|
|
|
| Application of 3D geological modeling in screening of sites preselected for geological disposal of high-level radioactive wastes: A case study of Tianhu preselected site, Xinjiang |
LUO Hui1( ), JIANG Shi2( ), JIANG Shi2( ), ZHAO Hong-Gang1, LI Ya-Wei1, TIAN Xiao1 ), ZHAO Hong-Gang1, LI Ya-Wei1, TIAN Xiao1 |
1. CNNC Key Laboratory on Geological Disposal of High-level Radioactive Waste, Beijing Research Institute of Uranium Geology, Beijing 100029, China
2. China Aero Geophysical Survey & Remote Sensing Center for Land and Resources,Beijing 100083, China |
|
|
|
|
Abstract Based on the theories and methods of 3D geological visualization models and the geological data of the Tianhu preselected site, a geological model of the site was established in this study using the Deep Insight TM geoscience modeling software. It describes the 3D tectonic morphology of the preselected site, carries out 3D visual analysis of the geological conditions of the study area from 2D to 3D, from overall to local, and from macroscopic to microscopic aspects,and intuitively expresses the distribution regularity of geological information in the main rockmass used for the disposal of high-level radioactive wastes. The granite rock massatthe Tianhu site occurs in equiaxed rock stocks, with simple lithology and large volume.There is only an NW-tending fault with a length of 2 km developing in the southeastern part of the rock mass. Besides, veins and alteration zones are relatively developed in the rock mass, which affects the integrity of the rock mass to a certain degree. The model can be used to query and update geological data at any time, analyze the distribution characteristics and laws of various geological information in the whole model, and improve the understanding of geological laws. All these willassist in better guiding the site selection, assessment, and construction of disposal repositories.
|
|
Received: 01 September 2021
Published: 21 December 2021
|
|
|
|
Corresponding Authors:
JIANG Shi
E-mail: luo1029hui@163.com;45493666@qq.com
|
|
|
|
|
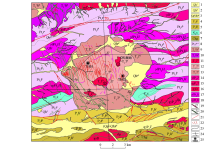
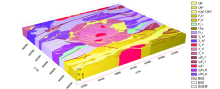
Geological map of Tianhu area
1—Quaternary Holocene lake deposits; 2—Holocene alluvial deposits; 3—Pleistocene-Holocene alluvial deposits; 4—gray metamorphic conglomerate and sandstone of the middle section of Hongliuhe group; 5—gray metamorphic sandstone of the lower section of Hongliuhe group; 6—grey-black siliceous rock with breccia limestone of Cambrian Xidashan formation; 7—marble, dolomitic marble and schist of Changcheng system Gudongjing formation; 8—gray biotite schist, gneiss and marble of Tianhu iron ore rock formation ; 9—early Triassic Weiya monzonitic granite; 10—early Triassic Weiya sub-quartz syenite; 11—early Triassic Tianhu medium grain porphyritic biotite monzonitic granite unit; 12—early Triassic Tianhu fine-grained biotite granodiorite unit; 13—early Triassic Tianhu fine-grained monzonitic granite unit; 14—late Permian medium-grain biotite granodiorite; 15—late Permian medium-grain biotite monzonitic granite; 16—Devonian monzonitic granite; 17—Mesoproterozoic gneissic biotite granodiorite; 18 —Mesoproterozoic gneissic biotite potassium feldspar granite; 19—fine-grained granite veins; 20—medium-basic dykes; 21—faults; 22—fracture alteration zone; 23—geological boundary ; 24—profile position;25—drilling position and number
|
|
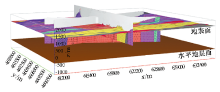
Work area construction and data loading
|
|
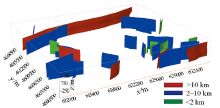
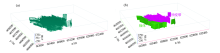
Fault model
|
Fig.1)
">
|
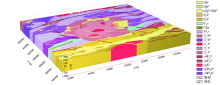
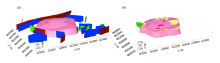
Geological body model(the legend description is the same as Fig.1)
|
|
Model of dyke and alteration zone
|
Fig.1)
">
|
Geological model of Tianhu area(the legend description is the same as Fig.1)
|
Fig.1 and Fig.3)
">
|
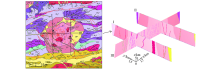
3D relationship between rock mass and fault, dyke and alteration zone(the legend description is the same as Fig.1 and Fig.3)
|
Fig.1)
">
|
Generation of geological section in Tianhu area(the legend description is the same as Fig.1)
|
Fig.1)
">
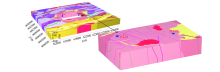
|
Local excavation of Tianhu model(the legend description is the same as Fig.1)
|
| [1] |
李亦纲, 曲国胜, 陈建强. 城市钻孔数据地下三维地质建模软件的实现[J]. 地质通报, 2005, 24(5):470-475.
|
| [1] |
Li Y G, Qu G S, Chen J Q. Realization of a 3D subsurface geological modeling software in urban areas based on borehole data[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 2005, 24(5):470-475.
|
| [2] |
Houlding S W. 3D geolscience modeling-computer techniques for geological characterization[M]. Berlin Heidelberg: Springer-Verag, 1994.
|
| [3] |
曾钱帮, 何小萍. 三维地质建模的数学模型与显示方法[J]. 工程地质计算机应用, 2006(3):1-8.
|
| [3] |
Zeng Q B, He X P. Mathematical model and display method of 3D geological modeling[J]. Engineering Geology Computer Application, 2006,(3):1-8.
|
| [4] |
刘少华, 程朋根, 陈红华. 三维地质建模及可视化研究[J]. 桂林工学院学报, 2003, 23(2):154-158.
|
| [4] |
Liu S H, Cheng P G, Chen H H. Study of 3D geology modeling and visualization[J]. Journal of Guilin Institute of Technology, 2003, 23(2):154-158.
|
| [5] |
朱良峰, 潘信, 吴信才. 三维地质建模及可视化系统的设计与开发[J]. 岩土力学, 2006, 27(5):828-832.
|
| [5] |
Zhu L F, Pan X, Wu X C. Design and development of 3D geological modeling and visualization system[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2006, 27(5):828-832.
|
| [6] |
曾钱帮, 刘大安, 张菊明, 等. 地质工程复杂地质体三维建模与可视化研究[J]. 工程地质计算机应用, 2005(3):29-33.
|
| [6] |
Zeng Q B, Liu D A, Zhang J M, et al. Research on 3D modeling and visualization of complex geological body in geological engineering[J]. Engineering Geology Computer Application, 2005(3):29-33.
|
| [7] |
王永志, 王慧, 廖丽霞, 等. 三维地质建模方法与应用[M]. 长沙: 中南大学出版社, 2018.
|
| [7] |
Wang Y Z, Wang H, Liao L X, et al. 3D geological modeling method and application[M]. Changsha: Central South University Press, 2018.
|
| [8] |
王驹. 高放废物地质处置: 进展与挑战[J]. 中国工程科学, 2008, 10(3):58-65.
|
| [8] |
Wang J. Geological disposal of high level radio active waste:Progress and challenges[J]. Engineering Science, 2008, 10(3):58-65.
|
| [9] |
潘自强, 钱七虎. 高放废物地质处置战略研究[M]. 北京: 原子能出版社, 2009.
|
| [9] |
Pan Z Q, Qian Q H. The geological disposal of high-level radioactive waste strategy research[M]. Beijing: Atomic Energy Press, 2009.
|
| [10] |
国家核安全局. HAD 401/06-2013 高水平放射性废物地质处置设施选址[S]. 北京:国家核安全局, 2013.
|
| [10] |
National Nuclear Safety Administration. HAD 401/06-2013 Site selection of geological disposal facilities for high-level radioactive waste[S]. Beijing: National Nuclear Safety Administration, 2013.
|
| [11] |
王驹, 徐国庆, 郑华铃, 等. 中国高放废物地质处置研究进展:1985~2004[J]. 世界核地质科学, 2005, 22(1):5-16.
|
| [11] |
Wang J, Xu G Q, Zhen H L, et al. Geological disposal of high level radioactive waste in China: Progress during 1985~2004[J]. World Nuclear Geoscience, 2005, 22(1):5-16.
|
| [12] |
徐国庆. 国际高放废物处置研发工作在花岗岩地区的进展[J]. 世界核地质科学, 2016, 33(3):178-186.
|
| [12] |
Xu G Q. Abroad progress in R&D work on high-level radioactive waste disposal in granite areas[J]. World Nuclear Geoscience, 2016, 33(3):178-186.
|
| [13] |
王驹. 中国高放废物地质处置21世纪进展[J]. 原子能科学技术, 2019, 53(10):2072-2082.
|
| [13] |
Wang J. Progress of geological disposal of high-level radioactive waste in China in the 21st century[J]. Atomic Energy Science and Technology, 2019, 53(10):2072-2082.
|
| [14] |
冉勇康, 陈立春, 吴富峣, 等. 甘肃北山地区区域地壳稳定性研究[R]. 北京:中国地震局地质研究所, 核工业北京地质研究院, 2014.
|
| [14] |
Ran Y K, Chen L C, Wu F R, et al. Study on regional crustal stability in Beishan area, Gansu[R]. Beijing:Institute of Geology, China Earthquake Administration, Beijing Research Institute of Uranium Geology, 2014.
|
|
|
|

