0 引言
目前在琼东南海域开展了多次高分辨率多道地震调查,对该海域的构造、沉积环境进行分析和讨论,发现了天然气水合物的重要地球物理标志BSR,对相关的地球物理特征如BSR极性反转、振幅空白带、速度异常等进行识别及判读,估算了该海域的天然气水合物资源量,推断了该海域的天然气水合物资源前景。为全面挖掘天然气水合物存在的信息及证据,在该海域开展OBS地震调查。
本文针对OBS海面放炮海底接收、接收点稀疏等特点,采用有别于常规海洋拖缆资料和OBS单节点处理的方式对调查区的OBS数据进行共反射点偏移成像处理,最终获得PP和PS的速度结构和偏移成像成果。在此基础上进行纵横波联合反演,获得调查区纵波阻抗、横波阻抗剖面以及纵横波速度比,综合分析成像与反演结果,进一步确定了水合物储存有利位置及游离气存在位置。
1 OBS资料采集
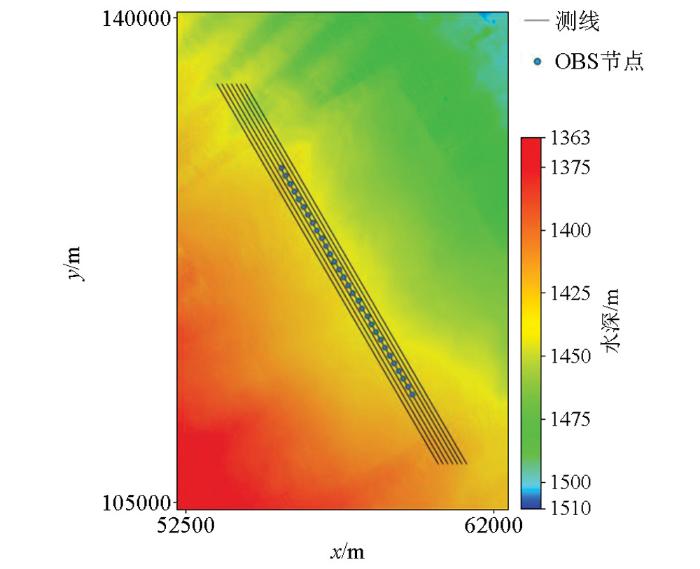
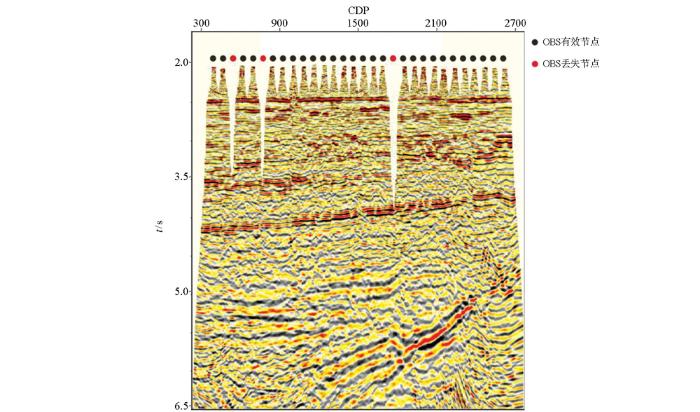
调查区位于琼东南海域,布设7条测线,OBS投放测线两侧各平行采集3条测线,测线间隔为50 m,测线长度为20 km,采用双震源放炮,放炮间隔为25 m,激发震源为GI枪,容量为10 160 cm3,工作压力为13.79 MPa,采样率为2 ms。共投放30个OBS,OBS节点间距为400 m,采样率为2 ms,记录长度为8 s,回收27个,第3、6、19号节点在回收过程中丢失。调查区海底地形相对平坦,水深约为1 400~1 500 m之间。图1为OBS及采集测线布设图。
图1
2 成像处理关键技术
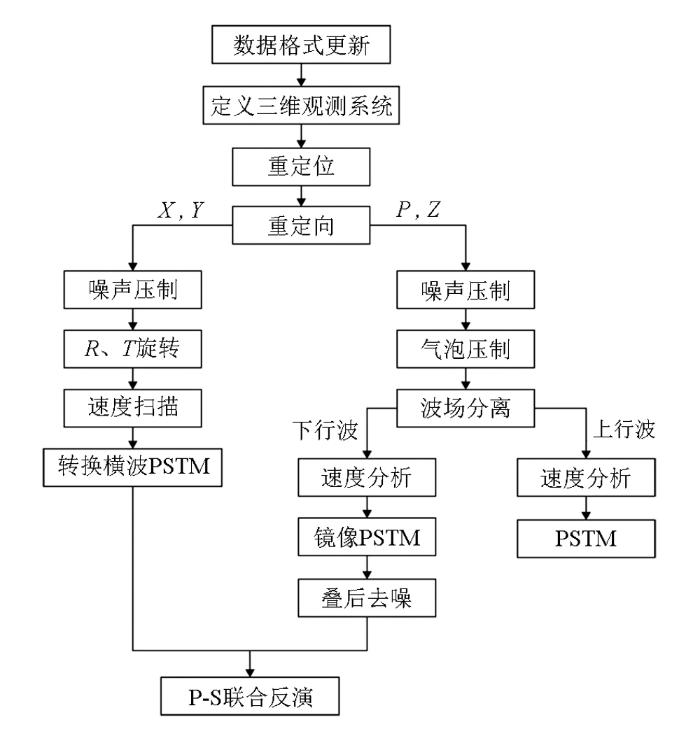
OBS成像处理,有别于常规的拖缆多道资料处理和单节点OBS处理方式,本文基于geovation软件对OBS数据进行重定位、波场分离、镜像偏移、RT旋转、转换波偏移等处理,图2为OBS成像处理关键技术流程。
图2
2.1 节点重定位
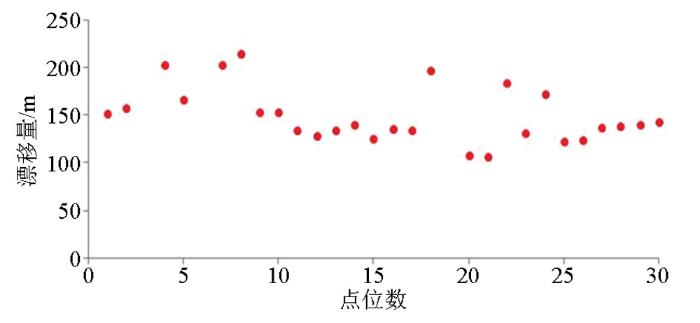
OBS的投放方式为利用钢缆将OBS投放到预设位置海面上,然后脱开钢缆让其自由下沉,在自由下沉过程中受水流、海底地形等的影响,在海底的位置与海面投放位置会存在一定偏差,而OBS不具备海底位置记录功能,需要运用实际数据对海底OBS位置进行重定位处理[5]。
图3
图4
2.2 波场分离
地震波从地层传播到海底或者从海面传播到海底后即刻反射的信号称为上行波,包括一次波和微曲多次波;地震波从海面传播到海底,直接被检波器接收的称为下行波,主要指鬼波。OBS检波器的水检分量P和陆检分量Z对上、下行波具有不同的响应特征:对上行波而言,二者极性相同;对下行波而言,二者极性相反[7,8]。基于此,可以通过水陆检合并的方式将波场分为上行波场和下行波场,但两分量的仪器响应以及与介质的耦合性不同,导致在能量和频率上均存在差异。在实际处理过程中,以水检分量为期望输出,基于自相关函数方差模最小原理求取标定因子并对陆检分量进行能量和相位匹配[9,10],将匹配后的水检P分量与陆检Z分量求差获得下行波场;利用交叉鬼波化双检合并技术[11]获得上行波场。
图5
图5
波场分离效果
a—P分量;b—标定后Z分量;c—上行波;d—下行波
Fig.5
The result of the wave field separation
a—P component;b—calibrated Z component;c—up going field;d—down going field
2.3 纵波镜像偏移成像
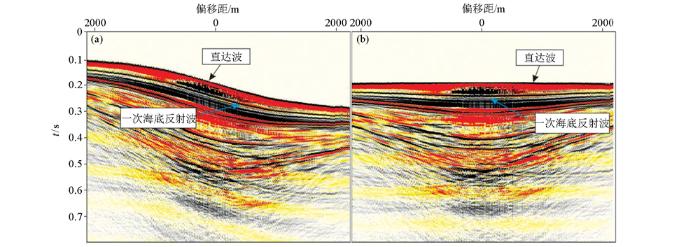
图6
图6
共反射点上(a)、下行波(b)偏移成像
Fig.6
The result of CRP imaging with up going(a) and down going(b)
2.4 重定向与极化旋转
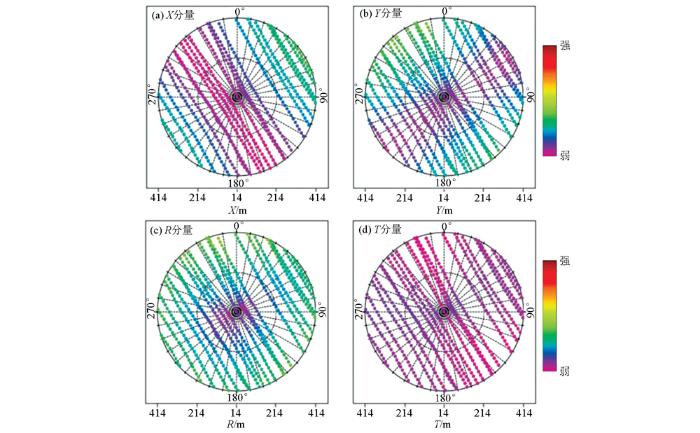
图7为极化旋转前后转换横波各分量能量分布对比图。旋转以前,X、Y分量中均有较强的横波能量,旋转以后,横波能量主要集中在R分量中, T分量能量很小。不做各向异性分析时,对转换波的偏移成像主要针对R分量。
图7
2.5 转换横波偏移成像
转换波偏移成像不同于纵波偏移成像[18],本次成像基于geovation 软件,除道集外还需有纵波速度、垂直gamma、转换波速度参与计算,其中纵波速度来自于前期的PP处理,垂直gamma与转换波速度分别对应式(1)、式(2):
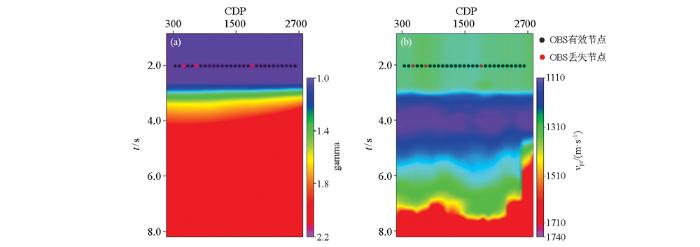
式中:γ0为垂直gamma,tps为转换波旅行时,tp为纵波旅行时,vp、vs分别为纵波速度和横波速度。由式(1)、式(2)可知,垂直gamma与转换波速度均与纵波速度与横波速度相关,已知纵波速度,本文通过时空变的横波速度扫描,获得对应的垂直gamma和转换横波速度,其中时空变的控制点通过纵波镜像偏移成像剖面确定。
图8
图9
3 应用
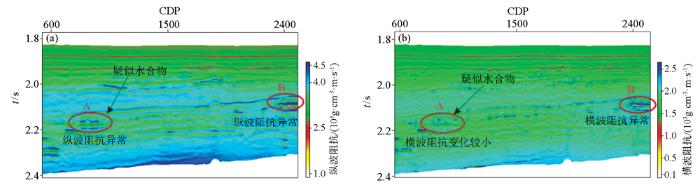
地层含天然气水合物后会引起纵横波速度的增加,与周围地层形成较大的波阻抗差[21]。当BSR下方含有游离气时,纵波阻抗会减小;由于含气对横波速度影响较小,因此,含气对横波阻抗影响较小。在OBS纵波镜像叠加剖面利用统计法提取地震子波,并结合纵波速度对纵波数据进行叠后波阻抗反演,获得如图10a所示的纵波阻抗反演结果,在海底以下350 ms左右有两处低阻抗异常区域A、B,在水合物解释中,低阻抗异常通常对应游离气特征,高阻抗异常对应BSR。同样利用统计法在转换横波阻抗剖面中提取地震子波,结合转换横波速度对叠加剖面进行波阻抗反演,获得如图10b所示的横波波阻抗反演结果。横波阻抗异常与纵波阻抗异常不存在一一对应关系,A区域横波具有与纵波阻抗相同的高阻抗值,但下方低阻抗异常不明显,B区域仍有较明显的低阻抗异常。水合物通常具有高阻抗特征,而通常由于气源的因素,水合物下方会含有游离气,而通过联合分析发现,A区域含游离气的可能性更大。因此,经过联合分析提高了解释的精度。
图10
图10
联合反演结果
a—纵波阻抗;b—横波阻抗
Fig.10
The joint inversion result
a—the sonic wave impedance;b—the shear wave impedance
4 结论和认识
通过对OBS数据进行成像处理、反演解释等工作,获得以下几点认识:
1)OBS采用400 m间距稀疏接收,导致照明范围窄,尤其海底以下深度小于接收间距的范围内,分辨率低,成像连续性差,通过水陆检合并、镜像偏移等方法,成功获得OBS纵波成像结果,成像信噪比高、连续性好;
2)基于纵波速度、利用R分量数据,结合纵波镜像偏移成像结果,分层进行时空变扫描,获得垂直gamma和转换横波速度,基于此进行转换横波偏移,最终成果构造形态与纵波成像一致,可进行联合分析;
3)综合分析纵波阻抗、横波阻抗、纵横波速度比等结果能提高对水合物相关的含游离气特征解释的精度,达到OBS调查的目的;
4)OBS资料具有长偏移距、转换横波等优势,目前虽然已获得成像及反演结果,但资料中仍有很多待挖掘的地方,需后续进一步加强,提高OBS资料的实际利用程度。
参考文献
Seismic imaging with ocean-bottom nodes:new acquisition designs and the atlantis 4C OBN survey
[D].
深地震探测的分辨率分析——以南海北部OBS数据为例
[J].
Lateral resolution analysis of deep crustal sounding:A case study on the data form ocean bottom seismometers in the northern South China Sea
[J].
Crustal structure and fracture zone in the central sea basin of the South China Sea from wide angle seismic experiments using OBS
[J].
DOI:10.1016/j.tecto.2012.03.016
URL
PMID:27065501
[本文引用: 1]

According to new apatite fission track, zircon- and apatite (U-Th)/He data, we constrain the near-surface history of the southeastern Tauern Window and adjacent Austrolapine units. The multi-system thermochronological data demonstrate that age-elevation correlations may lead to false implications about exhumation and cooling in the upper crust. We suggest that isothermal warping in the Penninic units that are in the position of a footwall, is due to uplift, erosion and the buildup of topography. Additionally we propose that exhumation rates in the Penninic units did not increase during the Middle Miocene, thus during the time of lateral extrusion. In contrast, exhumation rates of the Austroalpine hangingwall did increase from the Paleogene to the Neogene and the isotherms in this unit were not warped. The new zircon (U-Th)/He ages as well as zircon fission track ages from the literature document a Middle Miocene exhumation pulse which correlates with a period of enhanced sediment accumulation during that time. However, enhanced sedimentation- and exhumation rates at the Miocene/Pliocene boundary, as observed in the Western- and Central Alps, cannot be observed in the Eastern Alps. This contradicts a climatic trigger for surface uplift, and makes a tectonic trigger and/or deep-seated mechanism more obvious to explain surface uplift in the Eastern Alps. In combination with already published geochronological ages, our new data demonstrate Oligocene to Late Miocene fault activity along the Moll valley fault that constitutes a major shear zone in the Eastern Alps. In this context we suggest a geometrical and temporal relationship of the Katschberg-, Polinik-Moll valley- and Mur-Murz faults that define the extruding wedge in the eastern part of the Eastern Alps. Equal deformation- and fission track cooling ages along the Katschberg-Brenner- and Simplon normal faults demonstrate overall Middle Miocene extension in the whole alpine arc.
Results from the first OBS to OBS time-lapse survey in the Mars Basin
[C]//
琼东南海域水合物OBS资料成像处理关键技术
[J].
Key technid of hydrate OBS imaging processing in Qiongdongnan area
[J].
海底电缆地震中二次定位法的探讨
[J].
Discussion on secondary position in OBC survey
[J].
Attenuation of water-column reverberations using pressure and velocity detectors in a water-bottom cable
[J].
基于Echos处理系统的OBC双检资料处理技术
[J].
OBC dual-sensor data processing on the Echos processing system
[J].
OBC水陆检数据匹配技术
[J].
A method for OBC dual-sensor data matching
[J].
OBC水陆检数据标定因子估算方法
[J].
Scale factor estimation for OBC dual-sensor data
[J].
海底电缆交叉鬼波化双检合并技术改进及应用
[J].
An improvement of the dual-sensor summation technique for corss-ghosting from OBC and its application
[J].
Mirror imaging of OBS data
[J].
Benefits and limitations of imaging multiples:Mirror migration
[J].
Interferometric OBS imaging for wide-angle seismic data
[J].
Wide-area imaging from OBS multiples
[J].
OBS技术在南海北部白云深水区储层含气性识别中的应用
[J].
Gas bearing reservoir identification on OBS data in the Baiyun deep-water area,northern South China Sea
[J].
直角坐标系的欧拉旋转变换及动力学方程
[J].
The rulers rotation and dynamic equation of rectangular coordinate system
[J].
波阻抗反演在南海北部神狐海域天然气水合物勘探中的应用
[J].
Impedance inversion and its application in gas hydrate exploration shenhu area,Northern South China Sea
[J].
基于波阻抗反演的天然气水合物地震检测技术
[J].
The seismic detecting technique on gas hydrate based on wave impedance inversion
[J].