|
|
|
| Bedrock surface and fault structures in the Rongcheng uplift revealed from reflection seismic profiles and their implications for the geothermal origin |
LIU Hong-Kai1( ), GAO Lei1, ZHANG Jie2, HOU He-Sheng1, XIE Min-Ying3, LI Hong-Qiang1( ), GAO Lei1, ZHANG Jie2, HOU He-Sheng1, XIE Min-Ying3, LI Hong-Qiang1( ) ) |
1. Chinese Academy of Geological Sciences, Beijing 100037,China
2. Institute of Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, Chinese Academy of Geological Sciences, Langfang 065000, China
3. China Aero Geophysical Survey and Remote Sensing Center for Natural Resources, Beijing 100083, China |
|
|
|
|
Abstract The Rongcheng uplift in North China boasts abundant geothermal resources. Research indicates that the Rongcheng uplift exhibits significantly different physical properties between the bedrock surface and the overlying Cenozoic strata. Moreover, the bedrock surface serves as the primary top boundary of the geothermal reservoir in the Wumishan Formation. Investigating the fine-scale structures, burial depths, and faults of the bedrock surface in the Rongcheng uplift holds critical significance for understanding the distribution and enrichment of geothermal resources in the area and guiding their exploration and production. Through elaborative processing of the north-south reflection seismic profile data of the Rongcheng uplift, collected by the Chinese Academy of Geological Sciences in 2018, this study obtained the high-precision geometric structure of the Rongcheng uplift within a depth of 4 km. The geometric structure was calibrated using geothermal borehole data before interpretation. Key findings are as follows: (1) The Cenozoic sedimentary strata overlying the bedrock surface of the Rongcheng uplift exhibit a nearly horizontal layered distribution, serving as cap rocks of the Rongcheng geothermal field; (2) The bedrock surface of the Rongcheng uplift manifests burial depths ranging from 700 to 3 000 m, with gentle changes in the central portion, and rapidly deepening to around 3 000 m towards the periphery; (3) The Niunan and Rongdong faults converge in the deep part, constituting a fault system along with other medium and small faults, thus facilitating the conduction of water and heat; (4) The geometric structure of the Rongcheng uplift on the bedrock surface contributes to the convergence of heat flow beneath the uplift.
|
|
Received: 25 July 2023
Published: 19 September 2024
|
|
|
|
|
|
23])
">
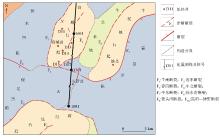
|
Rongcheng tectonic unit and main fault distribution map(revised according to reference[23])
|
13,24])
">

|
Comprehensive drilling histogram of Rongcheng uplift(revised according to references [13,24])
|

| 采集系统 | 检波器
主频/Hz | 检波点
间距/m | 炮点
深度/m | 接收
道数 | 记录长
度/s | 最小偏
移距/m | 最大偏
移距/km | 炮间距/m | 覆盖次数 | 药量/kg | 采样间
隔/ms | | Sercel 428XL | 10 | 40 | 30~45 | 720 | 30 | 40 | 14.38 | 80 | 180 | 10~18 | 2 |
|
Parameters of Rongcheng uplift reflection seismic profile data
|
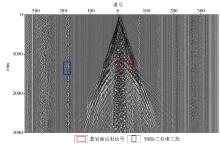
|
Original single-shot record map(within 3 s)
|
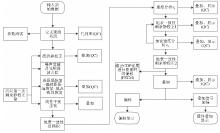
|
Reflection seismic data processing flow
|
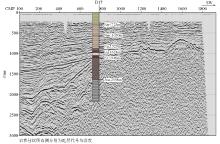
|
The reflection seismic migration profile of Rongcheng uplift
|
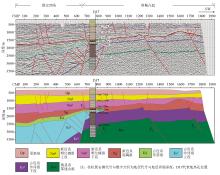
|
seismic reflection profile interpretation map
|
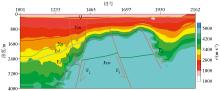
|
P-wave velocity profile of Rongcheng uplift
|
| [1] |
邱楠生, 许威, 左银辉, 等. 渤海湾盆地中—新生代岩石圈热结构与热—流变学演化[J]. 地学前缘, 2017, 24(3):13-26.
|
| [1] |
Qiu N S, Xu W, Zuo Y H, et al. Evolution of Meso-Cenozoic thermal structure and thermal-rheological structure of the lithosphere in the Bohai Bay Basin,eastern North China Craton[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2017, 24(3):13-26.
|
| [2] |
王贵玲, 高俊, 张保建, 等. 雄安新区高阳低凸起区雾迷山组热储特征与高产能地热井参数研究[J]. 地质学报, 2020, 94(7):1970-1980.
|
| [2] |
Wang G L, Gao J, Zhang B J, et al. Study on the thermal storage characteristics of the Wumishan Formation and huge capacity geothermal well parameters in the Gaoyang low uplift area of Xiong’an New Area[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2020, 94(7):1970-1980.
|
| [3] |
陈墨香, 黄歌山, 张文仁, 等. 冀中牛驼镇凸起地温场的特点及地下热水的开发利用[J]. 地质科学, 1982, 17(3):239-252.
|
| [3] |
Chen M X, Huang G S, Zhang W R, et al. The temperature distribution pattern and the utilization of geothermal water at Niutuozhen basement protrusion of central Hebei Province[J]. Chinese Journal of Geology, 1982, 17(3):239-252.
|
| [4] |
马峰, 王贵玲, 张薇, 等. 雄安新区容城地热田热储空间结构及资源潜力[J]. 地质学报, 2020, 94(7):1981-1990.
|
| [4] |
Ma F, Wang G L, Zhang W, et al. Structure of geothermal reservoirs and resource potential in the Rongcheng geothermal field in Xiong’an New Area[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2020, 94(7):1981-1990.
|
| [5] |
朱日祥, 徐义刚, 朱光, 等. 华北克拉通破坏[J]. 中国科学:地球科学, 2012, 42(8):1135-1159.
|
| [5] |
Zhu R X, Xu Y G, Zhu G, et al. Destruction of the North China Craton[J]. Sci China Earth Sci, 2012, 42(8):1135-1159.
|
| [6] |
常健, 邱楠生, 赵贤正, 等. 渤海湾盆地冀中坳陷现今地热特征[J]. 地球物理学报, 2016, 59(3):1003-1016.
|
| [6] |
Chang J, Qiu N S, Zhao X Z, et al. Present-day geothermal regime of the Jizhong depression in Bohai Bay Basin,East China[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2016, 59(3):1003-1016.
|
| [7] |
王凯, 张杰, 白大为, 等. 雄安新区地热地质模型探究:来自地球物理的证据[J]. 中国地质, 2021, 48(5):1453-1468.
|
| [7] |
Wang K, Zhang J, Bai D W, et al. Geothermal-geological model of Xiongan New Area:Evidence from geophysics[J]. Geology in China, 2021, 48(5):1453-1468.
|
| [8] |
郭世炎, 李小军. 河北保定容城凸起地热田储层属性与资源潜力[J]. 地质科学, 2013, 48(3):922-931.
|
| [8] |
Guo S Y, Li X J. Reservoir stratum characterstics and geothermal resources potential of Rongcheng uplift geothermal field in Baoding,Hebei[J]. Chinese Journal of Geology:Scientia Geologica Sinica, 2013, 48(3):922-931.
|
| [9] |
高锐, 周卉, 卢占武, 等. 深地震反射剖面揭露青藏高原陆—陆碰撞与地壳生长的深部过程[J]. 地学前缘, 2022, 29(2):14-27.
|
| [9] |
Gao R, Zhou H, Lu Z W, et al. Deep seismic reflection profile reveals the deep process of continent-continent collision on the Tibetan Plateau[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2022, 29(2):14-27.
|
| [10] |
陈墨香, 汪集旸, 汪缉安, 等. 华北断陷盆地热场特征及其形成机制[J]. 地质学报, 1990, 64(1):80-91.
|
| [10] |
Chen M X, Wang J Y, Wang J A, et al. The characteristics of the geothermal field and its formation mechanism in the North China down-faulted basin[J]. Acta Geological Sinica, 1990, 64(1):80-91.
|
| [11] |
唐博宁, 朱传庆, 邱楠生, 等. 雄安新区雾迷山组岩溶裂隙发育特征[J]. 地质学报, 2020, 94(7):2002-2012.
|
| [11] |
Tang B N, Zhu C Q, Qiu N S, et al. Characteristics of the Karst thermal reservoir in the Wumishan Formation in the Xiong’an New Area[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2020, 94(7):2002-2012.
|
| [12] |
孙冬胜, 刘池阳, 杨明慧, 等. 渤海湾盆地冀中坳陷中区中新生代复合伸展构造[J]. 地质论评, 2004, 50(5):484-491.
|
| [12] |
Sun D S, Liu C Y, Yang M H, et al. Study on complex extensional structures in the middle Jizhong depressionin the Bohai Bay basin[J]. Geological Review, 2004, 50(5):484-491.
|
| [13] |
何登发, 单帅强, 张煜颖, 等. 雄安新区的三维地质结构:来自反射地震资料的约束[J]. 中国科学:地球科学, 2018, 48(9):1207-1222.
|
| [13] |
He D F, Shan S Q, Zhang Y Y, et al. 3D geologic architecture of Xiongan New Area:Constraints from seismic reflection data[J]. Scientia Sinica:Terrae, 2018, 48(9):1207-1222.
|
| [14] |
翟明国. 华北克拉通的形成演化与成矿作用[J]. 矿床地质, 2010, 29(1):24-36.
|
| [14] |
Zhai M G. Tectonic evolution and metallogenesis of North China Craton[J]. Mineral Deposits, 2010, 29(1):24-36.
|
| [15] |
于福生, 漆家福, 王春英. 华北东部印支期构造变形研究[J]. 中国矿业大学学报, 2002, 31(4):402-406.
|
| [15] |
Yu F S, Qi J F, Wang C Y. Tectonic deformation of indosinian period in eastern part of North China[J]. Journal of China University of Mining & Technology, 2002, 31(4):402-406.
|
| [16] |
安美建, 赵越, 冯梅, 等. 什么控制了华北克拉通东部在新近纪的构造活动?[J]. 地学前缘, 2011, 18(3):121-140.
|
| [16] |
An M J, Zhao Y, Feng M, et al. What resulted in new tectonic activities in the eastern North China Craton in the Neogene?[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2011, 18(3):121-140.
|
| [17] |
朱日祥, 陈凌, 吴福元, 等. 华北克拉通破坏的时间、范围与机制[J]. 中国科学:地球科学, 2011, 41(5):583-592.
|
| [17] |
Zhu R X, Chen L, Wu F Y, et al. Timing,scale and mechanism of the destruction of the North China Craton[J]. Sci China Earth Sci, 2011, 41(5):583-592.
|
| [18] |
商世杰, 丰成君, 谭成轩, 等. 雄安新区附近主要隐伏断裂第四纪活动性研究[J]. 地球学报, 2019, 40(6):836-846.
|
| [18] |
Shang S J, Feng C J, Tan C X, et al. Quaternary activity study of major buried faults near Xiongan new area[J]. Acta Geoscientica Sinica, 2019, 40(6):836-846.
|
| [19] |
梁苏娟. 冀中坳陷晚新生代地质构造特征及其油气赋存[D]. 西安: 西北大学, 2001.
|
| [19] |
Liang S J. The Characteristics of Tectonics and Hydrocarbon Accumulation of Jizhong Depression in late Cenozoic era[D]. Xi’an: Northwest University, 2001.
|
| [20] |
索艳慧, 李三忠, 曹现志, 等. 中国东部中新生代反转构造及其记录的大洋板块俯冲过程[J]. 地学前缘, 2017, 24(4):249-267.
|
| [20] |
Suo Y H, Li S Z, Cao X Z, et al. Mesozoic-Cenozoic inversion tectonics of East China and its implications for the subduction process of the oceanic plate[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2017, 24(4):249-267.
|
| [21] |
胡秋韵, 高俊, 马峰, 等. 雄安新区容城凸起区地热可采资源量动态预测[J]. 地质学报, 2020, 94(7):2013-2025.
|
| [21] |
Hu Q Y, Gao J, Ma F, et al. Dynamic prediction of geothermal recoverable resources in the Rongcheng uplift area of the Xiong’an New Area[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2020, 94(7):2013-2025.
|
| [22] |
戴明刚, 雷海飞, 胡甲国, 等. 雄安新区顶面埋深在3500m以浅的中元古界热储可采地热资源量和开发参数评估[J]. 地质学报, 2019, 93(11):2874-2888.
|
| [22] |
Dai M G, Lei H F, Hu J G, et al. Evaluation of recoverable geothermal resources and development parameters of Mesoproterozoic thermal reservoir with the top surface depth of 3500 m and shallow in Xiongan New Area[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2019, 93(11):2874-2888.
|
| [23] |
黄元溢, 孟凡厚, 张占恩, 等. 雄安新区深部结构三维探测——雄安新区深地震反射剖面数据采集与常规处理项目采集施工总结[R]. 中国石油集团东方地球物理勘探有限责任公司, 2018.
|
| [23] |
Huang Y Y, Meng F H, Zhang Z E, et al. 3 D detection of deep structure in Xiongan New Area:The collection and construction summary of deep seismic reflection profile data collection and routine processing project in Xiongan New Area[R]. China National Petroleum Corporation. 2018.
|
| [24] |
单帅强. 太行山山前断层的构造几何学、运动学及其对渤海湾盆地发育的控制作用[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学(北京), 2018.
|
| [24] |
Shan S Q. Structural geometry and kinematics of the Taihang Mountain piedmont fault and its controlling on the development of the Bohai Bay basin[D]. Beijing: China University of Geosciences, 2018.
|
| [25] |
马岩, 张保建, 闫金凯, 等. 雄安新区深部储热构造探测研究与地热井优选技术[J]. 地球学报, 2022, 43(5):699-710.
|
| [25] |
Ma Y, Zhang B J, Yan J K, et al. Deep geothermal reservoir structure detection and geothermal well optimization technology in Xiongan new area[J]. Acta Geoscientica Sinica, 2022, 43(5):699-710.
|
| [26] |
鲁锴, 鲍志东, 季汉成, 等. 雄安新区蓟县系雾迷山组岩溶热储特征、主控因素及有利区预测[J]. 古地理学报, 2019, 21(6):885-900.
|
| [26] |
Lu K, Bao Z D, Ji H C, et al. Characteristics,main controlling factors and favorable area prediction of karstic geothermal reservoirs of the Jixianian Wumishan Formation in Xiongan New Area[J]. Journal of Palaeogeography, 2019, 21(6):885-900.
|
| [27] |
王贵玲, 李郡, 吴爱民, 等. 河北容城凸起区热储层新层系——高于庄组热储特征研究[J]. 地球学报, 2018, 39(5):533-541.
|
| [27] |
Wang G L, Li J, Wu A M, et al. A study of the thermal storage characteristics of Gaoyuzhuang Formation,A new layer system of thermal reservoir in Rongcheng uplift area,Hebei Province[J]. Acta Geoscientica Sinica, 2018, 39(5):533-541.
|
| [28] |
熊亮萍, 高维安. 隆起与拗陷地区地温场的特点[J]. 地球物理学报, 1982, 25(5):448-456.
|
| [28] |
Xiong L P, Gao W A. Characteristics of geotherm in uplift and depression[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 1982, 25(5):448-456.
|
| [29] |
熊亮平, 张菊明. 热流的折射和再分配的数学模拟[J]. 地质科学, 1984, 19(4):445-454.
|
| [29] |
Xiong L P, Zhang J M. Mathematical simulation of refract and redistribution of heat flow[J]. Chinese Journal of Geology, 1984, 19(4):445-454.
|
| [1] |
WANG Guo-Jian, HU Wen-Hui, LI Guang-Zhi, ZHU Huai-Ping, HU Bin, XIAO Peng-Fei, ZHANG Ying. Geochemical characteristics and formation mechanism of thermal spring water in the Chuhe fault zone in Anhui Province[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2024, 48(5): 1223-1231. |
| [2] |
WU Yang, ZHAO Fu-Yuan, HU Xin-Jun, CHEN Xiao-Jing, BU Jin-Bing, GUO Shao-Peng. Electrical structure characteristics and geothermal exploration directions of the upper crust on the eastern margin of the Yinchuan Basin[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2024, 48(5): 1258-1267. |
|
|
|
|

