|
|
|
| Application of microtremor survey technology in shield tunnels passing through urban karst formations |
ZHANG Zhong1,2,3,4( ), FENG Wen-Cheng2,3,4, LIN Yang2,3,4 ), FENG Wen-Cheng2,3,4, LIN Yang2,3,4 |
1. School of Civil Engineering & Transportation, South China University of Technology, Guangzhou 510640, China
2. Guangzhou Construction Co., Ltd., Guangzhou 510640, China
3. Guangzhou Municipal Construction Group Co., Ltd., Guangzhou 510640, China
4. Guangzhou Dunjian Construction Co., Ltd., Guangzhou 510640, China |
|
|
|
|
Abstract Due to dense buildings and structures and insufficient drilling surveys, the construction of shield tunnels passing through urban karst formations that host dense buildings faces significant risks of surface fracturing and subsidence caused by karst development. Hence, this study employed the microtremor survey technology with strong anti-interference capability in complex environments to address this challenge. Based on the technology, it analyzed the structural characteristics of wave velocities in underground rock formations through the inversion of the apparent shear-wave velocity profile. Combined with geological drilling data, it inferred the bedrock interface, highly weathered unconsolidated formations, and karst cave anomaly zones. Key findings are as follows: (1) The apparent shear-wave velocities in the study area gradually increased from the shallow to deep formations. Formations with wave velocities above and below 300 m/s were inferred to be limestone and Quaternary formations, respectively, with the rock-soil interface at depths approximately between 10~15 m; (2) Seven low-value anomaly zones of apparent shear-wave velocities ranging from 150~240 m/s were interpreted. They were presumed to be unconsolidated formations or karst caves at depths ranging from 8~30 m. Relying on strong anti-interference and high accuracy, the microtremor survey technology can accurately identify the shear-wave velocity structures of underground profiles, lithologic interfaces of formations, unconsolidated formations, and karst cave anomalies. Therefore, the technology is effective in the geological exploration of urban dense building areas with karst development.
|
|
Received: 01 April 2024
Published: 22 April 2025
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
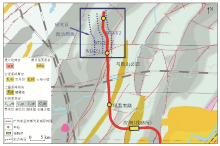
Structual geology of the study area and micro motion survey line layout
|

| 地层岩性 | 反演横波速度vs/(m·s-1) | | 第四系覆盖层 | 100~240 | | 强风化灰岩地层 | 150~300 | | 中、微风化灰岩地层 | >300 |
|
Stratigraphic shear wave velocity parameters
|
|
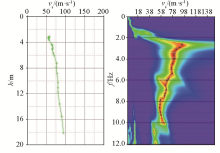
Typical measurement point dispersion curve
|
|
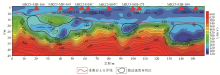
Contour map of apparent shear wave velocity in Y1 profile
|
|
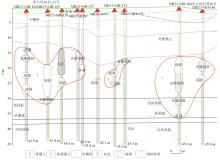
Interpretation of geological profile corresponding to Y1 profile
|

| 异常圈定溶洞深度 | 对应钻孔编录 | 对比验证 | 1号异常区
圈定13.7~29.6 m为溶洞 | 钻孔MRNZ3-MH-166,编录12.7~15 m揭示为溶洞,15~16.1 m揭示为石灰岩,16.1~18.4 m揭示为溶洞,18.4~22.1 m揭示为石灰岩,22.1~24 m揭示为溶洞,24~26.1 m揭示为石灰岩,26.1~29.6 m揭示为溶洞 | 基本准确 | 1号异常区
圈定19.2~32.7 m为溶洞 | 钻孔MRNZ3-MH-169,编录19.2~30.3 m揭示为溶洞,30.3~30.9 m揭示为石灰岩,30.9~32.7 m揭示为溶洞 | 基本准确 | 1号异常区
圈定13.5~27 m为溶洞 | 钻孔MRNZ3-MH-170,编录13.5~22.8 m揭示为溶洞,22.8~23.9 m揭示为石灰岩,23.9~27 m揭示为溶洞 | 基本准确 | 1号异常区
圈定15~24.7 m为溶洞 | 钻孔MRNZ2-B18C,编录15~18.7 m揭示为溶洞,18.7~24.7 m揭示为石灰岩 | 基本准确 | 1号异常区
圈定19~23.5 m为溶洞 | 钻孔MRNZ3-MH-172编录,19~19.4 m揭示为石灰岩,19.4~23.3 m揭示为溶洞,23.3~23.5 m揭示为石灰岩 | 基本准确 | 2号异常区
圈定21.2~26.5 m为溶洞 | 钻孔MRNZ3-MH-175,编录21.2~23.4 m揭示为溶洞,23.4~25.2 m揭示为石灰岩,25.2~26.5 m揭示为溶洞 | 基本准确 | 2号异常区
圈定17.6~19.6 m为溶洞 | 钻孔MRNZ3-MH-176,编录17.6~17.8 m揭示为石灰岩,17.8~19.6 m揭示为溶洞 | 基本准确 | 3号异常区
圈定17.2~38.5 m为溶洞 | 钻孔MRNZ3-MH-184,编录17.2~29.5 m揭示为溶洞,29.5~30.7 m为石灰岩,30.7~34 m揭示为溶洞,34~36.8 m揭示为石灰岩,36.8~38.5 m揭示为溶洞 | 基本准确 |
|
Comparison between abnormal areas and drilling records in Y1 profile
|
|
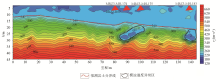
Contour map of apparent shear wave velocity in Z1 profile
|
|
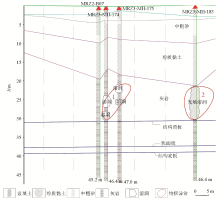
Interpretation of geological profile corresponding to Z1 profile
|

| 微动异常圈定溶洞深度 | 钻孔编录 | 对比验证 | 1号异常区
圈定24.3~30.6 m为溶洞 | 钻孔MRNZ3-MH-174,编录24.3~27.3 m揭示为溶洞,27.3~28.6 m揭示为石灰岩,28.6~30.6 m揭示为溶洞 | 基本准确 | 1号异常区
圈定21.2~26.5 m为溶洞 | 钻孔MRNZ3-MH-175,编录21.2~23.4 m揭示为溶洞,23.4~25.2 m揭示为石灰岩,25.2~26.5 m揭示为溶洞 | 基本准确 | 2号异常区
圈定22~30.8 m为溶洞 | 钻孔MRNZ3-MH-183,编录22~30.8 m揭示为溶洞 | 准确 |
|
Comparison between abnormal areas and drilling records in Z1 profile
|
|
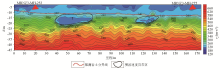
Contour map of apparent shear wave velocity in Y2 profile strata
|
|
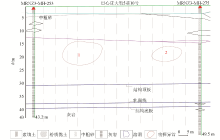
Interpretation of geological profile corresponding to Y2 profile
|

| 剖面 | 序号 | 异常里程/m | 异常深度/m | 钻探编录 | Y1
剖面 | 1号异常 | 15~65 | 15~30 | 验证基本准确 | | 2号异常 | 90~105 | 8~26 | 验证基本准确 | | 3号异常 | 130~155 | 18~34 | 验证基本准确 | Z1
剖面 | 4号异常 | 80~105 | 19~30 | 验证基本准确 | | 5号异常 | 135~145 | 22~31 | 验证基本准确 | Y2
剖面 | 6号异常 | 40~70 | 11~22 | 无验证 | | 7号异常 | 115~135 | 13~21 | 无验证 |
|
Abnormalities in geophysical exploration of karst caves
|
| [1] |
张雯, 张磊, 朱尚明. 新型微动探测技术在砂卵石复合地层盾构隧道中的应用[J]. 兰州工业学院学报, 2023, 30(6):74-79.
|
| [1] |
Zhang W, Zhang L, Zhu S M. Application of new micromotion detection technology in shield tunnel of sandy cobble composite stratum[J]. Journal of Lanzhou Institute of Technology, 2023, 30(6):74-79.
|
| [2] |
李安源, 谢绍彬, 龙秀洁, 等. 微动探测方法在城市深部探测中的应用——以广州南沙区三维深地探测项目为例[J]. 矿产与地质, 2023, 37(6):1264-1270.
|
| [2] |
Li A Y, Xie S B, Long X J, et al. Application of micro motion detection method in urban deep exploration:An example of 3D deep exploration project in Nansha District of Guangzhou[J]. Mineral Resources and Geology, 2023, 37(6):1264-1270.
|
| [3] |
姚金, 徐佩芬, 凌甦群, 等. 地铁线路采空区微动剖面法探测研究——以广州地铁14号线二期为例[J]. 地球物理学报, 2023, 66(10):4279-4289.
|
| [3] |
Yao J, Xu P F, Ling S Q, et al. Research on microtremor profile method to detection of goaf along subway line:A case study in the second phase of subway line 14[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2023, 66(10):4279-4289.
|
| [4] |
邱振东, 郭长宝, 杨志华, 等. 基于微动探测的四川德达古滑坡空间结构特征与形成机理研究[J]. 地质力学学报, 2024, 3(31):1-17.
|
| [4] |
Qiu Z D, Guo C B, Yang Z H, et al. Study on the spatial structural characteristics and formation mechanism of the Dedagu landslide in Sichuan Based on micro motion detection[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 2024, 3(31):1-17.
|
| [5] |
李华, 王东辉, 张伟, 等. 地球物理方法在城市地质结构精细化探测中最优方法组合研究——以成都市天府新区为例[J]. 中国地质, 2023, 50(6):1691-1704.
|
| [5] |
Li H, Wang D H, Zhang W, et al. The application effect of geophysical method in fine exploration of urban geological structure and study of optimal combination method:A case study of Tianfu New Area in Chengdu,Sichuan Province[J]. Geology in China, 2023, 50(6):1691-1704.
|
| [6] |
卓启亮, 于强. 微动探测方法在城市工程地质勘察中的应用[J]. 工程地球物理学报, 2020, 17(5):658-664.
|
| [6] |
Zhuo Q L, Yu Q. The application of microtremor survey method in urban engineering geological investigation[J]. Chinese Journal of Engineering Geophysics, 2020, 17(5):658-664.
|
| [7] |
刘志清, 赵振国, 李添才, 等. 山区公路微动探测方法应用试验研究[J]. 地球物理学进展, 2023, 38(2):823-831.
|
| [7] |
Liu Z Q, Zhao Z G, Li T C, et al. Research for the application of microtremor survey method to high-way construction in mountainous areas[J]. Progress in Geophysics, 2023, 38(2):823-831.
|
| [8] |
林朝旭. 地铁盾构区间孤石与基岩凸起等不良地质体探测新方法[J]. 工程地球物理学报, 2018, 15(4):432-439.
|
| [8] |
Lin C X. A new method to detect adverse geological such as bodies and boulder bedrock bulge etc in urban metro shield construction[J]. Chinese Journal of Engineering Geophysics, 2018, 15(4):432-439.
|
| [9] |
李应战, 计鹏, 张德强, 等. 综合物探技术在城市轨道交通不良地质体探测中的应用分析[J]. 工程地球物理学报, 2023, 20(4):471-479.
|
| [9] |
Li Y Z, Ji P, Zhang D Q, et al. Application analysis of comprehensive investigation technology in the detection of unfavorable geological bodies in urban railway engineering[J]. Chinese Journal of Engineering Geophysics, 2023, 20(4):471-479.
|
| [10] |
蔡祖华, 刘宏岳, 郑金伙, 等. 微动技术在城市地下病害体探测中的应用研究[J]. 工程地球物理学报, 2021, 18(6):893-902.
|
| [10] |
Cai Z H, Liu H Y, Zheng J H, et al. Research and application of micromotion technology in the detection of urban underground disease body[J]. Chinese Journal of Engineering Geophysics, 2021, 18(6):893-902.
|
| [11] |
杜亚楠, 徐佩芬, 凌甦群. 土石混合滑坡体微动探测:以衡阳拜殿乡滑坡体为例[J]. 地球物理学报, 2018, 61(4):1596-1604.
|
| [11] |
Du Y N, Xu P F, Ling S Q. Microtremor survey of soil-rock mixture landslides:An example of Baidian township,Hengyang City[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2018, 61(4):1596-1604.
|
| [12] |
田宝卿, 丁志峰. 微动探测方法研究进展与展望[J]. 地球物理学进展, 2021, 36(3):1306-1316.
|
| [12] |
Tian B Q, Ding Z F. Review and prospect prediction for microtremor survey method[J]. Progress in Geophysics, 2021, 36(3):1306-1316.
|
| [1] |
WANG He-Yu, WU Guo-Peng, CHEN Guo-Xiong, CHAI Jian-Zhou, MAO Jie, WANG De-Tao. Microtremor survey-based investigation of deep geothermal- and water-controlling structures in the Salt Lake geothermal field, Yuncheng City, Shanxi Province, China[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2025, 49(1): 32-40. |
| [2] |
ZHANG Ji-Wei, TAN Hui. Quasi-two-dimensional joint inversion of the data from the controlled source audio-frequency magnetotellurics and the microtremor survey[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2024, 48(4): 1094-1102. |
|
|
|
|

