0 引言
塔里木盆地塔北—塔中地区超深层奥陶系白云岩—灰岩组合地层缝洞型储层非常发育。截至目前,在灰岩地层中发现有潜山型油藏、礁滩型油气藏、内幕地层以走滑断裂为主控因素的油气藏[1]。目前这类缝洞型储层是油田产能建设的核心靶区。在实际钻井过程中,有数口井都在地震明显断裂破碎带位置钻遇了优质储层,出现大量泥浆漏失,尤其富满油田多口井在奥陶系一间房组地层获得稳定高产工业油气流,创造了灰岩地层缝洞型储层产油速度的新纪录,产油速度达到日产1000 t。目前油田进入开发阶段,这种断裂破碎带[2-3]的地震响应主要是次一级反射强度和中—小规模的串珠群反射的集合,也有不少与周围反射差异较大的弱反射特征[4⇓-6]。针对断裂破碎带的研究是油田管理中的一项非常重要的工作。但是,这类储层非均质性强,储层预测面临着很大困难[7]。
地震资料反演是连接地震、测井与地质的桥梁,其作为储层量化描述的核心技术已经发展多年。各类反演方法与软件也是层出不穷,但总体上看,主要分为两大类:确定性反演和地质统计学反演。其中,约束稀疏脉冲反演方法是目前应用比较广泛的一种确定性反演方法[8]。约束稀疏脉冲反演方法在油田勘探初期发挥了重要作用,该方法的低频模型是在构造解释的层位、断层建立的框架模型基础上,对测井数据沿横向采用反距离加权等方法插值出来的,主要识别强“串珠状”反射特征储层。但是,随着研究对象的复杂化,常规约束稀疏脉冲反演方法的低频模型,无法反映储层的非均质性以及断裂破碎带特征[9],因此反演的结果很难准确识别出弱“串珠状”反射以及杂乱状反射特征的储层,不能充分表征断控储层的特征,钻井靶点的确定一度陷入困难。
所以迫切地需要建立一种能反映断裂破碎带非均质性的模型,同时符合地层沉积特征,通过多次迭代反演提升储层识别能力。本文提出以“走滑断裂破碎带相”为约束的储层预测方法,可以凸显断控储层的空间展布规律性,提高储层预测精度,符合地质认识。通过在塔里木盆地富满油田多个三维区块的实际应用,取得了显著的效果,为研究区滚动评价、加密调整、措施挖潜等工作提供了可靠的基础资料。
1 断控缝洞型储层波阻抗迭代反演策略
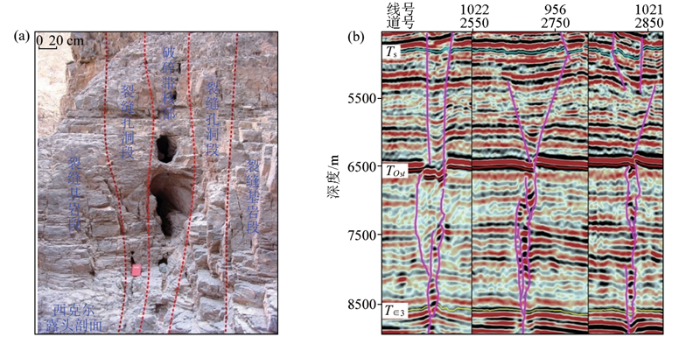
以位于塔里木盆地塔北隆起富满油田的富源Ⅲ期三维区块为例,研究区整体位于塔里木河南岸,北邻塔河油田,NW和NE方向分别是哈拉哈塘油田和轮古油气田,油气资源丰富。受构造运动作用,研究区奥陶系地层整体表现为西北高,东南低的斜坡,地层倾角整体变化不大,约2°~5°。奥陶系一间房组为主要目的层,岩性以灰岩类为主(亮晶颗粒灰岩、泥晶颗粒灰岩、生物灰岩等),是主要的储层发育段。区块内走滑断裂发育,以NE向和近SN向为主,优质储层集中分布在断裂附近,储集空间以岩溶作用形成的孔、洞、缝为主,非均质性强,表现为典型的断控储层特征。储层类型多样,主要有洞穴型储层、孔洞型储层、裂缝—孔洞型储层以及裂缝型储层,其中以裂缝—孔洞型储层比较普遍[10⇓⇓⇓-14](图1)。
图1
图1
走滑断裂破碎带岩溶模式(a)和储层地震反射特征剖面(b)
TS—志留系底;
Fig.1
Karst model diagram of the strike-slip fault fracture zone(a) and profile of seismic reflection characteristics of the reservoir(b)
TS—Silurian bottom;
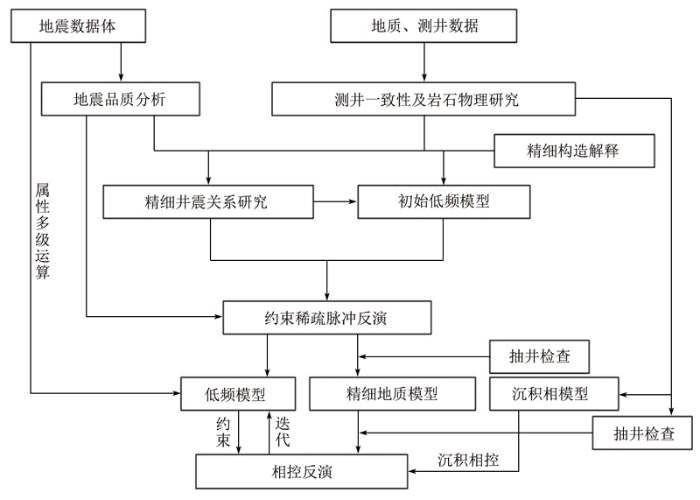
为精细储层预测,首先需要对地震偏移处理成果数据做解释性预处理、差异属性分析与优化,求得可反映致密灰岩地层断裂破碎带背景的低频模型。同时,开展井震约束的稀疏脉冲反演基本流程,求得高品质的纵波阻抗属性并雕刻出优质储层空间轮廓数据。其次,将断裂破碎带背景的低频模型与优质储层空间轮廓数据和稀疏脉冲反演流程中建立的低频模型进行比例融合,生成新的低频模型。最后,基于新的低频模型,同时兼顾地层沉积特征开展多轮次迭代反演,直至得到高质量的反演结果。技术流程见图2。
图2
图2
相控迭代反演方法流程
Fig.2
Flow chart of the phase-controlled iterative inversion method
对地震偏移处理成果或纯波数据做针对目标的解释性预处理的方法很多,如高品质本征值相干属性分析、微储层甜点属性等,通过差异属性进行分析,约束建立非均质模型。本流程采用后者,基于Geoeast软件的多分析窗口模块估算三维地震数据矢量倾角的方法,沿Inline和Crossline方向来估算地震数据体的视倾角[15⇓⇓-18]。模块中涉及的相关参数主要有两个:Window’s Length(值越小,计算越精细,耗时也越长。根据经验对于深度域资料,填100;对于时间域资料,填30)和Max Scan Dip(该参数的确定主要是依据研究区块的整体构造倾角,本研究区填10即可)。下一步,采用EasyTrack软件进行基于构造导向处理进行倾角滤波,涉及的参数主要是:水平平滑半径。通过多轮次测试,本研究区填5效果最佳。该流程纯粹以数据驱动,沿地层进行横向滤波(最常用的滤波有均值滤波器和中值滤波器)。通过滤波消除随机噪声并增强反射的横向连续性,目的是规避地层构造特征对非均质特性的影响,其关键是区分反射层的倾向方位角和叠置在反射层上的噪声[19]。
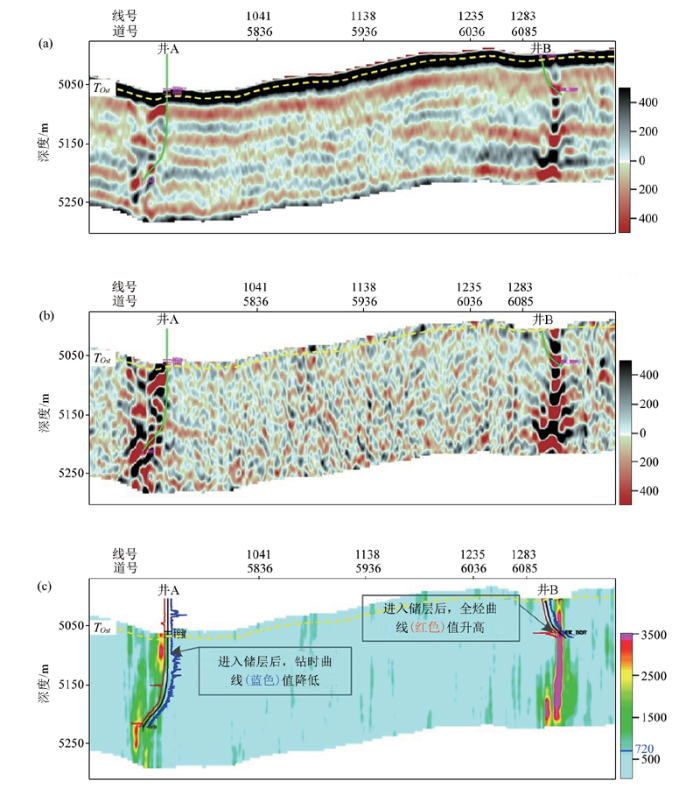
奥陶系地层中,强、弱串珠状反射以及杂乱状反射等均为缝洞型储集体反射波与地层界面反射波矢量叠加的结果[20]。基于构造导向的倾角滤波结果正是地层界面反射特征的响应,根据波的叠加原理,原始地震数据与倾角滤波数据相减,就得到能够反映缝洞型非均质断裂破碎带储集体反射特征的结果,也就是所谓的微储层甜点属性[21],从而达到削弱地层沉积背景干扰,凸显断裂破碎带非均质性特征的目的。需注意的是,这里要采用井震标定中获取的波阻抗曲线对微储层甜点属性进行刻度(图3)。图3为富源Ⅲ期区块奥陶系断裂破碎带空间轮廓刻画效果剖面图,可明显看出,该算法可以准确地刻画出碳酸盐岩断裂破碎带的储层特征,储层的纵向展布规律明显增强。采用算法可将微储层甜点数据体转为断裂破碎带体,再通过已钻井的全烃曲线(图3c红色曲线)或者钻时曲线(图3c蓝色曲线)对断裂破碎带体进行标定。进入储层时,井A钻时曲线(蓝色曲线)减小,井B的全烃含量值(红色曲线)增大,以此来确定断裂破碎带的门槛值为720(无量纲)。
图3
图3
富源Ⅲ期区块奥陶系断裂破碎带微储层刻画效果
a—原始地震剖面;b—微储层甜点属性剖面;c—断裂破碎带空间轮廓剖面
Fig.3
Depiction effect of micro-reservoir in the Ordovician fault fractured zone of Fuyuan Ⅲ block
a—the original seismic profile;b—the micro-reservoir sweet spot attribute profile;c—the spatial profile of the fault fractured zone
式中:
其次,约束稀疏脉冲反演依据目标函数逐一对地震道计算的初始波阻抗进行调整,并调整反射系数,得到目标函数:
式中:
图4
图4
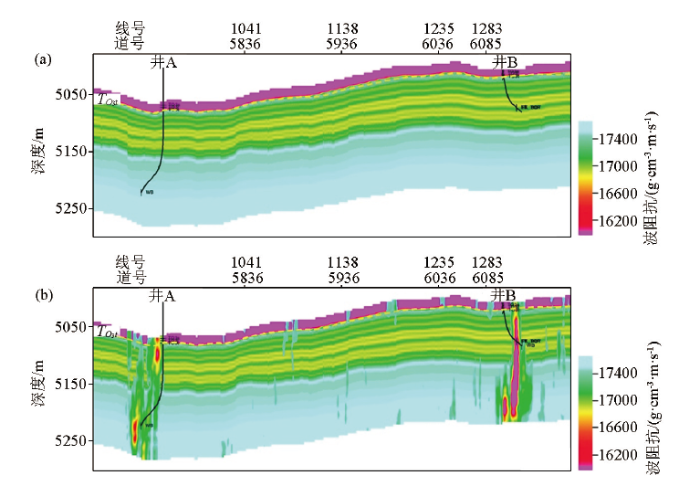
富源Ⅲ期区块奥陶系常规均质低频模型(a)和与断裂破碎带相融合后的非均质性低频模型(b)
Fig.5
The conventional homogeneous low-frequency model (a) and the heterogeneous low-frequency model afterfusion with the fault fractured zone facies (b) of the Ordovician of Fuyuan Ⅲ block
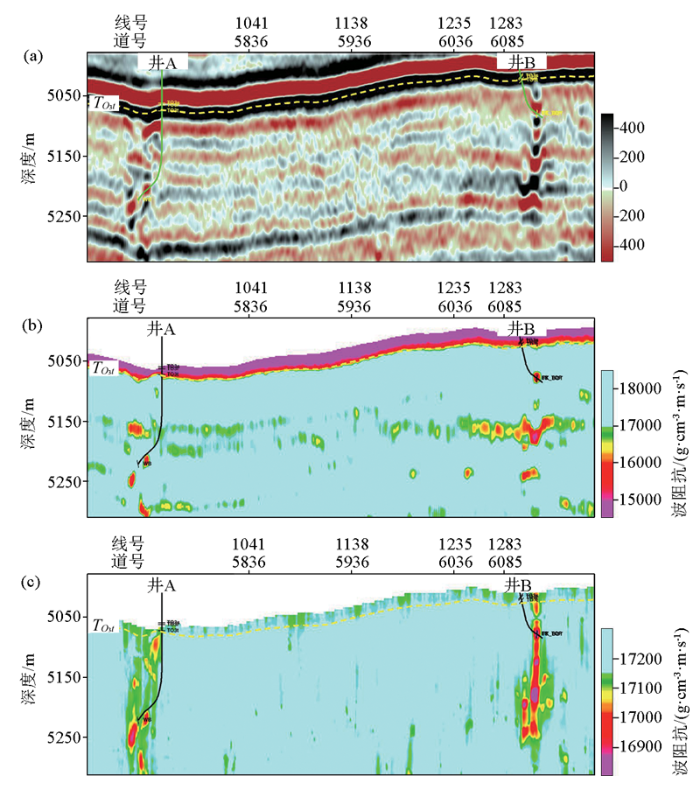
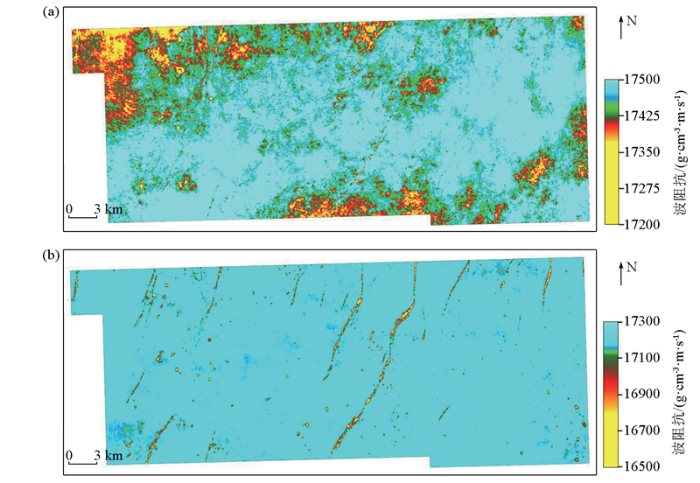
通过方法的实施,相比常规约束稀疏脉冲反演方法,本文“断裂破碎带相控”反演方法的效果得到明显改善(图5、图6)。如图5所示,地震剖面显示有明显断裂破碎带(长串珠反射+杂乱反射)特征(图5a)。常规确定性反演波阻抗剖面结果显示的储层规模很小且断裂破碎带特征基本无法分辨,同时受一间房组顶面表层地质特征干扰,显示为低波阻抗特征(图5b),与实际钻井不相符。在断裂破碎带相约束控制下的反演结果剖面(图5c),纵向上断裂破碎带特征明显,横向上一间房组表层的低阻抗现象也得到了很好的消除。图6为图5中两种反演方法(常规确定性反演方法和相控反演方法)对应的目的层波阻抗属性平面图。相控约束下反演结果的储层平面展布规律更加明显,与走滑断裂走向更吻合,也与富源Ⅲ期区块断控储层特征一致,符合区块的地质认识。
图5
图5
富源Ⅲ期区块常规确定性反演结果与相控(断裂破碎带相)反演结果对比剖面
a—原始地震剖面;b—常规确定性反演剖面;c—相控(断裂破碎带相)反演剖面
Fig.5
Contrasting profile of conventional deterministic inversion results and facies-controlled(fault fractured zone facies)inversion results in Fuyuan Ⅲ block
a—the original seismic profile;b—the conventional deterministic inversion profile;c—the facies-controlled(fault fractured zone facies) inversion profile
图6
图6
富源Ⅲ期区块目的层波阻抗均方根属性平面图对比
a—常规确定性反演平面;b—相控(断裂破碎带相)反演平面
Fig.6
Plan comparison of the RMS impedance property of the target layer in the Fuyuan Ⅲ block
a—the conventional deterministic inversion plan; b—the facies-controlled (fault fractured zone facies) inversion plan
2 应用效果
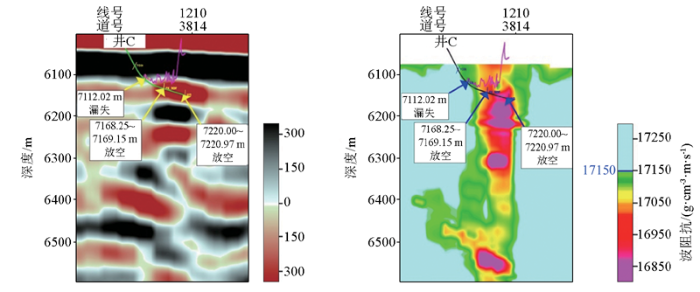
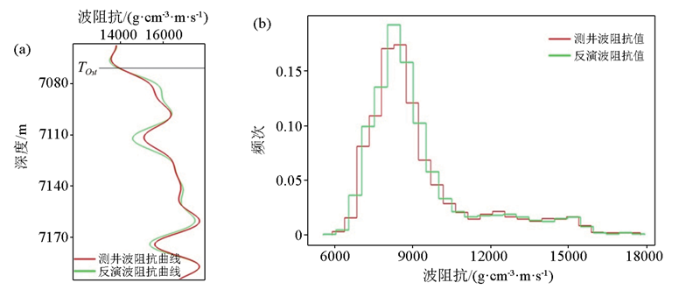
根据精细井震标定结果,实钻情况分析也验证了相控反演结果的准确性(图7)。图7为过C井地震剖面和相控反演剖面对比,该井钻至7 112.02 m时都发生钻井液漏失,漏失量不大,表明已钻遇裂缝—孔洞型储层;继续钻进至7 168.25~7 169.15 m、7 220.00~7 220.97 m位置时出现钻具放空异常,累计放空1.87 m,共漏失钻井液1 826.87 m3,表明已钻遇洞穴型储层。另外,从该井全烃曲线(图7中粉色曲线)上看,在钻井进入储层发生放空漏失段,全烃曲线值明显升高,以此来确定储层的波阻抗门槛值为17 150 g·cm-3·m·s-1。另外在目的层段提取该井的反演波阻抗曲线,与通过测井计算得到的波阻抗曲线作对比(图8所示),发现无论是波阻抗曲线趋势还是直方图分布,两者都有很好的一致性,也再次佐证了相控反演结果的可靠性和真实性。最后该井在完井试油阶段效果极好,对裸眼井段7 066.00~7 226.66 m放喷求产,用8 mm油嘴,油压27.52 MPa,折日产油433.00 m3,折日产气38 280.00 m3;无硫化氢。测试结论:油层。
图7
图7
富源Ⅲ期区块相控(断裂破碎带相)反演结果对井分析
Fig.7
Well analysis of facies-controlled (fault fractured zone facies) inversion results in the Fuyuan Ⅲ block
图8
图8
富源Ⅲ期区块C井目的层段测井波阻抗和反演波阻抗结果对比
a—目的层段测井波阻抗(计算)和反演波阻抗(提取)曲线对比;b—分布直方图
Fig.8
Comparison of logging impedance and inversion impedance at the target interval of Well C in the Fuyuan Ⅲ block
a—comparison of logging impedance(calculation) and inversion impedance(extraction) curves of the target interval;b—distribution histogram
统计研究区10口井放空漏失位置的反演波阻抗值,储层吻合率达到92.86%(表1)。
表1 富源Ⅲ期区块10口井反演结果吻合情况统计
Table 1
| 井号 | 漏失(放空) 深度/m | 漏失量 /m3 | 反演阻抗值 /(g·cm-3· m·s-1) | 是否 吻合 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| well3C | 7564.32~7567.67 | 1484.05 | 16981 | 是 |
| well303-H1 well303-H1 | 5042.00 | 534.66 | 17094 | 是 |
| 7138.07~7280.00 | 2153.90 | 16405 | 是 | |
| well303-H7 | 7140.70~7383.00 | 2118.90 | 16848 | 是 |
| well303H | 7316.63 | 2203.39 | 16742 | 是 |
| well25-H14 well25-H14 | 7019.32 | 0.50 | 17180 | 否 |
| 7308.32~7351.00 | 273.10 | 17113 | 是 | |
| well25-H6 well25-H6 | 2376.85~6818.00 | 503.00 | 16912 | 是 |
| 6943.87~7026.00 | 1877.70 | 16891 | 是 | |
| well25-H8 | 7086.66~7203.00 | 678.80 | 17101 | 是 |
| well302H | 7112.02~7226.66 | 1826.87 | 16603 | 是 |
| well32 | 7547.00 | 476.40 | 17086 | 是 |
| well32-H1 well32-H1 | 7219.36 | 22.00 | 17132 | 是 |
| 5100.00 | 1292.30 | 16675 | 是 |
综上所述,采用新提出的“断裂破碎带相控”约束反演方法一是能够充分挖掘地震信息中储层的异常响应;二是反演结果的细节明显增多,同时也削弱了一间房组顶面表层低波阻抗现象的干扰,储层沿断裂带发育规律更加明显,符合该区地质特点;三是通过实钻井验证,储层预测位置与实钻资料相匹配,结果真实可靠,这也将强有力地支撑和指导以后的井位部署工作。
3 结论与认识
1)对地震偏移处理成果或纯波数据做针对目标的解释性预处理,得到能表征碳酸盐岩非均质性的断裂破碎带体是相控迭代反演的基础。微储层甜点属性计算流程是一种相对准确且成熟的技术,该方法不仅适用于平缓地层,对于倾角大、变化剧烈的地层也同样适用。该技术纯粹以地层倾角数据驱动,规避地层构造特征的影响,极大削弱地层沉积背景干扰,准确凸显断裂破碎带非均质性的特征。
2)将精细刻画的断裂破碎带体数据与优质储层空间轮廓数据和原始低频模型进行刻度比例融合,形成新的非均质性低频模型,能够很好地反映出缝洞型储层的非均质性,符合碳酸盐岩断裂破碎带特征,从而提高储层预测精度。“断裂破碎带相控”迭代反演方法在富源Ⅲ期区块应用效果好,预测结果与实钻结果吻合率高,极具普遍实用性和推广性。
参考文献
塔里木盆地碳酸盐岩大油气区特征与主控因素
[J].
Characteristics and main controlling factors of carbonate oil and gas areas in Tarim Basin
[J].DOI:10.1016/S1876-3804(12)60002-0 URL [本文引用: 1]
塔里木盆地台盆区走滑断裂控储控藏作用及勘探潜力
[J].
DOI:10.7623/syxb201911002
[本文引用: 1]

塔里木盆地台盆区下古生界碳酸盐岩油气资源十分丰富。早期研究认为碳酸盐岩油气受控于礁滩体与风化壳岩溶储层,油藏呈准层状大面积分布,但近期的评价和开发实践发现油气富集与断裂带密切相关。立足新采集的三维地震等资料,阐明了台盆区的走滑断裂具有构造样式多样性、纵横结构分段性、形成演化多期性与继承性等特点,构建了走滑断裂带油气复式成藏地质模型。最新钻探发现,受走滑断裂控制,大型碳酸盐岩缝洞体呈线状、带状和羽状集中分布于走滑断层1.5 km范围内的破碎带上,且走滑断裂规模越大,缝洞体越发育。生产动态数据剖析与成藏分析表明,走滑断裂带上分布着90%以上的高效井,在大型走滑断裂及其分支断裂的顶端、走滑断裂张扭部位油气更为富集。在塔里木盆地台盆区超深层海相碳酸盐岩的油气勘探开发中,形成的"聚焦断裂带、突出富集段,横向扩边、纵向拓层"勘探开发一体化思路是推动油气藏效益开发的关键。
Reservoir-controlling and accumulation-controlling of strike-slip faults and exploration potential in the platform of Tarim Basin
[J].
DOI:10.7623/syxb201911002
[本文引用: 1]

The Lower Paleozoic carbonate rocks in the platform of Tarim Basin are abundant in oil and gas resources. Early studies suggest that carbonate oil and gas reservoirs are controlled by reef flat composites and weathering crust karsts, and are distributed in quasi-layered large area. However, recent evaluation and development practices have indicated that oil and gas enrichment is closely related to fault zone. Based on the newly acquired 3D seismic data, it is clarified that the strike-slip faults in the platform are characterized by diverse structural styles, vertical and horizontal structure segmentation, multi-stage and inheritance of formation and evolution; the geological model of multiple hydrocarbon accumulation in strike-slip fault zones has been established. The latest drilling practice reveals that under the control of strike-slip faults, large carbonate fracture-cavity bodies are concentrated in the fracture zone within 1.5 km of the strike-slip faults in linear, banded and pinnate shapes. The larger the scale of the strike-slip fault is, the better the development of the fracture-cavity body is. The analyses of production performance data and hydrocarbon accumulation show that more than 90% of high-efficiency wells are distributed in the strike-slip fault zones. Oil and gas are mainly accumulated at the top of the large strike-slip faults and their branch faults as well as the transtensional zones. In the exploration and development of ultra-deep marine carbonate rocks in the platform of Tarim Basin, the integrated exploration and development approach of "focusing on fault zones, highlighting hydrocarbon-enriched sections, horizontally expanding boundary and vertically expanding horizons" is the key to promote the profitable development of oil and gas reservoirs.
缝洞型碳酸盐岩储层地震综合预测——以塔里木盆地中古21井区为例
[J].
Comprehensive seismic prediction of fractured-vuggy carbonate reservoirs:A case study of ZG21 well area in Tarim Basin
[J].
塔河油田奥陶系缝洞型碳酸盐岩储层预测研究
[J].
Prediction of Ordovician fractured-vuggy carbonate reservoir in Tahe Oilfield
[J].
碳酸盐岩缝洞系统地震响应特征分析和塔中卡1区缝洞储层预测
[J].
Seismic response and prediction of fracture-cavity system in carbonate reservoir:A case study in the Ka-1 field
[J].
碳酸盐岩储层地震相控非线性反演技术及应用
[J].
Seismic phase-controlled nonlinear inversion of a carbonate reservoir
[J].
约束稀疏脉冲反演在哈得逊油田开发中的应用
[J].
Application of constrained sparse pulse inversion in the development of Hadexun Oilfield Petroleum
[J].
中国古生代海相油气田发现的回顾与启示
[J].
Review and revelation of oil/gas discoveries in the Paleozoic marine strata of China
[J].
塔中隆起海相碳酸盐岩大型凝析气田成藏特征与勘探
[J].
Hydrocarbon accumulation characteristic and exploration on large marine carbonate condensate field in Tazhong Uplift
[J].
塔里木盆地油气勘探历程与启示
[J].
Petroleum exploration history and enlightenment in Tarim Basin
[J].
塔里木盆地哈拉哈塘地区碳酸盐岩油气地质特征与富集成藏研究
[J].
Study on petroleum geological characteristics and accumulation of carbonate reservoirs in Hanilcatam area,Tarim basin
[J].
Robust estimates of 3D reflector dip and azimuth
[J].
Adopting multispectral dip components for coherence and curvature attribute computations
[J].DOI:10.1190/tle39080593.1 URL [本文引用: 1]
Volumetric dip and azimuth
[C]//
Processing of RI-angiocardiographic images.In Digital Processing of Biomedical Images
[M].
Seismic wave field anomaly identification of ultra-deep heterogeneous fractured-vuggy reservoirs:A case study in Tarim Basin,China
[J].DOI:10.3390/app112411802 URL [本文引用: 1]
地震趋势异常识别技术及其在碳酸盐岩缝洞型储层预测中的应用——以塔里木盆地英买2井区为例
[J].
Principles and application of a seismic trend anomaly diagnostic technique:A case study on carbonate fractured-cavity reservoirs in Yingmai 2 area,Tarim Basin
[J].
Improved workflow for identifying fault controlled fractured-vuggy body sweets of Ultra deep tight limestone
[C]//