|
|
|
| Feature identification model and seismic reservoir prediction of channel turbidite bodies: A case study of the MC block,Lower Congo Basin,West Africa |
| GAO Jun1, XU Rui2, HUANG Jia-Chen1, YUAN Shu-Jin1 |
1. Research Institute of Petroleum Exploration & Production, PetroChina, Beijing 102206, China
2. China Petroleum Pipeline Engineering Co., Ltd.,PetroChina, Langfang 065000, China |
|
|
|
|
Abstract A typical channel turbidite system is developed in the deep-water area of the Lower Congo Basin,West Africa,establishing this area as a significant target for deep-water oil and gas exploration.Turbidite bodies in this area are characterized by strong heterogeneity and a complex reservoir distribution.Traditional methods show limited turbidite body identification accuracy and reservoir prediction ability,failing to support efficient exploration.This study investigated the channel turbidite system in this area based on the deep-water gravity flow theory.It established feature identification models for four kinds of channel turbidites at different scales.The models integrate the turbidite depositional site,accommodation space geometry,internal turbidite characteristics,and the rock,log,and seismic facies obtained through drilling.Furthermore,guided by the principle of facies-controlled reservoir distribution,new composite elastic parameters were constructed based on an improved ray-path elastic impedance inversion method.These parameters provided enhanced resolution for turbidite sandstone reservoirs,enabling a quantitative prediction of such reservoirs.Validation with post-test wells demonstrates high accuracy and favorable application outcomes.Overall,this study serves as a foundational guide for oil and gas resource assessments and well placement in similar deep-water areas.
|
|
Received: 24 February 2025
Published: 07 August 2025
|
|
|
|
|
|
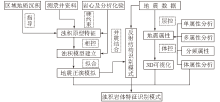
|
Technical flow of turbidite rock mass characteristic identification
|
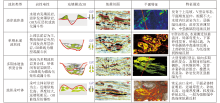
|
Feature recognition model of turbidite in the sea of Angola
|
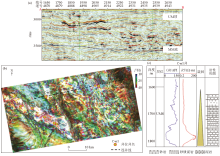
|
RGB fusion attribute map of seismic frequency and lithologic section of well C-n1
a—nearly east-west reflection seismic profile;b—RGB blended attribute from seismic spectral decomposition;c—well-traverse lithostratigraphic section
|
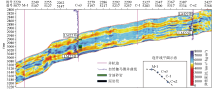
|
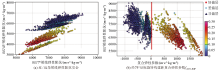
The ray-path elastic impedance inversion profile
|
|
A new AVO elastic impedance was constructed by plotting between the ray-path elastic impedances
|
|
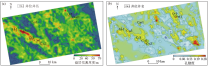
fAVO-IMP prediction turbidite sand thickness(a) and porosity(b) based on the ray-path elastic inversion
|
| [1] |
李相博, 刘化清, 杨田, 等. 深水重力流沉积与油气成藏[M]. 北京: 石油工业出版社, 2022.
|
| [1] |
Li X B, Liu H Q, Yang T, et al. Deep-water gravity flow deposition and hydrocarbon accumulation[M]. Beijing: Petroleum Industry Press, 2022.
|
| [2] |
朱伟林, 崔旱云, 吴培康, 等. 被动大陆边缘盆地油气勘探新进展与展望[J]. 石油学报, 2017, 38(10):1099-1109.
|
| [2] |
Zhu W L, Cui H Y, Wu P K, et al. New development and outlook for oil and gas exploration in passive continental margin basins[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2017, 38(10):1099-1109.
|
| [3] |
Reading H G, Richards M. Turbidite systems in deep-water basin margins classified by grain size and feeder system[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 1994, 78(5):792-822.
|
| [4] |
Kuenen P H, Migliorini. Turbidity currents as a cause of Graded bedding[J]. The Journal of Geology, 1950, 58(4):329-344.
|
| [5] |
Mennard H W. Deep-sea channels topography and sedimentation[J]. American Association of Petroleum Geologist Bulletin, 1955,39:236-255.
|
| [6] |
Bouma A H. Sedimentology of some flysch deposits[M]. Amsterdam,Netherland, Elsevier Pub,1962.
|
| [7] |
Normark W R. Growth patterns of deep sea fans[J]. American Association of Petroleum Geologists Bulletin, 1970,54:2170-2195.
|
| [8] |
Walker R G. Deep water sandstone facies and ancient submarine fans:Models for exploration of stratigraphic traps[J]. American Association of Petroleum Geologists Bul letin,1978.62:932-966.
|
| [9] |
庞雄, 陈长民, 朱明, 等. 深水沉积研究前缘问题[J]. 地质论评, 2007, 53(1):36-43.
|
| [9] |
Pang X, Chen C M, Zhu M, et al. Frontier of the deep-water deposition study[J]. Geological Review, 2007, 53(1):36-43.
|
| [10] |
蔡露露, 刘春成, 吕明, 等. 西非下刚果盆地深水水道发育特征及沉积储层预测[J]. 中国海上油气, 2016, 28(2):60-70.
|
| [10] |
Cai L L, Liu C C, Lyu M, et al. The development characteristics of deep water channel and sedimentary reservoir prediction in Lower Congo basin,West Africa[J]. China Offshore Oil and Gas, 2016, 28(2):60-70.
|
| [11] |
韩文明, 于水, 刘阳, 等. 复杂深水重力构造勘探研究新方法——以尼日尔三角洲深水区A构造为例[J]. 中国海上油气, 2012, 24(1):13-16.
|
| [11] |
Han W M, Yu S, Liu Y, et al. A new method to research complex gravity structures in deep water:A case of structure A in deep-water Niger Delta[J]. China Offshore Oil and Gas, 2012, 24(1):13-16.
|
| [12] |
张金淼, 韩文明, 范洪耀, 等. 西非深水区地震勘探关键技术研究及应用实践[J]. 中国海上油气, 2013, 25(6):43-47.
|
| [12] |
Zhang J M, Han W M, Fan H Y, et al. Some key techniques of seismic prospecting and their application in West Africa deep water region[J]. China Offshore Oil and Gas, 2013, 25(6):43-47.
|
| [13] |
廉桂辉, 朱亚婷, 王晓光, 等. 叠前反演技术在玛湖油田储层预测中的应用[J]. 特种油气藏, 2022, 29(1):80-84.
|
| [13] |
Lian G H, Zhu Y T, Wang X G, et al. Application of pre-stack inversion technology to reservoir prediction of Mahu Oilfield[J]. Special Oil & Gas Reservoirs, 2022, 29(1):80-84.
|
| [14] |
赵泽茜, 成丽芳, 范殿佐. 时变分频反褶积在提高薄砂体预测精度方面的应用[J]. 物探与化探, 2023, 47(6):1588-1594.
|
| [14] |
Zhao Z X, Cheng L F, Fan D Z. Application of time-varying frequency-division deconvolution in improving the prediction accuracy of thin sandbodies[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2023, 47(6):1588-1594.
|
| [15] |
Whitcombe D N. Elastic impedance normalization[J]. Geophysics, 2002, 67(1):60-62.
|
| [16] |
Ma J F, Morozov I B. Ray-path elastic impedance[R]. Calgary: Canadian Society of Exploration Geophysicists National Convention, 2004.
|
| [17] |
马劲风. 弹性阻抗EI意义的延伸与广义弹性阻抗[R]. 北京: CPS/SEG2004国际地球物理会议, 2004.
|
| [17] |
Ma J F. Extension of elastic impedance and generalized elastic impedance[R]. Beijing: CPS/SEG2004 Proceedings of International Geophysical Conference, 2004.
|
| [18] |
刘力辉, 王绪本. 一种改进的射线弹性阻抗公式及弹性参数反演[J]. 石油物探, 2011, 50(4):331-335,23.
|
| [18] |
Liu L H, Wang X B. One modified ray-path elastic impedance and elastic parameter inversion[J]. Geophysical Prospecting for Petroleum, 2011, 50(4):331-335,23.
|
| [1] |
YANG Guang, WANG Li-Xian, HU Jia, LIU Zhi-Jun, ZHANG Hong-Jie, WANG Yun-He, SUN Long, ZHANG Xu-Sheng, CHEN Yan-Hu. Application of the seismic meme inversion method in predicting superimposed thin sandstones: A case study of the Gaotaizi oil layer in the Qian'an oilfield,southern Songliao Basin[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2025, 49(4): 846-854. |
| [2] |
WANG Shu, WANG Rui, YANG Jia-Yi, ZHAO Wei-Sheng, LIAO Jian. High-resolution direct inversion of Poisson's impedance and fracture parameters using prestack seismic anisotropy data based on the non-stationary convolution model[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2025, 49(3): 642-652. |
|
|
|
|
