0 引言
三维矿体模型在矿产勘探、储量评估、开采设计、生产过程管理等矿山开采过程中具有重要作用[1]。三维矿体表面建模是三维矿体建模的关键内容,其主要目的是确定矿体的三维边界,准确地描述矿体的三维空间位置及几何形态。目前可用于建立三维矿体表面模型的方法主要有基于剖面的轮廓线建模方法[1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8]、钻孔直接表面建模法[9]、断面构模法和多层DEM建模法[1]等。基于剖面的轮廓线构模法的基本思路是将相邻剖面上地质意义相同的矿体轮廓线依次连接形成不规则三角网(triangular irregular networks, TIN),以此来模拟矿体的三维边界。由于该方法能处理复杂矿体的空间形态,目前已成为三维矿体表面建模的主流方法,同时也是三维地质界面生成的重要方法[10,11]。
利用轮廓线进行矿体表面建模与医学上利用CT或MRI断层切片构造三维人体表面有着一定的相似性,但是矿体表面建模却更加复杂,矿体轮廓线形态更加复杂且相似度低,且由于经济因素矿体轮廓线数据稀疏,矿体整体形态就更难以把握。传统的轮廓线连接算法主要解决对应(correspondence)、构网(tiling)、分支(branching)和光滑(surface-fitting)4个方面的问题[12,13]。对应问题指相邻剖面之间轮廓线的匹配问题;构网问题指轮廓线之间的构网问题;分支问题是指同一对象在不同剖面上组成部分的个数不同问题;光滑问题指如何来构建更加光滑的曲面,以解决初始生成的由三角面片表示的对象,往往存在大量的棱角而与实际对象不符的问题。
目前,基于轮廓线的三维表面建模算法研究已经取得一定的成果,包括最大体积法[14]、最小表面积法[15]、最短对角线法[16]、同步前进[17,18]、切开—缝合法[3]、周长投影方法[4]、Morphing法[19]等。这些方法主要解决了轮廓线构面的合理性问题,即当相邻轮廓线形态差异较大、点数相差较多,轮廓线构面容易出现三角形交叉、矿体扭曲错位连接等问题,影响建模的准确性。由于轮廓线建模法基本可以适应各种复杂矿体的三维形态表达,并且可以通过修改轮廓线、加密轮廓线、添加示踪线(人工指定控制线)等手段更精确地表达矿体。这些方法将人机交互融入到建模过程中,在客观上基本保证了建模的精度以及对各类复杂情况(如矿体扭曲、矿体分支)的适应。此外,何金国等[20]提出一种新的轮廓线分段匹配算法,然后利用空间多边形三角剖分,解决分支问题;该方法对于密度较大的轮廓线,如医学CT,利用效果较好,但对于复杂矿体则不适应。杨洋等[21]提出一种带有质量控制的轮廓线表面建模方法,但是该方法无法解决差异较大的轮廓线面网的质量,而且算法主要采用细分的方法,数据产生的冗余度较高。总体上,这些方法的轮廓线拼接通过人工选择两两轮廓线重建表面模型,但是难以从整体上把握矿体的整体趋势,三维矿体的形态也比较粗糙;在处理分支问题时,主要通过人工交互添加分支点,非常繁琐,耗费了大量人力和时间,并且难以保证结果;矿体表面模型出现大量的退化三角形,甚至矿体表面三角形相交或者重叠,模型的几何质量比较差,模型精度低,影响后续的可视化和模型计算。
笔者对于一组单轮廓线自动添加矿体趋势线,并且还可以进行人工编辑修改,然后利用中间加密轮廓线的方法实现对矿体形态的控制。通过投影计算封闭轮廓线之间的最短距离自动添加分支点,利用平面的带洞限定三角剖分实现分支的自动构建,大大节省了人力资源,同时保证了分支矿体的准确性。针对初始构建的三维矿体表面模型几何质量差,引入了质量控制,实现了表面模型的重构,保证了模型质量和后续的计算。
1 矿体趋势
多个矿体轮廓线可以反映出矿体的走向趋势,因此笔者引入矿体趋势线,即曲线拟合和矿体特征点匹配,利用插值方法加密轮廓线,以达到对矿体趋势的拟合。具体步骤:
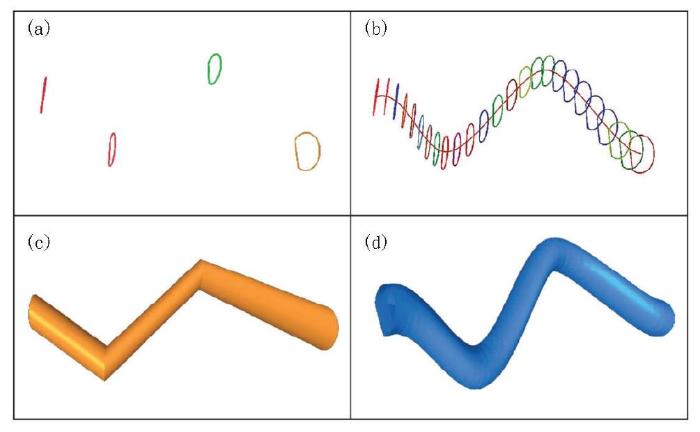
1) 人工选择能够反映矿体趋势的一组轮廓线(图1a)。
2) 为了方便表述假设每条轮廓线上的所有点均在一个平面上,并且这些平面相互平行。计算出选定的轮廓线形的重心,利用插值算法,将得到的重心点连接起来,形成光滑的轨迹线;该轨迹线还可以通过人工编辑进行修改(图1b)。
3) 对需要加密的区域进行加密处理,生成新的轮廓线, 新生成的轮廓线重心要位于轨迹线相应的位置上,同时还可以对新生成的剖面进行三维空间的可视化编辑,包括平移、缩放、旋转等各种几何变换,使之满足对矿体形态的控制需求(图1b)。
图1
图1
加入趋势线的轮廓线表面生成方法
a—原始4条剖面轮廓线,所在剖面近似平行;b—自动添加趋势线和中间过渡轮廓线;c—未添加趋势线的表面模型;d—添加曲线线后的表面模型
Fig.1
The method of surface generation form contours with the trend line
a— the original four profiles are approximately parallel; b— automatically adding trend lines and intermediate transition contours; c— surface model without trend lines; d— surface model with trend lines
2 分支问题
闭曲线簇{C(
1) 令计算闭曲线簇{C(
2) 将曲线簇{C(
3) 计算Hausdorff距离,即在两个轮廓线之间最短距离处添加分支点,使得每个分支点均在闭曲线簇{C(
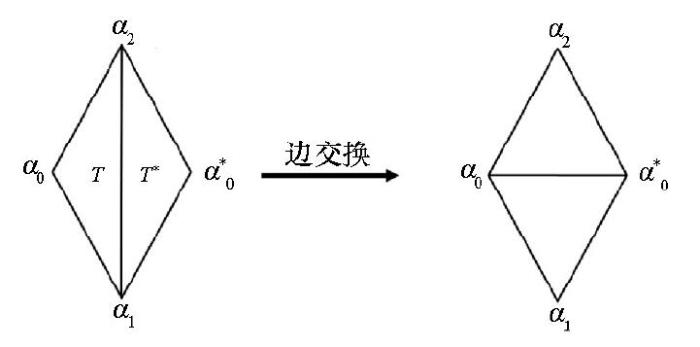
4) 利用限定三角剖分算法实现带洞的限定三角剖分[19],然后通过边交换,实现每条内边(即非边界的边)的两个端点不属于同一条轮廓线。
5) 将Cα上替换掉步骤(4)中产生的三角网的外边界上相应的点,并将其移到A、B平面中间且距离A面的一定距离处(图2c);该距离可以人为设置。
6) 针对闭曲线簇{C(
7) 利用同步前进方法实现闭曲线Cα与闭曲线Cβ的连接,如图2d。
8) 合并所产生的三部分三角网便形成分支矿体表面模型(图2d)。如有必要可以对分支矿体表面进行质量控制。
图2
图2
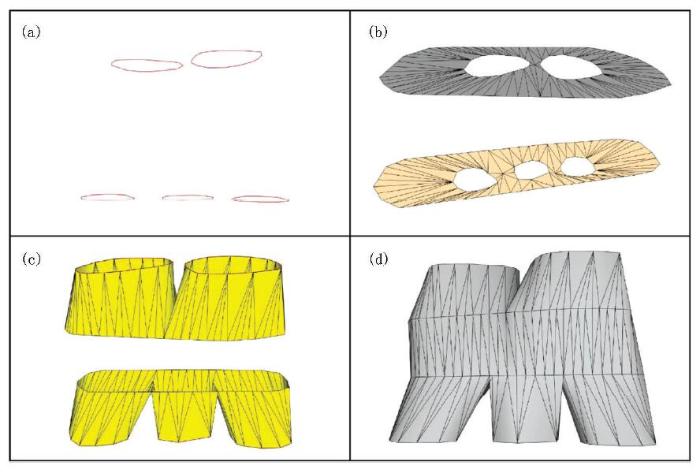
分支矿体表面模型的建立过程
a—原始数据为两簇闭曲线集合,每组曲线近似位于一个平面上;b—每簇曲线在所在平面上,添加分支节点和外扩的外包并实现带洞三角剖分和边交换;c—将外扩的外包回复到三维状态;d—利用同步前进方法实现两闭曲线的连接,实现分支模型的建立
Fig.2
The establishment process of the surface model of the branch orebody
a— two clusters of closed curves are the original data, each set of curves approximately located in a plane; b— on the plane of each cluster of curves, add branch points and enlarged convex hull, achieve triangulation with holes and exchange edges; c— the outspread outsourcing back to the three-dimensional state; d— using synchronous forward method to achieve the connection of the two closed curves, the branch model is established
3 矿体表面模型重构
图3
图3
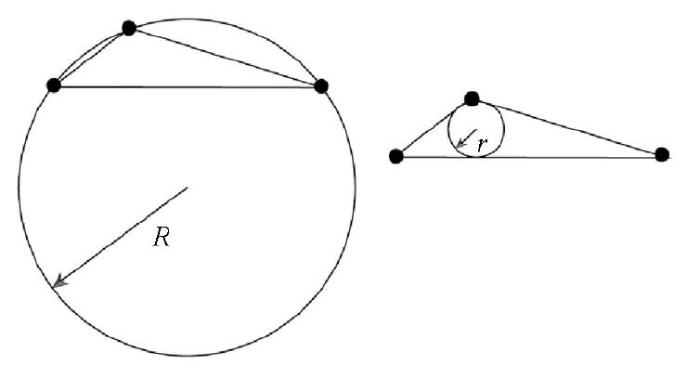
三角形的外接圆与内接圆示意
Fig.3
Schematic diagram of the circumcircle and inscribed circle of the triangle
首先引入三角面网质量的评价指标:元素大小和美化程度,然后利用面网优化技术,控制矿体表面形态和矿体表面模型的分辨率。三角形的大小一般由面积和外接圆半径来度量;三角形的质量是由内接圆半径和其外接圆半径的比值来确定。2002,Mallet定义了对于三角形的美化度的函数[18]:
其中:r(T)为三角形T的内切圆的半径,其中R(T)为三角形T的外接圆的半径[23],并且b(T)∈
图4
图5
图6
图7
4 应用案例
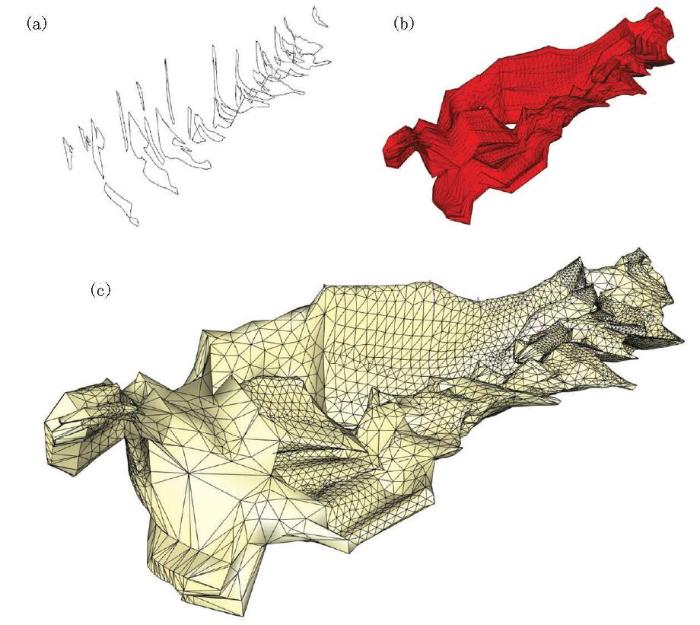
图8
图8
某矿体表面建模的实际应用效果
a—某矿区的三维矿体轮廓线;b—传统轮廓线建模方法的效果;c— 改进后的效果
Fig.8
The practical application of the surface modeling of an ore body
a— three-dimensional ore body contour of a mining area; b— the diagram of traditional contour modeling method; c— the diagram of improved method
5 总结
1) 笔者对于一组单轮廓线引入矿体趋势线,并且还可以对矿体的趋势线进行编辑修改,然后利用中间加密轮廓线的方法实现对矿体形态的控制;
2) 根据封闭轮廓线之间的最短距离自动添加分支点,利用平面的带洞限定三角剖分实现分支的自动构建,同时保证了分支矿体的准确性;
参考文献
三维固体矿产资源储量和潜力评价系统关键技术研究
[D].
Research on key technologies of three dimensional solid mineral resources reserves and potential evaluation system
[D].
平行轮廓线三维矿体重建算法
[J].
DOI:10.3321/j.issn:1003-9775.2006.07.021
URL
[本文引用: 1]

结合非层状矿体特点,提出带控制线的平行轮廓线三维矿体重建算 法.该算法通过人机交互指定轮廓线上的特征点形成若干条控制线,使得最小跨距三角网在指定的线之间生成;并提出添加辅助线的分支处理方法.在对复杂形态的 矿体实体建模和分支处理问题上进行了编程和实验.实验结果证明该算法简单、高效和实用,从底层开发的三维建模软件可提供相关矿山用户应用.
Building orebody solid model from planar contours
[J].
一种新的多轮廓线重构三维形体算法:切开—缝合法
[J].
DOI:10.3321/j.issn:1005-3026.2007.01.028
URL
[本文引用: 2]

综合评述了目前通过多轮廓线重构三维形体表面的算法研究现状。提出了一种新的多轮廓线重构三维形体算法——切开一缝合法(CS).该法通过引入控制点对作为切口,将轮廓线对进行坐标转换和轮廓对应后,切开并铺展成两条平行直线段,通过寻求轮廓线对顶点的对应关系,生成了符合Delaunay法则的三维形体表面三角面片,解决了形状和顶点数目差异较大的相邻轮廓线重构问题,并将其应用到基于剖面的三维地质建模中.实践证明,该算法行之有效,且对解决相似问题具有一定启发性.
Cut-and-sew algorithm: a new multi-contour reconstruction algothms
[J].
一种基于剖面轮廓线进行矿体三维建模的方法
[J].目的研究基于相邻剖面轮廓线进行矿体三维建模算法,提出周长投影法,解决目前矿体三维建模中存在的问题.方法通过坐标变换将相邻轮廓线上的顶点坐标投影到轮廓线所在平面,在相邻的两条轮廓线上通过内插按照距离比例加密点位,使相邻的两个轮廓线上具有相同的点数,然后在两个轮廓线之间构建三角网.结果在相邻剖面矿体轮廓线形体差异较大,点数较多的情况下,利用该方法进行矿体建模能够取得较好的建模效果,矿体模型表面过渡平滑,更具真实感.结论周长投影法符合同步规则,保证了矿体相邻轮廓线在形体上的一致性,在相邻矿体轮廓线形体差异较大、轮廓线线上点数相差较多的情况下,利用该方法能够取得较好的建模效果.
An orebody 3D modeling algorithm based on section contour Lines
[J].
三维矿体表面建模中的三角剖分技术及其应用
[J].介绍了如何根据勘探线剖面矿体边界线,用三角剖分方法逼近矿体表面,建立矿体三维可视化模型的技术。三维矿体表面建模技术主要包括勘探线剖面矿体边界线的圈定、相邻边界线之间三角剖分和单个边界线内部三角剖分等内容。针对矿体结构复杂的特点,提出应用“凸包投影法”和“凸点逐步消除法”,分别解决相邻凹多边形矿体边界线之间与单个凹多边形矿体边界线内部的三角剖分问题,从而建立起复杂矿体的三维可视化模型。应用研究表明:运用本文方法,根据矿区勘探数据,能够建立起符合实际的三维矿体表面模型。
复杂地质构造三维地质体建模方法研究
[J].
DOI:10.3969/j.issn.0253-6099.2012.03.006
URL
[本文引用: 1]

阐述了三维地质体建模的步骤及特点。分别就轮廓线对应、镶嵌和分枝等复杂地质建模中的关键性问题进行了详细论述。以区域面积重合判断法为基础,结合加权品位重心曲线和轮廓线缩放系数两个参数,从局部和整体两个层面解决了轮廓线的对应计算问题。讨论了复杂轮廓线下的镶嵌和分支问题,并给出了基于通过添加控制线和辅助分支信息的解决算法。结合尖灭模型构成了完整的实体建模算法解决方案。实验结果表明此方法具有很高的实用价值。
Research on 3D modeling of complex geologic bodies
[J].
矿床三维地质混合建模与属性插值技术的研究及应用
[D].
Study and application on 3D hybrid geological modeling and attribute interpolation of mineral deposit
[D].
基于剖面的层状与非层状矿体的三维可视化研究
[J].
DOI:10.3321/j.issn:1001-1250.2008.09.027
URL
[本文引用: 1]

二维轮廓线重构三维表面是矿体几何建模的重要技术手段。对几种重构中可能出现的问题(轮廓对应问题和轮廓拼接),提出了适合地质体剖面建模使用的轮廓线重构算法。基于剖面的三维地质建模流程,建立地质体的线框面模型及其相应的地质块体模型。
Section-based 3D visualization modeling of stratified and non-stratified orebodies
[J].
基于钻孔数据的三维地层模型的构建
[J].
DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1672-0504.2004.03.006
URL
[本文引用: 1]

三维地质建模是三维GIS在地学中的一个重要应用,三维地层模型对实际的地质分析极为有用.在综合前人研究成果的基础上,提出了一种由工程钻孔数据构建三维地层模型的方法.该方法以钻孔资料作为地层建模的源数据,具有简单实用、快速稳健的特点,并且能够将用户手工编辑修改的钻孔剖面图融入实际建模流程,解决了以往单纯依靠钻孔数据进行建模而导致的建模结果不精确且难以修正的问题.该文介绍了该方法的基本思想与实现流程,探讨了断层数据的加入对模型的影响及解决方案,并通过一个建模实例展示了该方法的实际建模效果.
Reconstruction of 3D strata model based on borehole data
[J].
三维复杂断层网建模方法及应用
[J].
DOI:10.13209/j.0479-8023.2014.173
URL
[本文引用: 1]

For complex fault network, a new path cut algorithm was proposed, by which all types of complicated fault intersection can be dealt with, such as Y, 位, X, half-Y, half-位 contact relations. This fault modeling method not only avoids the limitation of the Pillar method and binary tree method, but also greatly improves the flexibility and accuracy of fault modeling. The method improves semi-automatic processing of the contact relationship between faults and quick updating of fault models. Through the validation of practical model, the modeling of complex fault network can be successfully and quickly solved, and the efficiency of modeling was also greatly improved.
Research and application of the three-dimensional complex fault network modeling
[J].
三维构造建模技术
[J].
Three-dimensional structural modeling technique
[J].
Surfaces from Contours
[J].DOI:10.1145/130881.131213 URL [本文引用: 1]
Reconstruction of surfaces from planar contours
[D].
Approximating complex surfaces by triangulation of contour lines
[J].
DOI:10.1147/rd.191.0002
URL
[本文引用: 1]

An algorithm is described for obtaining an optimal approximation, using triangulation, of a three-dimensional surface defined by randomly distributed points along contour lines. The combinatorial problem of finding the best arrangement of triangles is treated by assuming an adequate objective function. The optimal triangulation is found using classical methods of graph theory. An illustrative example gives the procedure for triangulation of contour lines of a human head for use in radiation therapy planning.
Optimal surface reconstruction from planar contours
A triangulation algorithm from arbitrary shaped multiple planar contours
[J].
DOI:10.1145/108360.108363
URL
[本文引用: 3]

Conventional triangulation algorithms from planar contours suffer from some limitations. For instance, incorrect results can be obtained when the contours are not convex, or when the contours in two successive slices are very different. In the same way, the presence of multiple contours in a slice leads to ambiguities in defining the appropriate links. The purpose of this paper is to define a general triangulation procedure that provides a solution to these problems. We first describe a simple heuristic triangulation algorithm which is extended to nonconvex contours. It uses an original decomposition of an arbitrary contour into elementary convex subcontours. Then the problem of linking one contour in a slice to several contours in an adjacent slice is examined. To this end, a new and unique interpolated contour is generated between the two slices, and the link is created using the previously defined procedure. Next, a solution to the general case of linking multiple contours in each slice is proposed. Finally, the algorithm is applied to the reconstitution of the external surface of a complex shaped object: a human vertebra.
A new general triangulation method for planar contours
[J].
DOI:10.1145/965145.801264
URL
[本文引用: 1]

The problem of approximating the surface spanning a given set of 3D points as a polyhedron of triangular faces (“triangulation”) is a significant one, and has many applications in the fields of computer graphics and computer vision. In this paper, several solutions to this problem are reviewed. These solutions can be grouped into two classes, and particular emphasis is given to the class of surfaces spanned by parallel planar contours. For a contour pair P0,P1,Pm−1 and Q0,Q1,Qn−1, a graph theoretic approach can be used to arrive at a class of solutions, each requiring exactly m+n steps to triangulate the pair. Existing methods (both rigorous and heuristic) for extracting a particular solution from this group are reviewed, and a new heuristic based on inter-contour coherence is proposed. This heuristic is being used in the field of Ultrasonic Non-destructive Evaluation to produce images of flaws in pressure vessels, and its performance is shown to compare favorably with methods of greater computational complexity. It is believed that this heuristic can also be used with success in industrial vision systems where similar contours are obtained using a laser range finder.
基于Morphing 的三维地质界面生成
[J].
DOI:10.7702/dlydlxxkx20140108
URL
[本文引用: 2]

利用Morphing技术,参照四周地质界线的形态特征并以之为约束,插值生成一系列形态渐变的过渡曲线,采用轮廓线算法构建相邻曲线间的不规则三角网,并最终生成较为光滑的三维地质界面。将实际复合问题转化为4种基本问题进行求解,并详述了四边问题的实现细节。实验表明,该方法能够生成光滑三维地质界面,并较好地保留了已知地质界线的形态特征。
Three-dimensional geological surface creation based on morphing
[J].
基于BPLI二维平行轮廓线重建三维表面的新算法
[J].
DOI:10.3321/j.issn:0479-8023.2003.03.017
URL
[本文引用: 2]

The correspondence and branching problems are vexed problems when reconstructing 3-D surfaces from 2-D parallel contours. BPLI tries to reconstruct non-intersecting surfaces from arbitrary input set of contours and latch a lambent solution of the two problems; however, BPLI remains the shortages of producing degenerate portions and involving time-consuming operations. After an overall analysis of BPLI, this paper proposed a series of new algorithms to improve BPLI approach: first, we proposed a new contour matching algorithm so that the correct similar contour portions of each pair of adjacent slices can be found though the contours are not finely segmented. Secondly, we triangulate the unmatched portions with a new dynamic programming scheme, which has ability to handle degenerate portions in the mesh. These improvements result in a fast triangulating process.
New algorithms based on BPLI Solution for reconstructing 3D surfaces fron parallel contours
[J].
一种新的轮廓线三维地质表面重建方法
[J].
DOI:10.3724/SP.J.1047.2015.00253
URL
Magsci
[本文引用: 1]

<p>在三维地质建模中,由于地质剖面与医学CT有本质上的相似性,因此,轮廓线的三维表面重建技术有广泛的应用。目前,较为成熟的算法并没有考虑地质数据的特殊性,由于地质体形态复杂多变,地质剖面稀疏、数据来源多样等特点,将普适的算法应用到地质建模中,只是解决了重建曲面的合理性,并没有关注曲面的几何质量,导致曲面无法达到地质建模对于模型质量的要求。本文针对地质数据的特点,提出了一种新的轮廓线表面重构方法。在不改变轮廓线连接的合理性与正确性的情况下,通过生成过渡剖面轮廓线,克服传统方法生成曲面过于粗糙的缺点,以提高建模质量。在Creatar 三维地质基础平台上,对多种情况的剖面数据实验结果表明,在数据稀疏的情况下达到了良好的建模效果。该方法的扩展模型满足了地质剖面轮廓线建模中复杂地质情况,以及交叉剖面数据的曲面重建,且算法复杂度低,实现简单,有较强的实用性。</p>
High quality geological surface reconstruction from planar contours
[J].
Delaunay refinement algorithms for triangular mesh generation
[J].
DOI:10.1016/j.comgeo.2014.02.005
URL
[本文引用: 3]

Delaunay refinement is a technique for generating unstructured meshes of triangles for use in interpolation, the finite element method, and the finite volume method. In theory and practice, meshes produced by Delaunay refinement satisfy guaranteed bounds on angles, edge lengths, the number of triangles, and the grading of triangles from small to large sizes. This article presents an intuitive framework for analyzing Delaunay refinement algorithms that unifies the pioneering mesh generation algorithms of L. Paul Chew and Jim Ruppert, improves the algorithms in several minor ways, and most importantly, helps to solve the difficult problem of meshing nonmanifold domains with small angles. Although small angles inherent in the input geometry cannot be removed, one would like to triangulate a domain without creating any new small angles. Unfortunately, this problem is not always soluble. A compromise is necessary. A Delaunay refinement algorithm is presented that can create a mesh in which most angles are 30°61or greater and no angle is smaller than arcsin[(3/2)sin(01/2)]65(3/4)01, where 018160°61is the smallest angle separating two segments of the input domain. New angles smaller than 30°61appear only near input angles smaller than 60°. In practice, the algorithm's performance is better than these bounds suggest. Another new result is that Ruppert's analysis technique can be used to reanalyze one of Chew's algorithms. Chew proved that his algorithm produces no angle smaller than 30°61(barring small input angles), but without any guarantees on grading or number of triangles. He conjectures that his algorithm offers such guarantees. His conjecture is conditionally confirmed here: if the angle bound is relaxed to less than 26.5°, Chew's algorithm produces meshes (of domains without small input angles) that are nicely graded and size-optimal.
3-D geological modeling-concepts, methods and key techniques
[J].DOI:10.1111/j.1755-6724.2012.00727.x URL [本文引用: 4]
What is a good linear element? Interpolation, conditioning, and quality measures
Surface-based 3D modeling of geological structures
[J].
DOI:10.1007/s11004-009-9244-2
URL
[本文引用: 4]

Building a 3D geological model from field and subsurface data is a typical task in geological studies involving natural resource evaluation and hazard assessment. However, there is quite often a gap between research papers presenting case studies or specific innovations in 3D modeling and the objectives of a typical class in 3D structural modeling, as more and more is implemented at universities. In this paper, we present general procedures and guidelines to effectively build a structural model made of faults and horizons from typical sparse data. Then we describe a typical 3D structural modeling workflow based on triangulated surfaces. Our goal is not to replace software user guides, but to provide key concepts, principles, and procedures to be applied during geomodeling tasks, with a specific focus on quality control.
Mesh optimization