|
|
|
| Quantitative evaluation of the ability of elements in forming primary halos: A case study of the Zhajiatongna gold deposit, Qinghai Province |
YUAN Zhao-Xian1( ), HOU Zhen-Guang2( ), HOU Zhen-Guang2( ), REN Zhi-Dong3, LIU Yong-Le4, ZHANG Da-Ming4, ZHANG Jian-Ping4 ), REN Zhi-Dong3, LIU Yong-Le4, ZHANG Da-Ming4, ZHANG Jian-Ping4 |
1. Institute of Resource and Environmental Engineering,Hebei GEO University,Shijiazhuang 050031, China
2. No.5 Institute of Geology and Mineral Exploration, Qinghai Bureau of Geological Exploration and Development, Xining 810008, China
3. Qinghai Branch of China Building Material Industry Geological Survey Center, Xining 810008, China
4. No.3 Institute of Geology and Mineral Exploration, Qinghai Bureau of Geological Exploration and Development, Xining 810029, China |
|
|
|
|
Abstract A procedure to screen the elements used in the research on the elemental zonation in a primary halo is rarely conducted, which is not conducive to the acquisition of an accurate understanding of the rules of elemental zonation. In this paper, the authors chose the Zhajiatongna gold deposit in Qinghai Province as a study case and aimed to study the difference between ore-forming metallic elements in the ability of forming a primary halo through comparing the elemental enrichment degrees in the wall rocks, mineralized wall rocks, and orebodies and on the basis of 2 779 samples from the drill cores of the deposit. It is found that the concentrations of Au, As, Sb, Hg, W, and Ag progressively increase from the wall rocks through mineralized wall rocks to orebodies, indicating a greater possibility of forming a primary halo for these elements. Zinc is enriched only in the orebodies, with less possibility of forming a large-scale primary halo. Elements of Mo, Cu, Pb, and Sn show insignificant enrichment or even show depletion, indicating a less possibility of forming a primary halo.A trend of enrichment zonation of ore-forming elements was recognized: Au, As, Sb in the wall rocks, Au, As, Sb, W, Hg (Ag) in the mineralized wall rocks, and Au, As, Ag, Sb, W, Hg and Zn in the orebodies. Elements show a decreasing weight of enrichment in the mineralized wall rocks in order of As, Hg, Au, Sb, W, Mo, Sn, Pb, Zn, Cu, and Ag, suggesting the progressively decreasing ability of entering into the wall rocks from the orebodies in order of low-temperature metallogenic elements through medium-temperature metallogenic elements to high-temperature metallogenic elements. Therefore, in the Zhajiatongna gold deposit, elements such as As, Hg, Au, Sb and W are optimal for researches on elemental zonation and mineral prediction.
|
|
Received: 21 March 2020
Published: 29 April 2021
|
|
|
|
Corresponding Authors:
HOU Zhen-Guang
E-mail: sdyzx86@126.com;up.hzg@126.com
|
|
|
|

| 元素 | Ag | As | Au | Cu | Hg | Mo | Pb | Sb | Sn | Zn | | 方法 | ES | AF | ICP-MS | ICP-MS | AF | ICP-MS | ICP-MS | AF | ES | ICP-MS | | 检出限 | 20 | 0.33 | 0.25 | 1 | 0.5 | 0.15 | 0.85 | 0.046 | 0.85 | 4 |
|
Analytical methods and the limits of detection for the elements
|
|
Sketch of element enrichment in the wall rocks, mineralized wall rocks and orebodies
①—elemental enrichment in the wall rocks;②—elemental enrichment in the mineralized wall rocks;③—elemental enrichment in the orebodies
|

| 参数 | Au | As | W | Mo | Sb | Pb | Ag | Hg | Cu | Zn | Sn | | 平均值 | 40.34 | 93.77 | 2.59 | 0.62 | 3.75 | 23.36 | 71.79 | 20.61 | 38.18 | 90.53 | 2.82 | | Cv | 6.61 | 4.04 | 1.59 | 1.37 | 1.24 | 0.85 | 0.52 | 0.43 | 0.38 | 0.26 | 0.16 | | 富集系数 | 28.01 | 6.75 | 1.93 | 1.41 | 3.68 | 1.41 | 1.33 | 0.53 | 2.06 | 1.63 | 1.19 |
|
Characteristics of metal element contents of 2 779 samples from the Zhajiatongna deposit
|
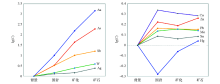
|
Trends of elemental enrichment factors changing in the wall rocks,the mineralized wall rocks and the orebodies
|
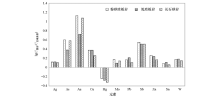
|
Enrichment factors of wall rock and the differences among rock types
|
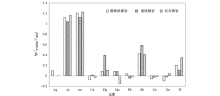
|
Enrichment factors of mineralized wall rock and the differences among rock types
|
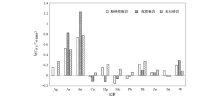
|
Elemental enrichment factors of orebody
|
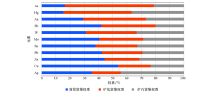
|
Weights of elemental enrichment in the three mediums
|

| 矿化 | 矿石 | 元素 | 原生晕 | | + | + | Au、As、Sb、W、Ag、Hg、(Mo) | √ | | + | - | | | | - | + | Zn | √ | | - | - | Pb、Cu、Sn | × |
|
Enrichment or depletion of element versus the ability of forming a primary halo
|
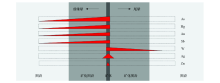
|
Spatial patterns of elemental enrichment in the Zhajiatongna deposit
|
| [1] |
欧阳宗圻, 李惠, 刘汉忠. 典型有色金属矿床地球化学异常模式[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 1990.
|
| [1] |
Ouyang Z X, Li H, Liu H Z. Geochemical anomaly models for typical nonferrous metal deposits[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 1990.
|
| [2] |
邵跃. 热液矿床岩石测量 (原生晕法) 找矿[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 1997.
|
| [2] |
Shao Y. Rock prospecting of hydrothermal deposit (primary halo method)[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 1997.
|
| [3] |
刘崇民. 金属矿床原生晕研究进展[J]. 地质学报, 2006,80(10):1528-1538.
|
| [3] |
Liu C M. Progress in studies on primary halos of ore deposit[J]. Acta Geologicasinica, 2006,80(10):1528-1538.
|
| [4] |
李惠, 禹斌, 李德亮, 等. 化探深部预测新方法综述[J]. 矿产勘查, 2010,1(2):156-160.
|
| [4] |
Li H, Yu B, Li D L, et al. Summary of new methods on deep prediction of geochemical exploration[J]. Mineral Exploration, 2010,1(2):156-160.
|
| [5] |
黄薰德, 郁彦. 地球化学找矿[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 1985.
|
| [5] |
Huang X D, Yu Y. Geochemical Prospecting[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 1985.
|
| [6] |
Beus A A, Grigorian S V. Geochemical exploration methods for mineral deposits[M]. Wilmette: Applied Publishing Ltd., 1977.
|
| [7] |
Zhou Y. Geochemical exploration for deeply hidden ore in southeastern Hubei Province[J]. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 1989,33(1):135-144.
|
| [8] |
Konstantinov M M, Strujkov S F. Application of indicator halos (signs of ore remobilization) in exploration for blind gold and silver deposits[J]. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 1995,54(1):1-17.
|
| [9] |
黄转莹, 路润安. 陕西省凤县铅硐山大型铅锌矿床原生异常分带及分带指数[J]. 地质与勘探, 2003,39(3):39-44.
|
| [9] |
Huang Z Y, Lu R A. Zoning characteristics and index of primary geochemical anomalies in Qiandongshan Pb-Zn deposit, Shaanxi Province, China[J]. Geology and Prospecting, 2003,39(3):39-44.
|
| [10] |
Liu L, Peng S. Prediction of hidden ore bodies by synjournal of geological, geophysical and geochemical information based on dynamic model in Fenghuangshan ore field, Tongling district, China[J]. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 2004,81(1):81-98.
|
| [11] |
Ghavami-Riabi R, Theart H F, De Jager C. Detection of concealed Cu-Zn massive sulfide mineralization below eolian sand and a calcrete cover in the eastern part of the Namaqua Metamorphic Province, South Africa[J]. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 2008,97(2-3):83-101.
|
| [12] |
李惠, 张文华, 刘宝林, 等. 中国主要类型金矿床的原生晕轴向分带序列研究及其应用准则[J]. 地质与勘探, 1999,35(1):32-35.
|
| [12] |
Li H, Zhang W H, Liu B L, et al. The study on axial zonality sequence of primary halo and some criteria for the application of this sequence for major types of gold deposits in China[J]. Geology and Prospecting, 1999,35(1):32-35.
|
| [13] |
王文, 李鹏, 夏有清, 等. 东昆仑大场金矿田扎家同哪矿床地质特征及找矿方向[J]. 青海大学学报: 自然科学版, 2012,30(5):60-68.
|
| [13] |
Wang W, Li P, Xia Y Q, et al. Geological features and prospecting orientation of Zhajiatongna deposit in Dachang golden orefield of Eastern Kunlun mountain[J]. Journal of Qinghai University:Nature Science Edition, 2012,30(5):60-68.
|
| [14] |
高永旺, 王福德, 李琳业, 等. 青海省曲麻莱县大场金矿床165-60线勘探报告[R]. 西宁:青海省第五地质矿产勘查院, 2011.
|
| [14] |
Gao Y W, Wang F D, Li L Y, et al. Report on the prospecting line 165-60 in the Dachang gold deposit, Qumalai county, Qinghai province, China[R]. Xining:No. 5 Institute of Geology and Mineral Exploration, Qinghai Bureau of Geological Exploration and Development, 2011.
|
| [15] |
刘英俊, 曹励明, 李兆麟, 等. 元素地球化学[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 1984.
|
| [15] |
Liu Y J, Cao L M, Li Z L, et al. Element geochemistry[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 1984.
|
| [16] |
季克俭, 吴学汉, 张国柄. 热液矿床的矿源、水源和热源及矿床的分布规律[M]. 北京: 北京科学技术出版社, 1989.
|
| [16] |
Ji K J, Wu X H, Zhang G B. Distribution regularity of source, water, heat and deposits about hydrothermal deposits [M]. Beijing: Beijing Science and Technology Press, 1989.
|
| [17] |
朴寿成, 刘树田, 连长云, 等. 地球化学负异常及其找矿意义[J]. 地质与勘探, 1996,32(2):46-50.
|
| [17] |
Piao S C, Liu S T, Lian C Y, et al. Geochemical negative anomaly and its prospecting significances[J]. Geology and Prospecting, 1996,32(2):46-50.
|
| [18] |
马生明, 朱立新, 刘海良, 等. 甘肃北山辉铜山铜矿地球化学异常结构研究[J]. 地球学报, 2011,32(4):405-412.
|
| [18] |
Ma S M, Zhu L X, Liu H L, et al. A study of geochemical anomaly structure of the Huitongshan copper deposit in Beishan area, Gansu Province[J]. Acta Geoscientica Sinica, 2011,32(4):405-412.
|
| [1] |
CHEN Wei, TAN You, CAO Zheng-Duan, LIAO Zhi-Quan, ZHANG Ning-Fa, FU Hai-Hui. Application of tectonic primary halos in the exploration of deep concealed ore bodies: A case study of the Niuxingba plumbum-zinc-gold-silver deposit in Yinkeng, southern Jiangxi[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2023, 47(4): 892-905. |
| [2] |
CHENG Pei-Sheng, WANG Shu-Chao, LI Zhuang, GU Da-Nian, ZHANG Jian-Ming, DU Dong-Xu. Primary halo characteristics on the top of the ore-bearing horizon in the Xiwan lead-zinc deposit in Anhui Province[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2022, 46(6): 1381-1387. |
|
|
|
|

