</div><div style="line-height: 150%">interbedded reservoir.By the application in Luojia Area,we conclude a practical workflow of prestack frequency-</div><div style="line-height: 150%">division AVO analysis.Through adopting the workflow,the distribution of thin-interbedded Es1 Biolithite reservoir is</div><div style="line-height: 150%">effectively predicted.</div>
应用反演谱分解去除调谐效应的分频AVO技术
[J].
Frequency-dependent AVO based on removing tuning effect via inverse spectral decomposition
[J].
分频振幅检测“亮点”型浅层气的方法研究及应用
[J].
The study and application of the method using frequency division amplitude to recognizing " bright spot" shallow gas layers
[J].
地震分频 AVO 技术在孟加拉湾海域深水沉积储层烃类检测中的应用
[J].
The application of seismic frequency decomposition AVO method in offshore deep-water sedimentary reservoirs hydrocarbon detection in the Bay of Bengal
[J].
建南地区须四段致密砂岩含气储层预测研究
[J].
Predicting tight gas-bearing Sandstone reservoir of the 4th Xijiahe Formation in Jiannan area
[J].
川中地区须二段气藏地震预测陷阱分析及对策——以龙女寺区块为例
[J].
Analysis and countermeasures of seismic prediction traps for Xu-2 gas reservoir in central Sichuan Basin:a case study from Longnyusi block
[J].
AVO交会分析及其应用
[J].
AVO cross plot analysis and its application
[J].
An empirical signal separation algorithm for multicomponent signals based on linear time-frequency analysis
[J].DOI:10.1016/j.ymssp.2018.11.037 URL [本文引用: 1]
频谱成像技术研究进展
[J].
The present research on frequency spectrum imaging technique
[J].
Analysis of the possibility of using various time-frequency transformation methods to Barkhausen noise characterization for the need of magnetic anisotropy evaluation in steels
[J].
DOI:10.3390/app11136193
URL
[本文引用: 1]

Magnetic Barkhausen Noise (MBN) is a method being currently considered by many research and development centers, as it provides knowledge about the properties and current state of the examined material. Due to the practical aspects, magnetic anisotropy evaluation is one of such key areas. However, due to the non-stationary and stochastic nature of MBN, it requires searching for postprocessing procedures, allowing the extraction of crucial information on factors influencing the phenomenon. Advances in the field of the analysis of non-stationary signals by various transformations or decompositions resulting into new time- and frequency-related representations, allow the interpretation of complex sets of signals. Therefore, in this paper, several time-frequency transformations were used to analyze the data of MBN for the purpose of the magnetic anisotropy evaluation of electrical steel. The three main transform types with their modifications were considered and compared: the Short-Time Fourier Transform, the Continuous Wavelet Transform and the Smoothed Pseudo Wigner–Ville Transform. By using Exploratory Data Analysis methods and the parametrization of time-frequency representation, the qualitative and quantitative analysis was made. The STFT presented good performance on providing useful information on MBN changes while simultaneously leading to the lowest computational efforts.
匹配追踪子波分解重构技术在气层检测中的应用
[J].
Application of matching pursuit wavelet decomposition and reconstruction technique to reservoir prediction and gas detection
[J].
Wave propagation and sampling theory partI:complex signal and scat-tering in multilayered media
[J].
DOI:10.1190/1.1441328
URL
[本文引用: 1]

From experimental studies in digital processing of seismic reflection data, geophysicists know that a seismic signal does vary in amplitude, shape, frequency and phase, versus propagation time. To enhance the resolution of the seismic reflection method, we must investigate these variations in more detail. We present quantitative results of theoretical studies on propagation of plane waves for normal incidence, through perfectly elastic multilayered media. As wavelet shapes, we use zero‐phase cosine wavelets modulated by a Gaussian envelope and the corresponding complex wavelets. A finite set of such wavelets, for an appropriate sampling of the frequency domain, may be taken as the basic wavelets for a Gabor expansion of any signal or trace in a two‐dimensional (2-D) domain (time and frequency). We can then compute the wave propagation using complex functions and thereby obtain quantitative results including energy and phase of the propagating signals. These results appear as complex 2-D functions of time and frequency, i.e., as “instantaneous frequency spectra.” Choosing a constant sampling rate on the logarithmic scale in the frequency domain leads to an appropriate sampling method for phase preservation of the complex signals or traces. For this purpose, we developed a Gabor expansion involving basic wavelets with a constant time duration/mean period ratio. For layered media, as found in sedimentary basins, we can distinguish two main types of series: (1) progressive series, and (2) cyclic or quasi‐cyclic series. The second type is of high interest in hydrocarbon exploration. Progressive series do not involve noticeable distortions of the seismic signal. We studied, therefore, the wave propagation in cyclic series and, first, simple models made up of two components (binary media). Such periodic structures have a spatial period. We present synthetic traces computed in the time domain using the Goupillaud‐Kunetz model of propagation for one‐dimensional (1-D) synthetic seismograms. Three different cases appear for signal scattering, depending upon the value of the ratio wavelength of the signal/spatial period of the medium. (1) Large wavelengths The composite medium is fully transparent, but phase delaying. It acts like an homogeneous medium, with an “effective velocity” and an “effective impedance.” (2) Short wavelengths For wavelengths close to twice the spatial period of the medium, the composite medium strongly attenuates the transmission, and superreflectivity occurs as counterpart. (3) Intermediate wavelengths For intermediate values of the frequency, velocity dispersion versus frequency appears. All these phenomena are studied in the frequency domain, by analytic formulation of the transfer functions of the composite media for transmission and reflection. Such phenomena are similar to Bloch waves in crystal lattices as studied in solid state physics, with only a difference in scale, and we checked their conformity with laboratory measurements. Such models give us an easy way to introduce the use of effective velocities and impedances which are frequency dependent, i.e., complex. They will be helpful for further developments of “complex deconvolution.” The above results can be extended to quasi‐cyclic media made up of a random distribution of double layers. For signal transmission, quasi‐cyclic series act as a high cut filter with possible time delay, velocity dispersion, and “constant Q” type of law for attenuation. For signal reflection they act as a low cut filter, with possible superreflections. These studies could be extended to three‐dimensional (3-D) binary models (grains and pores in a porous reservoir), in agreement with well‐known acoustic properties of gas reservoirs (theory of bright spots). We present some applications to real well data.
AVA analysis of BSR in fractured filled gas-hydrates reservoir in Krishna-Godavari Basin,India
[J].DOI:10.1007/s12594-022-2160-5 [本文引用: 1]
叠前AVA广义非线性纵、横波速度反演
[J].
Generalized non-linear P wave and S wave velocity inversion of prestack AVA
[J].
CRP道集优化处理及其在大庆油田S区的应用
[J].
CRP gather optimal processing and its application to S area of Daqing oilfield
[J].
四川盆地中部侏罗系沙溪庙组致密砂岩气藏地震一体化描述技术
[J].
Integrated seismic description technology for tight sandstone gas reservoir of Jurassic Shaximiao Formation in the central Sichuan Basin
[J].
AVO的内涵与外延
[J].
Intension and extension of AVO
[J].
A simplification of the Zoeppritz equations
[J].
DOI:10.1190/1.1441936
URL
[本文引用: 1]

The compressional wave reflection coefficient R(θ) given by the Zoeppritz equations is simplified to the following: [Formula: see text] The first term gives the amplitude at normal incidence (θ = 0), the second term characterizes R(θ) at intermediate angles, and the third term describes the approach to critical angle. The coefficient of the second term is that combination of elastic properties which can be determined by analyzing the offset dependence of event amplitude in conventional multichannel reflection data. If the event amplitude is normalized to its value for normal incidence, then the quantity determined is [Formula: see text] [Formula: see text] specifies the normal, gradual decrease of amplitude with offset; its value is constrained well enough that the main information conveyed is [Formula: see text] where [Formula: see text] is the contrast in Poisson’s ratio at the reflecting interface and [Formula: see text] is the amplitude at normal incidence. This simplified formula for R(θ) accounts for all of the relations between R(θ) and elastic properties first described by Koefoed in 1955.
叠前AVO反演技术在顺南地区碳酸盐岩储层含油气性预测中的应用
[J].
The application of pre-stack AVO inversion technology to the oil-bearing prediction of carbonate reservoirs in shunnan area
[J].
叠前地震反演方法对比分析——焦石坝页岩气藏勘探实例
[J].
Comparison and analysis of pre stack seismic inversion methods:An example of Jiaoshiba shale gas reservoir exploration
[J].