0 引言
1 热释汞应用于天然气水合物勘查的原理
2 区域地质背景
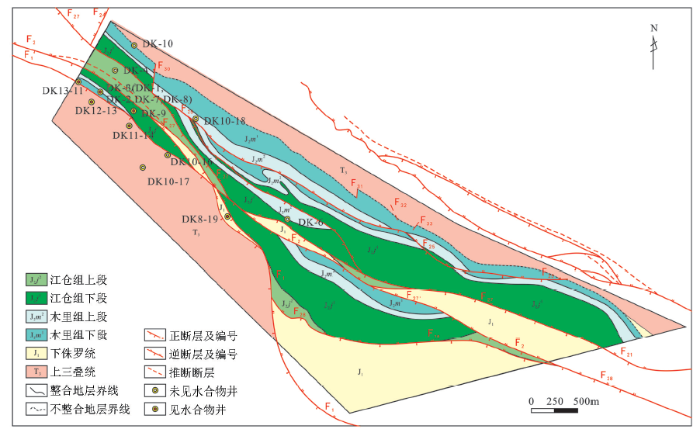
2.1 试验区地质概况
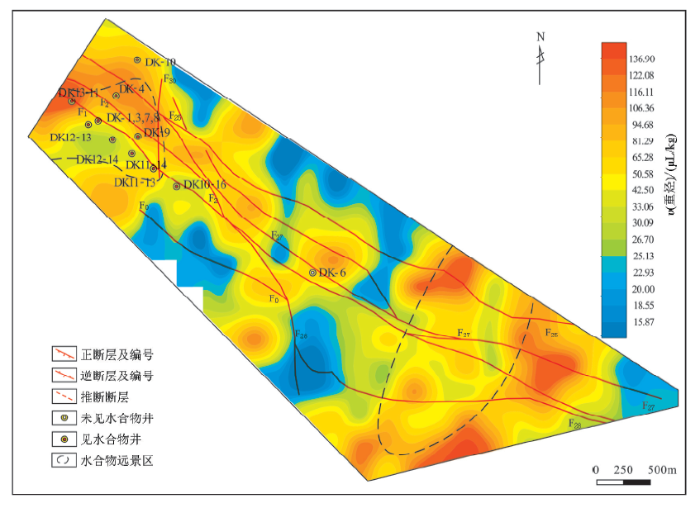
图1
中侏罗统木里组下岩性段为辫状河冲积平原沉积,岩性为中—粗粒碎屑岩,偶夹薄层碳质泥岩或薄层煤;上岩性段为湖泊—沼泽环境沉积相,岩性为深灰色粉砂岩、细砂岩及灰色细—中粒砂岩、粗粒砂岩夹两层主煤层。中侏罗统江仓组下岩性段为三角洲—湖泊环境的灰色细粒砂岩、中粒砂岩和深灰色泥岩、粉砂岩,含煤2~6层;上岩性段为厚层油页岩段,是一套浅湖—半深湖环境的细碎屑泥岩、粉砂岩。上侏罗统是半干旱和干旱气候下形成的一套红色碎屑岩[12]。
2.2 试验区天然气水合物矿藏特征
祁连山聚乎更天然气水合物分布在140~330 m深度区间,厚度将近200 m[20]。深度较极地冻土区浅[27],天然气水合物矿藏的稳定带厚度受冻土厚度分布制约。钻孔烃源岩镜质体反射率Ro值为0.78%~1.1%,最高热解峰峰温Tmax为470 ℃,处于热演化成熟并大量生成油气的阶段[28]。水合物层甲烷含量为54%~76%,乙烷含量为8%~15%,丙烷含量为4%~21%,并有少量的丁烷、戊烷等,CO2含量一般为1%~7%,高的可达15%~17%。水合物光谱曲线与墨西哥海底水合物样品相似,属于Ⅱ型水合物[12]。碳同位素研究表明,祁连山天然气水合物的气源主要在深部,气源岩生成的气体沿断裂运移至浅部,直接或间接被较晚形成的压型断裂封堵,形成浅部气体聚集,经晚更新世以来的冰期作用,形成水合物或仍以游离、吸附气形式存在于地层中[29]。
3 样品采集与测试
选择祁连山聚乎更天然气水合物已知区进行了方法试验,采样季节是为2012年9~10月份。测区面积150 km2,采样密度2个点/km2,样品采集深度40~60 cm,样品用玻璃纸包装,采集土壤样品300件。样品在室内阴干,加工至120~160目。
土壤样品磨研后放入未加热的热解炉中,然后同时启动气泵测量和热解炉250 ℃恒温加热,使样品连续升温至800 ℃,同时用自动记录仪记录下连续升温过程中的热释汞峰高值。
本次研究分析测试工作由中国地质科学院地球物理地球化学勘查研究所中心实验室完成。实验室在检测工作中,除常规的空白监控、标准样品仪器监控等手段外,采取管理样监控和重复密码样监控、异常点复测等方法进行质量保证。各项测试指标的报出率大于90%,相对误差小于20%,监控样合格率大于86.67%,达到规范和设计要求。
4 结果与讨论
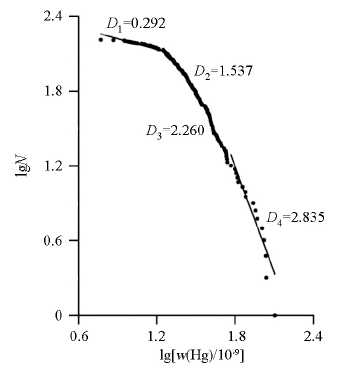
4.1 土壤热释汞含量的分形特征
分形统计模型:
其中:r表示He、Ne和CH4的含量;C为比例常数,C>0;D为分维(或分维数),D>0;N(r)表示土壤热释汞含量大于(等于)r的数目。该分形统计模型能够刻画地球化学异常的整体空间结构特性。对土壤热释汞分形统计模型两边取对数, 转化为一元线性回归方程:
图2为土壤热释汞分形图,利用热释汞含量和频数绘制散点图,用最小二乘法求出回归模型的分维数(D),从图中可以看出:① 土壤热释汞呈现多重分形,分维数D1为0.292,D2为1.537,D3为 2.260,D4为2.835(表1),第一层区间分维数较小,反映了检出限附近的低值区,这是土壤原始热释汞的地球化学分布;② 第二层分维数也较小,含量区间较小,频数较大,反映了土壤热释汞区域的背景值;③ 第三层分维数较大,含量区间增大,频数较小,反映了土壤热释汞区域异常值,这是地气迁移的土壤热释汞地球化学分布;④ 第四层分维数最大,含量区间最大,频数最小,反映了土壤热释汞局部高异常值,这是断裂渗漏的土壤热释汞地球化学分布特征;⑤ 木里地区土壤热释汞的多重分形分布,不但能从不同层次上揭示出不同地质作用土壤热释汞的分布模式,也能够确定元素异常下限值,本次分形确定的异常下限值为39.24×10-9(表1)。
图2
图2
祁连山聚乎更矿区土壤热释汞分形图
Fig.2
Fractal graphs of soil thermal-release mercury in Juhugeng in the Qilian mountain
表1 祁连山土壤热释汞分形特征统计
Table 1
| 分析层次 | 多重分维(Di) | 含量区间/10-9 | 样品数 | 界线点(ri0)/10-9 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.292 | 5.90~19.48 | 44 | r12=19.48 |
| 2 | 1.537 | 19.97~39.24 | 79 | r23=39.24 |
| 3 | 2.260 | 39.82~55.04 | 25 | r34=55.04 |
| 4 | 2.835 | 58.56~127.37 | 16 |
4.2 热释汞与烃类异常分布特征
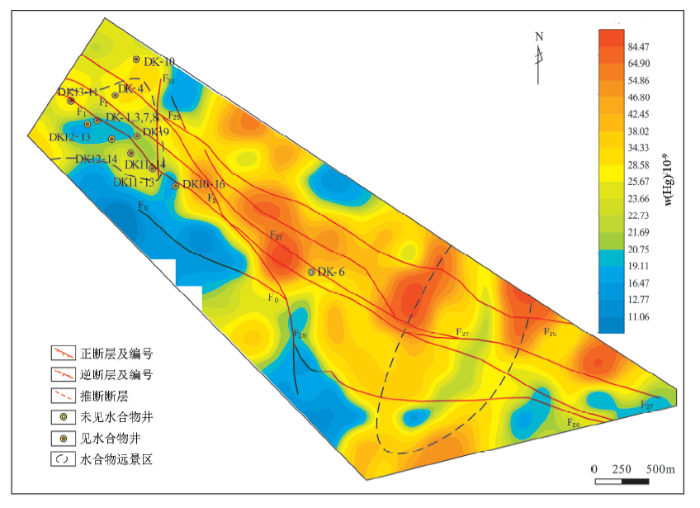
祁连山聚乎更矿区土壤酸解烃数据来源于中国地质科学院地球物理地球化学勘查研究所[35],取样深度40~60 cm,样品由中石化合肥培训测试中心完成,分析C1~C5 5种烃组分浓度。笔者利用酸解烃甲烷和酸解烃重烃数据使用Excel软件进行原始分析,通过分组频率统计及数据分布特征,利用对数间隔划分为15级,运用克里金方法进行插值处理,制作地球化学图,成图软件为地学信息处理研究应用系统(GeolPAS)。图3为土壤热释汞地球化学图,土壤热释汞最小值5.9×10-9,最大值127.37×10-9,平均值32.59×10-9,变异系数为0.66(表2),利用频率与含量双对数法确定异常下限39.24×10-9。在天然气水合物矿藏上方出现低值异常,该异常区冻土厚度大于65 m[36],满足天然气水合物形成的温压条件[5]。水合物勘探井显示DK-4井、DK-10井、DK10-16井、DK10-17井、DK10-18井均为干井,是水合物边界,土壤热释汞在水合物边界区为高值异常,与水合物勘探井结果相吻合。根据地球化学勘查成果(包括本次土壤热释汞调查)推断出的水合物有利区,布置了DK-9井、DK13-11井、DK12-13井和DK11-14井4口井,均发现天然气水合物(图3)。
表2 祁连山土壤地球化学指标含量特征
Table 2
| 指标 | 酸解烃 | 热释汞 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 甲烷 | 重烃 | ||
| 最大值 | 1167.4 | 103.59 | 127.37 |
| 最小值 | 1.3 | 0.05 | 5.9 |
| 平均值 | 25.97 | 2.2 | 32.59 |
| 变异系数 | 4.47 | 4.16 | 0.66 |
注:酸解烃含量单位μl/kg;热释汞含量单位10-9。
图3
图3
祁连山聚乎更矿区土壤热释汞地球化学异常与地质构造
Fig.3
Geochemical anomaly and tectonic map of soil thermal-release mercury in Juhugeng in the Qilian Mountain
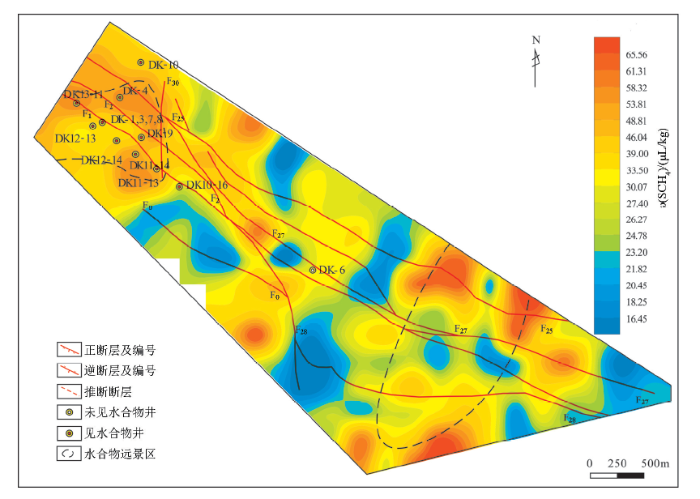
图4和图5分别为土壤酸解烃甲烷、重烃地球化学图,酸解烃甲烷、重烃与土壤热释汞异常分布有异同,主要表现在:① 酸解烃甲烷和重烃相关性很高(R2=0.661 4)[28],体现了同源性,在测区西北部煤田区和天然气水合物矿藏上方均有异常分布,在煤田区异常浓度较高,这是由煤层气引起的(下文有介绍),天然气水合物上方的酸解烃异常是由天然气水合物烃类运移引起的,酸解烃异常可以指示天然气水合物矿藏;② 酸解烃异常在天然气水合物异常区呈现环状异常特点,土壤热释汞表现为环状异常特征,异常重合度很高,均有异常面积大,强度高的特点;③ 测区东南部土壤酸解烃甲烷、重烃有异常分布,对应分布土壤热释汞环状异常,可以作为天然气水合物优先勘探区,土壤热释汞可以辅助烃类指标提高勘查率;④ 测区中部热释汞异常发育,这是由于该地区断层发育[12],热释汞的地气迁移比较活跃引起的,中部地区对应的酸解烃甲烷异常强度较低,形成天然气水合物的可能性较小。
图4
图4
祁连山聚乎更矿区土壤酸解烃甲烷地球化学异常
Fig.4
Geochemical anomaly map of acid extracted methane in Juhugeng in the Qilian Mountain
图5
图5
祁连山聚乎更矿区土壤酸解烃重烃地球化学异常
Fig.5
Geochemical anomaly map of acid extracted heavy hydrocarbons in Juhugeng in the Qilian Mountain
4.3 地球化学异常烃类气体成因与来源
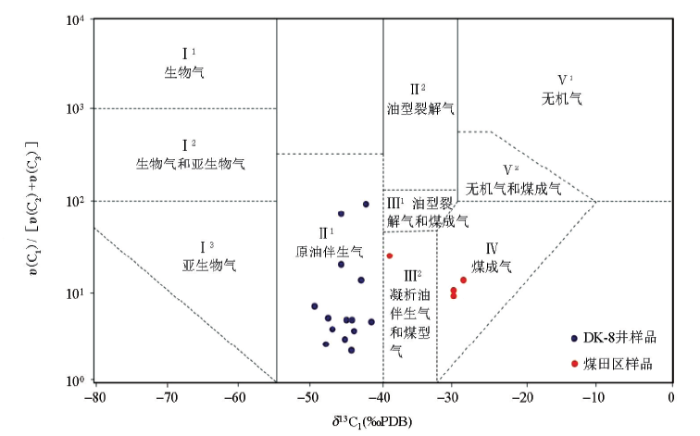
甲烷碳同位素结果显示,DK-8井甲烷稳定碳同位素值为-42.99‰~33.53‰,煤田区甲烷稳定碳同位素为-28.97‰~18.53‰,天然气水合物甲烷主要来源为原油伴生气,测区西北部的煤田区甲烷主要来源于煤成气(图6)。
图6
图6
祁连山冻土区钻井岩心气成因的气体组成和同位素综合判别
Fig.6
Interpretive of components and carbon isotopes of the gas desorbed from the drilled cores in the Qilian Mountain permafrost
4.4 热释汞地气迁移机理
综合国内外天然气水合物测井曲线、热释汞异常和天然气水合物矿藏上方的冻土层分布
冻土区天然气水合物矿藏上方的物理化学环境从下而上分为4个地球化学带:
1) 天然气水合物矿层:指天然气水合物矿体存在的层位。地球化学作用是以甲烷为主的烃类气体固化成藏,有机物吸收的汞释放。
2) 天然气水合物矿藏稳定带:是指冻土层下界至天然气水合物稳定带下界的地质环境,这也是地球化学分异带,从深部油气藏迁移上来的烃类物质经过地球化学分异作用,部分烃类形成天然气水合物。汞分子半径小,地球化学性质活泼,很容易穿过上覆岩石和冻土层,在水合物矿藏上方形成地球化学异常。
3) 冻土带:地表季节性融冻层至冻土层底界,这是长期冻结层,常规的地球化学反应受到抑制,但地气迁移活跃,汞元素和其它微量元素随地气迁移到近地表。
4) 季节性融化带:主要是近地表的季节性融冻层,土壤有机碳和土壤矿物(石英、长石、伊利石、高岭土等)吸收汞。
综上所述,天然气水合物热释汞的地气迁移机理比较复杂,包括天然气水合物自形成以来吸收的汞含量、烃类穿过永久冻土层垂向迁移、汞元素的渗透迁移、富集。天然气水合物矿藏与外围环境相比,热释汞含量有一定差异,配合其他的物化探资料,可以圈定、预测天然气水合物有利地区。
5 结论
1) 在祁连山聚乎更水合物矿藏上方发现了中等强度的热释汞异常,在未知区也发现了热释汞水合物靶区。热释汞可以作为一种地球化学勘查的辅助手段与甲烷异常、冻土和控矿断裂进行综合解释,可以提高水合物探测的成功率。
2) 从本次研究结果来看,热释汞异常与天然气水合物吻合关系很好,与烃类指标有较好的一致性,加之热释汞是烃类运移、渗漏长期综合作用的结果,信息比较稳定,不易受地表因素的干扰。热释汞是一种快捷、高效、经济的勘查手段之一,可以在冻土区天然气水合物勘查中推广。
3) 天然气水合物热释汞的地气迁移机理比较复杂,多种因素使天然辐射场发生了变化。近地表土壤样品热释汞强度可以明显地显示这种变化,辅助其它地球化学指标,能有效圈定、预测天然气水合物有利地区。
致谢:衷心感谢中国地质调查局青藏高原天然气水合物木里野外科学观测研究站给予工作上大力支持,祝有海研究员、庞守吉博士、张帅博士、吉林大学李冰博士等提供野外帮助,分析测试数据由中石化李广之研究员完成,均深表感谢。
参考文献
Permafrost-associated gas hydrate accumulations
[J].
DOI:10.1111/j.1749-6632.1994.tb38839.x
URL
[本文引用: 1]

First page of article
Regional gas hydrate occurrences,permafrost conditions,and Cenozoic geology,Mackenzie Delta area
[J].
Scientific results from the mallik 2002 gas hydrate production research well program,mackenzie delta,northwest territories,Canada
[J].
青藏高原天然气水合物潜在分布区预测
[J].
DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2011.12.016
URL
[本文引用: 2]

青藏高原冻土面积约150×104km2,是中国最大的冻土区,具备较好的天然气水合物找矿前景。运用热力学预测方法,根据青藏高原的年平均地表地温、冻土层厚度、冻土层内地温梯度(2.22℃/100m)、冻土层下地温梯度(4.18℃/100m)等参数,分纯甲烷组分、纯二氧化碳组分和各种实测气体组分,分别计算出天然气水合物的稳定带及其厚度,并编制出相应的分布预测图。结果显示,青藏高原大部分冻土区基本具备天然气水合物的形成条件,即使最难形成的纯甲烷水合物也能在部分冻土区内形成。若单纯从温压条件考虑,成矿条件最有利的地区是喀喇昆仑地区,其次为西昆仑地区,再次为羌塘盆地,最后才是祁连山等地区。综合考虑气源条件、运移条件、储层条件等,羌塘盆地是青藏高原天然气水合物形成条件和找矿前景最好的地区,其次是祁连山地区、风火山—乌丽地区,再次是昆仑山垭口盆地、唐古拉山—土门地区、喀喇昆仑地区、西昆仑—可可西里盆地等。
Potential distribution of gas hydrate in the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau
[J].
青海祁连山冻土区发现天然气水合物
[J].
DOI:10.3321/j.issn:0001-5717.2009.11.018
URL
Magsci
[本文引用: 1]

祁连山冻土区位于青藏高原北缘,多年冻土面积约10×10????4??km????2??,具有良好的天然气水合物形成条件和找矿前景。2008~2009年间中国地质调查局在青海省天峻县木里煤田聚乎更矿区施工“祁连山冻土区天然气水合物科学钻探工程”,迄今共完成钻探试验井4口,总进尺2059.13m,分别在DK 1、DK 2和DK 3钻井中钻获天然气水合物实物样品,取得了找矿工作的重大突破。天然气水合物产于冻土层之下,埋深133~396m。水合物呈白色、乳白色晶体,点火能燃烧,红外热像仪测温后呈明显的低温异常,放进水里强烈冒泡,水合物分解后能不断冒出气泡和水滴,并残留下特征的蜂窝状构造。激光拉曼光谱仪检测呈现特征的水合物光谱曲线,测井曲线也具有较明显的高电阻率和高波速标志。祁连山天然气水合物具有冻土层薄、埋深浅、气体组分复杂、以煤层气成因为主等明显特征,是一种新类型水合物。这是我国冻土区首次钻获的天然气水合物实物样品,也是全球首次在中低纬度高山冻土区发现天然气水合物实物样品,具有重要的科学意义和经济意义。
Gas hydrates in the Qilian mountain permafrost,Qinghai,northwest China
[J].
Gas hydrate occurrences in the Qilian Mountain permafrost,Qinghai Province, China
[J].
DOI:10.1016/j.coldregions.2011.01.008
URL
[本文引用: 1]

78 It was the first to discover gas hydrate in the Qilian Mountain permafrost of continental China in 2008 and 2009. 78 Gas hydrate and associated anomalies occur mainly in fractured mudstone, oily shale, siltstone, and fine-grained sandstone in a zone between 133 and 396 mbs. 78 Gas hydrate is primarily composed of CH 4, with secondary components of C 2H 6, C 3H 8 and CO 2, indicating a sII structure. 78 Gas from gas hydrate are mainly thermogenic with a biogenic fraction.
High-resolution seismic imaging over thick permafrost at the 2002 Mallik drill site
[J].
Acoustic impedance inversion and seismic reflection continuity analysis for delineating gas hydrate resources near the Mallik research sites,Mackenzie Delta,Northwest Territories,Canada
[J].
Detection and evaluation of the in-situ natural gas hydrates in the north Slope Regn,Alaska
[J].
Geophysical characteristics of gas hydrate in the Muli area, Qinghai province
[J].
DOI:10.1016/j.jngse.2016.12.001
URL
[本文引用: 1]

The Muli area is the only region where gas hydrates have been found in the mid-latitude permafrost regions of the world. The use of geophysical method and certain geophysical parameters have a strong predominance in identifying gas hydrates and optimizing the effective gas hydrate detection methods in hard rock permafrost areas. Since 2009, a series of tests has been performed in the Muli area, including seismic reflection and electromagnetic methods, and integrated geophysical well logging. The results show the presence of three types of gas hydrate reservoir, namely sandstone pore, mudstone fracture, and shale fracture types, with each showing a different well logging response. The gas hydrate reservoirs in the Muli area are characterized by high frequency and weak amplitude on the two-dimensional seismic profiles, and high horizontal resistivity on the electrical sections. The geophysical characteristics are complex, particularly as a result of the specific environments of gas hydrate reservoirs. These characteristics can be used to estimate the type and distribution of the gas hydrate reservoir, and to improve gas recovery rates by directing preliminary exploration.
祁连山冻土区天然气水合物岩性和分布特征
[J].
DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2011.12.005
URL
[本文引用: 4]

2008~2009年实施的"祁连山冻土区天然气水合物科学钻探工程",已完成DK-1、DK-2、DK-3和DK-4孔的钻探任务。施工期间多次钻获天然气水合物实物样品,证实祁连山冻土区存在天然气水合物。祁连山冻土区天然气水合物主要以裂隙型和孔隙型2种状态产出。基于天然气水合物存在的10个方面的特征,认为天然气水合物赋存层位主要为中侏罗统江仓组,产于冻土层之下,主要储集于133.0~396.0m区间,储集层岩性多以粉砂岩、油页岩、泥岩和细砂岩为主,含少量中砂岩。钻孔中天然气水合物纵向分布不具有连续性,钻孔间横向分布规律不明显。岩石质量指标(RQD)统计结果显示,RQD低值区与天然气水合物储集层段具有较好的一致性,表明裂缝系统对于该区天然气水合物的分布具有重要的控制作用。
Gas hydrate in the Qilian Mountain permafrost and its distribution characteristics
[J].
Geochemical characteristics of the shallow soil above the Muli gas hydrate reservoir in the permafrost region of the Qilian Mountains,China
[J].
DOI:10.1016/j.gexplo.2013.10.006
URL
[本文引用: 1]

61The study area is located on the Muli gas hydrate field in the Qilian Mountains.61Geochemical exploration techniques performed well in the delineation of hydrates.61Acidolysis hydrocarbon, headspace and carbon isotope were the major indicators.61The proposed accumulation model was also studied for the gas hydrate reservoir.
青海省天峻县木里地区天然气水合物发现区浅表地球化学特征
[J].
DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2011.12.011
URL
[本文引用: 1]

在青海木里天然气水合物发现区分别采集50件浅表土壤样品和顶空 气样品,采用顶空间轻烃法、酸解烃法和蚀变碳酸盐法研究其浅表地球化学特征.结果表明,顶空气中可检测出C1-C3,土壤中检测出C1-C5,酸解烃各指 标之间具有显著的相关性,碳酸盐指标与酸解烃也呈显著的正相关.地表烃类气体来源为原油伴生气、凝析油伴生气和煤型气,与水合物同源,显示出深部热解成因 气的特征.
Near-surface soil geochemistry of Muli natural gas hydrate area,Tianjun County,Qinghai Province
[J].
中纬度带天然气水合物地球化学勘查技术
[J].
DOI:10.13278/j.cnki.jjuese.201404101
URL
[本文引用: 2]

The first discovery of gas hydrate reservoir in middle-latitudes zone was made in the Qilian Mountain permafrost zone. To evaluate the geochemical exploration method for gas hydrate in middle-latitudes zone, Muli area was chosen as the test area. Soil headspace gas, acid extracted hydrocarbon, carbon isotope of methane and carbonate were tested. The results reveal that geochemical anomalies were consistent with the gas hydrate reservoir underneath. The carbon isotope of methane and hydrocarbon composition analysis of the surface geochemical anomaly zone indicated a thermo-pyrogenation origin, suggesting the gas source of the potential gas hydrate reservoir in this area may contribute by oil gas and coal-formed gas. The origin model was also studied for the gas hydrate reservoir. An integrated exploration project which targets at gas hydrate, oil and coal bed methane altogether was recommended as the next step in Muli area.
Geochemical exploration technology of natural gas hydrate in middle-latitudes permafrost Zone
[J].
油气地球化学场中的吸附相态汞特征及其应用价值
[J].系统地总结出油气地球化学场中的吸附相汞特征,并从地球化学理论角度探讨其成因机理。同时,结合典型油气藏实例,指明这一地球化学规律在石油与天然气勘查中的应用价值。
The features of absorption mercury and their application in oil-gas Geochemical field
[J].
烃、汞等气体组分垂向运移的主要控制因素
[J].
DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1000-3657.2001.08.005
URL
[本文引用: 1]

本文从断层与裂隙、盖层的封堵性、异常源的浓度差与压力差、各组分的地球化学性状与行为四大方面讨论了其对油气藏中烃类、汞等气体组分垂向运移的控制作用,并进一步说明了其是地表各类油气化探异常分布规律、形态和异常模式构成的主要因素。
Main controlling factors for vertical migration of hydrocarbon components such as hydrocarbons and mercury
[J].
利用土壤吸附态汞寻找油气田的有效实例
[J].汞具有化学性稳定、难氧化、挥发强的地球化学特性。在百色盆地花茶油田、雷公油田和黄河三角州的油气勘查中,应用土壤吸附相态汞新方法技术,在找油气的实践中,证明该方法具有独特的指示效果,显示勘查成本低、见效快的优点
An effective example of using oil-adsorbed mercury to find oil and gas fields
[J].
Study on the nature on the gas source for permafrost associated gas hydrate in Sanlutian of Muli,Qinghai
[J].
汞元素的石油地质意义
[J].<p>油气中都含有汞元素组分,汞的物理化学性质决定其可以从油气藏中向上垂向运移,根据采样介质类型及样品预处理的手段不同,地表中汞的分析方法可分为壤气、热释汞及土壤总汞分析方法。壤气汞、热释汞及土壤总汞指标都有着很好的示油气意义,同时也有着示断裂带的地质意义。</p>
Geological significance of mercury element for petroleum exploration
[J].
Local and regional surface geochemical exploration for oil and gas
[J].
DOI:10.1016/0375-6742(92)90022-Z
URL
[本文引用: 1]

The well-accepted annular (halo) and apical surface geochemical patterns can not always be found above oil and gas reservoirs. In many cases, patchy and irregular patterns are met, due to complex pathways through which materials from oil and gas reservoirs migrate to the surface. This problem is more keenly felt in local surface geochemical exploration aimed at defining the location and extent of underlying oil and gas. A multi-parameter correlation technique is used to improve such situations. This problem is not so serious in regional surface geochemical exploration for oil and gas, because the aim of regional surveys is to evaluate the regional oil and gas potential, delineate the most promising area and reduce the target for more expensive seismic survey. Some examples are given for illustration. Concerning the future of surface geochemical exploration for oil and gas, development of regional methods covering thousands, tens of thousands or more km 2 of ground in a basin or covering the whole basin should be given the highest priority.
油气藏上方汞异常成因机理浅析
[J].
DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1001-5663.2000.06.012
URL
[本文引用: 1]

油气藏形成过程中的物理、化学变化使沉积物中富集的汞与有机物具有相同的迁移富集过程 ,因而地表汞异常对油气藏有指示作用
Analysis on Hg anomaly froming mechanism above oil and gas reservoir
[J].
陆域天然气水合物地球化学勘查技术试验研究
[J].
DOI:10.11720/j.issn.1000-8918.2013.6.17
URL
Magsci
[本文引用: 1]

<p>选择青海省木里地区天然气水合物已知区作为试验区,探索和研究了传统油气地球化学方法(酸解烃、顶空气、ΔC)对陆域天然气水合物勘查的适用性和有效性。试验结果表明,天然气水合物已知区浅表层土壤酸解烃、顶空气、ΔC等地球化学指标具有顶部异常特征,各指标按累积频率圈定了3处异常,异常范围基本吻合且与地下天然气水合物分布具有良好的相关性,初步提出了“酸解烃+顶空气+ΔC”异常是地下天然气水合物赋存的重要标志。</p>
Experimental research on geochemical methods for prospecting gas hydrates in permafrost area
[J].
南祁连盆地石炭—侏罗纪地层区划及石油地质特征
[J].通过对南祁连盆地石炭─保罗系地质剖面的研究,依据古构造格架、基底特征、构造变形、岩浆活动、沉积建造特征、古生物群特征以及地层发育程度和接触关系等,把该盆地石炭─株罗系划分为3个地居区,并在地层区划的基础上讨论了南祁连盆地石炭一株罗纪原盆地环境格局及石油地质特征.
Carboniffrous-Jurassic stratigraphic provinces of the southern Qilian basin and their petro-geological features
[J].
青海省天峻县木里煤田聚乎更矿区构造轮廓和地层格架成果报告[R]
Report on the structural contour and stratigraphic framework of the Juhugeng mining area in Muli coalfield, Tianjun County, Qinghai Province[R]. No
Gas hydrate stability zone migration occurred in the Qilian mountain permafrost,Qinghai,Northwest China: Evidences from pyrite morphology and pyrite sulfur isotope
[J].DOI:10.1016/j.coldregions.2013.10.006 URL [本文引用: 1]
南祁连盆地木里冻土区天然气水合物烃源岩特征及评价
[J].中国地质调查局2008年在南祁连盆地木里冻土区采集到了中国陆域第一例天然气水合物实物样品,对于天然气水合物的气体来源存在不同的认识.利用新完钻3口井样品的化验分析结果,分析了中侏罗统和上三叠统烃源岩有机地球化学特征.结果表明,中侏罗统江仓组、木里组煤系地层烃源岩有机质丰度较高,TOC(总有机碳含量)大于1%的样品占78.9%;氯仿沥青“A”含量大于0.1%的占总数的72.2%;有机质类型以Ⅱ2、Ⅱ1型为主;镜质体反射率Ro多介于0.7%~1.2%之间;71个样品生烃潜量平均值为8.8mg/g,总体处于生烃高峰期的生油阶段或凝析油阶段,属于好、很好烃源岩,为天然气水合物主力生烃层系.上三叠统尕勒得寺组亦为煤系地层烃源岩,TOC含量大于1%的样品占76.9%;氯仿沥青“A”含量小于0.05%;有机质类型以Ⅲ、Ⅱ1型为主;镜质体反射率Ro介于1.1%~1.77%之间;总体处于生湿气或干气阶段,但由于构造抬升影响其生烃潜量,平均值仅为0.35mg/g,当前整体生烃能力较差,为非烃源岩或较差烃源岩,对天然气水合物成藏贡献不大.
Characterization and evaluation on the source rock of gas hydrate in Muli permafrost area, Nanqilian Basin
[J].
青藏高原湿地冻土区活动层甲烷排放特征
[J].
DOI:10.11720/wtyht.2017.6.06
URL
[本文引用: 1]

青藏高原作为地球陆地碳循环系统的重要组成部分,一直是科学家和环保工作者关注的热点,天然气水合物的发现是否会引发环境和地质灾害再次引起科学家甚至政府部门的重视。本文选用甲烷通量、近地表大气甲烷浓度、土壤甲烷浓度和甲烷稳定碳同位素为监测指标,以祁连山天然气水合物试采区为研究区,开展甲烷排放监测。结果表明:(1)祁连山高寒草原、高寒草甸区甲烷排放具有季节性变化和区域分布特点,最大排放值为19.2 mg/m~2·h,最大吸收值为-108 mg/m~2·h,表现出巨大的碳汇潜力,对青藏高原碳循环具有重要意义;(2)甲烷碳同位素显示冻土区活动层大量存在微生物,10~30 cm甲烷主要微生物成因,微生物活跃期在夏季,冬季则减弱,微生物的代谢影响着甲烷的氧化和产生,嗜甲烷菌的存在对甲烷的排放起很大的控制作用;(3)试采前后近地表大气甲烷含量没有出现"爆炸式"增长,这与研究区天然气水合物的赋存状态和储量及试采方式有关;(4)甲烷排放受多种因素的影响,应加强对土壤温度、土壤湿度和pH值等因素的进一步研究。
Methane emission of active layer in Qinghai-Tibet wetland permafrost area
[J].
Fractal, chaos and ANN in mineral exploration
[M].
The separation of geochemical anomalies from background by fractal methods
[J].
DOI:10.1016/0375-6742(94)90013-2
URL

Lithogeochemical data (major oxides and trace elements) from 1233 surface samples in the Mitchell-Sulphurets precious-metal district (鈮120 km2 in area), British Columbia, were analyzed using fractal and multifractal models. Log-log plots for element concentration-area and perimeter-area relations were employed to separate geochemically anomalous areas from background. The values used for perimeters and areas are the lengths and enclosed areas of geochemical isopleths obtained by interpolation.Elements and oxides, including Au, Cu, As, Ag, K2O and SiO2 within alteration zones associated with copper and gold porphyry system(s) in the district, show power-law type element concentration-area and perimeter-area relations, which can be fitted as straight lines on the log-log graphs. Separate relations inside and outside the potassic, sulphidic and silicic alteration areas can be used to delineate the anomalies. The slopes on the graphs show that Au is much more irregularly distributed than Cu and As in the porphyry systems.
Multifractality and spatial statistics
[J].
DOI:10.1016/s0098-3004(99)00060-6
URL
[本文引用: 1]

The concepts of fractals and multifractals have been increasingly applied in various fields of science for describing complexity and self-similarity in nature. Fractals and multifractals are a natural consequence of self-similarity resulting from scale-independent processes. In the present paper, a theoretical investigation is developed to illustrate: (1) the characteristics of multifractality as measured by the parameter t''(q); (2) relationships between multifractality and spatial statistics including semivariogram and autocorrelation in geostatistics, indexes used in lacunarity analysis and correlation coefficients. It can be shown that these statistics primarily are related to multifractality as determined by t''(1). This is an important result because not only does it provide the link between multifractals and spatial statistics but it also shows that statistics based on second-order moments are restrictive in that they only characterize a multifractal measure around the mean value. In applications where extreme values need to be taken into account, the entire multifractal spectrum should be used rather than local properties of the spectrum around the mean only; alternatively, statistics defined on the basis of higher-order moments can be employed for analysis of extreme values. These theoretical results are illustrated by means of application to Landsat TM imagery (bands 1 to 7) from the Mitchell-Sulphurets mineral district, northwestern British Columbia, Canada
多重分形与地质统计学方法用于勘查地球化学异常空间结构和奇异性分析
[J].
DOI:10.3321/j.issn:1000-2383.2001.02.010
URL
[本文引用: 1]

勘查地球化学和地球物理场的局部空间结构变化性应包括空间自相关性以及奇异性.前者可通过地质统计学中常用的变异函数来实现;后者可用多重分形模型进行刻划.具有自相似性或统计自相似性的多重分形分布(multifractaldistributions)的奇异性(α)可以反映地球化学元素在岩石等介质中的局部富集和贫化规律.而多重分形插值和估计方法可以同时度量以上两种局部结构性质(空间自相关性以及奇异性),因而,它不仅能够进行空间数据插值,同时还能保持和增强数据的局部结构信息,这对于地球化学和地球物理异常分析和识别是有益的.应用该方法处理加拿大NovaScotia省西南部湖泊沉积物地球化学砷等元素数据表明,地球化学数据的局部奇异性在该区能够反映局部金和钨-锡-铀矿化蚀变带或岩相变化以及构造交汇等局部成矿有利部位.
Multifactal and geostatistic methods for characterizing local structure and singularity properties of exploration geochemical anomalies
[J].
Fractal Chaos and Mineral Prediction
[M].
中纬度冻土区天然气水合物物化探技术成果报告[R]
Report on the results of natural gas hydrate geochemical exploration technology in mid-latitude frozen soil area[R].Institute of Geophysical& Geochemical Exploration,
陆域天然气水合物勘查技术研究与集成成果报告[R]
Report on research and integration results of land gas hydrate exploration technology[R].Institute of Geophysical& Geochemical Exploration,
Permafrost-associated natural gas hydrate occurrences on the Alaska North Slope
[J].
DOI:10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2009.12.001
URL
[本文引用: 1]

In the 1960s Russian scientists made what was then a bold assertion that gas hydrates should occur in abundance in nature. Since this early start, the scientific foundation has been built for the realization that gas hydrates are a global phenomenon, occurring in permafrost regions of the arctic and in deep water portions of most continental margins worldwide. In 1995, the U.S. Geological Survey made the first systematic assessment of the in-place natural gas hydrate resources of the United States. That study suggested that the amount of gas in the gas hydrate accumulations of northern Alaska probably exceeds the volume of known conventional gas resources on the North Slope. Researchers have long speculated that gas hydrates could eventually become a producible energy resource, yet technical and economic hurdles have historically made gas hydrate development a distant goal. This view began to change in recent years with the realization that this unconventional resource could be developed with existing conventional oil and gas production technology. One of the most significant developments was the completion of the BPXA-DOE-USGS Mount Elbert Gas Hydrate Stratigraphic Test Well on the Alaska North Slope, which along with the Mallik project in Canada, have for the first time allowed the rational assessment of gas hydrate production technology and concepts. Almost 40years of gas hydrate research in northern Alaska has confirmed the occurrence of at least two large gas hydrate accumulations on the North Slope. We have also seen in Alaska the first ever assessment of how much gas could be technically recovered from gas hydrates. However, significant technical concerns need to be further resolved in order to assess the ultimate impact of gas hydrate energy resource development in northern Alaska. [All rights reserved Elsevier].