|
|
|
| Comprehensive seismic reservoir prediction of M02 member in B Oilfield in Kazakhstan |
LIU Jia-Cai1( ), ZHANG Chong2, HAN Xu-Jun1 ), ZHANG Chong2, HAN Xu-Jun1 |
1. Chengdu North Petroleum Exploration and Development Technology Co.,Ltd.,Chengdu 610051,China
2. College of Geophysics and Petroleum Resources,Yangtze University,Wuhan 430100,China |
|
|
|
|
Abstract M02 member of Upper Dual Formation of Lower Cretaceous in B Oilfield in Kazakhstan belongs to braided fluvial deposits.The reservoirs are mainly gravel-bearing sandstone and fine sandstone.Sand bodies change rapidly in both vertical and horizontal directions.Uncertainty of reservoir distribution laws seriously restricts the progressive exploration and development process of the oilfield.Based on a new round of fine structure interpretation,the comprehensive application of a series of reservoir prediction techniques such as fine synthetic seismogram calibration,seismic forward modeling,seismic attribute analysis,conventional seismic inversion and geostatistical inversion was successfully implemented,which eliminated the multi-solution of seismic attribute analysis,made clear sand reservoir macroscopic distribution laws,and finely depicted the distribution characteristics of thin sand bodies in M02 breaking through the limitation of conventional seismic resolution.Finally,a comprehensive technological sequence of seismic reservoir prediction techniques suitable for this oilfield was established.Successful application of this technology sequence in this region provides a powerful basis for rolling evaluation and water injection development and has made a great contribution to increasing reserves and production of the oilfield.Meanwhile,it has reference and guidance significance for reservoir prediction in similar blocks.
|
|
Received: 02 December 2019
Published: 29 April 2021
|
|
|
|
|
|
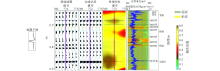
|
Synthetic calibration profile of well B-FA
|
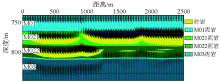
|
Forward modeling profile
|
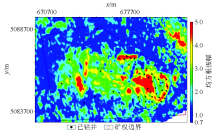
|
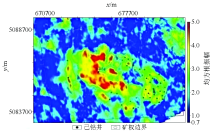
RMS amplitude attribute map of M021
|
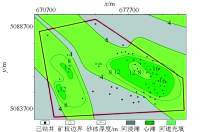
|
Well statistical sand thickness map of M021
|
|
RMS amplitude attribute map of M022
|
|
Well statistical sand thickness map of M022
|
|
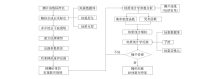
Flow chart of comprehensive seismic inversion reservoir prediction
|
|
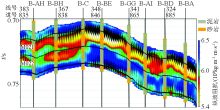
Constrained sparse spike inversion P-wave impedance profile
|
|
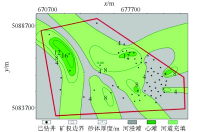
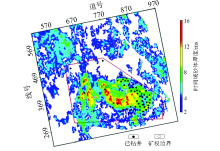
Predicted sand distribution map of M021
|
|
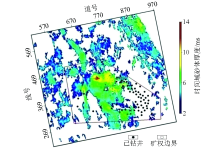
Predicted sand distribution map of M022
|
|
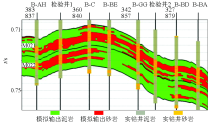
Blind well test lithologic profile of geostatistical inversion
|
|
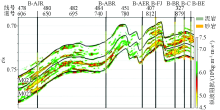
Geostatistical inversion P-wave impedance Hollowed-out profile
|
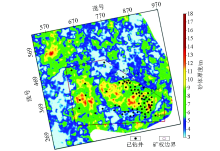
|
Predicted sand thickness map of M021
|
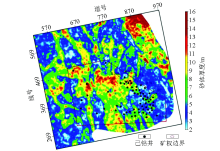
|
Predicted sand thickness map of M022
|
| [1] |
张金亮. 河流沉积相类型及相模式[J]. 新疆石油地质, 2019,40(2):247-248.
|
| [1] |
Zhang J L. Fluvial facies styles and their sedimentary facies models[J]. Xinjiang Petroleum Geology, 2019,40(2):247-248.
|
| [2] |
何顺利, 兰朝利, 门成全. 苏里格气田储层的新型辫状河沉积模式[J]. 石油学报, 2005,26(6):25-29.
|
| [2] |
He S L, Lan C L, Men C Q. New braided river model in Sulige gas field of Ordos Basin[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2005,26(6):25-29.
|
| [3] |
廖保方, 张为民, 李列, 等. 辫状河现代沉积研究与相模式—中国永定河剖析[J]. 沉积学报, 1998,16(1):34-39.

|
| [3] |
Liao B F, Zhang W M, Li L, et al. Study on modern deposit of a braided stream and facies model: taking the Yongding river as an example[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 1998,16(1):34-39.

|
| [4] |
毛平. 砂质辫状河储集层构型表征研究现状及展望[J]. 新疆石油地质, 2018,39(4):492-498.
|
| [4] |
Mao P. The status and prospects of research on characterization for sandy braided-river reservoir architecture[J]. Xinjiang Petroleum Geology, 2018,39(4):492-498.
|
| [5] |
李顺明, 宋新民, 蒋有伟, 等. 高尚堡油田砂质辫状河储集层构型与剩余油分布[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2011,38(4):474-482.
|
| [5] |
Li S M, Song X M, Jiang Y W, et al. Architecture and remaining oil distribution of the sandy braided river reservoir in the Gaoshangpu Oilfield[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2011,38(4):474-482.
|
| [6] |
于兴河, 马兴祥, 穆龙新, 等. 辫状河储层地质模式及层次界面分析[M]. 北京: 石油工业出版社, 2004: 56-58.
|
| [6] |
Yu X H, Ma X X, Mu L X, et al. Analysis of braided river reservoir geological model and hierarchy interface[M]. Beijing: Petroleum Industry Press, 2004: 56-58.
|
| [7] |
葛云龙, 逯径铁, 廖保方, 等. 辫状河相储集层地质模型—泛连通体[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 1998,25(5):77-79.
|
| [7] |
Ge Y L, Lu J T, Liao B F, et al. A braided river reservoir geological model:"pan communicated sandbody"[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 1998,25(5):77-79.
|
| [8] |
李海燕, 高阳, 王延杰, 等. 辫状河储集层夹层发育模式及其对开发的影响——以准噶尔盆地风城油田为例[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2015,42(3):364-373.
|
| [8] |
Li H Y, Gao Y, Wang Y J, et al. Intercalation pattern and its impact on development of braided river reservoirs:A case of Fengcheng Oilfield[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2015,42(3):364-373.
|
| [9] |
刘钰铭, 侯加根, 宋保全, 等. 辫状河厚砂层内部夹层表征——以大庆喇嘛甸油田为例[J]. 石油学报, 2011,32(5):836-841.
|
| [9] |
Liu Y M, Hou J G, Song B Q, et al. Characterization of interlayers within braided river thick sandstones:A case study on the Lamadian Oilfield in Daqing[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2011,32(5):836-841.
|
| [10] |
王晖, 胡光义, 范洪军, 等. 边际油田河流相储集层表征关键技术[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2012,39(5):626-631.
|
| [10] |
Wang H, Hu G Y, Fan H J, et al. Key technologies for the fluvial reservoir characterization of marginal oilfields[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2012,39(5):626-631.
|
| [11] |
刘金连, 张建宁. 济阳探区单一河道砂体边界地质建模及其地震正演响应特征分析[J]. 石油物探, 2010,49(4):344-350.
|
| [11] |
Liu J L, Zhang J N. Geological modeling and seismic forward response characteristics analysis of single channel sand body boundary in Jiyang prospecting area[J]. Geophysical Prospecting for Petroleum, 2010,49(4):344-350.
|
| [12] |
毕俊凤, 顾汉明, 刘书会, 等. 河道砂体地震响应特征及影响因素分析——以垦东1地区馆陶组上段河道砂为例[J]. 石油物探, 2013,52(1):97-103.
|
| [12] |
Bi J F, Gu H M, Liu S H, et al. Analysis on seismic response characteristics of channel sands and its influence factors: case study of Upper Guantao Formation in KD1 area[J]. Geophysical Prospecting for Petroleum, 2013,52(1):97-103.
|
| [13] |
刘兴艳, 李墨寒, 叶泰然. 川西侏罗系复杂河道精细刻画及沉积相带识别[J]. 石油物探, 2019,58(5):750-757.
|
| [13] |
Liu X Y, Li M H, Ye T R. Fine characterization of complicated channels in western Sichuan and identification of sedimentary facies[J]. Geophysical Prospecting for Petroleum, 2019,58(5):750-757.
|
| [14] |
马跃华, 吴蜀燕, 白玉花, 等. 利用谱分解技术预测河流相储层[J]. 石油地球物理勘探, 2015,50(3):502-509.

|
| [14] |
Ma Y H, Wu S Y, Bai Y H, et al. River sedimentary microfacies prediction based on spectral decomposition[J]. Oil Geophysical Prospecting, 2015,50(3):502-509.

|
| [15] |
郝杰, 吴鑫, 孙明, 等. 南堡地区浅层河道砂体的识别[J]. 石油地球物理勘探, 2018,53(s1):151-157.
|
| [15] |
Hao J, Wu X, Sun M, et al. Shallow channel sand identification in Nanpu Area[J]. Oil Geophysical Prospecting, 2018,53(s1):151-157.
|
| [16] |
秦雪霏, 齐荣, 李巍, 等. 杭锦旗地区盒1段辫状河道构型及心滩半定量地震识别[J]. 石油物探, 2019,58(4):572-579.
|
| [16] |
Qin X F, Qi R, Li W, et al. Braided channel architecture analysis and semi-quantitative seismic prediction for channel bars in P1x1 of the Hangjinqi area[J]. Geophysical Prospecting for Petroleum, 2019,58(4):572-579.
|
| [17] |
赵子豪, 李凌, 马跃华, 等. 辫状河沉积储层预测技术——以大港探区孔店油田为例[J]. 石油地球物理勘探, 2017,52(1):152-159.
|
| [17] |
Zhao Z H, Li L, Ma Y H, et al. Braided river sedimentary reservoir prediction: an example of Kongdian oilfield in Dagang[J]. Oil Geophysical Prospecting, 2017,52(1):152-159.
|
| [18] |
高改, 赵玉华, 黄黎刚, 等. 基于波形分析的辫状河道砂体识别——以鄂尔多斯盆地苏X井区为例[J]. 石油地球物理勘探, 2018,53(s2):301-305
|
| [18] |
Gao G, Zhao Y H, Huang L G, et al. Braided-river channel sand characterization based on waveform analysis: an example in Well Su X Area,Ordos Basin[J]. Oil Geophysical Prospecting, 2018,53(s2):301-305.
|
| [19] |
国春香, 郭淑文, 朱伟峰, 等. 河流相砂泥岩薄互层预测方法研究与应用[J]. 物探与化探, 2018,42(3):594-599.
|
| [19] |
Guo C X, Guo S W, Zhu W F, et al. Research and application of fluvial sand-shale thin interbedding prediction method[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2018,42(3):594-599.
|
| [20] |
黄文松, 陈和平, 李胜利, 等. 基于水平井信息的辫状河岩相单元与砂体定量研究——以委内瑞拉奥里诺科重油带MPE3区块为例[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2018,39(2):409-418.
|
| [20] |
Huang W S, Chen H P, Li S L, et al. Quantification of braided-river lithofacies units and sandbody based on horizontal well data:a case of MPE3 block in Orinoco heavy-oil zone,Venezuela[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2018,39(2):409-418.
|
| [21] |
孙家振, 李兰斌. 地震地质综合解释教程[M]. 武汉: 中国地质大学出版社, 2002: 23-25.
|
| [21] |
Sun J Z, Li L B. Course of comprehensive interpretation of seismology and geology[M]. Wuhan: China University of Geosciences Press, 2002: 23-25.
|
| [22] |
沈财余, 阎向华. 测井约束地震反演的分辨率与地震分辨率的关系[J]. 石油物探, 1999,38(4):96-106.
|
| [22] |
Shen C Y, Yan X H. Relationship between the resolution of well log constrained seismic inversion and seismic resolution[J]. Geophysical Prospecting for Petroleum, 1999,38(4):96-106.
|
| [23] |
李庆忠. 论地震约束反演的策略[J]. 石油地球物理勘探, 1998,33(4):423-438.

|
| [23] |
Li Q Z. On strategy of seismic restricted inversion[J]. Geophysical Prospecting for Petroleum, 1998,33(4):423-438.
|
| [24] |
李庆忠. 走向精确勘探的道路[M]. 北京: 石油工业出版社, 1993: 121-133.
|
| [24] |
Li Q Z. The way to precise exploration[M]. Beijing: Petroleum Industry Press, 1993: 121-133.
|
| [25] |
杨云岭. 地质模式在地震解释中的重要作用[J]. 油气地球物理, 2003,1(1):4-7.
|
| [25] |
Yang Y L. The important role of geological model in seismic interpretation[J]. Petroleum Geophysics, 2003,1(1):4-7.
|
| [26] |
侯伯刚, 韩大匡, 刘文岭, 等. 变差函数的参数和井数对随机反演精度影响的分析[J]. 石油物探, 2016,55(5):754-763.
|
| [26] |
Hou B G, Han D K, Liu W L, et al. Analysis on the influence of variogram and well number on the precision of seismic stochastic inversion[J]. Geophysical Prospecting for Petroleum, 2016,55(5):754-763.
|
| [27] |
张秀丽, 姜岩, 郝兰英, 等. 密井网条件下随机地震反演及其在河道砂体预测中的应用[J]. 石油地球物理勘探, 2014,49(5):954-963.

|
| [27] |
Zhang X L, Jiang Y, Hao L Y, et al. Stochastic seismic inversion and channel sandbody prediction in dense well pattern areas[J]. Oil Geophysical Prospecting, 2014,49(5):954-963.

|
| [1] |
YANG Guo-Jie, SONG Li-Yuan, SHANG Jian-Xia. The application of geostatistical inversion to reservoir prediction of Tuo 11 south area[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2015, 39(6): 1193-1198,1204. |
| [2] |
HAN Dong, HU Xiang-Yang, WU Xing-Wei, LIU Kun-Yan, SI Chao-Nian, FU Xin, JIA Zhi-Kun. The prediction research on fracture-cavity reservoirs by geostatistical inversion based on Markov Chain and Monte-Carlo algorithm in the Tahe oilfeild[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2015, 39(6): 1211-1216. |
|
|
|
|

