0 引言
1 研究区概况
黑龙江省海伦市位于松嫩平原东部,小兴安岭西麓,处于小兴安岭向松嫩平原的过渡地带,行政区域为绥化市。县内地势从东北到西南由低丘陵、高平原、河阶地、河漫滩依次呈阶梯状逐渐降低,东北部一般海拔在350~450 m,最高处海拔490 m。区内属温带大陆性季风气候,冬季干冷漫长,夏季湿热短暂,年平均气温1.2 ℃,年降水量550 mm左右,大部分集中在7月至8月,11月至翌年4月为冻结期。
海伦市资源丰富,是世界三大黑土地之一,素有“粮仓”的美誉。通肯河、克音河、海伦河等5条河流横贯东西。西部平原区盛产大豆、玉米、水稻等粮食作物和亚麻、烤烟等经济作物,北部山区盛产红松、白杨等木材和甘草、党参等中药及猴头、蕨菜等山产品,地下蕴藏丰富的煤炭、砂金、矿泉水等矿产资源,因此,海伦享有中国优质大豆之乡、中国高淀粉玉米之乡、中国甜菇娘之乡、中国民间艺术之乡、中国甜菜之乡、中国籽鹅之乡“六乡”美誉,是中国黑土硒都,国家重要的商品粮基地县。
2 样品采集及分析
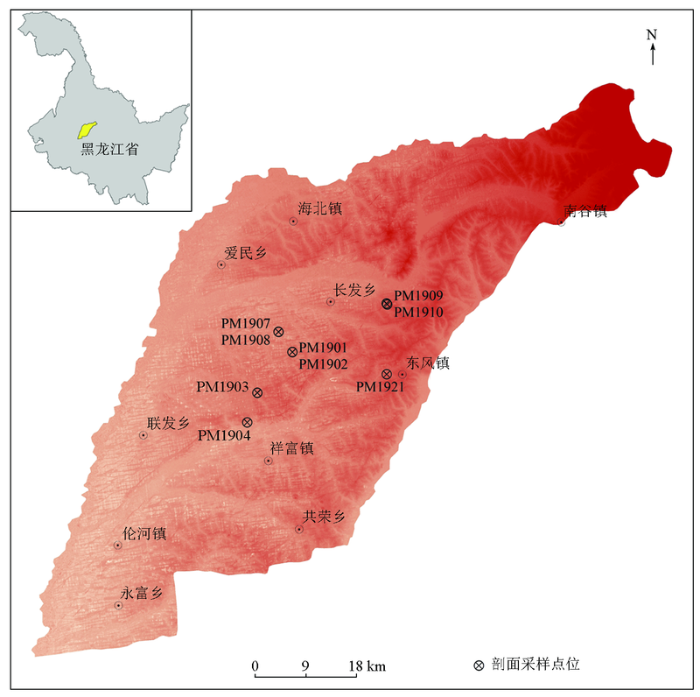
本次研究的9条典型黑土剖面均采自海伦市中南部,在每个典型黑土剖面采样点处均严格按照采样要求进行样品采集,由地表至200 cm深度,每20 cm等间距连续采集土壤及成土母质样品,共采集样品78件。样品采集均严格按照要求,离开公路200~300 m距离,在同一采样层位多点采样,组合成一个样品。具体采样位置如图1所示。根据野外实地观察,对剖面特征进行了划分:
图1
图1
海伦地区典型黑土剖面采样位置
Fig.1
The sampling position of typical black soil profile in Hailun area
Ah层(腐殖质层):20~50 cm,厚者可达80 cm,黑色,潮湿松软,黏壤土,团粒结构,大量木本或草本植物根系。Abs层(过渡层):厚度不等,在30~70 cm左右,暗灰棕色,黏壤土,团块结构,偶见上部腐殖质淋溶的条带。Btq层(淀积层):50~160 cm,底土母质黏重时层次较薄且距地面较浅,颜色不均一,黄棕色,土体紧实,上部为小棱块状,下部为柱状,偶见铁锰结核。C层(母质层):为黄褐色黄土状堆积物。
土壤样品装入布袋后风干、敲碎,用尼龙筛筛取20目部分,送至辽宁省地质矿产研究院实验室进行常量元素含量分析测试。主要使用X荧光光谱法(XRF)测定,大部分常量元素的测试误差小于5%。
3 结果分析
表1为本次得到的78件海伦典型黑土剖面常量元素数据与哈尔滨荒山黄土[19]、洛川黄土[20]、镇江下蜀土[21]、西峰红黏土[22]以及上部陆壳(UCC)的常量元素平均组成含量比较结果。由表1可知,典型黑土剖面主量元素以SiO2、Al2O3、Fe2O3和K2O为主,四者平均含量之和达88.38%。SiO2含量范围为65.34%~67.87%,平均66.08%,变异系数为0.54%;Na2O含量范围为1.59%~2.01%,平均1.81%,变异系数为3.31%;Al2O3含量范围为13.25%~15.26%,平均14.59%,变异系数为3.13%;Fe2O3含量范围为4.29%~5.50%,平均5.09%,变异系数为5.34%;K2O含量范围为2.47%~2.73%,平均2.57%,变异系数为1.80%;CaO含量范围为1.15%~1.64%,平均1.32%,变异系数为6.26%;MgO含量范围为1.15%~1.58%,平均1.40%,变异系数为7.07%(表1)。常量元素平均含量由高到低的顺序为SiO2>Al2O3>Fe2O3>K2O>Na2O>MgO>CaO。剖面各层均以SiO2、Al2O3 、Fe2O3平均含量最高,其次是K2O 和Na2O,平均含量最低的是CaO。一般而言,土壤中CaO主要以碳酸钙的形式存在,在温湿的环境下,碳酸钙溶解,而在干冷的环境下,碳酸钙生成[23]。因此温湿的气候环境可能是典型黑土中CaO含量低的主要原因。常量元素变异系数均小于10%,表明其含量变化相对稳定。
表1 海伦典型黑土剖面及其他地区典型风成堆积物的常量元素含量
Table 1
| 剖面号 | 参数 | SiO2 | Al2O3 | Fe2O3 | K2O | Na2O | MgO | CaO | TiO2 | CIA |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PM1901 n=7 | 最小值 | 65.51 | 13.53 | 4.57 | 2.51 | 1.71 | 1.22 | 1.25 | 0.77 | 60.80 |
| 最大值 | 66.51 | 15.21 | 5.41 | 2.61 | 1.79 | 1.54 | 1.52 | 0.81 | 65.03 | |
| 平均值 | 66.05 | 14.67 | 5.10 | 2.56 | 1.75 | 1.40 | 1.33 | 0.80 | 63.62 | |
| PM1902 n=7 | 最小值 | 65.51 | 13.83 | 4.69 | 2.5 | 1.74 | 1.24 | 1.28 | 0.77 | 61.68 |
| 最大值 | 66.32 | 15.26 | 5.50 | 2.6 | 1.84 | 1.57 | 1.44 | 0.80 | 64.77 | |
| 平均值 | 65.98 | 14.77 | 5.21 | 2.54 | 1.78 | 1.44 | 1.35 | 0.80 | 63.57 | |
| PM1903 n=10 | 最小值 | 65.34 | 13.96 | 4.72 | 2.49 | 1.74 | 1.29 | 1.30 | 0.77 | 61.78 |
| 最大值 | 66.62 | 15.14 | 5.40 | 2.73 | 1.96 | 1.57 | 1.47 | 0.80 | 73.05 | |
| 平均值 | 65.75 | 14.83 | 5.15 | 2.59 | 1.83 | 1.46 | 1.35 | 0.79 | 66.42 | |
| PM1904 n=7 | 最小值 | 65.77 | 13.71 | 4.53 | 2.52 | 1.80 | 1.23 | 1.27 | 0.77 | 60.67 |
| 最大值 | 66.61 | 15.01 | 5.38 | 2.6 | 1.88 | 1.49 | 1.53 | 0.80 | 63.83 | |
| 平均值 | 66.19 | 14.46 | 5.01 | 2.54 | 1.83 | 1.37 | 1.37 | 0.79 | 62.72 | |
| PM1907 n=11 | 最小值 | 65.52 | 13.78 | 4.53 | 2.51 | 1.70 | 1.24 | 1.19 | 0.78 | 61.69 |
| 最大值 | 66.17 | 15.09 | 5.50 | 2.68 | 1.81 | 1.48 | 1.42 | 0.81 | 65.31 | |
| 平均值 | 65.89 | 14.72 | 5.17 | 2.55 | 1.75 | 1.39 | 1.28 | 0.80 | 63.94 | |
| PM1908 n=10 | 最小值 | 65.56 | 14.02 | 4.46 | 2.54 | 1.69 | 1.20 | 1.21 | 0.78 | 62.17 |
| 最大值 | 66.27 | 15.07 | 5.44 | 2.62 | 1.91 | 1.58 | 1.37 | 0.81 | 64.56 | |
| 平均值 | 65.93 | 14.69 | 5.08 | 2.58 | 1.80 | 1.42 | 1.28 | 0.80 | 63.61 | |
| PM1909 n=9 | 最小值 | 65.43 | 13.42 | 4.62 | 2.47 | 1.59 | 1.23 | 1.24 | 0.76 | 60.55 |
| 最大值 | 66.69 | 14.73 | 5.26 | 2.66 | 1.97 | 1.35 | 1.64 | 0.81 | 63.94 | |
| 平均值 | 66.14 | 14.18 | 4.92 | 2.59 | 1.77 | 1.28 | 1.43 | 0.79 | 62.31 | |
| PM1910 n=10 | 最小值 | 65.67 | 13.67 | 4.64 | 2.53 | 1.71 | 1.24 | 1.17 | 0.78 | 60.47 |
| 最大值 | 66.87 | 15.07 | 5.38 | 2.61 | 1.95 | 1.49 | 1.47 | 0.82 | 65.29 | |
| 平均值 | 66.24 | 14.57 | 5.12 | 2.58 | 1.84 | 1.39 | 1.24 | 0.80 | 63.40 | |
| PM1921 n=10 | 最小值 | 65.9 | 13.25 | 4.29 | 2.52 | 1.75 | 1.15 | 1.15 | 0.77 | 60.58 |
| 最大值 | 67.87 | 14.86 | 5.39 | 2.71 | 2.01 | 1.57 | 1.39 | 0.82 | 63.61 | |
| 平均值 | 66.58 | 14.38 | 5.07 | 2.61 | 1.93 | 1.41 | 1.27 | 0.80 | 62.44 | |
| 荒山黄土 n=62 | 最小值 | 55.74 | 16.98 | 3.03 | 2.75 | 1.51 | 1.56 | 0.72 | ||
| 最大值 | 66.70 | 21.97 | 4.85 | 3.19 | 2.45 | 2.07 | 1.01 | |||
| 平均值 | 60.85 | 19.47 | 4.22 | 3.00 | 1.84 | 1.88 | 0.87 | 74.66 | ||
| 洛川黄土 n=12 | 平均值 | 66.4 | 14.2 | 4.81 | 3.01 | 1.66 | 2.29 | 1.02 | 63.73 | |
| 镇江下蜀 土n=54 | 平均值 | 68.07 | 13.32 | 5.3 | 2.35 | 0.92 | 1.61 | 1 | 70.45 | |
| 西峰红黏 土n=5 | 平均值 | 63.75 | 15.05 | 5.28 | 3 | 1.16 | 2.89 | 0.9 | 69.11 | |
| 上陆壳 (UCC) | 平均值 | 66.00 | 15.20 | 5.00 | 3.40 | 3.90 | 2.20 | 4.20 | 47.92 |
4 讨论
4.1 常量元素含量特征及分布模式
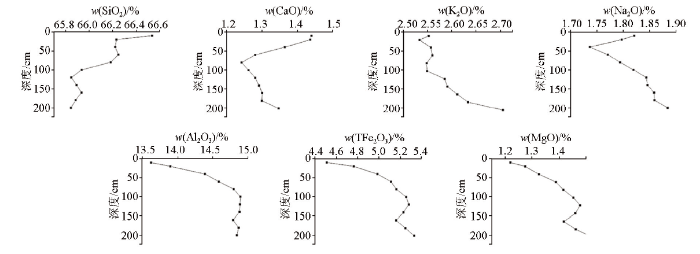
图2为选取的7条海伦典型黑土剖面常量元素含量随深度变化图。从剖面图中可以看出,海伦典型黑土常量元素在垂直方向上分布波动较明显。随着深度的增大,总体表现为SiO2含量降低,Fe2O3、Al2O3、MgO含量升高的趋势;Na2O表现为淋溶层降低,淀积层升高的变化规律,淋溶作用显著,显示了易移动元素的迁移特征;Fe2O3、MgO含量从腐殖质层到淀积层缓慢增加,在母质层先降低后增加;整体上 SiO2 和Al2O3 比较稳定,其他元素变化不明显。通过对比海伦黑土成土母质和其他地区典型风成堆积物常量元素的平均化学组成可知,典型黑土化学组成与典型风成堆积物类似,主要化学成分SiO2、Al2O3、Fe2O3之和与风成堆积物接近,表明海伦典型黑土成土母质可能为风成成因。
图2
图2
海伦黑土剖面常量元素分布特征
Fig.2
Distribution characteristics of major elements in Hailun black soil profile
表2 海伦黑土剖面常量元素含量相关系数
Table 2
| 指标 | SiO2 | Al2O3 | TFe2O3 | MgO | CaO | Na2O | K2O |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SiO2 | 1 | ||||||
| Al2O3 | -0.865** | 1 | |||||
| TFe2O3 | -0.894** | 0.984** | 1 | ||||
| MgO | -0.917** | 0.949** | 0.973** | 1 | |||
| CaO | 0.578** | -0.888** | -0.823** | -0.747** | 1 | ||
| Na2O | -0.654** | 0.398 | 0.412** | 0.583** | -0.132** | 1 | |
| K2O | -0.638** | 0.479 | 0.546 | 0.667 | -0.111** | 0.755 | 1 |
注:“**”表示置信度为 0.01时,相关性显著;“*”表示置信度为 0.05时,相关性显著。
在化学风化过程中,活动性元素容易淋失,所以稳定元素会相对富集,通常通过样品中常量元素与地球上部陆壳 (upper continetal curst,UCC)含量的比值来评价常量元素相对UCC 的亏损与富集程度,比值大于1 为相对富集,小于1 为相对亏损。海伦黑土剖面具有富Si、Fe,贫Mg、Ca、Na、K的特征,Si、Fe呈现一定程度的富集,Al稍显亏损但与UCC接近,这表明海伦黑土成土母质来源于上陆壳,并经过充分混合。Na、Ca的亏损可能是大陆化学风化的效应。通过对比其他典型风成堆积物常量元素UCC标准化结果可知,UCC标准化后的海伦典型黑土和典型风成堆积物具有良好的相似性,再次佐证了典型黑土成土母质为风成成因。
图3为海伦典型黑土及其他风成堆积物的UCC标准化曲线分布。通过将海伦剖面与洛川黄土、镇江下蜀土、西峰红黏土、哈尔滨荒山黄土等典型风成堆积物常量元素UCC标准化后对比可知,海伦黑土剖面与这些典型风成堆积物具有较好的相似性,化学组成基本相似,UCC标准化曲线变化趋势较为一致,表现为SiO2、Al2O3、Fe2O3、MgO、K2O接近于UCC,无明显的亏损或富集,Na2O、CaO位于UCC下面,处于明显的亏损状态,说明其成因的相似性,即海伦典型黑土可能为风成成因。
图3
图3
海伦黑土成土母质与其他风成堆积物常量元素的UCC标准化曲线分布模式
Fig.3
UCC-normalized pattern of elements of the Hailun black soil parent material and other aeolian dust deposits
4.2 化学风化程度
化学风化指数CIA及w(Na)/w(K)比值是目前衡量沉积物化学风化程度的最常用的指标[23],其中CIA计算公式为
式中:氧化物均为分子摩尔数;CaO*为硅酸盐矿物中的摩尔含量,采用McLennan计算方法[24]。CIA反映了长石风化成黏土矿物的程度,CIA值越高,指示气候温暖湿润,风化程度越高;反之,寒冷干燥,风化程度低。
一般而言,CIA值为50~65,指示初等化学风化程度,气候条件寒冷、干燥;CIA值为65~85,指示中等化学风化程度,气候条件为温暖、湿润[25⇓⇓-28]。海伦典型黑土剖面CIA值在61.91~64.96,平均值为63.97(表1),属于初等风化程度(图4),其中0~30 cm平均值为61.48,30 cm以下平均值为63.64。与典型风成堆积物、上陆壳(UCC)和陆源页岩相比,海伦黑土成土母质的CIA平均值远高于上陆壳(UCC)的47.92,明显小于西峰红黏土的69.11、陆源页岩的70.36、镇江下蜀土的70.45以及哈尔滨荒山黄土的71.6,与洛川黄土的63.73最接近(表1)。海伦黑土成土母质及以上几种典型风成堆积物及UCC和陆源页岩的风化强度顺序为:哈尔滨荒山黄土>镇江下蜀土≈陆源页岩>西峰红黏土>海伦黑土≈洛川黄土>>上陆壳(UCC)。不同深度的海伦典型黑土的化学风化程度均显著低于其他典型的风成堆积物(除洛川黄土外),化学风化程度的差异,可能反映了海伦典型黑土与其他典型风成堆积物的物源并不完全一致。由图4a可以看出,海伦黑土成土母质0~30 cm化学风化程度较30 cm以下较弱,反映0~30 cm黑土形成的气候条件较深处更寒冷、干燥,指示晚期海伦典型黑土寒冷干燥的气候环境。
图4
图4
海伦黑土成土母质化学风化参数CIA—w(Na)/w(K)关系散点图(a)以及w(Na)/w(K)(b)、CIA(c)随深度变化特征
Fig.4
Scatter diagram of CIA—w(Na)/w(K) molar ratio of the Hailun Black soil parent material(a), and variation of w(Na)/w(K)(b) and CIA(c) in Hailun area
4.3 稳定元素比值特征
Yang等[35]认为,科尔沁沙地全新世演化过程划分为3个阶段:10 kaBP以前以流动沙丘为主,10~8 kaBP由流动向半流动—半固定转变,8~3 kaBP砂质古土壤发育、沙地固定;3 kaBP左右土壤活化,之后经历频繁的固定和活化过程。根据海伦14C年龄结果,<30 cm的年龄结果为260~2 245 aBP,30 cm以上的年龄结果为3 300~7 850 aBP,故推测晚期海伦黑土的成土母质接受风积作用明显。
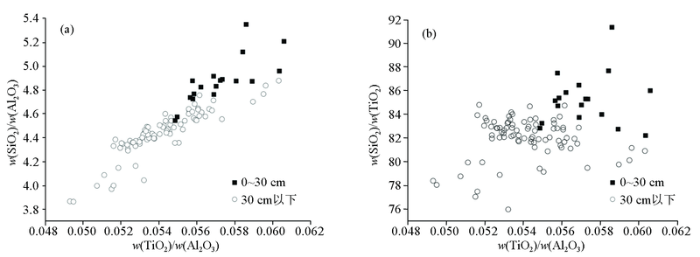
根据前人对黄土的研究[14,36],SiO2一般在粗颗粒物质中富集而Al2O3则在细颗粒物质中富集。随着与物源距离的增大,风成堆积物的粒度会逐渐减小,w(SiO2)/w(Al2O3)比值也会逐渐降低[15],因此被用作研究粒度的替代性指标[14-15,36]。而w(TiO2)/w(Al2O3)比值几乎不受粒度大小及风化作用的影响,也是研究风成堆积物物源的重要指标[15,34]。在w(TiO2)/w(Al2O3)—w(SiO2)/w(Al2O3)图解(图5a)中,海伦0~30 cm黑土中w(SiO2)/w(Al2O3)、w(TiO2)/w(Al2O3)比值明显偏高,反映其粒度可能偏大,推测表层与深层黑土的物源并非完全一致。
图5
图5
海伦黑土成土母质的w(TiO2)/w(Al2O3)—w(SiO2)/w(Al2O3) (a)和w(TiO2)/w(Al2O3)—w(SiO2)/w(TiO2) (b)图解
Fig.5
w(TiO2)/w(Al2O3) versus w(SiO2)/w(Al2O3) (a)and w(TiO2)/w(Al2O3) versus w(SiO2)/w(TiO2) (b)plots for the Hailun Black soil parent material
从元素地球化学的角度来看,w(SiO2)/w(TiO2)主要反映的是石英含量的变化,是一种对原始粉尘粒度更为灵敏的指标[14,37-38]。在w(TiO2)/w(Al2O3)—w(SiO2)/w(TiO2)图解(图5b)中,0~30 cm深度的海伦典型黑土比30 cm以下的黑土具有更高的w(SiO2)/w(TiO2),说明晚期海伦典型黑土中石英含量增加,粒度增大,暗示海伦黑土成土母质0~30 cm含有较多近源成分。从图中还可以看出,不同深度的海伦典型黑土w(TiO2)/w(Al2O3)比值明显不同。w(SiO2)/w(TiO2)、w(TiO2)/w(Al2O3)比值在不同深度典型黑土中的改变,可能反映了海伦黑土成土母质在30 cm左右物源的变化。
5 结论
本次获得了黑龙江海伦地区多个典型黑土剖面常量元素分析结果,通过上部陆壳(UCC)标准化对比、化学风化程度(CIA值、w(Na)/w(K))研究以及稳定元素(w(SiO2)/w(Al2O3)、w(SiO2)/w(TiO2)、w(TiO2)/w(Al2O3))比值的分析,得到如下结果:
1)元素地球化学特征显示,典型黑土化学组成与其他典型风成堆积物类似,主要化学成分SiO2、Al2O3、Fe2O3之和与风成堆积物接近,UCC标准化后的海伦典型黑土和典型风成堆积物具有良好的相似性,表明典型黑土成土母质可能为风成成因。
2)海伦典型黑土CIA值平均为63.97,属于初等风化程度,其中0~30 cm化学风化程度较30 cm以下弱,反映0~30 cm黑土形成的气候条件较深处更寒冷、干燥,指示晚期海伦典型黑土寒冷干燥的气候环境。
3)0~30 cm黑土比30 cm以下的黑土具有更高的w(SiO2)/w(TiO2)、w(SiO2)/w(Al2O3),说明晚期海伦典型黑土中石英含量增加,粒度增大,暗示海伦黑土成土母质0~30 cm含有较多近源成分,稳定元素的比值在不同深度的变化,可能反映了海伦黑土成土母质在30 cm左右物源的变化,表层和深层典型黑土母质的物源并非完全相同。
参考文献
Soil management in relation to sustainable agriculture and ecosystem services
[J].
东北松辽平原35年来耕地土壤全氮时空变化最新报道
[J],
Spatio-temporal variation of total N content in farmland soil of Songliao Plain in Northeast China during the past 35 years
[J].
A preliminary study on soil degradation and nutrient imbalance of typical black soil in Northeast China
[C]//
松嫩平原东部典型黑土剖面孢粉组合及其时代和古气候意义
[J].
Palynological Assemblages of typical black soil profile in the eastern Songliao Plain and their Age and Paleoclimatic Significances
[J].
东北松辽平原典型黑土—古土壤剖面AMS14C年龄首次报道
[J].
The first reported of the AMS14C age of typical black soil mollisol—Paleosol profile of Songliao Plain
[J].
松嫩平原南缘现代沉积物磁化率、粒度、色度特征及古气候环境意义
[J].
Characteristics of magentic susceptibility,grain size and chromaticity of modern sedimentsin the southern margin of Songnen Plain and their paleoclimate environment significance
[J].
黑龙江海伦地区垦殖前后典型黑土剖面主要养分元素垂直分布特征
[J].
Vertical distribution characteristics of main nutrient elements in typical black soil profile before and after reclamation in Helun Area,Heilongjiang Province
[J].
Temporal and spatial change of soil organic matter and pH in cultivated land of the Songliao Plain in Northeast China during the past 35 years
[J].
黑龙江省南部黑土区微量元素空间变异及影响因子——以双城市为例
[J].
Spatial variability of soil trace elements in black soil region of south Heilongjiang province and its affecting factors:A case study of Shuangcheng city
[J].
东北黑土区旱田改稻田后土壤有机碳、全氮的变化特征
[J].
Changes of the characteristics of soil organic carbon and total nitrogen after conversation from upland to paddy field in black soil region of Northeast China
[J].
中国东北黑土地研究进展与展望
[J].
DOI:10.13249/j.cnki.sgs.2018.07.004
[本文引用: 1]

东北黑土区是世界四大片黑土区之一,它以高有机质和高肥力而著称,不仅是东北农业发展的基础,也是中国的粮仓,在保障国家粮食安全中具有举足轻重的地位。针对东北黑土自身的特色和面临的问题,首先描述了东北黑土地形成的条件及自然黑土的属性特征;其次阐述了黑土被开垦后农田化过程中土壤属性和肥力的演化情况,土壤有机质大幅度下降,土壤肥力降低,已严重影响到东北黑土地农业的可持续发展;在此基础上分析了黑土区耕作土壤不同保护途经及其对土壤肥力的影响机制;最后展望了未来黑土地理论研究的侧重点:应加大新技术、新方法和跨学科交叉理论的研究,培育更适合东北黑土地气候条件的高产优质作物品种,并结合目前黑土地保护的技术调控模式,优化作物种植模式,提升作物品质和产量,提高黑土区农业的综合生产力和竞争力、保证黑土区农业的永续利用。
Research progress of black soil in Northeast China
[J].
DOI:10.13249/j.cnki.sgs.2018.07.004
[本文引用: 1]

The black soil region in Northeast China is one of the world’s four black soil regions. It is well known for its high organic matter content and high fertility. It is not only the basis for the development of agriculture in Northeast China, but also the granary of China, which plays a decisive role in safeguarding the national food security. According to the characteristics and problems of black soil in Northeast China, this review first elucidates the forming conditions of the black soil and the natural characteristics. Secondly, we describe the evolution of soil properties and fertility in the process of the reclamation of black soil. The soil organic matter content and soil fertility decreased significantly, which have severely affected the sustainable development of agriculture in black soil region in Northeastern China. Besed on this analysis, different protection pathways and their controlling mechanisms on soil fertility are analyzed. Future research on black soil should be emphasized on the development of new technologies, new methods, and cross-disciplinary theories to ascertain the evolutional characteristics of soil fertility and their influencing factors. It is necessary to cultivate high-yield, high-quality crop varieties that are more suitable for the climatic conditions in Northeast China, to optimize the cropping system in combination with the current technological regulation pattern in this region, to improve the quality and yield of crops, to increase the overall productivity and competitiveness of agriculture soil, and finally to ensure the sustainable use of agriculture in the black soil region.
东北典型黑土区气候、地貌演化与黑土发育关系
[J].
Relationship between black soil development and climate change and geomorphological evolution in Northeast China
[J].
DOI:10.11821/yj2008030006
[本文引用: 1]

Soil on slopes of the gentle hilly black soil region in Northeast China, one of the most important bases of cash rice, degraded seriously after dozens of years of intensive cultivation. The thickness of soil humus layer becomes thinner and less fertile year after year. So it is very essential to deepen the researches of soil restoration and improvement after severe soil erosion. Analysis of main reasons for black soil degradation revealed that the cultivation activities halted the accumulation of organic matter and then baffled the soil development which cannot compensate the decrease of the thickness of soil humus layer caused by soil erosion. Soil developing process and conditions are the most important foundation for soil restoration. So the developing history of black soil and chernozem was reconstructed and the geomorphological and climatic factors, which were the key factors affecting the formation of black soil, were analyzed through studying both the formation time of the underlying strata and the local climate change history since the late Pleistocene. The conclusion is that black soil and chernozem formed in different periods, from early period of late Pleistocene and the beginning of Holocene respectively. The former period was warm and wet, while the latter period was warm and dry. And they formed in different places, the black soil was mainly distributed on the second and the third terraces and the chernozem on the first terrace of the Nenjiang River, which is lower than the distributing places of black soil and can accept more carbonate from the highland to form the characteristic illuvial layer. The processes of the soil formation were very slow, so it is hard to restore. These results provide important basis for forulating policies to improve the quality of soils in the region.
南京下蜀土的地球化学特征及其物源指示意义
[J].
Geochemical characteristics of the Xiashu loess-palaeosol sequence in Nanjing and their implicationa for provence
[J].
邙山黄土L5以来的常量元素地球化学特征及其对物源的指示意义
[J].
Major element geochemical characteristics of Mangshan loess since L5 and its implications for provenance
[J].
Geochemical evidence for the provenance of Middle Pleistocene loess deposits in Southern China
[J].DOI:10.1016/j.quascirev.2010.08.004 URL [本文引用: 6]
Grain size,magnetic susceptibility and geochemical characteristics of the loess in the Chaohu Lake basin: Implications for the origin,palaeoclimatic change and provenance
[J].DOI:10.1016/j.jseaes.2015.12.013 URL [本文引用: 2]
Geochemical composition of Tajikistan loess and its provenance implications
[J].DOI:10.1016/j.palaeo.2016.01.025 URL [本文引用: 2]
Geochemistry of sediments from the Huaibei Plain (East China):Implications for provenance,weathering,and invasion of the Yellow River into the Huaihe River
[J].DOI:10.1016/j.jseaes.2016.02.008 URL [本文引用: 2]
哈尔滨荒山黄土的成因——粒度、地球化学、磁化率、沉积和地貌特征的整合记录
[J].
The genesis of Huangshan loess in Harbin: Integrated evidence from grain size,geochemistry,magnetization,sedimentation and landform
[J].
陕西洛川黄土化学风化程度的地球化学研究
[J].
Geochemical study on chemical weathering degree of loess in Luochuan,Shaanxi Province
[J].
Chemical weathering intensity and element migration features of the Xiashu loess profile in Zhenjiang,Jiangsu Province
[J].
甘肃西峰晚第三纪红粘土的化学组成及化学风化特征
[J].
Chemical composition and characterization of chemical weathering of late tertiary red clay in Xifeng,Gansu Province
[J].
丰宁黄土—古土壤剖面常量元素地球化学特征
[J].
Elemental composition features of loess-paleosol profile in Fengning,Hebei Provinc
[J].
Weathering and global denudation
[J].DOI:10.1086/648222 URL [本文引用: 1]
黑龙江省拜泉地区典型黑土剖面元素地球化学特征及其环境指示意义
[J].
Elemental geochemistry characteristics and environmental indication of typical black soil profile in Baiquan Area,Heilongjiang Province
[J].
吴起全新世土壤剖面常量元素地球化学特征
[J].
Geochemical characteristics of major elements of holocene soil from Wuqi,Shaanxi Province
[J].
山东平阴黄土剖面常量元素地球化学特征
[J].
Geochemical characteristics of major elements of the Pingyin loess in Shandong Province
[J].
Geochemistry of precambrian and paleozoic siliciclastic rocks from the iberian range(NE Spain):Implications for source-area weathering,sorting,provenance,and tectonic setting
[J].
北京平原区土壤地球化学特征及影响因素分析
[J].
Soil geochemical characteristics and influencing factors in Beijing Plain
[J].
福建龙海土壤垂向剖面元素分布特征
[J].
Distribution characteristics of elements in vertical soil profile in Longhai,Fujian province
[J].
Geochemical characterizati0n of the Luochuan loess paleosol sequence,China,and paleoclimatic implications
[J].DOI:10.1016/S0009-2541(96)00070-8 URL [本文引用: 1]
Variations in chemical compositions of the eolian dust in Chinese Loess Plateau over past 2.5Ma and chemical weathering in the Asian inland
[J].
灵台红粘土和黄土—古土壤序列的地球化学演化
[J].
A seven million geochemical record from Chinese red-clay and loess-paleosol sequence:Weathering and erosion in northwestern China
[J].
Lateglacial and Holocene dune evolution in the Horqin dunefield of northeastern China based on luminescence dating
[J].DOI:10.1016/j.palaeo.2010.06.014 URL [本文引用: 1]
Geochemical indicator of original eolian grain size and implications on winter monsoon evolution
[J].
Grain size of quartz as an indicator of winter monsoon strength on the Loess Plateau of Central China during the last 130,000 yr
[J].DOI:10.1006/qres.1995.1003 URL [本文引用: 1]
Millennia1 scale climatic oscillations during the last interglaciation in Central China
[J].DOI:10.1130/0091-7613(1997)025<0603:MSCODT>2.3.CO;2 URL [本文引用: 1]
Geochemical studies on the source region of asian dust
[J].