|
|
|
| The principle and application of zero phase measurement of resonant frequency of transient electromagnetic induction antenna |
XI Zhen-Zhu1( ), MU Ren1, XU Yu2( ), MU Ren1, XU Yu2( ), ZHOU Sheng1,3, CHEN Xing-Peng3 ), ZHOU Sheng1,3, CHEN Xing-Peng3 |
1. School of Geosciences and Info-Physics,Central South University,Changsha 410083,China
2. Hunan Institute of Metrology and Test,Changsha 410014,China
3. Hunan Wuwei Geological Technology Co., Ltd., Changsha 410205,China |
|
|
|
|
Abstract When the transient electromagnetic receiving antenna is in a critically damped state, the output signal is the pure target induction signal. This critical damping state is related to electrical parameters such as inductance, distributed capacitance, and resistance of the receiving antenna. The resistance and inductance values can be directly measured by a spectrum analyzer, but the distributed capacitance cannot be directly obtained. In order to develop a high-performance receiving antenna, this paper proposes a method to accurately calculate the distributed capacitance of the receiving antenna. First, the equivalent circuit model of the transient electromagnetic induction receiving antenna is constructed; then, the calculation formula of the zero-phase resonance frequency of the output signal is derived; Finally, by measuring the resonant frequency of the antenna, the distributed capacitance is calculated. For the purpose of verifying the feasibility of this method, the standard capacitance is compared with the calculated capacitance, and different types of transient electromagnetic induction antennas are tested. The test results show that the zero-phase method can be used to calculate the distributed capacitance with high accuracy, convenience and fastness and can be used to design and produce high-performance transient inductive sensors.
|
|
Received: 26 October 2020
Published: 27 July 2021
|
|
|
|
Corresponding Authors:
XU Yu
E-mail: xizhenzhu@163.com;xuyu19952020@163.com
|
|
|
|
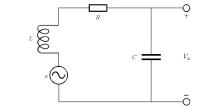
|
Equivalent circuit model
|

| 标准实验电子元件 | 标准参数 | 实际数值 | | 电感L/mH | 7.2×(1±0.05) | 7.298 | | 电阻R/Ω | 500.0×(1±0.05) | 512.0 | | 电容C/pF | 30.0×(1±0.1) | 31.8 | | 100.0×(1±0.05) | 99.0 | | 220.0×(1±0.05) | 222.8 | | 330.0×(1±0.05) | 328.2 | | 470.0×(1±0.05) | 474.0 | | 680.0×(1±0.05) | 689.6 |
|
Parameters of electronic components
|

| 谐振频率/kHz | 实际值/pF | 零相位法计算值/pF | 误差/% | | 332.410 | 31.8 | 31.44 | 1.1 | | 187.579 | 99.0 | 98.74 | 0.3 | | 125.142 | 222.8 | 221.86 | 0.4 | | 102.397 | 328.2 | 331.36 | 1.0 | | 84.346 | 474.0 | 488.36 | 3.0 | | 69.680 | 689.6 | 715.58 | 3.8 |
|
Capacitance measurement results
|
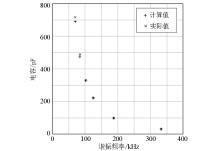
|
Comparison of calculation with zero phase method and standard capacitance value
|
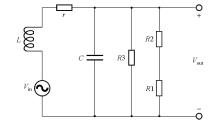
|
Transient electromagnetic induction antenna equivalent circuit
|

| R/Ω | L/mH | f/kHz | C/pF | | 1号线圈 | 15.309 | 10.297 | 358.995 | 19.09 | | 2号线圈 | 15.268 | 10.348 | 361.122 | 18.77 | | 总线圈 | 30.634 | 29.140 | 223.335 | 17.43 |
|
Coil parameters
|

| 阻尼系数K | 电阻 | RT/kΩ | | R1/kΩ | R2/kΩ | R3/kΩ | | 0.080 | 560 | 560 | 470 | 331.069 | | 0.209 | 270 | 270 | 120 | 98.182 | | 0.437 | 75 | 75 | 68 | 46.789 | | 1.000 | x | x | y | 20.453 | | 1.097 | 30 | 30 | 27 | 18.621 | | 24.629 | 3.900 | 3.900 | 0.910 | 0.815 | | 50.819 | 1.100 | 1.100 | 0.470 | 0.387 | | 97.799 | 0.510 | 0.510 | 0.240 | 0.194 |
|
Resistance parameters
|
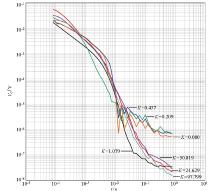
|
Comparison of received signals with different damping coefficients
|
| [1] |
Nabighian M N, Macnae J C. Time domain electromagnetic prospecting methods[C]// Electromagnetic Methods in Applied Geophysics, 1991:427-520.
|
| [2] |
蒋邦远. 实用近区磁源瞬变电磁法勘探[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 1998.
|
| [2] |
Jiang B Y. Practical transient electromagnetic method prospecting in near zone of magnetic dipole source[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 1998.
|
| [3] |
薛国强, 李貅, 底青云. 瞬变电磁法理论与应用研究进展[J]. 地球物理学进展, 2007, 22(4):1195-1200.
|
| [3] |
Xue G Q, Li X, Di Q Y. The progress of TEM in theory and application[J]. Progress in Geophysics, 2007, 22(4):1195-1200.
|
| [4] |
薛国强, 于景邨. 瞬变电磁法在煤炭领域的研究与应用新进展[J]. 地球物理学进展, 2017, 32(1):319-326.
|
| [4] |
Xue G Q, Yu J C. New development of TEM research and application in coal mine exploration[J]. Progress in Geophysics, 2017, 32(1):319-326.
|
| [5] |
底青云, 朱日祥, 薛国强, 等. 我国深地资源电磁探测新技术研究进展[J]. 地球物理学报, 2019, 62(6):2128-2138.
|
| [5] |
Di Q Y, Zhu R X, Xue G Q, et al. New development of the electromagnetic(EM) methods for deep exploration[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2019, 62(6):2128-2138.
|
| [6] |
林君, 符磊, 王言章. 接地电性源空地瞬变电磁探测传感器的研制[J]. 吉林大学学报:工学版, 2014, 44(3):888-894.
|
| [6] |
Lin J, Fu L, Wang Y Z. Development of an air-to-ground transient electromagnetic detection sensor for grounded electrical sources[J]. Journal of Jilin University:Engineering and Technology Edition, 2014, 44(3):888-894.
|
| [7] |
林君, 王琳, 王晓光. 矿井瞬变电磁探测中空芯线圈传感器的研制[J]. 地球物理学报, 2016, 59(2):721-730.
|
| [7] |
Lin J, Wang L, Wang X G. Development of hollow core coil sensor for mine transient electromagnetic detection[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2016, 59(2):721-730.
|
| [8] |
嵇艳鞠, 林君, 王忠. 瞬变电磁接收装置对浅层探测的畸变分析与数值剔除[J]. 地球物理学进展, 2007, 22(1):262-267.
|
| [8] |
Ji Y J, Lin J, Wang Z. Research on Distortion of Whole Transient Field in Shallow Transient Electromagnetic Method[J]. Progress in Geophysics, 2007, 22(1):262-267.
|
| [9] |
王华军. 阻尼系数对瞬变电磁观测信号的影响特征[J]. 地球物理学报, 2010, 53(2):428-434.
|
| [9] |
Wang H J. Characteristics of damping coefficient effect on transient electromagnetic signal[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2010, 53(2):428-434.
|
| [10] |
Matthaei G L, Chinn G C, Plott C H, et al. A simplified means for computation for interconnect distributed capacitances and inductances[J]. IEEE Transactions on Computer-Aided Design of Integrated Circuits and Systems, 2006, 11(4):513-524.

|
| [11] |
林辛, 张雄金. 空芯线圈分布电容测试的研究[J]. 电测与仪表, 1997(7):25-27.
|
| [11] |
Lin X, Zhang X J. Research on test of distributed capacitance of air core coil[J]. Electrical Measurement and Instrumentation, 1997(7):25-27.
|
| [12] |
Prieto M J, Fernandez A, Diaz J M, et al. Influence of transformer parasitics in low-power applications[C]// Applied Power Electronics Conference & Exposition, 1999:1175-1180.
|
| [13] |
Yu Q, Holmes T W. A study on stray capacitance modeling of inductors by using the finite element method[J]. IEEE Transactions on Electromagnetic Compatibility, 2001, 43(1):88-93.

|
| [14] |
Lu H Y, Zhu J G, Ramsden V S, et al. Measurement and modeling of stray capacitances in high frequency transformers[C]// IEEE Power Electronics Specialists Conference, 1999:763-768.
|
| [15] |
Lu H Y, Zhu J G, Ramsden V S. Comparison of experimental techniques for determination of stray capacitances in high frequency transformers[C]// IEEE Power Electronics Specialists Conference, 2000:1645-1650.
|
| [16] |
Massarini A, Kazimierczuk M K. Self-capacitance of inductors[J]. IEEE Transactions on Power Electronics, 1997, 12(4):671-676.

|
| [1] |
ZHANG Fan, FENG Guo-Rui, QI Ting-Ye, YU Chuan-Tao, ZHANG Xin-Jun, WANG Chao-Yu, DU Sun-Wen, ZHAO De-Kang. Feasibility of the transient electromagnetic method in the exploration of double-layer waterlogged goafs with different layer spacings in coal mines[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2023, 47(5): 1215-1225. |
| [2] |
ZHOU Zhong-Hang, ZHANG Ying-Ying. Correction of the influence of mountains on grounded-source transient electromagnetic responses[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2023, 47(5): 1236-1249. |
|
|
|
|

