|
|
|
| Turbidite reservoir identification technology based on prestack multi-parameter sensitivity factor fusion |
SHANG Wei( ), ZHANG Yun-Yin, KONG Xing-Wu, LIU Feng ), ZHANG Yun-Yin, KONG Xing-Wu, LIU Feng |
| Geophysical Research Institute of Shengli Oilfield Company,SINOPEC,Dongying 257000,China |
|
|
|
|
Abstract Turbidite reservoirs have always been an important exploration type in the Jiyang depression.After years of exploration and development,the turbidites are mainly of the heterogeneous isomorphic type.The sandstone reservoirs of this type of turbidites have similar velocity,density,and seismic waveforms to those of non-reservoirs and thus are difficult to identify using conventional seismic attributes and poststack impedance.Therefore,a reservoir description method based on prestack multi-parameter sensitivity factor fusion was established.This method mainly included three steps.Firstly,major factors affecting the accuracy of shear wave estimation were analyzed,and then the multi-mineral-component shear wave prediction technology based on a modified xu-white model was established to improve the accuracy of shear wave prediction and lay a foundation for the accurate prediction of elastic parameters. Secondly,a quantitative evaluation method of sensitivity factors was proposed based on reflection coefficient ratios to obtain three sensitive elastic parameters,namely Murho,Lambrho,and POIS.The fusion index F of sensitivity factors was constructed by using the three elastic parameters.The purpose is to reduce the strong multiplicity of solutions of a single parameter and accurately identify rock properties.Thirdly,the prestack inversion technology was used for the inversion of sensitive elastic parameters.The three sensitivity parameters of sandstone information were fused using the fusion model of the RGB primary color information to realize a fine-scale prediction of lithology.This method was applied to the exploration of a deep-water turbidite reservoir around well-Tuo-71 in the Jiyang depression.The distribution of deep-water turbidite fan reservoirs in the study area was accurately predicted.The coincidence degree between the prediction results and the actual drilling reached 85%,indicating the improved accuracy of reservoir identification and description.The results of this study have contributed to an interpreted favorable sand body area of 9.5 km2 and the deployment of more than 10 exploration and development wells.Among these wells,five have yielded industrial oil flow after competition and being put into operation,and their new production capacity is expected to be 2×104 t。
|
|
Received: 24 August 2021
Published: 17 August 2022
|
|
|
|
|
|

| 矿物成分 | 孔隙
度φ | 含水饱
和度Sw | 灰岩孔
隙纵横
比αca | 砂岩孔
隙纵横
比αsa | 泥岩孔
隙纵横
比αsh | 速度 | 密度
ρ/(g·cm-3) | 灰岩
含量Vca | 砂岩
含量Vsa | 泥质
含量Vsh | 纵波速度
vp/(m·s-1) | 横波速度
vs/(m·s-1) | | 参数值 | 0.4 | 0.3 | 0.3 | 0.2 | 0.5 | 0.12 | 0.05 | 0.09 | 2742 | 1651.5 | 2.307 |
|
Model trial data
|

| 矿物成分 | 孔隙度φ | 流体替换 | 孔隙纵横比 | | Vca | Vsa | Vsh | Sw | Sg | So | αca | αsa | αsh | | 0~0.6 | 0.3 | 1-Vca-Vsa | 0.1~0.5 | 0.1~1 | 0 | 1-Sw-Sg | 0.02~0.2 | 0.06~0.12 | 0.03~0.07 |
|
Parameter setting of shear wave prediction
|
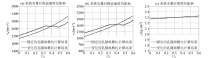
|
The effect of limy content on P-wave velocity,S-wave velocity and density
|
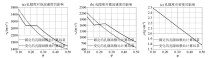
|
Effect of porosity on P-wave velocity,S-wave velocity and density
|
|
Influence of water saturation on P-wave velocity,S-wave velocity and density
|
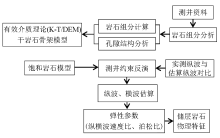
|
Flow chart of petrophysical modeling
|
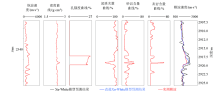
|
The map of predicted shear wave in Y926-x1 well
|

| 序号 | 岩性
因子 | 砂岩 | 泥岩 | 砂岩—泥岩
识别因子 | 灰质泥岩 | 砂岩—灰质岩
识别因子 | | 1 | 纵波速度vp/(m·s-1) | 3.80×103 | 2.90×103 | 0.134 | 3.10×103 | 0.101 | | 2 | 横波速度vs/(m·s-1) | 1.70×103 | 1.50×103 | 0.063 | 1.60×103 | 0.030 | | 3 | 密度ρ/(g·cm-3) | 2.50×103 | 2.27×103 | 0.048 | 2.40×103 | 0.020 | | 4 | 纵波阻抗Zp/[(kg·m-3)(m·s-1)] | 9.50×106 | 6.58×106 | 0.181 | 7.44×106 | 0.122 | | 5 | 横波阻抗Zs/[(kg·m-3)(m·s-1)] | 4.25×106 | 3.41×106 | 0.110 | 3.84×106 | 0.051 | | 6 | 纵横波速度比vp/vs | 2.24 | 1.93 | 0.072 | 1.94 | 0.071 | | 7 | 泊松比σ | 3.75×10-1 | 3.17×10-1 | 0.083 | 3.18×10-1 | 0.081 | | 8 | 体积模量K/MPa | 3.61×1010 | 1.91×1010 | 0.308 | 2.77×1010 | 0.220 | | 9 | 剪切阻抗μ/(Pa·kg·m-3) | 7.23×109 | 5.11×109 | 0.172 | 6.14×109 | 0.081 | | 10 | 拉梅阻抗λρ/(kg2·m-4·s-2) | 7.22×1013 | 3.17×1013 | 0.389 | 4.06×1013 | 0.280 | | 11 | 剪切阻抗μρ/(Pa·kg·m-3) | 1.81×1013 | 1.16×1013 | 0.218 | 1.47×1013 | 0.101 | | 12 | 杨氏模量E/(N·m-2) | 1.99×1010 | 1.35×1010 | 0.192 | 1.62×1010 | 0.102 | | 13 | 拉梅系数λ | 3.61×1010 | 1.91×1010 | 0.308 | 2.31×1010 | 0.220 |
|
13 Kinds of lithological identification factors
|

| 参数 | 砂岩 | 泥岩 | R | 灰质泥岩 | R | | 体积模量K/MPa | 3.61×1010 | 1.91×1010 | 0.308 | 2.31×1010 | 0.220 | | 纵波阻抗Zp/[(kg·m-3)·(m·s-1)] | 9.50×106 | 6.58×106 | 0.181 | 7.44×106 | 0.122 | | 拉梅阻抗λρ/(kg2·m-4·s-2) | 7.22×1013 | 3.17×1013 | 0.389 | 4.06×1013 | 0.280 | | 岩性信息融合指数F | 1.23 | 2.92×10-1 | 0.616 | 5.17×10-1 | 0.408 |
|
|
|
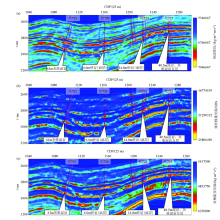
|
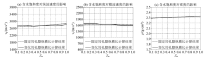
Three sensitive elastic parameter profiles
a—longitudinal wave impedance;b—bulk modulus profile;c—Lame impedance profile
|
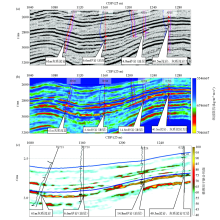
|
Comparison of profile effect
|
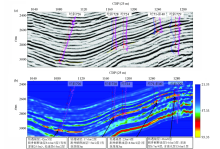
|
Comparison of profile effect
|
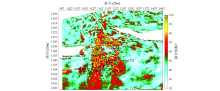
|
Favorable reservoir prediction diagram
|
| [1] |
孙淑艳, 朱应科, 沈正春. 东营凹陷东部浊积岩储层地震识别技术及描述思路[J]. 油气地球物理, 2015, 3(2):1-6.
|
| [1] |
Sun S Y, Zhu Y K, Sheng Z C. Seismic identification technology and description ideas of the turbid rock reservoir in dongying depression[J]. Petroleum Geophysics, 2015, 3(2):1-6.
|
| [2] |
张营革. 能量半衰时属性在浊积岩储层预测中的应用研究[J]. 石油物探, 2013, 52(6):662-668.
|
| [2] |
Zhang Y G. The application of energy half-time attribute to turbidite reservoir prediction[J]. Geophysical Prospecting for Petroleum, 2013, 52(6):662-668.
|
| [3] |
董文波, 刘恩君, 杨洪, 等. 地震属性在克拉玛依油田滑塌浊积岩圈闭勘探中的应用[J]. 工程地球物理学报, 2011, 8(1):87-90.
|
| [3] |
Dong W B, Liu E J, Yang H, et al. Application of seismic attribute technology to the fluxoturbidite reservoir exploration of Kara-may oilfield[J]. Chinese Journal of Engineering Geophysics, 2011, 8(1):87-90.
|
| [4] |
于正军, 董冬冬, 余红, 等. 浊积岩分序级描述技术及其在东营凹陷油气勘探中的应用[J]. 地球物理学进展, 2012, 27(3):1086-1093.
|
| [4] |
Yu Z J, Dong D D, Yu H, et al. The technology of turbidite different-level sequence description and its application to the oil exploration in the Dongying Sag[J]. Progress in Geophysics, 2012, 27(3):1086-1093.
|
| [5] |
孔省吾, 张云银, 沈正春, 等. 波形指示反演在灰质发育区薄互层浊积岩预测中的应用——以牛庄洼陷沙三中亚段为例[J]. 物探与化探, 2020, 44(3):665-671.
|
| [5] |
Kong X W, Zhang Y Y, Sheng Z C, et al. The application of waveform inversion Prediction of thin turbidite reservoir to calcareous depositional area:A case study of E3s23 in Niuzhuang sag[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2020, 44(3):665-671.
|
| [6] |
王慧勇, 陈世悦, 张云银, 等. 东营凹陷浊积岩优质储层预测技术[J]. 石油地球物理勘探, 2014, 49(4):776-783.
|
| [6] |
Wang H Y, Chen S Y, Zhang Y Y, et al. Turibidite high-quality reservoir prediction in Dongying depression[J]. OGP, 2014, 49(4):776-783.
|
| [7] |
陈昌. 兴隆台构造带沙河街组三段浊积岩优质储层叠前地震预测[J]. 大庆石油地质与开发, 2017, 36(1):144-149.
|
| [7] |
Chen C. Pre-stack seismic prediction of the high-quality turbidite reservoir in E3s3 of Xinglongtai structural belt[J]. Petroleum Geology and Oilfield Development in Daqing, 2017, 36(1):144-149.
|
| [8] |
周游, 高刚, 桂志先, 等. 灰质发育背景下识别浊积岩优质储层的技术研究——以东营凹陷董集洼陷为例[J]. 物探与化探, 2017, 41(5):899-906.
|
| [8] |
Zhou Y, Gao G, Gui Z X, et al. Study on the identification of turbidite high-quality reservoirs under gray background: A case study in dongji sag of Dongying depression[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2017, 41(5):899-906.
|
| [9] |
于正军. 灰质背景下浊积岩储层地震响应特征及识别方法——以东营凹陷董集洼陷为例[J]. 油气地质与采收率, 2014, 21(2):95-97.
|
| [9] |
Yu Z J. Seismic response characteristics and recognition method of turbidite under carbonate depositional environment: A case in Dongji sag of Dongying sag[J]. Petroleum Geology and Recovery Efficiency, 2014, 21(2):95-97.
|
| [10] |
商伟. 灰质地层发育区浊积岩的地震识别技术研究及应用——以dj洼陷为例[J]. 当代石油石化, 2017, 25(4):25-30.
|
| [10] |
Shang W. Research and application of seismic identification technology for Turbidite in Ash Formation development area:Using dj depression as an example[J]. Petroleum and Petrochemical Today, 2017, 25(4):25-30.
|
| [11] |
印兴耀, 张世鑫, 张翻昌, 等. 利用基于Russell近似的弹性波阻抗反演进行储层描述和流体识别[J]. 石油地球物理勘探, 2010, 45(3):373-380.
|
| [11] |
Yin X Y, Zhang S X, Zhang F C, et al. Utilizing russell approximation based elastic wave impedance inversion to conduct reservoir description and fluid identification[J]. OGP, 2010, 45(3):373-380.
|
| [12] |
张建芝, 李谋杰, 张云银, 等. 灰质背景下浊积岩储层地震响应特征及识别方法[J]. 油气地质与采收率, 2019, 26(6):70-79.
|
| [12] |
Zhang J Z, Li M J, Zhang Y Y, et al. Seismic response characteristics and identification methods of turbidite reservoir in limestone background:A case study of well Tuo71 area in Dongying sag[J]. Petroleum Geology and Recovery Efficiency, 2019, 26(6):70-79.
|
| [13] |
沈禄银, 潘仁芳, 谢冰, 等. 多信息融合的页岩油储层自动分层技术[J]. 中国石油勘探, 2016, 21(5):110-116.
|
| [13] |
Shen L Y, Pan R F, Xie B, et al. Automatic layering of shale oil reservoir with multiple information[J]. China Petroleum Exploration, 2016, 21(5):110-116.
|
| [1] |
XIE Rui, YAN Jian-Guo, CHEN Qi. Prestack inversion of anisotropic coefficients and its application in fracture prediction[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2022, 46(4): 968-976. |
| [2] |
LIU Hao-Jie, CHEN Yu-Mao, WANG Yan-Guang, ZONG Zhao-Yun, WU Guo-Chen, HOU Qing-Jie. Prestack four-parameter synchronous inversion method based on viscoelastic medium theory and its applications[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2021, 45(1): 140-148. |
|
|
|
|

