0 引言
本文基于多目标区域地球化学获得的土壤常量元素数据,尝试利用主成分聚类法,对东北典型黑土区进行地球化学分类研究并探讨其地质意义。
1 研究区概况
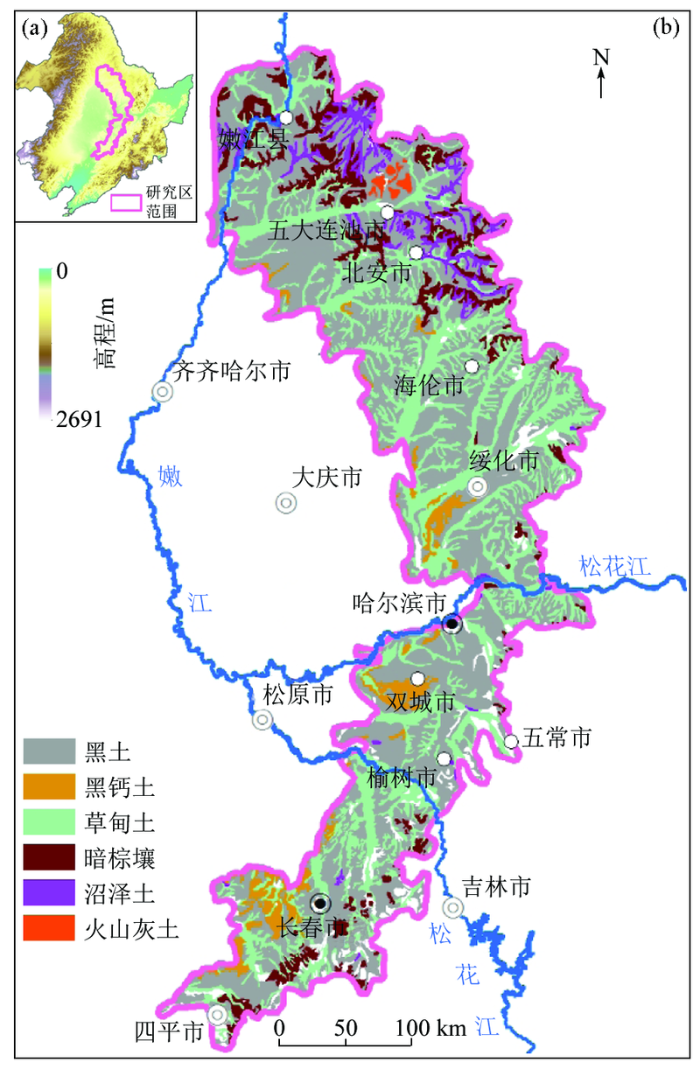
图1
图1
研究区区域位置(a)及土壤类型分布(b)
Fig.1
Regional location(a) and soil type distribution(b) of the study area
研究区位于松嫩平原东部、北部的山前台地和高平原区,北起黑龙江省嫩江县,南至辽宁省昌图县,沿哈尔滨—北安、哈尔滨—长春铁路沿线形成一条完整的黑土带。该区年降雨量在500~600 mm,绝大部分集中于7~9月,干燥度≤1。年平均气温0.5~6 ℃,土壤冻结时间为120~200 d。研究区土壤类型以黑土为主,其次为草甸土、暗棕壤,也包含有少量的黑钙土、沼泽土和火山灰土。研究区尚未编制精度较高的成土母质图,不同成土母质的分布尚不清晰,文献中多简单叙述为以第四纪更新世砂砾、黏土层和全新世砂砾、黏土层为主[23]。
2 材料和方法
2.1 数据来源
本次研究采用的土壤地球化学数据全部来源于多目标区域地球化学调查[2]。土壤样品获取采用双层网格化土壤测量方法,分别采集表层(0~20 cm)和深层(150 cm以下)土壤,采样质量为1 kg,样品在自然风干后过20目尼龙筛。表层土壤采样密度1点/km2,深层土壤采样密度1点/4 km2,每4个原始样品组合后测试分析54项元素和指标,因此每个表层测试样品代表4 km2范围,每个深层测试样品代表16 km2范围。测试元素和指标共54项,其中常量元素SiO2、Al2O3、Fe2O3、MgO、CaO、Na2O、K2O采用X荧光光谱仪测试完成,测试准确度和精密度均达到相关规范[24]要求。在剔除个别异常点后,研究区内共选取22 888个表层土壤样品和5 754个深层土壤样品用于本次研究。
2.2 数据处理方法
2.2.1 描述性统计
元素含量的平均值、中位数、标准差等利用SPSS软件进行计算。富集系数(q)代表元素在表层土壤和深层土壤中含量的比值,在ArcGIS中按空间对应关系将1个深层样品化学属性赋予4个表层土壤样品,进而计算每个表层土壤的q值。变异系数(CV)是标准差与平均值的比值,用以代表元素含量的离散程度。
2.2.2 主成分分析
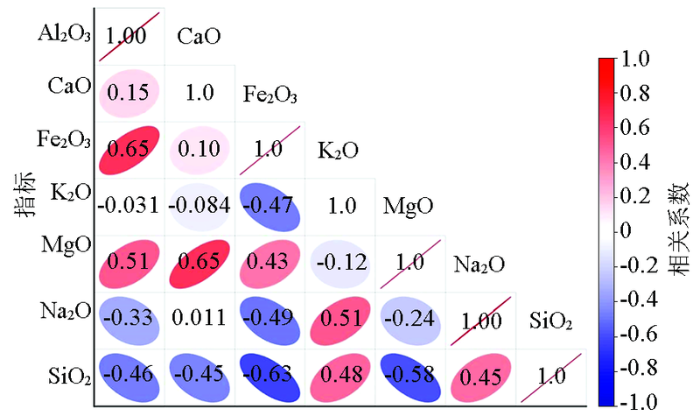
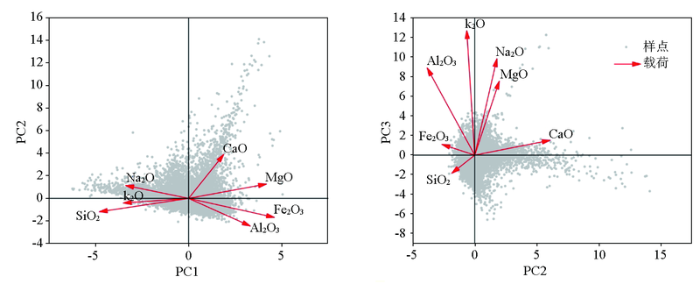
主成分分析是常用的多元统计方法之一,主要用于多元数据的降维,本文使用SPSS 软件进行主成分分析操作。主成分分析的前提是参与分析的各变量间具有相关性,图2显示各常量元素之间多具有显著相关性,KMO检验系数为0.6,Bartlett’s检验结果P<0.001,说明常量元素之间存在共线性,可进行主成分提取。
图2
2.2.3 K均值聚类
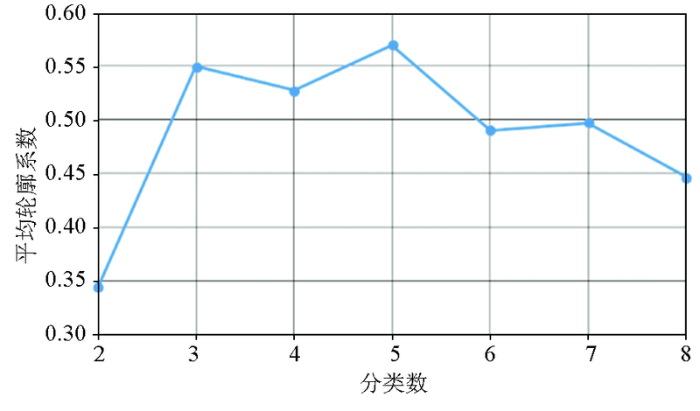
K均值聚类由于要手动输入聚类数目,因此其难点之一就是确定最优分类数(K值)[27]。通常,当对数据集的属性非常了解时,可以靠经验来确定分类数,但这对数据处理者的知识储备提出了非常高的要求,往往难以实现。因此,大多数情况下人们通过计算不同分类数的某些特征,进行比较后来决定最优分类数。安光辉等[28]利用一致性检验和区间差异显著性检验来评价不同分类数目效果,但该方法的主观性较大。Rousseuw[29]于1987年提出利用轮廓系数来判断分类数,轮廓系数结合了内聚度和分离度两种因素,可以用来在相同原始数据的基础上评价不同算法或者算法不同运行方式对聚类结果所产生的影响,目前得到较广泛的应用。轮廓系数计算公式如下:
式中:ai为第i个对象到其所属簇中所有对象的平均距离;bi为该对象到所有非所属簇中对象的平均距离。轮廓系数在-1~1间变化,越趋近于1代表内聚度和分离度都相对较优,聚类效果相对较好。因此,本文利用平均轮廓系数对分类结果进行评价。K均值聚类和轮廓系数计算利用Matlab软件实现。
3 结果与讨论
3.1 常量元素含量特征
表1为研究区表层和深层土壤的常量元素统计数据,其元素含量高低趋势一致,均为SiO2>Al2O3>Fe2O3>K2O>Na2O>CaO>MgO,其中SiO2、Al2O3和Fe2O3含量占80%以上,具有明显的硅铝土特点。从元素含量分布形态看,除CaO以外的其他元素偏度在1附近,基本符合正态分布,而CaO表层和深层偏度值分别为6.25和4.30,呈右偏形态,说明存在一定数量的极大值。
表1 黑土区常量元素参数统计
Table 1
| 类型 | 元素 | 最小值/% | 最大值/% | 平均值/% | 中位数/% | 标准偏差/% | 偏度 | 峰度 | 变异系数 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 表层土壤 | SiO2 | 41.87 | 80.46 | 64.55 | 64.80 | 2.95 | -0.67 | 2.87 | 0.05 |
| Al2O3 | 7.88 | 16.62 | 13.95 | 13.98 | 0.78 | -0.59 | 2.95 | 0.06 | |
| Fe2O3 | 0.95 | 10.49 | 4.77 | 4.76 | 0.62 | 0.08 | 4.67 | 0.13 | |
| K2O | 1.72 | 3.98 | 2.50 | 2.50 | 0.15 | 0.63 | 4.31 | 0.06 | |
| Na2O | 0.72 | 4.66 | 1.62 | 1.56 | 0.29 | 1.82 | 6.44 | 0.18 | |
| CaO | 0.55 | 15.03 | 1.56 | 1.39 | 0.82 | 6.25 | 57.76 | 0.53 | |
| MgO | 0.21 | 3.50 | 1.29 | 1.30 | 0.21 | 0.24 | 3.21 | 0.17 | |
| 深层土壤 | SiO2 | 44.67 | 75.41 | 64.34 | 64.66 | 2.51 | -0.36 | 3.10 | 0.04 |
| Al2O3 | 9.01 | 18.50 | 14.79 | 14.89 | 0.80 | -0.80 | 3.61 | 0.05 | |
| Fe2O3 | 1.38 | 9.08 | 5.12 | 5.16 | 0.78 | -0.27 | 2.58 | 0.15 | |
| K2O | 1.61 | 3.68 | 2.62 | 2.63 | 0.17 | 0.30 | 4.69 | 0.06 | |
| Na2O | 0.53 | 3.66 | 1.67 | 1.64 | 0.28 | 1.38 | 5.60 | 0.17 | |
| CaO | 0.35 | 15.41 | 1.41 | 1.25 | 0.66 | 4.30 | 28.73 | 0.47 | |
| MgO | 0.36 | 3.09 | 1.37 | 1.40 | 0.24 | -0.37 | 2.92 | 0.17 |
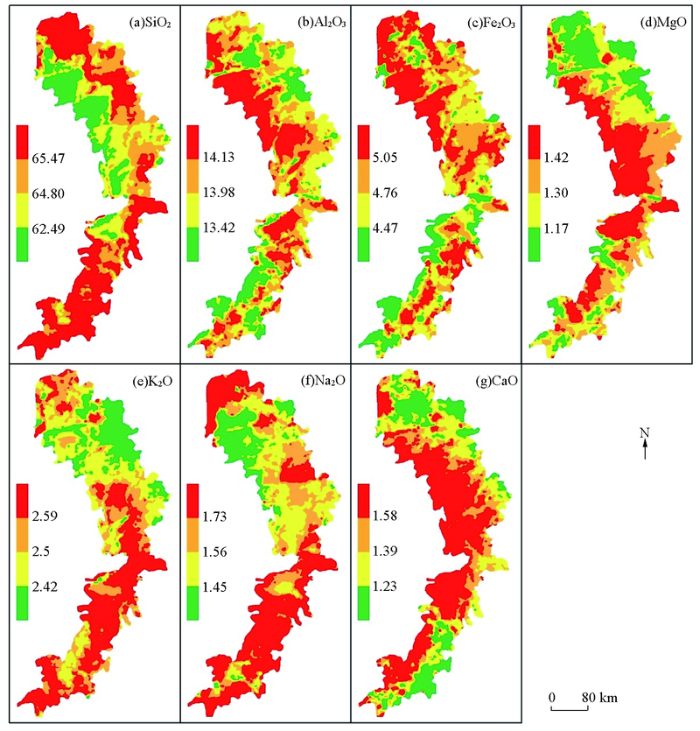
图3
图4
图4
东北黑土区常量元素含量空间分布(各元素含量区间取值为四分位数,数据单位为%)
Fig.4
Spatial distribution of major elements in black soil area of Northeast China(interval value of element content is quartile and data unit is %)
3.2 主成分分析结果
本文采用累积贡献率法来判断主成分的最优数量。表2显示前3位主成分的特征值大于1,分别解释46.708%、21.056%和15.289%的数据变异,因此本研究最终选取3个主成分(PC1、PC2、PC3),提取后的主成分共可解释83.05%的数据变异。
表2 主成分特征值及方差贡献率
Table 2
| 主成分 | 初始特征值 | 提取载荷平方和 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 总计 | 方差百 分比 | 累积贡 献率/% | 总计 | 方差百 分比 | 累积贡 献率/% | |
| PC1 | 3.270 | 46.708 | 46.708 | 3.270 | 46.708 | 46.708 |
| PC2 | 1.474 | 21.056 | 67.764 | 1.474 | 21.056 | 67.764 |
| PC3 | 1.070 | 15.289 | 83.053 | 1.070 | 15.289 | 83.053 |
图5显示PC1与Al2O3、Fe2O3、MgO和CaO为正相关,指示PC1代表黏土矿物和铁铝氧化物。PC2与CaO及MgO呈正相关,表明PC2代表了碳酸盐矿物。PC3与K2O、Na2O相关性最强,说明PC3代表长石类矿物。
图5
3.3 K均值聚类结果
图6
图6
不同分类数及对应的平均轮廓系数
Fig.6
Mean silhouette coefficients of different classification numbers
表3 各类别样品常量元素平均值统计
Table 3
| 类别 | 样品数 | SiO2 | Al2O3 | Fe2O3 | CaO | K2O | MgO | Na2O |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| I类 | 18 | 56.15 | 14.37 | 6.16 | 3.06 | 2.90 | 3.63 | 2.19 |
| II类 | 6512 | 64.66 | 13.59 | 4.87 | 1.26 | 2.39 | 1.21 | 1.45 |
| III类 | 10023 | 63.07 | 14.46 | 5.19 | 1.57 | 2.50 | 1.45 | 1.54 |
| IV类 | 778 | 59.24 | 12.86 | 4.39 | 5.04 | 2.35 | 1.70 | 1.66 |
| V类 | 5557 | 66.75 | 13.51 | 4.24 | 1.38 | 2.65 | 1.18 | 1.94 |
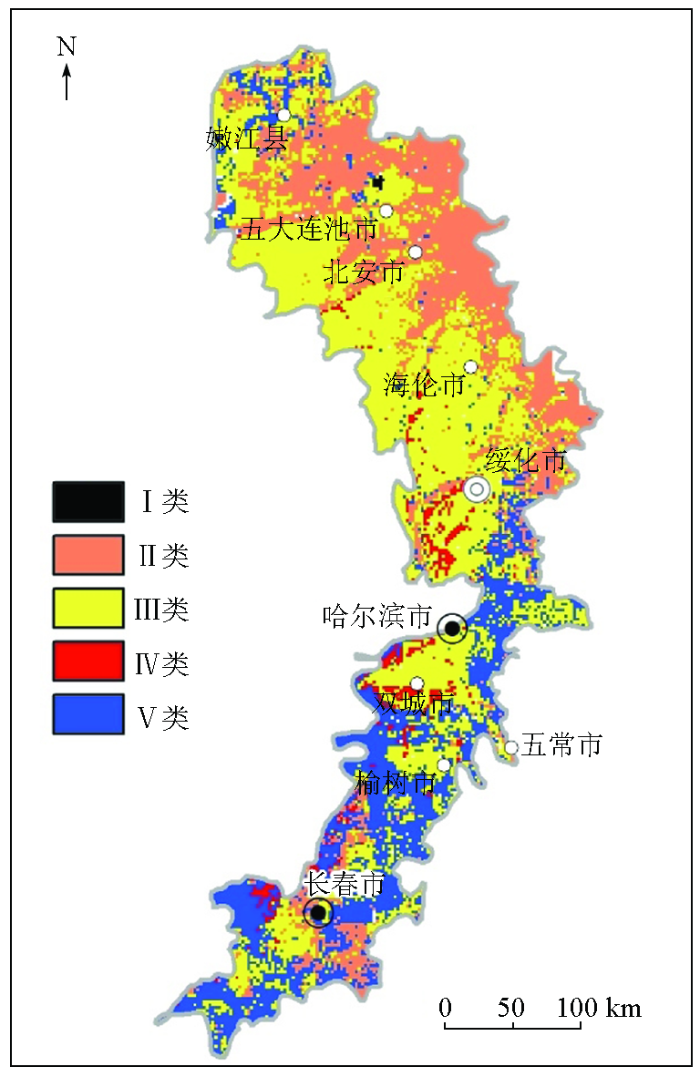
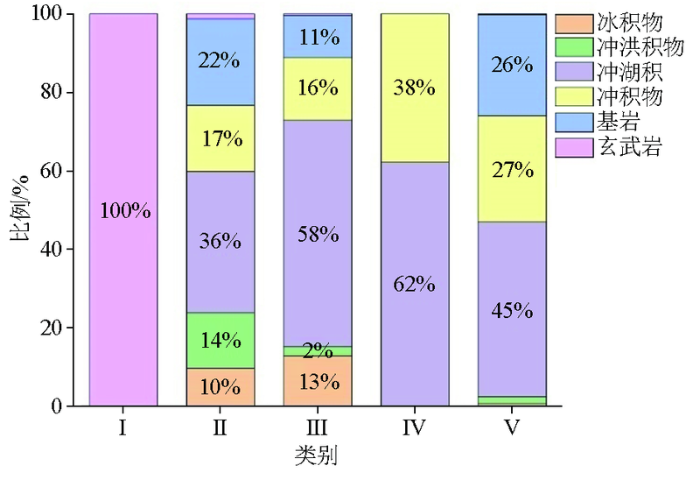
为研究分类结果的实际内涵及应用价值,绘制了样品类别的空间分布(图7)。
图7
第Ⅰ类样品数最少,仅为18个,但其元素含量特征明显,SiO2含量最低,平均值仅56.15%,而Fe2O3、MgO、CaO含量最高(表3),常量元素含量特征与基性岩较一致。第Ⅰ类样品空间上位于五大连池玄武岩区,土壤类型为火山灰土。
第Ⅱ类样品与第Ⅲ类样品元素含量特征较为类似,其样品数量也占绝对优势,分别占全区的28.5%和43.8%。第Ⅱ类样品的SiO2含量(平均值64.66%)略高于第Ⅲ类样品(平均值63.07%),反映其相对含有更高的砂质成分。在空间上,第Ⅱ类样品主要分布在小兴安岭西麓丘陵地区,海拔普遍大于200 m(图1),该地区在第四纪时期以隆升为主,地形切割较剧烈,下部的砂层和砂砾石层多出露近地表,土壤类型以暗棕壤为主。
第Ⅲ类样品数量最多,占全区的43.8%,其常量元素特征与典型黑土的成土母质——黄土状亚黏土[34]基本一致,广泛分布在松辽平原东北部的高平原区,土壤类型多为黑土和草甸土。
第Ⅳ类样品仅778件,常量元素表现为含有较丰富的CaO和MgO,其平均含量分别达5.04%和1.7%,代表土壤中碳酸盐矿物含量较高。空间上沿个别河流分布,并均分布在隆起抬升的陡坡一侧,与黑钙土的分布吻合度较高。
第Ⅴ类样品SiO2、K2O、Na2O含量较高,说明土壤中含有较多的石英和长石类矿物。在空间上,第Ⅴ类样品主要分布在松花江南部各河流两岸及一级阶地。
3.4 地球化学分类结果与地质单元的关系
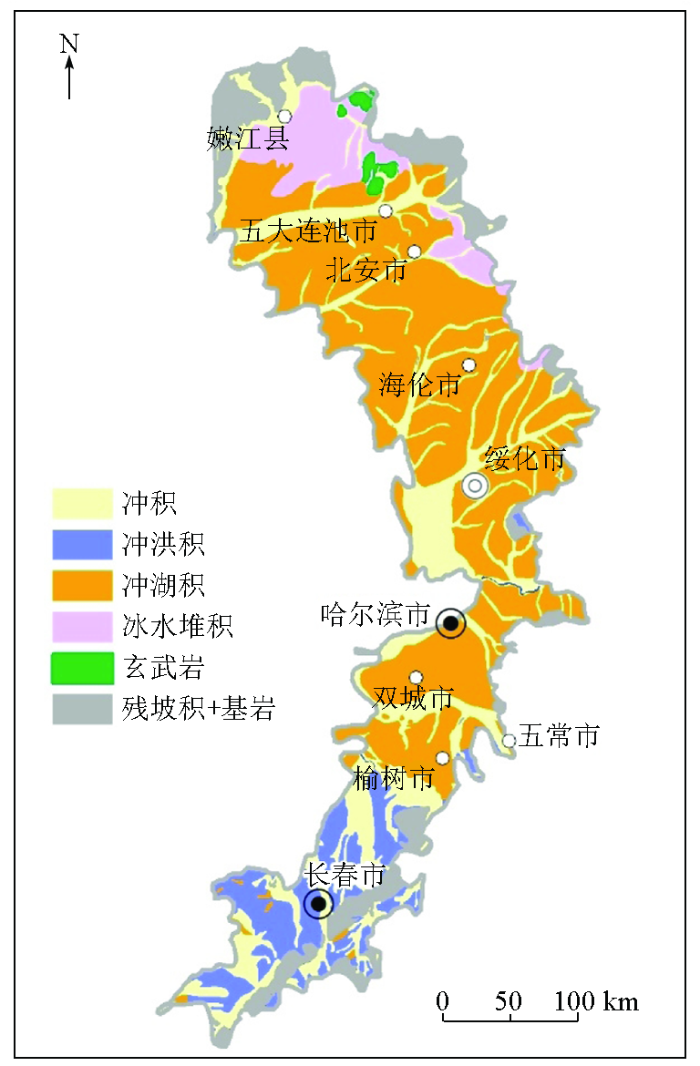
本次聚类结果中,除第Ⅰ类样品与玄武岩区完全对应外,其他4类样品在空间上与地质单元的对应性并不明显(图7、图8),其统计学结果也得出同样结论(图9)。原因可能包括两个方面:一方面,地质图的比例尺与土壤地球化学调查尺度不匹配,在以往开展的基础地质调查工作中,第四系广泛覆盖的平原区并不是调查重点,东北平原区目前编制的第四系地质图仅为1:100万比例尺,精度较低;另一方面,同一地质单元的地表岩性差异显著,第四纪地质单元通常由多个沉积地层构成,如本区冲湖积物通常上部为亚黏土,下部则为砂层、砂砾层,受地表侵蚀、沉积、风化等作用影响,同一地质单元在不同地区出露岩性有较大差异,因此,地质单元与地球化学的对应关系并不完全一致[37-38],也是造成二者对应性低的一个原因。
图8
图9
图9
不同类别所包含地质单元的累积频率
Fig.9
Cumulative frequency map of geological units in different classifications
由于区域多目标地球化学调查为1:25万比例尺,采样密度大,因此地球化学分类结果比地质图能更清晰地反映成土母质的空间分布情况。综合地理、地质和土壤特征,可将5个类别分别命名为:Ⅰ—五大连池玄武岩母质发育的火山灰土;Ⅱ—小兴安岭山前丘陵冲洪积物母质发育的暗棕壤;Ⅲ—松辽平原东部高平原低钙黄土状土母质发育的黑土;Ⅳ—松辽平原东部高平原边缘富钙冲湖积母质上发育的黑钙土;Ⅴ—松辽平原东南部冲积物母质上发育的黑土。该结果较客观地反映了典型黑土区的成土母质分布情况。
3.5 地球化学分类结果反映的黑土生态环境问题
地球化学分类结果表明,松花江南部土壤中砂质含量较北部明显偏高(图7),原因一方面是由于南部成土母质以河流冲积物、冲洪积物和残坡积物为主(图8),普遍含有较高的砂质成分,但另一方面可能也反映出局部地区的黑土存在沙化现象。近期研究表明,中国东北部地区已成为沙尘暴的多发区,尤其是松花江、嫩江流域的局部草地退化和沙化地区[39]。受季风和沙尘暴作用影响,每年都有大量细粒沙尘由西向东吹至黑土区。以哈尔滨地区为例,现代尘暴中干沉降和湿沉降粉尘的REE模式和Sr-Nd同位素组成都表明,沙尘来源于科尔沁沙地和浑善达克沙地[40-41],这些沙尘的加入会增加黑土中砂质含量,从而造成土壤沙化。在本次研究结果中,松花江南部冲湖积母质上发育的黑土中目前也具有较高的SiO2含量,指示这些地区土壤可能已发生沙化,未来应作为黑土区的生态问题加以关注。
4 结论
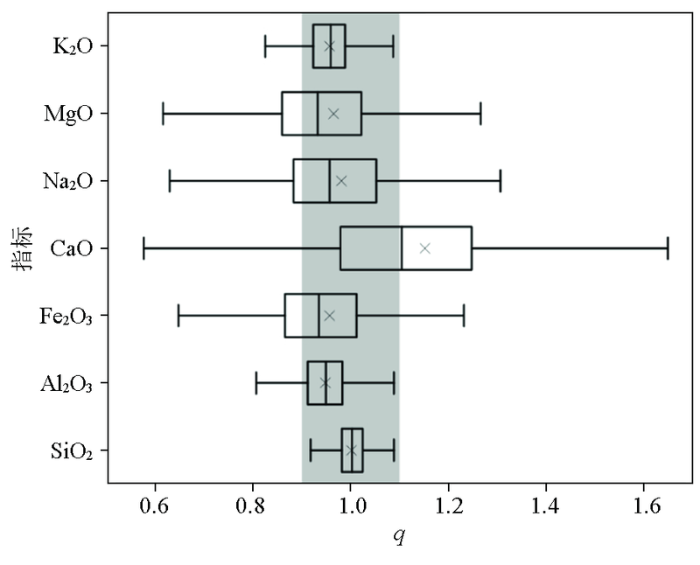
1)典型黑土区常量元素SiO2、Al2O3和Fe2O3含量占80%以上,具有明显的硅铝土特点,表层土壤和深层土壤的常量元素比以0.9~1.1为主,说明土壤常量元素主要受控于成土母质。
2)利用主成分聚类法将黑土区土壤样品划分为5类最为合理,各类别地球化学特征差异显著,其空间分布能较清晰地反映出成土母质的空间分布情况。根据地理、地质及土壤特征分别命名为:I—五大连池玄武岩母质发育的火山灰土;Ⅱ—小兴安岭山前丘陵冲洪积物母质发育的暗棕壤;Ⅲ—松辽平原东部高平原低钙黄土状土母质发育的黑土;Ⅳ—松辽平原东部高平原边缘富钙冲湖积母质上发育的黑钙土;Ⅴ—松辽平原东南部冲积物母质上发育的黑土。
3)松花江南部冲湖积母质发育的黑土局部具有较高的SiO2含量,指示该地区黑土已出现沙化生态问题,在黑土地保护中应给予关注。
参考文献
全国土地质量地球化学调查二十年
[J].
DOI:10.13745/j.esf.sf.2019.8.25
[本文引用: 1]

土地质量地球化学调查计划是我国继区域化探全国扫面计划之后一个新的国家地球化学填图计划,该计划实施20年来,在支撑土壤环境污染防控、土地资源管理、国家重大立法、精准扶贫等方面做出了重大贡献,显著拓展了地质工作服务链。本文从计划的提出背景、项目的组织实施、主要进展、调查技术的进步和分析测试技术的提高与质量控制方案的完善等方面回顾了该计划的发展历程。从全国耕地地球化学状况、全国省会城市土壤环境质量状况、中国主要淡水湖泊沉积物环境质量状况、中国主要农耕区20年来土壤碳库变化4个方面对调查成果做了全面总结。全方位介绍了调查应用成果在土地管理、土壤污染防治、农业种植结构调整、脱贫攻坚、地方病防治、油气勘查、固体矿产勘查等7个领域中的应用。并在调查技术革新、评价方法创新和调查与研究融合三个方面对土地质量地球化学调查工作的未来发展趋势做了展望。
Vicennial implementation of geochemical survey of land quality in China
[J].
DOI:10.13745/j.esf.sf.2019.8.25
[本文引用: 1]

The geochemical survey of land quality project launched in 1999 is a new national geochemical mapping project, succeeding the regional geochemistry-national reconnaissance project in China. The project has since made significant contributions in supporting governmental actions in soil pollution prevention and control, land resource management, major agricultural legislation and precision poverty relief—expanding greatly its role of geological service. We provided here a historical review on the projects background, organization, main progress, survey methodology development, analysis and testing technology improvement and quality control scheme. We made a comprehensive summary of the projects achievements in the overview of the geochemical status of national cultivated land, environmental qualities of soils in provincial capital cities and sediments in nations main freshwater lakes, and changes of soil organic carbon pools in the main agricultural areas of China in the past 20 years. We then gave an all-around introduction of the applications of survey data in land management, soil pollution prevention and control, agricultural planting structural adjustment, poverty relief, endemic disease prevention and control, and explorations for oil & gas and metallic minerals. Finally, we offered a prospective view on the future developmental trend of geochemical survey of land quality regarding innovative survey technology, new evaluation methods and integration of survey and research.
东北黑土地质量调查成果
[J].
Progress in the quality survey of black soil in northeast China
[J].
东北平原土壤碳库构成及其与土壤性质的关系
[J].
Soil carbon pool in northeast plain of China and its relations between the soil properties
[J].
三江平原土壤碳库时空变化和影响因素研究
[J].
Temporal and spatial changes of soil carbon pool and its influencing factors in the Sanjiang Plain
[J].
松辽平原土壤碳库变化及其原因分析
[J].
Change in soil carbon pool in Sonlgiao Plain and its cause analysis
[J].
黑龙江省海伦市长发镇土地质量地球化学评价及开发建议
[J].
Geochemical evaluation of land quality and development suggestion of land in Hailun city,Heilongjiang Province
[J].
黑龙江省五常市东部土壤中硒分布及影响因素
[J].
Selenium distribution and influencing factors of soil in eastern Wuchang City,Heilongjiang Province
[J].
黑龙江海伦地区垦殖前后典型黑土剖面主要养分元素垂直分布特征
[J].
Vertical distribution of major nutrient elements in typical black soil sections in Hailun,Heilongjiang Province:Before and after reclamation
[J].
山东半岛沿岸海域表层沉积物的常量元素及其地质意义
[J].
Geochemistry of major elements in the surface sediments of the offshore area of Shandong Peninsula and its geological implications
[J].DOI:10.3724/SP.J.1140.2012.03045 URL [本文引用: 1]
Major element geochemical variations in a Miocene-Pliocene Siwalik paleosol sequence:Implications to soil forming processes in the Himalayan foreland basin
[J].DOI:10.1007/s12594-009-0061-5 URL [本文引用: 1]
Major element geochemistry of purple soils/rocks in the red Sichuan Basin,China:Implications of their diagenesis and pedogenesis
[J].DOI:10.1007/s12665-012-2019-y URL [本文引用: 1]
A comparative analyses of granulometry,mineral composition and major and trace element concentrations in soils commonly ingested by humans
[J].DOI:10.3390/ijerph120808933 URL [本文引用: 1]
Exploratory analysis of geochemical data and inference of soil minerals at sites across Canada
[J].DOI:10.1007/s11004-020-09912-y URL [本文引用: 1]
Geochemistry of soils derived from selected sedimentary parent rocks in Kopet Dagh,North East Iran
[J].DOI:10.1016/j.gexplo.2018.07.008 URL [本文引用: 1]
Surficial and deep earth material prediction from geochemical compositions
[J].DOI:10.1007/s11053-018-9423-2 URL [本文引用: 1]
Discovering geochemical patterns by factor-based cluster analysis
[J].
Regional geochemical zonation of cultivated floodplains-Application of multi-element associations for soil quality evaluation along the Ohǐe (Eger) River,Czech Republic
[J].DOI:10.1016/j.gexplo.2020.106491 URL [本文引用: 1]
主成分分析、聚类分析在土地评价中的应用——以福建沙县夏茂镇水稻土为主要评价对象
[J].
Application of principle component analysis and hierarchical cluster analysis in land evaluation
[J].
基于K均值动态聚类分析的土样识别
[J].
The recognition of soil sample based on the K-means dynamic clustering analysis
[J].
基于多源数据和模糊k-均值方法的农田土壤管理分区研究
[J].
Zoning of soil management based on multi-sources data and fuzzy-K means
[J].
东北黑土区演化历程及范围界定研究
[J].
Developing history and defining boundary of the black soil regions in Northeast China
[J].
东北黑土区和东北典型黑土区的范围与划界
[J].
Delineating the black soil region and typical black soil region of northeastern China
[J].
The concept of compositional data analysis in practice:Total major element concentrations in agricultural and grazing land soils of Europe
[J].DOI:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2012.02.032 URL [本文引用: 1]
Some methods for classification and analysis of multivariate observations
[C]//
K-means算法初始聚类中心选择的优化
[J].针对传统K-means算法对初始聚类中心敏感的问题,提出了基于数据样本分布情况的动态选取初始聚类中心的改进K-means算法。该算法根据数据点的距离构造最小生成树,并对最小生成树进行剪枝得到K个初始数据集合,得到初始的聚类中心。由此得到的初始聚类中心非常地接近迭代聚类算法收敛的聚类中心。理论分析与实验表明,改进的K-means算法能改善算法的聚类性能,减少聚类的迭代次数,提高效率,并能得到稳定的聚类结果,取得较高的分类准确率。
Optimization to K-means initial cluster centers
[J].To solve this problems that the traditional K-means algorithm has sensitivity to the initial cluster centers, a new improved K-means algorithm is proposed. The algorithm builds minimum spanning tree and then splits it to get K initial clusters and the relevant initial cluster centers. The initial cluster centers are found to be very closed to the desired cluster centers for iterative clustering algorithms. Theory analysis and experimental results demonstrate that the improved algorithms can enhance the clustering performance, get stable clustering in a higher accuracy.
基于K-均值聚类的绿洲农田管理分区提取的研究
[J].
Delineation of precision agriculture management zones in oasis field based on K-means algorithm
[J].
Sihouettes:A graphical aid to the interpretation and validation of cluster analysis
[J].DOI:10.1016/0377-0427(87)90125-7 URL [本文引用: 1]
华东多目标区域地球化学调查区土壤常量元素地球化学特征
[J].
Geochemical characteristics of macro elements in soils in the region covered by multi-purpose geochemical survey in Eastern China
[J].
Principal component analysis of the geochemistry of soil developed on till in Northern Ireland
[J].DOI:10.1080/17445647.2013.789414 URL [本文引用: 1]
Geochemical distribution of major and trace elements in agricultural soils of Castilla-La Mancha (central Spain):Finding criteria for baselines and delimiting regional anomalies
[J].DOI:10.1007/s11356-017-0010-6 URL [本文引用: 2]
Multivariate analysis of the geochemistry and mineralogy of soils along two continental-scale transects in North America
[J].DOI:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2010.08.004 URL [本文引用: 1]
黑龙江省拜泉地区典型黑土剖面元素地球化学特征及其环境指示意义
[J].
Element geochemistry of the typical black soil sections in Baiquan area,Heilongjiang Province:Environmental implication
[J].
Geochemistry of soils along a transect from Central Mexico to the Pacific Coast:A pilot study for continental-scale geochemical mapping
[J].DOI:10.1016/j.apgeochem.2009.04.012 URL [本文引用: 1]
The importance of parent material in soil classification:A review in a historical context
[J].
From geological to soil parent material maps:A random forest-supported analysis of geological map units and topography to support soil survey in South Tyrol
[J].DOI:10.1016/j.geoderma.2019.113884 URL [本文引用: 1]
Investigating surficial geologic controls on soil properties,inorganic nutrient uptake,and northern hardwood growth in Western Massachusetts,USA
[J].DOI:10.1007/s42729-019-00096-x URL [本文引用: 1]
东北地区春季沙尘天气变化特征及其与大气环流变化的关系
[J].
Characteristics of sand-dust events and their relationships with atmospheric circulation in spring in Northeast China
[J].
哈尔滨尘暴天气沉降物的物质组成及其对物源的限制
[J].
Material charateristics of dust fallouts during the dust-storm weather in Harbin:Constraint on the provenance
[J].
哈尔滨沙尘沉降物稀土元素地球化学特征及其物源分析
[J].
REE Geochemistry for sand-dust fallouts in Harbin,Heilongjiang Province and provenance analysis
[J].DOI:10.3799/dqkx.2013.091 URL [本文引用: 1]