|
|
|
| Effects of well types on the visco-acoustic reverse time migration based on borehole seismics |
WANG Ji-Chuan( ), GU Bing-Luo, LI Zhen-Chun ), GU Bing-Luo, LI Zhen-Chun |
| School of Geosciences,China University of Petroleum (East China),Qingdao 266580,China |
|
|
|
|
Abstract The current hydrocarbon exploration targets are concealed,scattered,thin,and small.These characteristics put forward higher requirements for the migration imaging technique.Owing to the special acquisition method,the data derived from borehole seismic have the advantages of high resolution,rich wave field information,and less interference.In theory,borehole seismic can be used to realize high-precision imaging of complex reservoirs,such as concealed,scattered,thin and small ones around the well.Well types greatly limit the layout of the seismic sources.In practice,besides vertical wells,there are also many types of wells,such as inclined wells,curved inclined wells,and horizontal wells.For different well types,the seismic sources at the same depth have different positions and the same number of seismic sources have different spatial distributions,leading to significantly different seismic wave propagation paths and further affecting the imaging quality.However,there is no qualitative or quantitative understanding of the effects of well types on migration imaging currently.Using the visco-acoustic inverse time migration imaging method,this study analyzed the effects of well types on migration quality by comparing the seismic migration imaging results of theoretical models under various well types.The numerical results provide the qualitative relationships between well types and borehole seismic migration imaging quality and effective imaging range.The results also provide corresponding theoretical support for the design of a borehole seismic acquisition system.
|
|
Received: 29 September 2021
Published: 03 January 2023
|
|
|
|
|
|
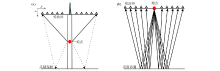
|
Schematic diagram of 2D borehole seismic(a) and ground seismic(b) observation system
|
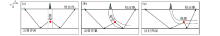
|
Propagation path of seismic wave in well
a—schematic diagram of vertical well path;b—schematic diagram of curved inclined shaft path;c—schematic diagram of horizontal well path
|
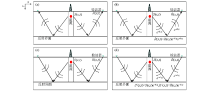
|
Principles of wavefield propagation and reverse time migration in boreholes seismic
a—forward continuation of wave field in non attenuating medium;b—forward continuation of wave field in attenuating medium;c—acoustic inverse time migration;d—Q compensation inverse time migration
|
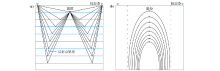
|
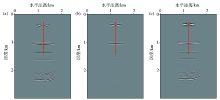
Seismic ray path(a) and coverage map with different excitation depth(b) in well
|
|
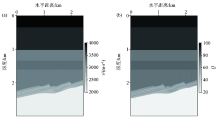
Veolocity model(a) and Q model(b) of sand-shale thin interbed
|
|
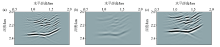
Reverse time migration profile of thin interbedded model
a—acoustic migration profile;b—viscoelastic uncompensated migration profile;c—migration profile after viscoelastic compensation
|
|
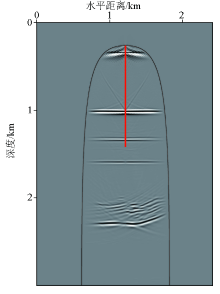
Partial enlarged view of reverse time migration profile of thin interbedded model
a—acoustic migration profile;b—viscoelastic uncompensated migration profile;c—migration profile after viscoelastic compensation
|
|
Reverse time migration reference profile of thin interbedded model
|
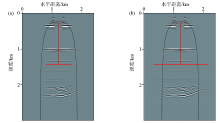
|
Reverse time migration profile of horizontal well with thin interbed model
a—horizontal well section with 500 m;b—horizontal well section with 1 000 m
|
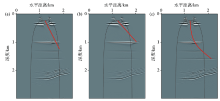
|
Reverse time migration profile of right inclined well in thin interbedded model
a—offset profile with slope of 0.5;b—offset profile with slope of 1;c—offset profile of right inclined shaft
|
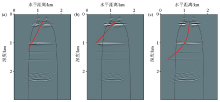
|
Reverse time migration profile of left inclined well in thin interbedded model
a—offset profile with slope of -0.5;b—offset profile with slope of -1;c—offset profile of left inclined shaft
|
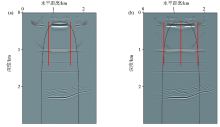
|
Reverse time migration profile in thin interbed model with multiple wells
a—double well migration profile;b—mitsui migration profile
|
| [1] |
何海清, 范土芝, 郭绪杰, 等. 中国石油 “十三五” 油气勘探重大成果与 “十四五” 发展战略[J]. 中国石油勘探, 2021, 26(1): 17-30.
|
| [1] |
He H Q, Fan T Z, Guo X J, et al. PetroChina: Major achievements in oil and gas exploration during the 13th Five-Year Plan period and development strategy for the 14th Five-Year Plan[J]. China Petroleum Exploration, 2021, 26(1): 17-30.
|
| [2] |
何登发, 李德生, 童晓光, 等. 中国沉积盆地油气立体综合勘探论[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2021, 42(2):265-284.
|
| [2] |
He D F, Li D S, Tong X G, et al. Integrated 3D hydrocarbon exploration in sedimentary basins of China[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2021, 42(2): 265-284.
|
| [3] |
杨勤勇, 杨江峰, 王咸彬, 等. 中国石化物探技术新进展及发展方向思考[J]. 中国石油勘探, 2021, 26(1): 121-130.
|
| [3] |
Yang Q Y, Yang J F, Wang X B, et al. Sinopec:Progress and development direction of geophysical prospecting technology[J]. China Petroleum Exploration, 2021, 26(1): 121-130.
|
| [4] |
Weatherby B B. Method of making sub-surface determinations[P]. US, US2062151,1936-11-24.
|
| [5] |
Deily F H, Dareing D W, Paff G H, et al. Downhole measurements of drill string forces and motions[J]. Journal of Engineering for Industry, 1968, 90(2):217-225.

|
| [6] |
Squire W D, Alsup J M. Linear signal processing and Ultrasonic transversal filters[J]. IEEE Transactions on Microwave Theory & Techniques, 1969, 17(11):1020-1040.

|
| [7] |
Haldorsen J, Miller D E, Walsh J J. Walk-away VSP using drill noise as a source[J]. Geophysics, 1995, 60(4):978.

|
| [8] |
杨微. 随钻地震信号检测方法研究[D]. 北京: 中国地震局地球物理研究所, 2007.
|
| [8] |
Yang W. Single detection of the drill bit seismic wave whlie drilling[D] .Beijing: Institute of Geophysics,China Earthquake Administration, 2007.
|
| [9] |
吕海川, 朱伟伦, 贾衡天, 等. 随钻VSP测量中地震波场的数值模拟[J]. 石油机械, 2017, 45(2):10-12,44.
|
| [9] |
Lyu H C, Zhu W L, Jia H T, et al. Numerical simulation of seismic wave field in VSP-WD[J]. China Petroleum Machinery, 2017, 45(2):10-12,44.
|
| [10] |
Liang Z H. Wavefield processing of reverse VSP data[J]. SEG Technical Program Expanded Abstracts, 1991, 10(1):1646.
|
| [11] |
胡建平. 变偏移距VSP射线追踪模型[J]. 西安工程学院学报, 1998, 20(S1):10-13.
|
| [11] |
Hu J P. Walkaway VSP ray tracing model[J] .Journal of Earth Sciences and Environment, 1998, 20(S1):10-13.
|
| [12] |
朱龙生. 多方位角逆VSP层析成像[D]. 西安: 长安大学, 2003.
|
| [12] |
Zhu L S. Multi-azimuth Inverse VSP tomography[D] .Xi'an: Chang’an University, 2003.
|
| [13] |
胡明顺. 煤层气RVSP地震勘探成像方法研究[D]. 北京: 中国矿业大学, 2013.
|
| [13] |
Hu M S. Study on RVSP Seismic Imaging for Coalbed Methane Exploration[D] .Beijing: China University of Mining and Technology, 2013.
|
| [14] |
金红娣, 潘冬明, 杨光. RVSP等效地面处理方法研究[J]. 地球物理学进展, 2015, 30(2):641-649.
|
| [14] |
Jin H D, Pan D M, Yang G. Study on equivalent surface data processing method in RVSP[J] .Progress in Geophysics, 2015, 30(2):641-649.
|
| [15] |
张辉. 碳酸岩裸露区煤田RVSP勘探技术研究与应用[D]. 北京: 中国矿业大学, 2018.
|
| [15] |
Zhang H. Research and application of RVSP exploration technology in Carbonate exposed coalfield[D] .Beijing: China University of Mining and Technology, 2018.
|
| [16] |
Hu M S, Pan D M, Zhou F B, et al. Multi-hole joint acquisition of a 3D-RVSP in a karst area:Case study in the Wulunshan Coal Field,China[J]. Appl. Geophys., 2020, 17:37-53.

|
| [17] |
邹才能, 张国生, 杨智, 等. 非常规油气概念, 特征, 潜力及技术——兼论非常规油气地质学[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2013, 40(4): 385-399,454.
|
| [17] |
Zou C N, Zhang G S, Yang Z, et al. Geological concepts, characteristics, resource potential and key techniques of unconventional hydrocarbon:On unconventional petroleum geology[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2013, 40(4): 385-399,454.
|
| [18] |
范廷恩, 余连勇, 杨飞龙, 等. 斜井 VSP 高斯射线束正演方法[J]. 中国海上油气, 2014, 26(5):30-35.
|
| [18] |
Fan T E, Yu L Y, Yang F L, et al. A method of Gaussian beam forward modeling in deviated-well VSP[J]. China Offshore Oil and Gas, 2014, 26(5):30-35.
|
| [19] |
刘财, 冯晅, 张瑾. 稳定的迭代法反Q滤波[J]. 石油地球物理勘探, 2013, 48(6):890-895.
|
| [19] |
Liu C, Feng X, Zhang J. A stable inverse Qfiltering using the iterative filtering method[J]. OGP, 2013, 48(6):890-895.
|
| [20] |
吴吉忠, 杨晓利, 龙洋. 一种稳定高效的等效Q值反Q滤波算法及应用[J]. 石油地球物理勘探, 2016, 51(1): 63-70.
|
| [20] |
Wu J Z, Yang X L, Long Y. A robust approach of inverse Q filtering with equivalent Q[J]. OGP, 2016, 51(1):63-70.
|
| [21] |
Hale D. Q-adaptive deconvolution[J]. SEG Technical Program Expanded Abstracts, 1982:82-83.
|
| [22] |
Hargreaves N D. Similarity and the inverse Q filter:Some simple algorithms for inverse Q filtering[J]. Geophysics, 1992, 57(7): 944-947.

|
| [23] |
Deng F, McMechan G A. Viscoelastic true-amplitude prestack reverse-time depth migration[J]. Geophysics, 2008, 73(4):S143-S155.

|
| [24] |
Dutta G, Schuster G T. Attenuation compensation for least-squares reverse time migration using the viscoacoustic-wave equation[J]. Geophysics, 2014, 79(6): S251-S262.

|
| [25] |
Bai J, Chen G, Yingst D, et al. Attenuation compensation in viscoacoustic reverse time migration[J]. SEG Technical Program Expanded Abstracts, 2013:3825-3830.
|
| [26] |
Tian K, Huang J, Bu C, et al. Viscoacoustic reverse time migration by adding a regularization term[C]// New Orleans:2015 SEG Annual Meeting, 2015:4127-4131.
|
| [27] |
田坤, 张学涛, 李国磊. 添加正则化项的黏声逆时偏移成像方法研究[J]. CT 理论与应用研究, 2017, 26(6):669-677.
|
| [27] |
Tian K, Zhang X T, Li G L. Viscoacoustic reverse time migration by adding a regularization term[J]. Computerized Tomography Theory and Applications, 2017, 26(6):669-677.
|
| [28] |
Kjartansson E. Constant Q-wave propagation and attenuation[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research:Solid Earth, 1979, 84(B9):4737-4748.
|
| [29] |
Zhang Y, Zhang P, Zhang H. Compensating for visco-acoustic effects in reverse-time migration[M]// SEG Technical Program Expanded Abstracts, 2010:3160-3164.
|
| [30] |
Zhu T, Harris J M. Modeling acoustic wave propagation in heterogeneous attenuating media using decoupled fractional Laplacians[J]. Geophysics, 2014, 79(3):S165-S174.
|
| [31] |
吴玉, 符力耘, 陈高祥. 基于分数阶拉普拉斯算子解耦的黏声介质地震正演模拟与逆时偏移[J]. 地球物理学报, 2017, 60(4): 1527-1537.
|
| [31] |
Wu Y, Fu L Y, Chen G X. Forward modeling and reverse time migration of viscoacoustic media using decoupled fractional Laplacians[J]. Chinese J. Geophys., 2017, 60(4):1527-1537.
|
| [32] |
Zhu T, Harris J M. Improved seismic image by Q-compensated reverse time migration:Application to crosswell field data, west Texas[J]. Geophysics, 2015, 80(2):B61-B67.

|
| [33] |
罗文山, 陈汉明, 王成祥, 等. 时间域黏滞波动方程及其数值模拟新方法[J]. 石油地球物理勘探, 2016, 51(4):707-713.
|
| [33] |
Luo W S, Chen H M, Wang C X, et al. A novel time-domain viscoacoustic wave equation and its numerical simulation[J]. OGP, 2016, 51(4):707-713.
|
| [34] |
Hu W, Zhou T, Ning J. An efficient Q-RTM algorithm based on local differentiation operators[M]// SEG Technical Program Expanded Abstracts, 2016:4183-4187.
|
| [35] |
Li Q, Zhou H, Zhang Q, et al. Efficient reverse time migration based on fractional Laplacian viscoacoustic wave equation[J]. Geophysical Journal International, 2016, 204(1):488-504.

|
| [36] |
Sun J, Zhu T. Strategies for stable attenuation compensation in reverse-time migration[J]. Geophysical Prospecting, 2018, 66(3):498-511.

|
| [37] |
Zhao Y, Mao N, Ren Z. A stable and efficient approach of Q reverse time migration[J]. Geophysics, 2018, 83(6):S557-S567.

|
| [38] |
冀国强, 石颖. 正则化形式的稳定粘声逆时偏移成像方法[J]. 石油物探, 2020, 59(3):374-381.
|
| [38] |
Ji G Q, Shi Y. Stable and regularized visco-acoustic reverse time migration[J]. Geophysical Prospecting for Petroleum, 2020, 59(3):374-381.
|
| [39] |
陈汉明, 汪燚林, 周辉. 一阶速度—压力常分数阶黏滞声波方程及其数值模拟[J]. 石油地球物理勘探, 2020, 55(2): 302-310.
|
| [39] |
Chen H M, Wang Y L, Zhou H. A novel constant fractional-order Laplacians viscoacoustic wave equation and its numerical simulation method[J]. OGP, 2020, 55(2): 302-310.
|
| [40] |
Liu Y, Sen M K. A hybrid scheme for absorbing edge reflections in numerical modeling of wave propagation[J]. Geophysics, 2010, 75(2): A1-A6.

|
| [1] |
XI Yu-He, WANG Hong-Hua, WANG Yu-Cheng, WU Qi-Ming. Application of the minimum entropy method based on a velocity-controlled moving window to the reverse time migration of ground-penetrating radars[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2023, 47(5): 1250-1260. |
| [2] |
XU Lei-Liang, ZHAO Guo-Yong, ZHANG Jian, ZHONG Tian-Miao, GU Jia-Ying, YOU Jian, QU Ying-Ming. Joint Q-compensated least-squares reverse time migration using primary and diffracted waves[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2023, 47(1): 91-98. |
|
|
|
|

