|
|
|
| Post-stack P-wave impedance inversion based on spectral inversion |
XING Wen-Jun( ), CAO Si-Yuan, CHEN Si-Yuan, SUN Yao-Guang ), CAO Si-Yuan, CHEN Si-Yuan, SUN Yao-Guang |
| College of Geosciences,China University of Petroleum,Beijing 102249,China |
|
|
|
|
Abstract Based on spectral inversion,this study proposed a p-wave impedance inversion algorithm for post-stack seismic data to improve inversion accuracy.Spectral inversion is widely used in high-resolution seismic inversion and the reflection coefficient inversion.Based on the odd-even decomposition of reflection coefficients,spectral inversion can reduce the tuning effect between thin layers and enhance the resolution of inverted data volumes.However,the calculation of p-wave impedance using reflection coefficients is ill-posed, and the step-by-step inversion of p-wave impedance tends to introduce a large cumulative error.Therefore,this study proposed a post-stack p-wave impedance inversion method based on spectral inversion.This method introduced the objective equation constrained by TV regularization and calculated the relative p-wave impedance using the iterative method.Then,the absolute p-wave impedance was determined through the frequency-domain fusion of the relative p-wave impedance and the pre-built low-frequency model.As demonstrated by the model and actual data,the method proposed in this study has a higher inversion resolution than the impedance inversion based on sparse-spike deconvolution and is more conducive to subsequent research such as reservoir prediction.
|
|
Received: 18 May 2022
Published: 27 April 2023
|
|
|
|
|
|
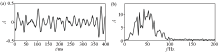
|
Synthetic signal in time domain and its amplitude spectrum
a—signal in time domain;b—amplitude spectrum
|
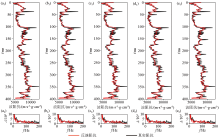
|
Regularization parameter tests
a—regularization parameter:5e-5;b—regularization parameter:1e-4;c—regularization parameter:5e-4;d—regularization parameter:1e-3;e—regularization parameter:5e-3
|
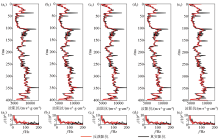
|
Upper limit frequency tests
a—upper limit frequency:120 Hz;b—upper limit frequency:135 Hz;c—upper limit frequency:150 Hz;d—upper limit frequency:165 Hz;e—upper limit frequency:180 Hz
|
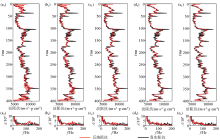
|
Pre-whiten factor parameter tests
a—pre-whiten factor:0.005;b—pre-whiten factor:0.01;c—pre-whiten factor:0.02;d—pre-whiten factor:0.04;e—pre-whiten factor:0.08
|
|
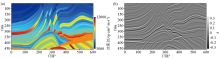
Partial Marmousi2 model and corresponding synthetic record
a—partial Marmousi2 model;b—synthetic record
|
|
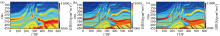
Low-frequency model and acoustic impedance inversion results
a—low-frequency model;b—the proposed method;c—recursive inversion of sparse spike deconvolution
|
|
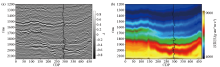
Field data and low-frequency model
a—field data;b—low-frequency model
|
|
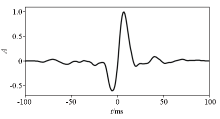
Wavelet
|
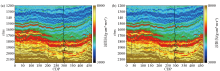
|
Acoustic impedance inversion results before fx-Decon
a—the proposed method;b—recursive inversion of sparse spike deconvolution
|
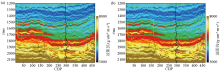
|
Acoustic impedance inversion results after fx-Decon
a—the proposed method;b—recursive inversion of sparse spike deconvolution
|
| [1] |
刘喜武, 年静波, 吴海波. 几种地震波阻抗反演方法的比较分析与综合应用[J]. 世界地质, 2005, 24(3):270-275.
|
| [1] |
Liu X W, Nian J B, Wu H B. Comparison of seismic impedance inversion methods and an application case[J]. Global Geology, 2005, 24(3):270-275.
|
| [2] |
Geyer C J. Practical Markov chain Monte Carlo[J]. Statistical Science, 1992:473-483.
|
| [3] |
张广智, 王丹阳, 印兴耀, 等. 基于MCMC的叠前地震反演方法研究[J]. 地球物理学报, 2011, 54(11):2926-2932.
|
| [3] |
Zhang G Z, Wang D Y, Yin X Y, et al. Study on prestack seismic inversion using Markov Chain Monte Carlo[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2011, 54(11):2926-2932.
|
| [4] |
Vestergaard P D, Mosegaard K. Inversion of post-stack seismic data using simulated annealing[J]. Geophysical Prospecting, 1991, 39(5):613-624.

|
| [5] |
Haas A, Dubrule O. Geostatistical inversion:a sequential method of stochastic reservoir modeling constrained by seismic data[J]. First Break, 1994, 12(11):561-569.
|
| [6] |
Le Ravalec M, Noetinger B, Hu L Y. The FFT moving average(FFT-MA) generator:An efficient numerical method for generating and conditioning Gaussian simulations[J]. Mathematical Geology, 2000, 32(6):701-723.

|
| [7] |
王保丽, 印兴耀, 丁龙翔, 等. 基于FFT-MA谱模拟的快速随机反演方法研究. 地球物理学报, 2015, 58(2):664-673.
|
| [7] |
Wang B L, Yin X Y, Ding L X, et al. Study of fast stochastic inversion based on FFT-MA spectrum simulation[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2015, 58(2):664-673.
|
| [8] |
王治强, 曹思远, 陈红灵, 等. 基于TV约束和Toeplitz矩阵分解的波阻抗反演[J]. 石油地球物理勘探, 2017, 52(6):1193-1199.
|
| [8] |
Wang Z Q, Cao S Y, Chen H L, et al. Wave impedance inversion based on TV regularization and Toeplitz-sparse matrix factorization[J]. Oil Geophysical Prospecting, 2017, 52(6):1193-1199.
|
| [9] |
Cooke D A, Schneider W A. Generalized linear inversion of reflection seismic data[J]. Geophysics, 1983, 48(6):665-676.

|
| [10] |
Lancaster S, Whitcombe D. Fast-track “colored” inversion[C]// SEG Technical Program Expanded Abstracts, 2000:1572-1575.
|
| [11] |
Taylor H L, Banks S C, Mocoy J F. Deconvolution with the L1-norm[J]. Geophysics, 1979, 44(1):39-52.

|
| [12] |
夏红敏, 刘兰锋, 张显辉, 等. 地震数据谱反演压缩感知算法实现及应用[J]. 石油地球物理勘探, 2021, 56(2):295-301.
|
| [12] |
Xia H M, Liu L F, Zhang X H, et al. Implementation and application of compressed sensing algorithm for seismic spectrum inversion[J]. Oil Geophysical Prospecting, 2021, 56(2):295-301.
|
| [13] |
宋磊, 印兴耀, 宗兆云, 等. 基于先验约束的深度学习地震波阻抗反演方法[J]. 石油地球物理勘探, 2021, 56(4):716-727.
|
| [13] |
Song L, Yin X Y, Zong Z Y, et al. Deep learning seismic impedance inversion based on prior constraints[J]. Oil Geophysical Prospecting, 2021, 56(4):716-727.
|
| [14] |
王泽峰, 许辉群, 杨梦琼, 等. 时域卷积神经网络地震波阻抗反演因素影响的研究[J]. 地球物理学进展, 2022, 37(5):280-289.
|
| [14] |
Wang Z F, Xu H Q, Yang M Q, et al. Study on the influence of preprocessing and hyperparameters on Temporal convolutional network seismic impedance inversion[J]. Progress in Geophysics, 2022, 37(5):280-289.
|
| [15] |
印兴耀, 刘晓晶, 吴国忱, 等. 模型约束基追踪反演方法[J]. 石油物探, 2016, 55(1):115-122.
|
| [15] |
Yin X Y, Liu X J, Wu G C, et al. Basis pursuit inversion method under model constraint[J]. Geophysical Prospecting for Petroleum, 2016, 55(1):115-122.
|
| [16] |
边国柱, 张立群. 地震数据的谱白化处理[J]. 石油物探, 1986, 25(2):26-33.
|
| [16] |
Bian G Z, Zhang L Q. Spectral whitening of seismic data[J]. Geophysical Prospecting for Petroleum, 1986, 25(2):26-33.
|
| [17] |
孙雷鸣, 曾维辉, 方中于. 地震薄层反射系数谱反演算法研究及应用[J]. 物探化探计算技术, 2014, 36(4):462-470.
|
| [17] |
Sun L M, Zeng W H, Fang Z Y. Thin-bed reflectivity inversion and seismic application[J]. Computing Techniques for Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2014, 36(4):462-470.
|
| [18] |
迟唤昭, 刘财, 单玄龙, 等. 谱反演方法在致密薄层砂体预测中的应用研究[J]. 石油物探, 2015, 54(3):337-344.
|
| [18] |
Chi H Z, Liu C, Shan X L, et al. Application of spectral inversion for tight thin-bed sand body prediction[J]. Geophysical Prospecting for Petroleum, 2015, 54(3):337-344.
|
| [19] |
Donoho D L. Compressed sensing[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 2006, 52(4):1289-1306.

|
| [20] |
Wang Y H. Inverse Q-filter for seismic resolution enhancement[J]. Geophysics, 2006, 71(3):V51-V60.

|
| [21] |
Chen S Y, Cao S Y, Sun Y G, et al. Nonstationary spectral inversion of seismic data[C] // SEG Technical Program Expanded Abstracts, 2021:2934-2938.
|
| [22] |
Wang L Q, Zhou H, Wang Y F, et al. Three-parameter prestack seismic inversion based on L1-2 minimization[J]. Geophysics, 2019, 84(5):R753-R766.
|
| [23] |
Liu J, Zhang J, Huang Z. Accurate estimation of acoustic impedance based on spectral inversion[J]. Geophysical Prospecting, 2018, 66(1):169-181.

|
| [24] |
Boyd S, Parikh N, Chu E. Distributed optimization and statistical learning via the alternating direction method of multipliers[J]. Foundations and Trends in Machine Learning, 2010, 3(1):1-122.

|
| [25] |
Martin G S, Wiley R, Marfurt K J. Marmousi2:An elastic upgrade for Marmousi[J]. Lead. Edge, 2006, 25(2):156-166.

|
| [1] |
ZHU Jian-Bing, GAO Zhao-Qi, TIAN Ya-Jun, LIANG Xing-Cheng. Globally optimized seismic impedance inversion with lateral constraints and its application[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2022, 46(6): 1477-1484. |
| [2] |
WAN Xiao-Ming, LIANG Jing, LIANG Jin-Qiang, LIN Lin, SHA Zhi-Bin, CHAI Yi, CAI Zhen-Hua. The application of post-stack impedance inversion without well to the prediction of gas hydrate distribution in T study area[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2016, 40(3): 438-444. |
|
|
|
|

