0 引言
裂缝介质成因特殊且分布具有很强的特征性,这些因素使其具有很强的油气藏潜力。因此裂缝介质备受地球物理能源勘探领域的关注。Hudson J A在20世纪80年代提出了一系列较完整的裂缝介质理论[1],其理论模型中的裂缝结构是椭球状的。所有裂缝定向排列,模仿自然环境中应力造成的结构效果。Hudson裂缝理论描述了裂缝的密度、纵横比、响应的裂缝介质等效弹性模量。随后他对不同裂缝包裹体种类做出研究,并得到了不同包裹体对波动传播的影响规律[2]。1990年,Hudson以多重散射理论为前提提出裂缝介质中的波动衰减理论[3]。随后,他对裂缝结构中的包裹体粘滞性和纵横比在满液条件下对波动频率的影响规律进行了研究,提出孔、裂缝并存状态地质模型,这是Hudson理论首次将孔隙结构融于裂缝模型中[4]。1996年,Hudson提出裂缝、孔隙结构关系模型:裂缝之间无连通,裂缝与基质中孔隙存在连通[5]。2000年,Hudson提出了流体静力平衡理论,随后提出以微观力学理论为前提的粘弹性裂缝介质理论,并以量子散射理论为基础手段将Lippmann-Schwinger方程与T-矩阵算法相结合得到孔—裂缝介质等效弹性模量[6]。Vilhelm对地层中的裂缝形状和分布状态进行反演计算并得到了裂缝介质特征值[7,8,9];Nishizawa通过裂缝介质的参数特性模拟了裂缝介质的形成环境因素[10,11];Gueguen等人分析了各向异性裂缝介质中的波动衰减规律以及裂缝性各向异性介质的特征[12,13,14,15]。
就中子测井而言,脉冲中子测井一般被用于分析储层的饱和度。20世纪80年代,数值模拟技术初步被应用于中子测井研究。中子测井模拟方法主要包括蒙特卡罗法、玻尔兹曼法。在模拟研究初始阶段,由于计算机技术的限制,蒙卡算法耗时过长,因此中子测井的数值解法被大量应用,其主要用于研究中子源热中子密度分布,并对中子扩散作用作出分析[16]。21世纪以后,计算机技术发展,蒙卡模拟技术被大量应用于中子测井模拟。Scott Fricke以蒙卡方法为基础对热中子孔隙度进行模拟计算[17]。就国内研究情况而言,张锋等人建立了孔隙地层的中子模拟研究模型,并数值模拟了不同孔隙度、地层水矿化度、饱和度等环境因素条件下的中子慢化作用[18,19]。
1 建立水层裂缝介质井孔模型
首先建立脉冲中子井孔模型,设井孔为垂直井,纵向无限延伸,围岩基质主要为石灰岩。围岩各向异性主要来自其中的裂缝群结构。裂缝结构定向排列,遵循相同走向。脉冲中子源安置于井轴中心处,井孔中充满泥浆,裂缝群组均匀、稀疏地分布在围岩介质中,并且每条裂缝结构的主体部分的法向与井轴方向成同等大小角度,此角度在0°~90°间变化。
脉冲中子源是一种通过源发射出中子,使中子与目标探测介质进行反应进而对目标介质进行探测的测井方法。中子放射源通过发生核反应产生14 MeV的快中子,次反应公式如下:
此处,
在反应过程中,弹性散射反应和吸收俘获反应分别产生非弹性伽马射线和俘获伽马射线,中子测井探测仪通过探测各种伽马射线谱或探测没有被俘获吸收的热中子来得到目标探测介质的性状。水层中存在大量的氢元素,氢元素又是自然界中常见元素中对中子的慢化作用效果最强的元素,因此水层的存在会对中子产生明显的慢化作用。
中子测井的工作目的主要是解释研究中子的传播问题,即中子在介质中运动、碰撞的随机过程。单个粒子的传播寿命会被单独记录,通过统计大数量单独粒子的传播寿命进而得到统计传播输运结果。
本文的模拟地质环境取材于中国塔河油田地区,此地区主要地质特征为富含碳酸盐岩裂缝群结构,其中,基质岩层中的孔隙结构是该地区常见孔隙类型,一般直径为微米级;裂缝结构主要通过构造应力造成,呈群组走向一致性特征。由于裂缝结构和基质孔隙结构并存与岩层中,因此笔者以此地区为基础选取双孔理论裂缝模型。Hudson理论模型中:裂缝群走向一致;双孔结构;孔隙结构体积小分布均匀,孔隙与裂缝结构之间渗透率低;基于以上地质特征,笔者以Hudson多角度裂缝理论为基础对井孔地质结构进行模拟分析。
粒子的传播过程可分为三个主要步骤。
首先,确定粒子的状态参数和状态序列,如下式:
式中:r是粒子的碰撞位置,E是粒子碰撞后的能量,t是粒子的碰撞时间点,W是粒子碰撞后的权重,Ω是粒子碰撞后运动方向。
通过式(2)可得,通过m次碰撞后的粒子状态参数为:
式中:rm是经过m次碰撞后粒子的位置,Em是经过m次碰撞后的粒子能量,Ωm是经过m次碰撞后的粒子运动方向,Wm是m次碰撞后粒子权重,tm是m次碰撞后的时间。源发出的中子与地层介质的原子核发生若干次碰撞,其动能逐渐下降,最后被地层原子核俘获。
然后,确定粒子的输运传播过程,其中,中子在探测目标介质中的自由飞行距离的抽样值为lf=-lnξ/Σt。式中:Σt是宏观截面之和,ξ是在区间(0,1)上服从均匀分布的随机数。与中子发生反应的地层核素种类通过以下抽样规则确定:
式中,P是中子与核素发生反应的几率。中子与地层原子核发生反应的种类包括弹性散射和非弹性散射、俘获反应或裂变等,它们的宏观截面分别是σel、σin、σa、σf,由此得到基于离散随机变量采样确定的核反应类型:
反应过后,还需要对粒子碰撞后的状态进行确定。如果粒子与地层原子核发生作用并被其俘获,则粒子历史终结;如果粒子发生散射反应,则还需要继续跟踪粒子之后的反应状态;如果发生非弹性散射,则可根据核数据库计算反应后的能量和方向。最后,对反应结果进行记录。记录的方法一般分为直接记录法和加权记录法两种。其中,加权记录法是使未被俘获的粒子权重增加,进而比直接记录法效率高。
为了得到裂缝井孔介质中的热中子密度,需要确定相应的宏观截面。因为脉冲源是瞬时源,需要通过动态扩散方程对热中子分布问题进行计算:
上式还可以写为:
式中:v是粒子的速度(cm/s),D0是粒子的扩散系数,n是粒子密度(单位体积内粒子数量),S是粒子源的密度,Σ是粒子的俘获截面。
中子源发射出快中子后,只经过极短时间(1 μs)就会减速为热中子。当脉冲中子源发出的中子分布达到一种稳定状态时,可以看做是在均匀介质中点源发出的热中子分布,即可用下式表达:
式中:R是观察点与源的距离,Dt是热中子的扩散系数,Q是源强度,L是减速距离。式(7)(扩散方程)的初始条件由式(8)给出,即0时刻的热中子密度。扩散方程的边界条件:流量密度有限;介质分界面上,垂直方向粒子通量相等;无穷远处粒子通量为0。将扩散方程初始条件和边界条件联立,再通过扩散方程数值解法便可得到热中子密度分布的数值模拟结果。
其中,井孔和围岩环境下,热中子扩散俘获过程呈双指数衰减规律,即,热中子计数为井孔计数和围岩计数的和:
式中:τ1和τ2分别为井孔热中子寿命和地层热中子的寿命,N10和N20是初始状态井孔热中子计数和地层中热中子计数。热中子的计数值取决于地层介质的俘获能力(宏观截面),包括地层介质岩石骨架和裂缝中包裹体的俘获能力。宏观截面为:
式中:Σma是围岩骨架的宏观俘获截面,Σw是地层水的宏观俘获截面,φ是围岩孔隙度,Sw是裂缝流体的饱和度。
2 水层裂缝介质测井响应特征
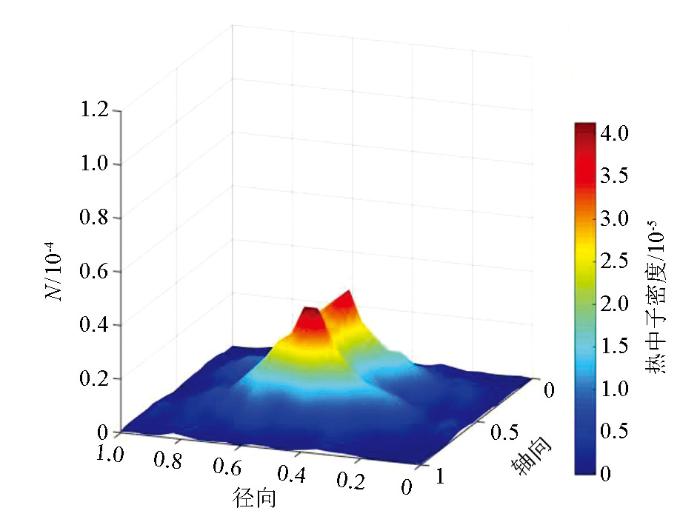
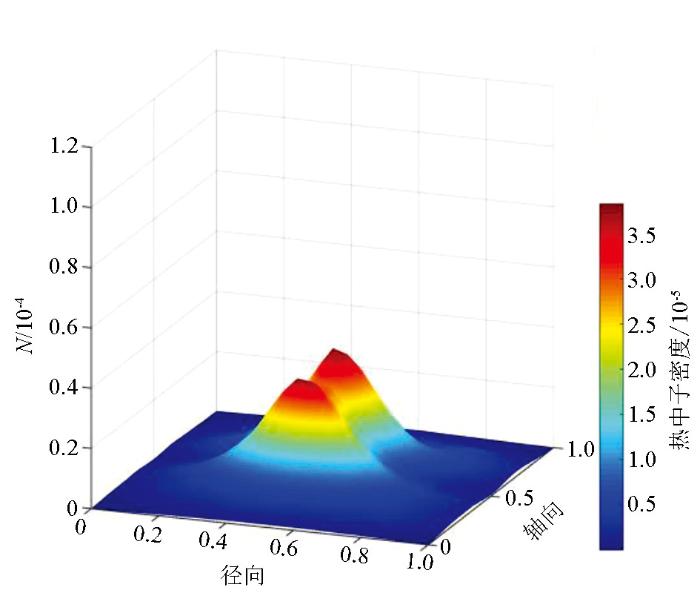
图1
图2
图3
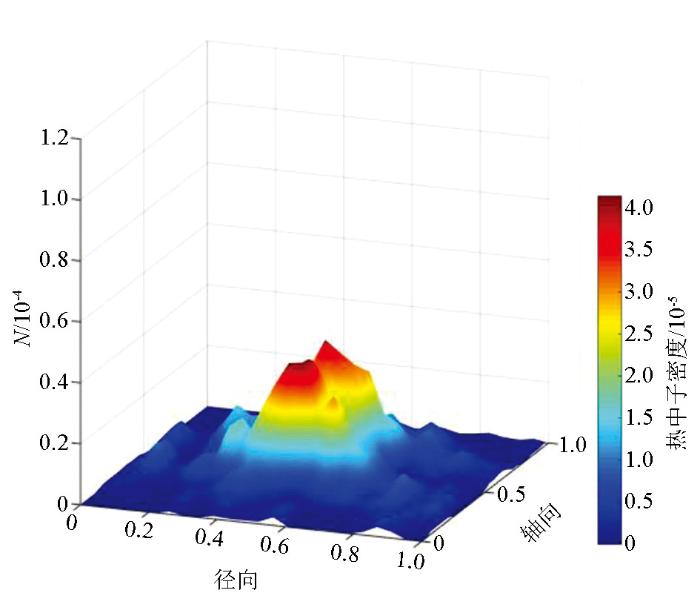
图4
图5
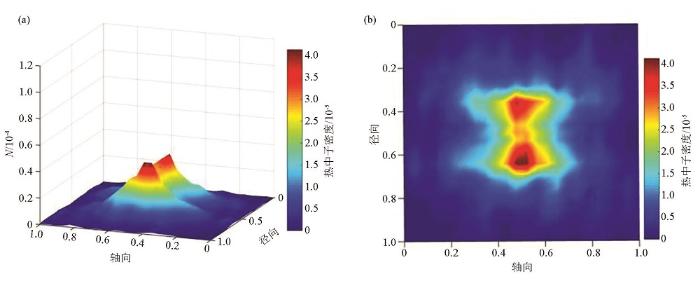
由图可知,在低角度(0°~20°)水层裂缝介质中,只有在热中子扩散边界带存在少量的极小值点(图中阴影、峡谷凹陷带)。在中等角度(40°~50°)裂缝水层中,极小值点明显增加,并且,热中子计数极大值也显著升高;以上现象说明低角度水层裂缝介质对热中子的俘获作用明显低于中等角度裂缝介质,并且,水层中的热中子对中等角度裂缝介质环境更加敏感,更容易被慢化;在高角度(80°~90°)水层裂缝介质中,热中子密度分布图中非常平滑,几乎不存在极小值点(阴影凹陷部分),这说明与其他角度裂缝介质相比,高角度裂缝介质对热中子的俘获作用最低。
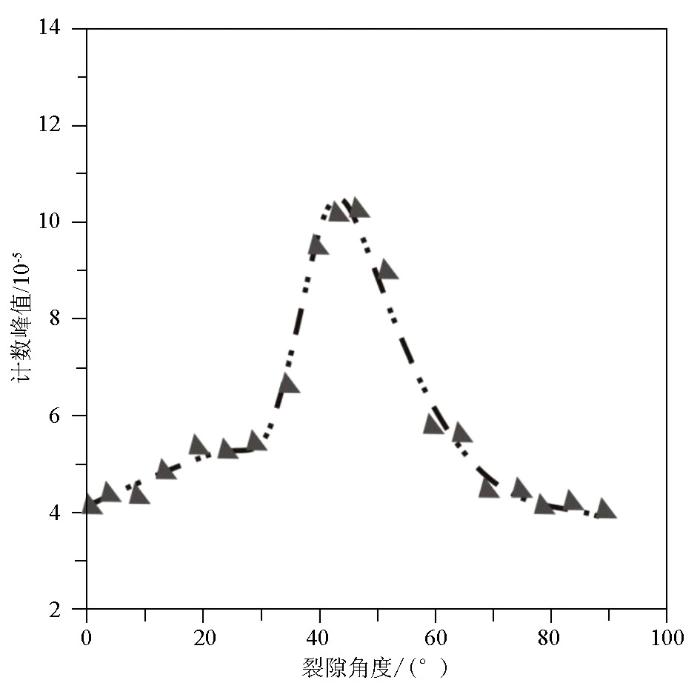
图6是水层中不同裂缝角度条件下的热中子密度极大值图。由图可知,随着水层裂缝角度从0°~90°逐渐增大,极大值首先小幅上升,在26°~30°之间达到平台期;当裂缝角度超过30°并持续增大,热中子极大值开始急剧上升并在50°左右达到峰值,之后随着角度增大而下降,在70°左右开始下降缓慢;随着裂缝角度逐渐接近90°,热中子极大值下降速度放缓并最后接近恒定值。
图6
以上现象说明,水层中的热中子极大值对低角度(0°~30°)裂缝条件有一定敏感性,对中等角度(50°)裂缝环境最敏感(极大值最大达到10.68×10-5)。由此可见,50°水层裂缝介质对中子的慢化作用最强烈。
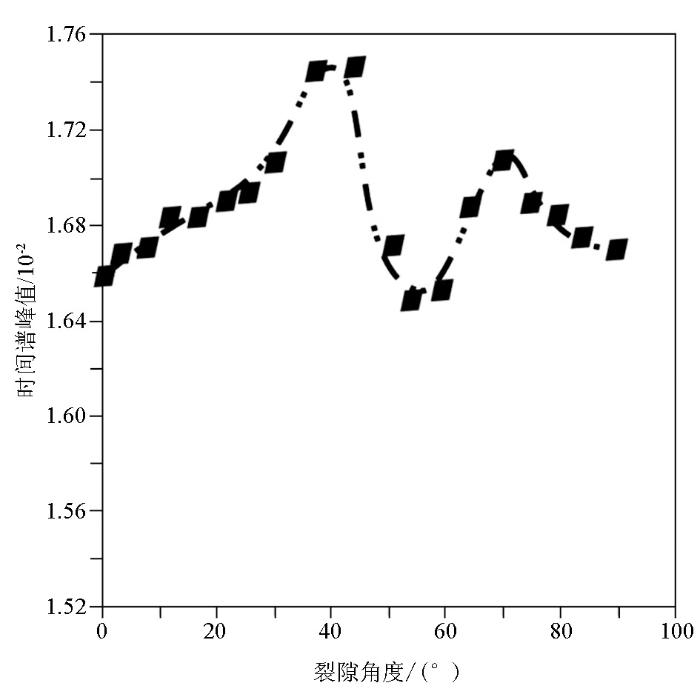
图7是时间谱极大值与裂缝角度的变化关系图。时间谱是粒子计数随着时间变化的规律统计图,其记录从瞬时源发射快中子开始,随着时间的推移粒子计数会从一个峰值下降到零的过程。对于不同角度的裂缝介质而言,时间谱极大值有所不同,这说明裂缝的角度是影响粒子计数的一个重要因素,也可说明热中子时间谱可以从一定程度反映水层裂缝的特征。图中,两个峰值点分别出现在40°和70°处,在58°左右出现了一个最小值点。就整体趋势而言,随着裂缝角度从0°上升到25°的这段区间中,时间谱极大值随着裂缝角度的上升而逐渐升高;在裂缝角度大于70°并逐渐接近90°的过程中,时间谱极大值逐渐下降,且下降速率逐渐放缓最后接近一个恒定值。
图7
3 有效性验证
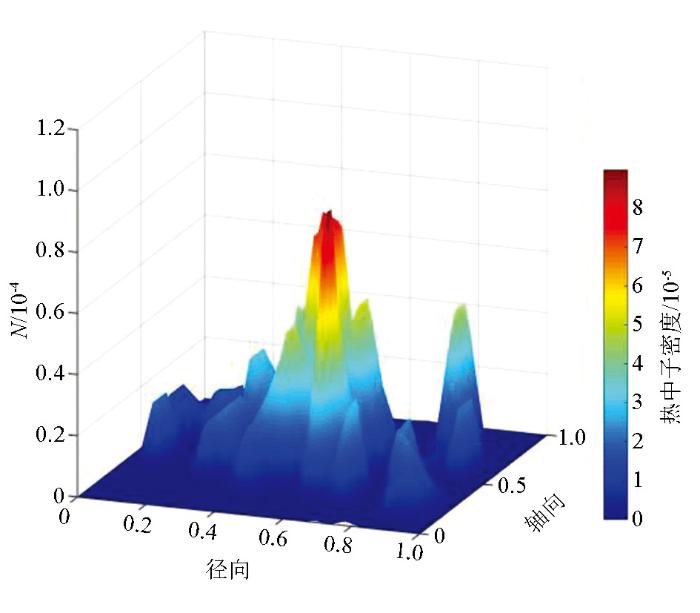
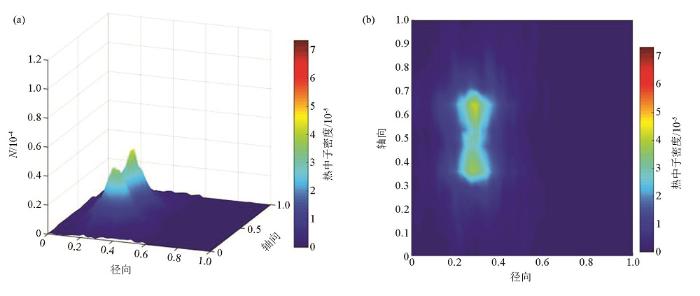
图8
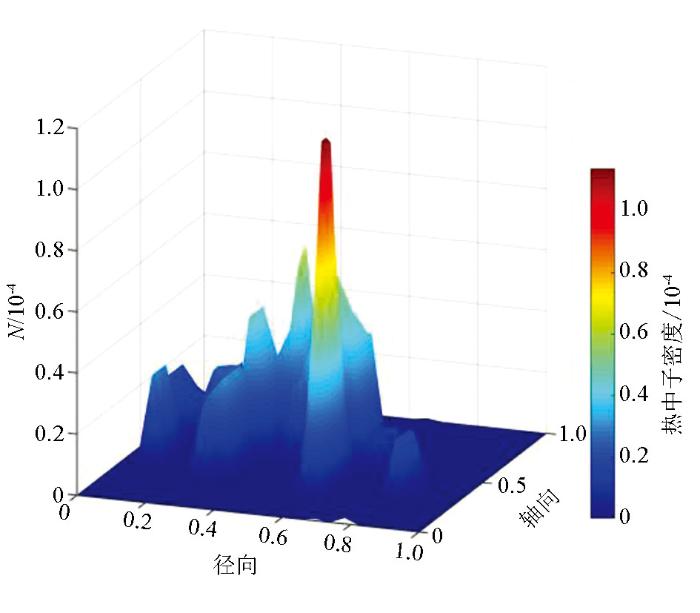
图9
通过对比图8和图9可知,自然条件下由于井孔结构的存在,裂缝结构被井孔贯穿,导致裂缝与围岩基质间的渗透率增大,大于数值模拟模型中的渗透率。并且,由于自然条件下地层包含物质复杂,干扰结构多样,热中子被地层物质俘获较多,俘获速率较快,因此自然条件下热中子密度分布峰值点比较靠近井孔结构,且传播距离较近,在较远处几乎不存在热中子计数点。就整体而言,图8和图9中热中子密度分布规律相似,都存在近似双峰值点,靠近井孔热中子计数较少,这是由于井壁对热中子的俘获作用较强,随着远离井孔结构,出现峰值点;当离井孔距离继续增大,计数点减少并逐渐消失。由此可见,野外数据测井结果与数值模拟结果相似,说明本文数值模拟结果有实际参考价值。
4 结论
笔者通过多角度裂缝理论模拟,得到了水层中不同裂缝角度条件下的热中子密度分布和输运规律。研究结果表明,低角度和中等角度水层裂缝介质条件下,热中子计数极大值较高;尤其是中等角度裂缝介质中的热中子分布灵敏度最大;高角度水层裂缝介质对热中子的吸收俘获作用小;热中子密度分布平面图中,水层中的热中子扩散面积不大,粒子计数点连贯,属逐渐变化规律。通过对比热中子密度分布规律、热中子计数极大值情况和时间谱最大值变化规律可知,本文中多角度裂缝理论可以对水层裂缝介质进行理论分析,进而定量识别水层裂缝角度,此研究结果可应用于野外裂缝性地质地球物理勘探工作。
参考文献
Overall properties of a cracked solid
[J].DOI:10.1017/S0305004100057674 URL [本文引用: 1]
Wave speeds and attenuation of elastic waves in material containing cracks
[J].
DOI:10.1111/j.1365-246X.1981.tb02662.x
URL
[本文引用: 1]

Summary. Expressions now exist from which may be calculated the propagation constants of elastic waves travelling through material containing a distribution of cracks. The cracks are randomly distributed in position and may be randomly orientated. The wavelengths involved are assumed to be large compared with the size of the cracks and with their separation distances so that the formulae, based on the mean taken over a statistical ensemble, may reasonably be used to predict the properties of a single sample. The results are valid only for small concentrations of cracks. Explicit expressions, correct to lowest order in the ratio of the crack size to a wavelength, are derived here for the overall elastic parameters and the overall wave speeds and attenuation of elastic waves in cracked materials where the mean crack is circular, and the cracks are either aligned or randomly orientated. The cracks may be empty or filled with solid or fluid material. These results are achieved on the basis of simply the static solution for an ellipsoidal inclusion under stress. The extension to different distributions of orientation or to mixtures of different types of crack is quite straightforward.
Attenuation due to second-order scattering in material containing cracks
[J].
DOI:10.1111/j.1365-246X.1990.tb04480.x
URL
[本文引用: 1]

The method of smoothing has lead to the calculation of overall or effective elastic parameters for wave propagation in material containing cracks, valid to second order in the number density of the cracks. Wavespeeds are obtained for wavelengths long compared with crack dimensions by working to the lowest order in frequency. To find the attenuation due to scattering of energy out of the mean wave, calculations to higher order in frequency are necessary and, up to now, attenuation has been obtained by summing over the scattering cross-sections of the cracks, thus neglecting any crack-crack interactions. Here we evaluate scattering attenuation to higher order in the series obtained from the smoothing approximation in order to allow for multiple scattering. It turns out that, for crack radii and crack spacing small compared with a wavelength, the term of lowest order taken from the double scattering component exactly cancels out the sum over scattering cross-sections, leaving only higher order terms to account for attenuation due to scattering. In other words, the effective material parameters contain no attenuation component arising from scattering.
Overall properties of heterogeneous material
[J].
DOI:10.1111/j.1365-246X.1991.tb01411.x
URL
[本文引用: 1]

Small-scale heterogeneity in crustal structure can be very complex and difficult to describe in detail and yet, at the same time, can be very important for the description of, for instance, tectonic stress and porosity. Statistical properties of such heterogeneity can be derived from the properties of waves of relatively large wavelength as they propagate through the crust. The differences between measured wavelengths and attenuation coefficients and those of compact rock and the variations of these quantities in space and time provide, in principle, a means of determining quantities like the density and orientations of microfractures and the nature of crack infill material. The theoretical basis for inferences of this kind is the concept of the 'effective' or 'equivalent' material based on an averaging process taken over the microstructure. A number of methods have been used to calculate the properties of the effective medium, several of which are described here.
The Mechanical properties of materials with interconnected cracks and pores
[J].
DOI:10.1111/j.1365-246X.1996.tb06355.x
URL
[本文引用: 1]

This paper studies the effect on the overall properties of a cracked solid of the existence of connections between otherwise isolated cracks and of small-scale porosity within the 'solid' material. The intention is to provide effective medium models for the calculation of elastic wave propagation with wavelengths greater than the dimensions of the cracks. The method follows that of earlier papers in which the overall elastic properties are directly related to parameters governing the microstructure, such as crack number density and the mean radius and spacing distance of the cracks. Expressions derived by the method of smoothing are evaluated to second order in the number density of cracks, thereby incorporating crack crack interactions through both the strain field in the solid and the flow field of fluids in the pores. Flow of interstitial liquids tends to weaken the material; the limit of zero flow is equivalent to isolating the cracks and the limit of free flow is equivalent to dry (gas-filled) cracks. It also introduces additional attenuation. The inclusion of small-scale porosity gives a model of 'equant porosity' which is more closely constrained by the details of crack dynamics than earlier models.
Effective-medium theories for fluid-saturated materials with aligned cracks
[J].DOI:10.1046/j.1365-2478.2001.00272.x URL [本文引用: 1]
Characteristics and controlling factors of fractures in lacustrine dolostones reservoirs in Tanggu district
[J].The E_1s_3~5 member in Tanggu district is a fault block,high-pressure and fractured lacustrine dolostones reservoirs.Based on the core observation,thin sections and log data with Ansys,the authors study on the causes and formation periods of fractures in lacustrine dolostones reservoirs,describe the fracture characteristics and analyze the control factors of fractures.The results show that the fractures are mainly of the tectonic origin,with a few bedding fractures and dissolution fractures,and the seepage ability decreases successively.There are four stages of fractures development including bedding fractures parallel to beddings,oblique fractures with 45 and 60 degrees,tensile fractures with 75 to 90 degrees,and high angel fractures with70 to 85 degrees.The structure,lithology,diagenesis and overpressure are the key control factors of fractures in lacustrine dolomite reservoir,which are obviously influenced by cracks and stress field.The fractures mainly develop near the fault cross zone with 2 groups of NW and NE trending faults,and the above mentioned fracture development zone with high pressure called the sweet spots should be valued in oil-gas exploration.
Energy dissipation of P and S-waves in fluid-saturated rocks:An overview focusing on hydraulically connected fractures
[J].DOI:10.1007/s12583-015-0613-0 URL [本文引用: 1]
孔洞型碳酸盐岩储层饱和度建模新方法及应用
[J].
DOI:10.11764/j.issn.1672-1926.2016.11.009
URL
[本文引用: 1]

碳酸岩复杂的孔隙结构和强烈的非均质性,导致传统的阿尔奇模型存在一定不适用性,主要体现在,m,n值的变化范围大.从岩石体积物理模型出发,设定n为常数,扩展m的含义并重新定义为孔隙结构指数,用它代替原Archie公式中胶结指数和饱和度指数对含水饱和度计算的影响.鉴于碳酸盐岩孔隙成因的复杂性和孔隙结构的复杂性,特别是裂缝型和溶蚀孔洞型碳酸盐岩储层取心困难,采用数值模拟手段考察碳酸盐岩孔隙结构指数m的影响因素及变化规律, 主要包括孔隙结构特征参数孔喉比、孔隙度、泥质含量等因素对表征岩石导电性的F和岩石孔隙结构指数m的影响,又通过引入孔隙结构组分建立了变m的饱和度模型.应用效果表明新模型成功解决了四川磨溪溶蚀孔洞型碳酸岩储层水层段自由烃饱和度计算偏高的难题.
Crack density tensor inversion for analysis of changes in rock frame architecture
[J].
DOI:10.1111/j.1365-246X.2008.03748.x
URL
[本文引用: 1]

This paper presents a development of the use of multi-axial ultrasonic data for the quantification of extrinsic, crack or grain-contact induced elastic anisotropy in core samples with application to a UKCS oil field. An approach for inversion of multi-axial velocity measurements is presented, which extends the previous work by Sayers (2002) for the determination of second- and fourth-order crack density tensors from inversion of multi-axial ultrasonic velocity data. The extensions to the inversion approach provide improved consideration of data uncertainties, by using all available P - and S -wave data and also permit the inclusion of an orthorhombic background anisotropy in the inversion [e.g. due to intrinsic lattice preferred orientation(LPO) effects]. The latter aspect leads to estimates of the extrinsic anisotropy, that is, the quantified crack density tensors, that are 'unpolluted' by the effects of the intrinsic anisotropy, thus permitting extrinsic and intrinsic anisotropies to be distinguished. For the samples considered, the extrinsic crack-induced anisotropy is strong relative to that of the intrinsic LPO effects, and the pre-dominant crack-set is commonly aligned parallel to the depositional fabric (which is generally horizontal). However, the LPO and extrinsic anisotropies are in general aligned, which indicates a linked origin. Furthermore, a strong correlation is observed between the degree of VTI anisotropy and the modal content of micas in the samples, which cannot be explained solely by the LPO effect. In fact, it is shown that increased horizontal (grain parallel) crack densities are associated with higher mica content. These horizontal cracks in the mica-rich samples often show moderate-to-strong variations in crack density with loading that might be detected in situ with non-hyperbolic moveout. Additionally, three samples show significant pressure sensitivity of the vertical crack sets indicating that loading-induced azimuthal anisotropy might also exist in some layers in situ and be detectable using azimuthal AVO type analyses. Analysis of the fourth-order crack density tensor allows insight into the relative sizes of the normal and tangential crack compliances, B N and B T . For one case it is found that B N B T (i.e. the crack-sets are more compliant in compression than in shear). For another sample B N < B T ; this sample had been cleaned prior to the analysis, which appears to facilitate shear in the cracks. This conclusion may have significant implications for the use of analogue samples acquired at the surface where organic products, which lead to the reduced shear compliance, are not present.
浅层初至波旅行时层析并行算法及在地裂缝调查中的应用
[J].
DOI:10.11720/wtyht.2017.5.28
URL
[本文引用: 1]

随着浅层地裂缝等地质灾害问题精细探测需求的增大,采用初至波速度层析反演技术,可以提供较高精度的浅层速度场的纵横向异常变化,可为识别地裂缝等地质灾害现象提供依据。通常,在采集参数一定的条件下,其反演成像精度受算法、网格类型和剖分尺度的限制,在网格类型不变的条件下,要提高精度就必须加密正反演计算网格,改进算法,从而实现增量而不减速且高精度的效果。文中利用OpenMP的单机多核并行技术,探讨并实现了初至波层析成像并行算法,其中正演部分使用了改进的旅行时线性插值法,针对原有的按列计算,加入了按行计算,充分考虑到来自各方向的射线,使得计算出的旅行时最小,反演部分使用了能迅速稳定收敛的LSQR法以及正则化技术,通过理论和实际资料测试,其收敛速度快,反演结果较好。同时,在加密采样和缩小网格尺度的条件下,与常规串行算法相比,其运算速度和效率有较大提高,与商业软件比较,其运算效率差异不大,但反演结果的精度和可分辨性较好。
Reflection and refraction at an imperfectly bonded interface between poroelastic solid and cracked elastic solid
[J].
DOI:10.1007/s10950-012-9311-x
URL
[本文引用: 1]

Porous solid is in contact with a cracked elastic solid at a plane interface between them. For the presence of vertically aligned microcracks, the elastic solid behaves transversely isotropic to wave propagation. The coefficients of elastic anisotropy depend on the crack density and crack porosity in the medium. A loose bonding is considered between the two solids so that a limiting case could be the welded contact. At the plane interface, the imperfection in welded bonding is represented by tangential slipping and, hence, results in the dissipation of a part of strain energy. Three types of waves propagate in an isotropic fluid-saturated porous medium, which are considered for incidence at the interface. Incidence of a wave results in three reflected waves and two refracted waves. Partition of incident energy among the reflected and refracted waves is studied for each incidence, varying from normal to grazing directions. Numerical example calculates the energy shares of reflected and refracted waves at the plane interface between water-saturated sandstone and basalt. These energy shares are computed and analyzed for different values of crack parameters as well as loose bonding parameter.
勘探地震物理震源模拟分析
[J].
DOI:10.11720/wtyht.2017.2.23
URL
[本文引用: 1]

震源是油气资源勘探和微地震监测中很重要的部分。为恰当地选择地震波勘探震源、节约野外勘探成本,文中基于加载压力源、剪切源和集中力源的理论公式,通过交错网格有限差分法数值模拟获得震源在各向同性介质中的地震波场图,详细讨论震源激发波的分布特征。通过波的偏振理论,从物理上细致地分析震源产生地震波的机理,与解析解一并验证数值模拟结果。所得结果说明:震源力是数值模拟地震波场的可控性因素;震源在三维裂缝介质中可观测到横波分裂现象;物理分析是很好地解释地震波场分布图的一种验证方法。
Towards fast quantitative modelling of pulsed neutron logging tools
[C]//
Thermal neutron porosity using pulsed neutron measurement
[C]//
脉冲中子—中子测井影响因素的数值模拟
[J].
DOI:10.3321/j.issn:1673-5005.2009.06.010
URL
[本文引用: 1]

利用蒙特卡罗方法建立各种条件下的套管井计算模型,模拟相应的热 中子时间谱,进而计算地层宏观吸收截面.模拟结果表明:地层的宏观吸收截面随着孔隙度和含水饱和度的增加而增加,且源距越小、地层水的矿化度和泥质含量越 高、套管的尺寸越大、仪器越居中、俘获截面越高的岩性地层条件下,地层的宏观吸收截面值也越大;套管壁厚和水泥环对地层宏观吸收截面没有影响,但套管壁越 厚、水泥环厚度越小,热中子总计数越低.利用脉冲中子测井数据确定地层含水饱和度时应对各种影响因素作相应的校正.
蒙特卡罗方法在脉冲中子测井中的应用
[J].
DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1000-7512.2005.01.005
URL
[本文引用: 1]

The time spectrum of all kinds energy neutrons and thermal neutrons, which resulted from the interaction between the formation and neutrons induced by the pulsed neutron source of the different pulsed width, are simulated by Monte Carlo Neutron-particles code. The time spectrum of thermal neutrons under the conditions of the different porosities, salinities and saturations are simulated. The linear relations between formation macroscopic cross sections and porosity, salinity and saturation are gained by the time spectrums, respectively. The results will lay the foundation for the study of PNN logging.
A comparative study of the anisotropic dynamic and static elastic moduli of unconventional reservoir shales:implication for geomechanical investigations
[J].
DOI:10.1190/geo2015-0427.1
URL
[本文引用: 1]

Abstract We obtained the complete set of dynamic elastic stiffnesses for a suite of "shales" representative of unconventional reservoirs from simultaneously measured P- and S-wave speeds on single prisms specially machined from cores. Static linear compressibilities were concurrently obtained using strain gauges attached to the prism. Regardless of being from static or dynamic measurements, the pressure sensitivity varies strongly with the direction of measurement. Furthermore, the static and dynamic linear compressibilities measured parallel to the bedding are nearly the same whereas those perpendicular to the bedding can differ by as much as 100%. Compliant cracklike porosity, seen in scanning electron microscope images, controls the elastic properties measured perpendicular to the rock's bedding plane and results in highly nonlinear pressure sensitivity. In contrast, those properties measured parallel to the bedding are nearly insensitive to stress. This anisotropy to the pressure dependency of the strains and moduli further complicates the study of the overall anisotropy of such rocks. This horizontal stress insensitivity has implications for the use of advanced sonic logging techniques for stress direction indication. Finally, we tested the validity of the practice of estimating the fracture pressure gradient (i.e., horizontal stress) using our observed elastic engineering moduli and found that ignoring anisotropy would lead to underestimates of the minimum stress by as much as 90%. Although one could ostensibly obtain better values or the minimum stress if the rock anisotropy is included, we would hope that these results will instead discourage this method of estimating horizontal stress in favor of more reliable techniques. 2016 Society of Exploration Geophysicists. All rights reserved.
Application of fluid inclusion analysis for buried dissolution predicting in the Tahe oilfield of Tarim basin,NW China
[J].
DOI:10.1007/s12583-013-0338-x
URL
[本文引用: 1]

This study was undertaken to establish an evaluation method for buried dissolution of carbonate reservoir in the Tahe ( ) Oilfield. Because of the difficulty in tracing the dissolution in geologic record, the precipitation is taken as a useful indicator to presume the dissolution reversed. The fluid inclusions data is a useful tool to identify the precipitation. On the basis of the principle that the temperature data of fluid inclusions captured in the calcite fillings of caves and cracks can reflect the fluid activity time, a total of 256 fluid inclusions samples in 12 drills were collected and analyzed to study their forming time in buried environment in the Tahe Oilfield, Tarim Basin, NW China. Results show that the temperature data of fluid inclusions captured by Ordovician cave and crack fillings accumulated in six intervals, which indicated six stages of fluid activity in the area of study. Meanwhile, it is clear that a different number of temperature intervals was captured in different wells, representing a different number of precipitation distributed in space. According to this conclusion, the buried precipitation trend in late Himalayan stage (the sixth stage) was supposed in space and its effectiveness has been approved by the chemical thermodynamics method. This method was also used in all of the other five stages of fluid activity and the comprehensive trend of the buried precipitation in space for Ordovician strata was evaluated. It shows that more temperature intervals were captured in the southwestern region (wells S76, S79, S65 and S75) and the eastern region (well S69) in the area of study, indicating intensive precipitation and weak dissolution in this area. This evaluation method for buried dissolution is a new attempt and may have important implications for further petroleum exploration in the Tarim Basin.
非常规油藏地应力和应力甜点地球物理预测——渤南地区沙三下亚段页岩油藏勘探实例
[J].
DOI:10.13810/j.cnki.issn.1000-7210.2016.04.022
URL
[本文引用: 1]

渤南地区沙三下地层发育非常规油气藏,预测地应力及应力甜点是该类油藏勘探及评价的关键。本文提出的地应力及应力甜点地球物理预测方法结合了前人研究成果,以测井岩石物理参数分析为基础,建立地应力、破裂压力与岩石弹性参数的关系,通过多元线性回归拟合力学计算公式,并以弹性参数反演和多体融合技术为依托,实现了应力场及应力甜点的地震预测。理论研究及钻探结果均表明,渤南洼陷中部及南部的低应力区是油气成藏的优势条带,Ⅰ型和Ⅱ型应力甜点是泥岩裂缝型油藏的主要发育区,且具有页岩油产能。实际应力数据和钻探效果验证了方法的有效性,该方法可为非常规油藏勘探提供参考依据。
The late mesozoic granodiorites from the Southwest Basin in the South China Sea and its tectonic implication
[J].
DOI:10.1007/s12583-012-0252-7
URL
[本文引用: 1]

The southwest basin is a key to study the origin and development of the South China Sea(SCS).We do not know much about its boundaries,geological history,and the formation of its sea floor because it has a complex and highly re-gional structural background,notable sediment activity,and yet few floor rocks.Here a grano-diorite sample was collected from the southern margin of the southwest basin of the South China Sea.The results indicated that the 40Ar-39Ar ages of biotites in the sample are 110.3卤0.5 Ma,suggesting that they were prod-ucts of magmatic intrusion during the Early Cretaceous period.The sample's geochemistry showed it had high SiO2,K2O,and Al2O3 but low TiO2 levels.Tectonic discriminant diagrams suggested that the sample might represent extrusion-related magmatism,either in an arc or forearc setting in the SCS area and that the sample mainly belonged to the syncollision type,whose formation was related to orogenies.The sample may be part of the main rock that made up the boundaries of rift system.The process of tension cracking was similar to the development of the Red Sea,in which the rifting and sagging occurred in the continental crust.The southwest basin may not be an original ocean,but a rift developed through finite extension on continental crust basement.The oceanic crust came into being when the width and depth of the rift valley reached a certain scale.The granodiorite sample we collected provides a means of determining the boundary of the southwest basin and the clues that may help researchers expand relevant models.It constitutes an important datum regarding the analysis of the formation and development of the SCS.
Simulation of wave propagation in a fluid-filled borehole embedded in a cracked medium using a coupled BEM/TBEM formulation
[J].DOI:10.1785/0120090047 URL [本文引用: 1]
Distinguishing oil and water layers by interpreting acoustic logging data with changing well diameters
[J].
DOI:10.1111/1365-2478.12220
URL
[本文引用: 1]

ABSTRACT During surveys, water layers may interfere with the detection of oil layers. In order to distinguish between oil and water layers, research on the properties of well diameters and oil and water layers and their relation to acoustic logging rules is essential. Using Hudson's crack theory, we simulated oil and water layers with different well diameters or crack parameters (angle and number density). We found that when the well radius increases from 0.03 m to 0.05 m, the variation ratio of compressional wave amplitude for the oil layer is less than that for the water layer. The difference of Stoneley wave amplitude between the crack parameters (angle and number density) is greater in the case of the water layer than in the case of the oil layer. The response sensitivity of wave energy is greater for the water layer than that for the oil layer. When the well radius increases from 0.05 m to 0.14 m, the maximum excitation intensity for oil layer is greater than that for the water layer. We conclude that the propagation of an elastic wave is affected by medium composition and well diameter, and the influence has certain regularity. These results can guide further reservoir logging field exploration work.