|
|
|
| Preliminary exploration into the monitoring technology for distributed weak electric field during hydraulic fracturing for shale gas extraction |
WU Wen1( ), WANG Meng1,2( ), WANG Meng1,2( ), YANG Di-Kun3, CHEN Mo1, REN Lin-Bin1 ), YANG Di-Kun3, CHEN Mo1, REN Lin-Bin1 |
1. School of Geophysics and Information Technology, China University of Geosciences(Beijing), Beijing 100083,China
2. State Key Laboratory of Geological Processes and Mineral Resources, China University of Geosciences(Beijing), Beijing 100083, China
3. Department of Earth and Space Sciences,Southern University of Science and Technology,Shenzhen 518055,China |
|
|
|
|
Abstract In the process of hydraulic fracturing for shale gas extraction, the injection, flowback, retention, and absorption of fracturing fluids will cause changes in electric fields in the case of the excitation by the electromagnetic field from an artificial source in a far area or the excitation by the geoelectric field. The time-dependent change in the information on fracturing can be reflected by monitoring the change in weak electric fields above the hydraulic fracturing area. To meet the needs of the real-time monitoring of the fracturing field, this study focuses on the preliminary study of the monitoring technology based on the nodal acquisition devices of distributed weak electric fields. The monitoring system only collects two horizontally orthogonal electric field signals, monitors the real-time information on the electric field within a certain range, and transmits the preliminarily processed data back to the data center in a wireless way. Test results show that the monitoring system has stable performance, a standby time of more than 10 days, and high sealing performance, and is applicable to complex field environments. Therefore, this monitoring system can provide important technical support for obtaining images of fracturing fluid migration in the future.
|
|
Received: 20 August 2021
Published: 21 June 2022
|
|
|
|
Corresponding Authors:
WANG Meng
E-mail: 2010200030@cugb.edu.cn;wangmeng@cugb.edu.cn
|
|
|
|
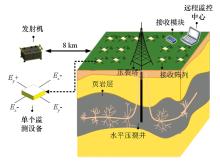
|
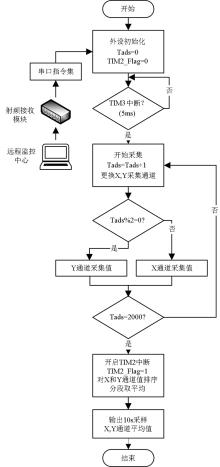
Schematic diagram of weak electric field monitoring in fracturing
|
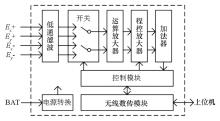
|
Overall structure block diagram of monitoring system
|
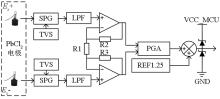
|
Schematic diagram of x-direction electric field signal conditioning circuit
|
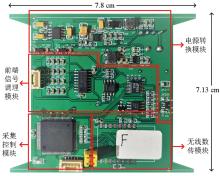
|
Physical diagram of core acquisition circuit
|

|
Front (left) and back (right) of the mechanical package
|
|
Block diagram
|

|
Upper computer running interface
|
|
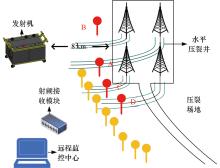
Schematic diagram of field test
|
|
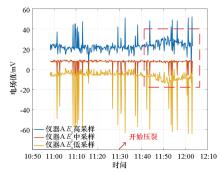
East West test data of instrument A on May 29
|
| [1] |
朱维耀, 陈震, 宋智勇, 等. 中国页岩气开发理论与技术研究进展[J]. 工程科学学报, 2021, 43(10):1397-1412.
|
| [1] |
Zhu W Y, Chen Z, Song Z Y, et al. Research progress in theories and technologies of shale gas development in China[J]. Chinese Journal of Engineering, 2021, 43(10): 1397-1412.
|
| [2] |
邹才能, 董大忠, 王玉满, 等. 中国页岩气特征、挑战及前景(一)[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2015, 42(6):689-701.
|
| [2] |
Zou C N, Dong D Z, Wang Y M, et al. Shale gas in China: Characteristics, challenges and prospects (Ⅰ)[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2015, 42(6): 689-701.
|
| [3] |
王世谦. 页岩气资源开采现状,问题与前景[J]. 天然气工业, 2017, 37(6):115-130.
|
| [3] |
Wang S Q. Shale gas exploitation:Status, issues and prospects[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2017, 37(6): 115-130.
|
| [4] |
刘振武, 撒利明, 杨晓, 等. 页岩气勘探开发对地球物理技术的需求[J]. 石油地球物理勘探, 2011, 46(5):810-818.
|
| [4] |
Liu Z W, Sa L M, Yang X, et al. Needs of geophysical technologies for shale gas exploration[J]. Oil Geophysical Prospecting, 2011, 46(5): 810-818.
|
| [5] |
张永华, 陈祥, 杨道庆, 等. 微地震监测技术在水平井压裂中的应用[J]. 物探与化探, 2013, 37(6):1080-1084.
|
| [5] |
Zhang Y H, Chen X, Yang D Q, et al. The application of Micro-Seismic monitoring technology to the study of horizontal well fracturing[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2013, 37(6): 1080-1084.
|
| [6] |
田建涛, 赵超峰, 张伟, 等. 水力压裂井中监测方法不对称压裂裂缝分析[J]. 石油物探, 2019, 58(4):341-345
|
| [6] |
Tian J T, Zhao C F, Zhang W, et al. Analysis of asymmetric hydraulic fracture for borehole microseismic monitoring[J]. Geophysical Prospecting for Petroleum, 2019, 58(4): 341-345.
|
| [7] |
芮拥军. 地面微地震水力压裂监测可行性分析[J]. 物探与化探, 2015, 39(2):341-345.
|
| [7] |
Rui Y J. Feasibility analysis of surface micro-seismic hydraulic fracturing monitoring[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2015, 39(2): 341-345.
|
| [8] |
杨松霖, 袁博, 李帝铨. 高陡双复杂地区多种页岩气勘探方法效果对比[J]. 物探与化探, 2016, 40(5):941-946.
|
| [8] |
Yang S L, Yuan B, Li D Q. An analysis of some different exploration methods in complex terrain area[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2016, 40(5): 941-946.
|
| [9] |
周印明, 刘雪军, 张春贺, 等. 快速识别页岩气“甜点”目标的时频电磁勘探技术及应用[J]. 物探与化探, 2015, 39(1): 60-63.
|
| [9] |
Zhou Y M, Liu X J, Zhang C H, et al. The TEEM technology for quick identification of “sweet spot” of shale gas and its applications[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2015, 39(1): 60-63.
|
| [10] |
田巍, 李旭兵, 王保忠. 大地电磁测深在湘东南坳陷页岩气勘探中的应用[J]. 物探与化探, 2019, 43(2):281-289.
|
| [10] |
Tian W, Li X B, Wang B Z. The application of magnetotelluric sounding to shale gas exploration in Southeast Hunan Depression[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2019, 43(2): 281-289.
|
| [11] |
凌帆, 朱裕振, 周明磊, 等. 广域电磁法在南华北盆地长山隆起页岩气资源潜力评价中的应用[J]. 物探与化探, 2017, 41(2):369-376.
|
| [11] |
Ling F, Zhu Y Z, Zhou M L, et al. Shale gas potential assessment of Changsan uplift area in southern North China basin by using wide field electromagnetic method[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2017, 41(2): 369-376.
|
| [12] |
林君. 分布式无缆遥测地震勘探系统的设计与应用[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2016.
|
| [12] |
Lin J. The design and application of distributed cableless telemetry seismic exploration system[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2016.
|
| [13] |
刁瑞, 吴国忱, 尚新民, 等. 地面阵列式微地震监测关键技术研究[J]. 岩性油气藏, 2017, 29(1):104-109.
|
| [13] |
Diao R, Wu G C, Shang X M, et al. Key techniques for surface array microseismic monitoring[J]. Horologic Reservoirs, 2017, 29(1): 104-109.
|
| [14] |
吴海成. 中国物探仪器发展博览——地球物理学会60年发展之见证[J]. 地球物理学进展, 2007, 22(4):1338-1343.
|
| [14] |
Wu H C. The progress of the instruments of exploration geophysics in China——An overview of the past sixty years of CGS[J]. Progress In Geophysics, 2007, 22(4): 1338-1343.
|
| [15] |
王永兵, 何继善. WSJ-4 多功能高精度数字化伪随机信号接收系统及应用[J]. 物探与化探, 2014, 38(5):1012-1017.
|
| [15] |
Wang Y B, He J S. Development and a-pplication of the WSJ-4 multifunction digital IP instrument receiving system based on pseudo-random signa[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2014, 38(5): 1012-1017.
|
| [16] |
张文秀, 林君, 刘立超, 等. 分布式电磁探测宽频数据采集系统设计与实现[J]. 吉林大学学报:工学版, 2012, 42(6):1426-1431.
|
| [16] |
Zhang W X, Lin J, Liu L C, et al. Design and implementation of broadband data acquisition system for distributed electromagnetic exploration[J]. Journal of Jilin University:Engineering and Technology Edition, 2012, 42(6): 1426-1431.
|
| [17] |
黄大年, 于平, 底青云. 地球深部探测关键技术装备研发现状及趋势[J]. 吉林大学学报:地球科学版, 2012, 42(5):1485-1496.
|
| [17] |
Huang D N, Yu P, Di Q Y. Development of key instruments and technologies of deep exploration today and tomorrow[J]. Journal of Jilin University:Earth Science Edition, 2012, 42(5): 1485-1496.
|
| [18] |
林品荣, 郭鹏, 石福升, 等. 大深度多功能电磁探测技术研究[J]. 地球学报, 2010, 31(2):149-154.
|
| [18] |
Lin P R, Guo P, Shi F S, et al. A study of the techniques for large-depth and multi-functional electromagnetic survey[J]. Acta Geoscientia Sinica, 2010, 31(2): 149-154.
|
| [19] |
陈凯, 金胜, 魏文博, 等. 坑(井)—地多参数电磁接收系统[J]. 地球物理学报, 2019, 62(10):3803-3818.
|
| [19] |
Chen K, Jin S, Wei W B, et al. Surface tunnel borehole multi-parameter EM receiver[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2019, 62(10): 3803-3818.
|
| [20] |
高雅, 底青云, 付长民, 等. 巷道CSAMT法的目标体分辨能力研究[J]. 地球物理学报, 2019, 62(9):3591-3600.
|
| [20] |
Gao Y, Di Q Y, Fu C M, et al. Research on resolving ability of deep subsurface targets from mine roadway using CSAMT method[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2019, 62(9): 3591-3600.
|
| [21] |
刘长胜, 马金发, 朱文杰, 等. 深井电场测量不极化电极特性研究[J]. 物探与化探, 2020, 44(4):816-819.
|
| [21] |
Liu C S, Ma J F, Zhu W J, et al. A study of the characteristics of non-polarized electrode in deep well electric field measurement[J]. Geophysical and Geo-chemical Exploration, 2020, 44(4): 816-819.
|
| [22] |
陆阳泉, 梁子斌, 刘建毅. 固体不极化电极的研制及其应用效果[J]. 物探与化探, 1999, 23(1):65-66.
|
| [22] |
Lu Y Q, Liang Z B, Liu J Y. Development and application of solid non-polarized electrode[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 1999, 23(1): 65-66.
|
|
|
|

