|
|
|
| Synergistic optimization and on-site fine-tuning methods for sampling point arrangement for geochemical survey in an alpine gorge area, Southwest China |
ZENG Liang1,2( ), YANG Ming-Long1,2( ), YANG Ming-Long1,2( ), PANG Yong1,2, HUANG Jia-Zhong1,2, BAI Ping-Yan1,2, WANG Bing-Jun1,2 ), PANG Yong1,2, HUANG Jia-Zhong1,2, BAI Ping-Yan1,2, WANG Bing-Jun1,2 |
1. Kunming Comprehensive Natural Resources Investigation Center, China Geological Survey, Kunming 650000, China
2. Technology Innovation Center for Natural Ecosystem Carbon Sink, Ministry of Natural, Kunming 650000, China |
|
|
|
|
Abstract Stream sediment survey is the most widely applied method in regional geological surveys due to its simplicity, efficiency, low cost, and proven effectiveness in mineral exploration. This method shows promising application potential in Southwest China, characterized by well-developed hydrographic nets. Sampling quality directly determines the representativeness and accuracy of geochemical exploration data. However, sampling point arrangements in alpine gorge areas remain challenged by insufficient coverage of lower-order streams, omission of coarse-grained clastics in high-energy zones, and interference from human-induced contamination. To address these challenges, this study innovatively proposed an optimization strategy combining synergistic optimization and the on-site fine-tuning method for the 1∶50 000 stream sediment survey in the Fanshen Village area, Huize County, Yunnan Province. This strategy integrates critical technologies, including two-level dynamic grids (a 1 km×1 km basic grid and a 500 m infill grid), dynamic channel alignment offset (50 m to 100 m), and pre-set contamination buffer zones (200 m), for fieldwork. The results indicate that compared to traditional fixed-grid methods, the optimization strategy achieved a significantly increased coverage rate of 72% for tertiary tributaries, a capture rate of 82 % for coarse-grained clastics (>2 mm), and a reduced occurrence rate of 5% for human-induced pseudo-anomalies, with the overall cost increase controlled within 12%. Overall, the optimization strategy can effectively enhance the reliability of sampling data and the accuracy of anomaly delineation in complex topographic areas, providing an optimized solution for geochemical surveys in alpine gorge areas, Southwest China.
|
|
Received: 18 March 2025
Published: 30 December 2025
|
|
|
|
Corresponding Authors:
YANG Ming-Long
E-mail: zengliang3332022@163.com;351008671@qq.com
|
|
|
|
|
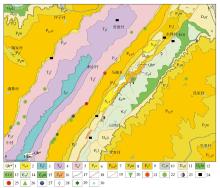
Geological sketch map of the Fanshen Village area
1—Holocene; 2—Xiaolongtan Formation; 3—Ziliujing Formation; 4—Jialingjiang Formation; 5—Feixianguan Formation; 6—Xuanwei Formation; 7—Emeishan basalt Formation; 8—Maokou Formation; 9—Liangshan Formation; 10—Wanshoushan Formation; 11—Zaijieshan Formation; 12—Hongshiya Formation; 13—Loushanguan Formation; 14—Longwangmiao Formation; 15—Meishucun Formation; 16—Dengying Formation; 17—measured unconformity boundary; 18—main fault; 19—measured fault of unknown nature; 20—phosphate deposit; 21—copper mineralization point; 22—lead-zinc mineralization point; 23—bauxite mineralization point; 24—anthracite mineralization point; 25—hematite mineralization point; 26—barite mineralization point; 27—rare earth mineralization point; 28—calcite mineralization point; 29—agate mineralization point; 30—place name
|
|
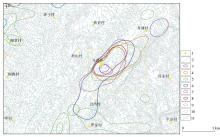
Water system distribution in the Fenshen Village area
1—village; 2—watercourse line; 3—lower limit of F anomaly (1000×10-6) delineation range; 4—lower limit of Ba anomaly (600×10-6) delineation range; 5—lower limit of Cd anomaly (1×10-6) delineation range; 6—lower limit of Pb anomaly (60×10-6) delineation range; 7—lower limit of Ag anomaly (0.12×10-6) delineation range; 8—lower limit of Zn anomaly (200×10-6) delineation range; 9—lower limit of Mo anomaly (3×10-6) delineation range; 10—lower limit of Sb anomaly (2×10-6) delineation range; 11—elevation contour line
|

| 测量网/m | 采样点数/个 | | 250×250 | 16 | | 333×333 | 9 | | 500×250 | 8 | | 500×200 | 10 | | 500×100 | 20 |
|
Reference network for soil geochemical measurements
|
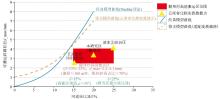
S>15% and α>35° indicates a high=energy transport zone, and an offset ≤100 m ensures the represent-ativeness of the medium (RD<20%)
">
|
Schematic diagram of the theoretical model of sampling bias in steep slope areas
note: according to A.N. Strahler's "Principles of Physical Geography", S>15% and α>35° indicates a high=energy transport zone, and an offset ≤100 m ensures the represent-ativeness of the medium (RD<20%)
|

| 地形标志 | 偏移方向 | 最大偏移量/m | 有效性保障措施 | V型谷(谷宽/
谷高<0.3) | 顺流向下游 | 100 | 优先选择基岩裸露河床段,采集底部砾石层 | U型谷(谷宽/
谷高≥0.3) | 垂直河道
两侧 | 80 | 增加2个辅助采样点,控制细粒沉积夹层 | 基岩裸露率
>60% | 任意方向 | 50 | 直接采集基岩风化碎屑,剔除风积物干扰 |
|
Decision guidelines for sampling offsets in steep slope areas
|
|
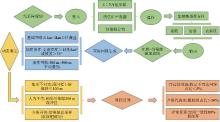
Methodological system technical processes
|

|
Layout of specimen points for typical geomorphological units in the study area
|
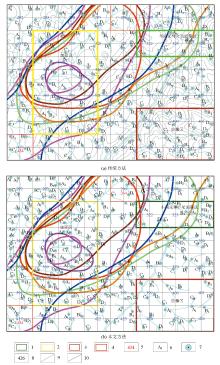
|
Comparison between the traditional method(a) and the “Co-optimisation-field fine-tuning method” (b) for the deployment of sample points of typical geomorphological units in the study area
1—different sampling medium zone ranges; 2—encryption zone ranges; 3—dilution zone ranges; 4—repeated sample large grid; 5—repeated sample large grid number; 6—small grid number annotation; 7—sampling point; 8—large grid number; 9—water system line; 10—elevation line
|

| 地貌类型 | 次级支流控制难点 | 本方法优化措施 | | 深切峡谷区 | 陡坡支流短小密
集,传统网格遗漏 | 500 m加密网格+下游偏移
补偿 | | 岩溶洼地区 | 季节性溪流沉积
中心偏移 | 间歇性/季节性流水双模式
采样(基岩露头+沉积物) | | 台地农耕区 | 农业活动导致的
金属元素迁移 | 预设200 m污染缓冲区
主动避开 |
|
Typical geomorphological unit method adaptation strategies
|

| 评价指标 | 传统方法 | 本方法 | 变化率 | 数据来源 | | 三级支流覆盖率 | 46.3% | 72% | +55.7% | 马生明等[17]
本研究 | | 粗粒碎屑捕获率 | 58% | 82% | +41.4% | 本研究 | | 浓集中心偏移误差 | 120~150 m | ≤50 m | -58.3% | 图6空间分析 | | 人为伪异常率 | 18% | 5% | -72.2% | 图2统计 | | 综合成本增幅 | 基准 | +12% | 可控优化 | 马生明等[17] |
|
Comparison of key indicators
|
| [1] |
李本茂, 叶丽梅, 王宝禄, 等. 云南省勘查地球化学方法及其应用[J]. 云南大学学报: 自然科学版, 2017, 39(S2):147-150.
|
| [1] |
Li B M, Ye L M, Wang B L, et al. Exploration geochemistry method and its application in Yunnan[J]. Journal of Yunnan University:Natural Sciences Edition, 2017, 39(S2):147-150.
|
| [2] |
姜俊野. 试论水系沉积物测量在找矿中的应用[J]. 黑龙江科技信息, 2013(9):45.
|
| [2] |
Jiang J Y. Discussion on the application of river sediment survey in ore prospecting[J]. Heilongjiang Science and Technology Information, 2013(9):45.
|
| [3] |
和成忠, 武睿, 郭军, 等. 云南待补镇—德泽镇一带地球化学特征及异常评价[J]. 物探与化探, 2020, 44(2):235-244.
|
| [3] |
He C Z, Wu R, Guo J, et al. Geochemical characteristics and anomaly evaluation in Daibu Town-Deze Town area,Yunnan Province[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2020, 44(2):235-244.
|
| [4] |
云南省地质调查局. 滇东北高山峡谷区地球化学勘查技术指南[M]. 昆明: 云南地质出版社, 2021.
|
| [4] |
Yunnan Provincial Bureau of Geological Survey. Technical guidelines for geochemical exploration in the high mountain gorge area of northeast Yunnan[M]. Kunming: Yunnan Geological Publishing House, 2021.
|
| [5] |
王学求. 勘查地球化学近十年进展[J]. 矿物岩石地球化学通报, 2013, 32(2):190-197.
|
| [5] |
Wang X Q. A decade of exploration geochemistry[J]. Bulletin of Mineralogy,Petrology and Geochemistry, 2013, 32(2):190-197.
|
| [6] |
中华人民共和国国土资源部. [S]. 2015.
|
| [6] |
Ministry of Land and Resources of the People's Republic of China. DZ/T 0011—2015 Specification of geochemical reconnaissance survey(1∶50,000)[S]. 2015.
|
| [7] |
赫帅. 湖南古台山1∶5万水系沉积物采样点位设计及实地采样经验[J]. 四川地质学报, 2024, 44(S1):153-156.
|
| [7] |
He S. Sampling site design and field sampling experience of 1∶50,000 stream sediments in Gutaishan,Hunan Province[J]. Acta Geologica Sichuan, 2024, 44(S1):153-156.
|
| [8] |
黄加忠. 普宜幅1∶5万水系沉积物地球化学特征及找矿方向[J]. 云南地质, 2024, 43(S1):365-376.
|
| [8] |
Huang J Z. Geochemical characteristics of 1∶50,000 stream sediments and prospecting direction in Puyi area[J]. Yunnan Geology, 2024, 43(S1):365-376.
|
| [9] |
杨少平, 弓秋丽, 文志刚, 等. 地球化学勘查新技术应用研究[J]. 地质学报, 2011, 85(11):1844-1877.
|
| [9] |
Yang S P, Gong Q L, Wen Z G, et al. Application research of the new technologies for geochemical survey[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2011, 85(11):1844-1877.
|
| [10] |
张文博, 郑冲. 水系沉积物地球化学测量在印宝山铅锌多金属矿勘查中的应用[J]. 低碳世界, 2023.10,43-45.
|
| [10] |
Zhang W B, Zheng C. Application of geochemical measurements of water system sediments in the exploration of the Yingbaoshan lead-zinc polymetallic mine[J]. Low Carbon World, 2023.10,43-45.
|
| [11] |
谢学锦. 区域化探全国扫面工作方法的讨论[J]. 物探与化探, 1979, 3(1):18-26.
|
| [11] |
Xie X J. Discussion on the national scanning method of regional geochemical exploration[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 1979, 3(1):18-26.
|
| [12] |
李博秦, 刘铭涛, 刘志军, 等. 西昆仑东段1∶5万水系沉积物测量粒度试验[J]. 矿产勘查, 2016, 7(4):667-675.
|
| [12] |
Li B Q, Liu M T, Liu Z J, et al. Granularity test in 1∶50,000 scale stream sediment survey in the eastern part of western Kunlun area[J]. Mineral Exploration, 2016, 7(4):667-675.
|
| [13] |
Flett H, Cohen D R, Dunlop A C. Significance of coarse-grained particles in geochemical surveys of stream sediments[J]. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 2020, 218:106623.
|
| [14] |
Quantitative analysis of watershed geomorphology[J]. Eos,Transactions American Geophysical Union, 1957, 38(6):913-920.
|
| [15] |
斯特拉勒A N. 自然地理学原理[M].李孝芳,译. 北京: 地质出版社, 1987.
|
| [15] |
Strale A N. Principles of physical geography[M].Translated by Li X F. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 1987.
|
| [16] |
张永三, 胡兆国, 刘静, 等. 水系沉积物测量在云南临沧地区离子吸附型稀土矿找矿中的应用[J]. 矿物学报, 2021, 41(2):171-180.
|
| [16] |
Zhang Y S, Hu Z G, Liu J, et al. Application of stream sediment survey for prospecting the ion adsorption type REE deposit in the Lincang area,Yunnan Province[J]. Acta Mineralogica Sinica, 2021, 41(2):171-180.
|
| [17] |
马生明, 朱立新, 周国华, 等. 高山峡谷区快速评价找矿靶区的化探方法技术[J]. 物探与化探, 2002, 26(3):185-191.
|
| [17] |
Ma S M, Zhu L X, Zhou G H, et al. Geochemical techniques for rapid appraisal of ore prospecting targets in high mountain and canyon areas[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2002, 26(3):185-191.
|
| [18] |
赵娟, 王泰山, 李德彪, 等. 青海祁漫塔格地区1∶5万水系沉积物测量方法技术及应用成果[J]. 地质与勘探, 2017, 53(4):739-745.
|
| [18] |
Zhao J, Wang T S, Li D B, et al. The techniques and application achievements in 1∶50,000 stream sediment survey of the qimantage area,Qinghai Province[J]. Geology and Exploration, 2017, 53(4):739-745.
|
| [19] |
姜俊野. 试论水系沉积物测量在找矿中的应用[J]. 黑龙江科技信息, 2013(9):45.
|
| [19] |
Jiang J Y. Discussion on the application of river sediment survey in ore prospecting[J]. Heilongjiang Science and Technology Information, 2013(9):45.
|
| [20] |
谢学锦. 勘查地球化学:发展史·现状·展望[J]. 地质与勘探, 2002, 38(6):1-9.
|
| [20] |
Xie X J. Exploration geochemistry:Retrospect and prospect[J]. Geology and Prospecting, 2002, 38(6):1-9.
|
| [1] |
XU Yun-Feng, HAO Xue-Feng, QIN Yu-Long, WANG Xian-Feng, XIONG Chang-Li, LI Ming-Ze, WU Weng-Hui, ZHAN Han-Yu. Geochemical characteristics of stream sediments and prospecting direction in Chahe area of Sichuan Province[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2021, 45(3): 624-638. |
| [2] |
HAN Deng-Hui, GAO Shun-Bao, ZHENG You-Ye, CHEN Xin, JIANG Xiao-Jia, GU Yan-Rong, YAN Chen-Chen. A processing technique of step effect in concentration-area multifractal method[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2020, 44(6): 1420-1428. |
|
|
|
|

