0 引言
1 碳酸岩型稀土矿地质特征
2 碳酸岩型稀土化探找矿中存在的问题
2.1 中国碳酸岩型稀土化探找矿的困境
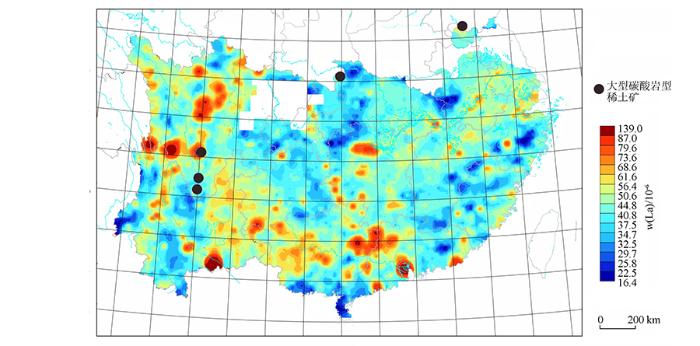
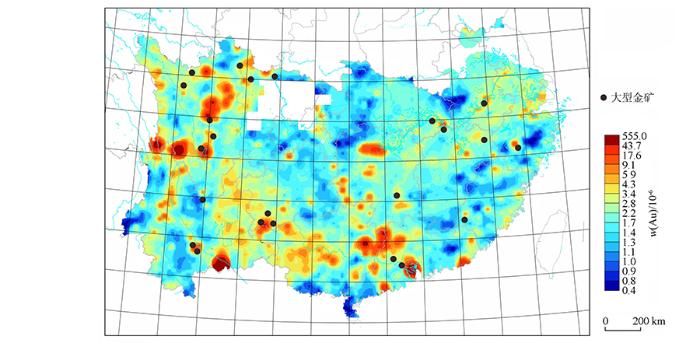
利用区域尺度地球化学图圈定成矿远景区或成矿靶区,可为稀土勘查的战略部署提供依据。将区域尺度La元素地球化学图与碳酸岩型稀土矿床的分布拟合(图1), 虽然矿床均落在La异常区内, 但是矿致异常的衬度低且规模小。然而这几处矿床的稀土储量占据了中国南方总储量的大半。与稀土元素形成鲜明对比的是, Au异常与金矿床有密切的空间对应关系(图2) 。1:20万区域尺度Au异常在中国金化探勘查中发挥了重要的先导作用[4]。虽然稀土成矿过程常见伴生元素F、Ba、U、Th、Nb、Ta、Ti、Fe异常, 但其极易受到其他地质过程干扰, 成矿指示性意义远不如稀土元素本身[23]。综上, 由于所圈定稀土异常衬度不够强, 找矿指示性意义弱, 导致稀土化探找矿效果不好, 这正是当前稀土勘查的困境。
图1
图1
中国南方镧地球化学模式与碳酸岩型稀土矿分布[24]
Fig.1
Lanthanum geochemical patterns and carbonatite-type REE deposits in southern China
图2
图2
中国南方金地球化学模式与大型金矿床分布[24]
Fig.2
Gold geochemical patterns and carbonatite-type REE deposits in southern China
2.2 稀土化探困境之原因
2.2.1 稀土矿致异常易被稀释
稀土矿低富集且出露少的特性,导致水系沉积物中的矿致异常极易被削弱甚至掩盖。成矿元素从矿体运移并沉积在水系沉积物过程中, 不可避免受到背景区物质稀释作用影响。成矿元素在矿体相对地壳丰度富集程度越高, 越不易受稀释作用影响, 所圈定的矿致异常越突出。
2.2.2 稀土矿物鉴定统计困难
2.3 解决困境的关键
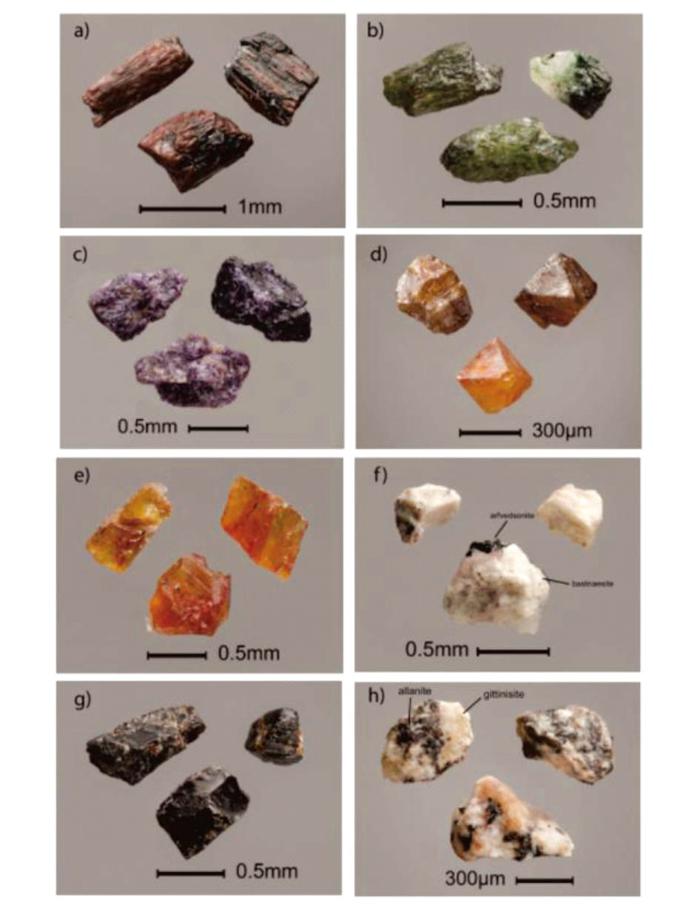
图3
图3
部分常见富稀土矿物镜下照片[35]
a—钠铁闪石;b—针状霓石;c—萤石;d—绿石;e—独居石;f—氟碳铈矿(白色);g—硅钛铈矿;h褐帘石(暗色部分)
Fig.3
Some common REE-rich minerals under a microscope
a—sodium amphibole; b—acicular neonite; c—fluorite; d—chlorite; e—monazite; f—bastnasite (white); g—nastite; h—epidote (dark part)
稀土矿物的表生迁移富集规律是稀土化探工作的理论根基, 能够对整个稀土化探的工作体系产生影响。对该规律认识不清,是使稀土化探勘查陷入困境的根本原因。因此,必须使用一种行之有效的手段,精确分选、鉴定和定量统计各稀土矿物及其各项参数,攻克稀土矿物表生迁移富集规律这一亟待解决的难题, 才能为稀土化探打牢理论根基, 从根本上走出稀土化探找矿的困境。
3 QEMSCAN等矿物自动分析系统的引入
3.1 传统矿物鉴定方法的局限性
传统的光学镜下矿物统计鉴定技术(后文统称“传统方法”)往往需要先对矿物进行富集, 利用矿物自身的密度、磁性、电性及表面能等特性, 从疏松沉积物中分选出粒度较大(>63 μm) 的目标矿物, 再通过人工光学镜进行鉴定和定量统计。
3.2 矿物自动分析系统优势
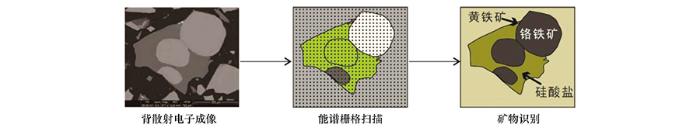
MLA(mineral liberation analyzer)和QEMSCAN(quantitative evaluation of minerals by scanning electron microscopy)技术分别由澳大利亚昆士兰大学和澳大利亚CSIRO发明[46-47]。二者的发明之初为满足采矿业需求, 目前已逐渐广泛应用于矿床学、沉积学、石油地质等领域[48⇓-50]。此外还有Tescan 公司的TIMA(tescan-integrated mineral analyser)和Zeiss公司的ZMM(ZEISS mineralogic mining)技术。这些分析技术原理相近(图4), 都是结合了电子背散射图像、能(波)谱以及分析系统来获得并统计各项矿物参数, 差别在于配备了不同型号的扫描电镜、能(波)谱仪、软件系统和分析流程。
图4
得益于扫描电镜的超高分辨率能谱和先进的统计软件相结合, QEMSCAN技术的优势是对微细粒矿物进行精准定量分析统计。QEMSCAN的扫描栅格可小至0.8~10 μm[51], 对72种化学元素进行能谱分析, 可以胜任对微细粒稀土矿物的鉴定和统计工作[34]。QEMSCAN另一大优势是具有灵活多样的分析模式, 可针对某种特定微细粒矿物的数量和质量占比, 以及每个颗粒的粒径、周长和面积分别进行分别统计[34,51]。前人利用QEMSCAN统计矿物周长与面积比值刻画矿物磨圆度, 在区分磷灰石成因研究中取得良好效果[51]。此外还可通过配套的能谱仪对矿物表面进行元素面扫描来获得主要组成元素的分布模式。虽然其测试精度不如LA-ICP-MS等手段, 但是在元素含量较高的情况下, 能谱分析能够较精确反映元素相对含量差异, 并将矿物的化学成分与粒径等其他属性之间建立关系。
3.3 矿物自动鉴定系统在稀土勘查研究中的应用实例
在研究稀土矿物表生风化、迁移规律中,需要了解汇水域系统中,沉积物样品的稀土矿物含量变化规律。但是,随着迁移距离增加,稀土矿物不断被稀释,传统方法难以分选出痕量目标稀土矿物,因此无法开展相关矿物迁移规律研究。利用矿物自动分析系统的高精度和先进统计方式,能够增加相关研究的精度和维度。这对研究稀土矿物远距离迁移规律研究具有重要意义。
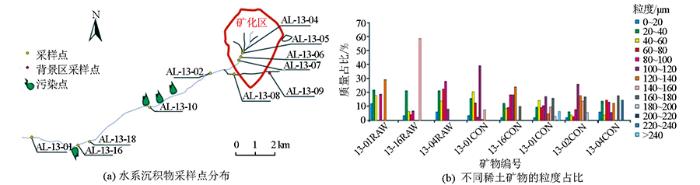
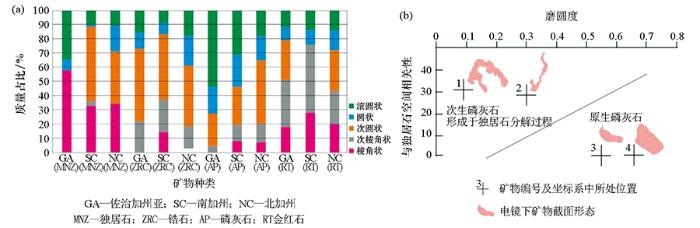
加拿大著名指示性矿物找矿科学家在利用传统方法对稀土矿物的表生迁移规律研究的文章中指出, 在未来相关研究中, 应该引入MLA、QEMSCAN等矿物自动分析系统技术,以克服传统鉴定方法无法避免的局限性[35]。Lehtonen等[33]利用 MLA系统对冰碛物中的指示性矿物含量进行定量统计,认为矿物含量可反映地质背景的变化。该研究解决了自动矿物分析系统的采样代表性问题,即使其采样重量远小于传统方法。Mackay等[34]利用QEMSCAN方法,对加拿大大不列颠一处碳酸岩体及其下游水系沉积物系统中的稀有和稀土矿物开展了探索性研究,通过对岩体及下游沉积物连续采样直至13 km处(图5a),发现了大量传统方法难以分选的0~60 μm微细粒稀土矿物,并给出了精确的矿物占比(图5b),指出QEMSCAN方法特别适合用于矿物粒度细且成分复杂的稀土矿勘查。Grammatikopoulos等[53]利用QEMSCAN对滨海砂矿中的磷灰石的磨圆度和矿物伴生关系进行了精确的定量统计,以此辨别磷灰石成因类型及其含量(图6),从而更加精准评价独居石砂矿的成矿潜力。该研究展示了QEMSCAN对矿物粒度和磨圆度准确定量评价的能力。上述一系列研究表明,在稀土矿物表生迁移研究中,矿物自动分析系统可对样品中所有微细粒稀土矿物的各项参数进行全面而精准的定量统计,相对传统方法具有显著优势。
图5
图5
QEMSCAN用于表生稀土矿物迁移规律研究实例[34]
Fig.5
An example of studying the surficial migration law of rare earth minerals with QEMSCAN
图6
图6
QEMSCAN定量评价稀土矿物磨圆度(a)和矿物伴生关系(b)的实例[52]
Fig.6
An example of quantitative evaluation of roundness and mineral association of rare earth minerals with QEMSCAN
4 矿物自动分析系统在稀土勘查研究中的应用方向
目前我国对碳酸岩型稀土矿的地球化学勘查研究工作开展较少,特别是基础理论研究基本属于空白,国际上也处于起步阶段。这与稀土重要的战略地位极不相称。本文在深入分析稀土地球化学勘查中存在的问题基础上,提出利用矿物自动鉴定系统开展稀土矿物表生迁移富集规律的想法。相关研究可以从如下两个方面开展: ①不同景观区风化过程中稀土矿物粒度变化规律研究。风化是矿物表生行为的第一步,而粒度对水系中矿物的迁移规律具有决定性的影响[53⇓-55]。矿物自动分析系统能够准确鉴定稀土矿物,并精准定量计算出各稀土矿物的粒度分布,从而搞清楚不同景观区的风化作用对稀土矿物的改造规律。②水系沉积物中稀土矿物的分布规律研究。了解矿体—水系沉积物系统中,从上游至下游随迁移距离变长过程中,稀土矿物含量的变化,以及在相同迁移距离下,不同沉积部位的稀土矿物富集程度差异。通过上述研究,可为不同景观区碳酸岩型稀土化探工作方法提供理论依据,包括采样粒度、介质、密度以及异常解释,助力中国实现稀土找矿新突破。
5 结语
制约中国稀土化探找矿效果的关键因素是稀土矿致异常容易被稀释,但由于对稀土成矿指示性矿物的表生迁移规律认识不深,难以制定有针对性的采样方法。稀土矿物一般粒度较细,相比于传统矿物挑选统计方法,基于高分辨率扫描电镜和能谱分析的矿物自动分析系统(如QEMSCAN和MLA)在矿物定量统计分析方面具有显著优势。通过将QEMSCAN等引入稀土化探理论研究中,有助于深入认识稀土矿物表生迁移富集规律,从而为稀土化探提供理论支撑。
参考文献
Strategic and critical materials 2013 report on stockpile requirements
[R].
中国与美国和欧盟稀土资源形势对比分析
[J].
Comparative analysis of rare earth resources situation between China, the U. S. and EU
[J].
腾冲地块稀土地球化学背景与泥岩中稀土超长富集特征
[J].
Geochemical background of REEs: Super-enrichment in argillaceous rocks in Tengchong block
[J].
中国内生稀土矿床类型,成矿规律与资源展望
[J].
The types, ore genesis and resource perspective of endogenic REE deposits in China
[J].
中国稀土元素地球化学背景与远景区优选
[J].
Geochemical background and distribution of rare earth elements in China: Implications for potential prospects
[J].
Rare earth element ore geology of carbonatites
[J].
中国碳酸岩型稀土矿床:时空分布与成矿过程
[J].
Rare earth elements deposits in China: Apatio-temporal distribution and ore-forming processes
[J].
与碳酸岩—碱性杂岩体相关的内生稀土矿床成矿作用研究进展
[J].
Review of the metallogenesis of the endogenetic rare earth elements deposits related to carbonatite-alkaline complex
[J].
四川牦牛坪稀土矿区的氟碳铈矿
[J].
Bastnaesitefrom rare earth mining in Maoniuping, Sichuan province
[J].
John Jambor’s contributions to the mineralogy of the Strange Lake peralkaline complex, Quebec-Labrador, Canada
[J].DOI:10.3749/canmin.1400051 URL [本文引用: 1]
Rare earth element mines, deposits, and occurrences
[R].
Rare earth minerals and resources in the world
[J].DOI:10.1016/j.jallcom.2005.04.033 URL [本文引用: 1]
China geochemical baselines: Sampling methodology
[J].DOI:10.1016/j.gexplo.2014.05.018 URL [本文引用: 1]
中国区域化探全国扫面计划卅年
[J].
The implementation of the regional geochemistry-national reconnaissance program (RGNR) in China in the past thirty years
[J].
The chemical composition evolution of the continental crust
[J].DOI:10.1029/95RG00262 URL [本文引用: 1]
Carbonatites: Related ore deposits, resources, footprint, and exploration methods
[J].DOI:10.1080/03717453.2018.1435035 URL [本文引用: 2]
牦牛坪稀土资源综合利用探讨
[J].
Discussion on comprehensive utilization of rare earth resources in Maoniuping
[J].
微山稀土矿原生矿选矿试验研究
[J].
Benification experiment on primary mineral s of Weishan rare earth mine
[J].
竹山庙垭稀土矿的选冶联合工艺技术
[J].
Beneficiation-metallurgy combination technology of Zhushan Miaoya rare earth mine
[J].
白云鄂博矿稀土资源的特点及研究开发现状
[J].
Characteristics and current research situation of rare earth resources in Bayan Obo ore
[J].
Exploring for RE and REE mineralization using indicator minerals
[C]//
Novel technologies for indicator mineral-based exploration
[R].
Indicator mineral-based exploration for carbonatites and related specialty metal deposits:A QEMSCAN orientation survey, British Columbia, Canada
[J].DOI:10.1016/j.gexplo.2016.03.005 URL [本文引用: 5]
Rare metal indicator minerals in bedrock and till at the Strange Lake peralkaline complex, Quebec and Labrador, Canada
[J].
DOI:10.1139/cjes-2018-0299
[本文引用: 5]

A study of rare metal indicator minerals and glacial dispersal was carried out at the Strange Lake Zr- Y - heavy rare earth element deposit in northern Quebec and Labrador, Canada. The heavy mineral (>3.2 specific gravity) and mid-density (3.0-3.2 specific gravity) nonferromagnetic fractions of mineralized bedrock from the deposit and till up to 50 kin down ice of the deposit were examined to determine the potential of using rare earth element and high field strength element indicator minerals for exploration. The deposit contains oxide, silicate, phosphate, and carbonate indicator minerals, some of which (cerianite, uraninite, fluorapatite, rhabdophane, thorianite, danburite, and aeschynite) have not been reported in previous bedrock studies of Strange Lake. Indicator minerals that could be useful in the exploration for similar deposits include Zr silicates (zircon, secondary gittinsite (CaZrSi2O7), and other hydrated Zr +/- Y +/- Ca silicates), pyrochlore ((Na,Ca)(2)Nb2O6(OH,F)), and thorite (Th(SiO4))/thorianite (ThO2) as well as rare earth element minerals monazite ((La,Ce,Y,Th)PO4), chevkinite ((Ce,La,Ca,Th)(4)(Fe,Mg)(2)(Ti,Fe)(3)Si4O22), parisite (Ca(Ce,La)(2)(CO3)(3)F-2), bastnaesite (Ce(CO3)F), kainosite (Ca-2(Y,Ce)(2)Si4O12(CO3).H2O), and allanite ((Ce,Ca,Y)(2)(ALFe)(3)(SiO4)(3)(OH)). Rare metal indicator minerals can be added to the expanding list of indicator minerals that can be recovered from surficial sediments and used to explore for a broad range of deposit types and commodities that already include diamonds and precious, base, and strategic metals.
金矿化探(一):金矿化探的现状与研究方向
[J].
Geochemical exploration of gold deposits (1): Present situation and research direction of geochemical exploration of gold deposits
[J].
金矿化探(二)——采样与取子样的难关·为《国外地质勘探技术》创刊第100期而作
[J].
Geochemical exploration of gold deposits (2): Difficulties in sampling and sampling · for the 100th issue of Foreign Geoexploration Technology
[J].
金矿化探(三)——金的颗粒分布与取子样误差关系的研究
[J].
Geochemical exploration of gold deposit (3): Study on the relationship between gold particle distribution and sampling error
[J].
非传统金矿化探的理论与方法技术研究
[J].
Unconventional geochemical exploration for gold
[J].
Rare earth elements: Minerals, mines, magnets (and more)
[J].DOI:10.2113/gselements.8.5.333 URL [本文引用: 1]
Geochemical and mineralogical characteristics of ion-adsorption type REE mineralization in Phuket, Thailand
[J].DOI:10.1007/s00126-011-0380-5 URL [本文引用: 1]
Rare earth element mineralogy and geochemistry in a laterite profile from Madagascar
[J].DOI:10.1016/j.apgeochem.2013.12.013 URL [本文引用: 1]
云南临沧花岗岩中离子吸附型稀土矿床的成矿规律
[J].
Mineralization regularity of ion-adsorption type REE deposits on Lincang granite in Yunnan Province
[J].
Mineral chemistry: Modern techniques and applications to exploration
[C]//
REE-Sr-Ba minerals from the Khibina carbonatites, Kola Peninsula, Russia: Their mineralogy, paragenesis and evolution
[J].DOI:10.1180/002646198547594 URL [本文引用: 2]
Advances in the quantification of gold deportament by QemSCAN
[C]//
JRMRC mineral liberation analyser — A modern tool for ore characterisation and plant optimisation
[J].
鄂尔多斯盆地延长组长7致密油储层微观孔隙特征研究
[J].
Study of pore features in Chang7 tight oil reservoir,Yanchang layer,Ordos Basin
[J].
Automated scanning electron microscopy (QEMSCAN)-based mineral identification and quantification of the Jabali Zn-Pb-Ag nonsulfide deposit (Yemen)
[J].DOI:10.2113/econgeo.110.4.1083 URL [本文引用: 1]
High throughput petrochronology and sedimentary provenance analysis by automated phase mapping and LA-ICP-MS
[J].DOI:10.1002/2017GC007109 URL [本文引用: 1]
Automated quantitative rare earth elements mineralogy by scanning electron microscopy
[J].
Investigation of low-grade REE offshore sands from North and South Carolina, and Georgia, USA, using automated mineralogy
[J].DOI:10.1016/j.gexplo.2019.03.004 URL [本文引用: 1]
Grain-size dependence of sediment composition and environmental bias in provenance studies
[J].DOI:10.1016/j.epsl.2008.11.007 URL [本文引用: 2]
Heavy-mineral concentrates in geochemical exploration
[J].
Transport of cassiterite in a Malaysian stream: Implications geochemical exploration
[J].DOI:10.1016/S0375-6742(96)00012-X URL