|
|
|
| The method of predict sand liquefaction based on random forest algorithm |
| PENG Liu-Ya, XIE Hui-Ting, FENG Wei-Dong |
| Anhui Earthquake Engineering Institution,Anhui Earthquake Administration,Hefei 230031,China |
|
|
|
|
Abstract Among a variety of complicated factors that are related to sand liquefaction,8 discriminant factors have been picked out of 72 samples in the earthquake event happened in Tangshan without losing any tiny but useful information.By calculating Gini coefficient with CART algorithm,a decision tree has been undertaken to divide the features of original sample dataset.Moreover,in order to reduce overfitting risk of a single decision tree,random forest with multiple trees have been created.Meanwhile,with 10-fold cross validation,best estimators with 5 max-depth and 20 trees can perform with much more stable and reliable results.The research shows that,compared to standard penetration test from Code for seismic design of buildings,both decision tree and random forest have a better predicting precision, especially there have been no false classifications with higher stability using random forest model.
|
|
Received: 25 November 2019
Published: 29 December 2020
|
|
|
|
|
|
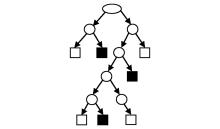
|
Decision tree classification model sketch
|
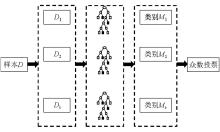
|
Random forest classification model sketch
|

| 序号 | 判别指标 | 液化情况 | | I | L/km | D50/mm | Cu | dw/m | ds/m | N63.5/击 | τd/ | | 1 | 7 | 68.6 | 0.410 | 2.90 | 1.09 | 4.15 | 5 | 0.1000 | 1 | | 2 | 7 | 83.3 | 0.187 | 4.00 | 1.20 | 2.45 | 8 | 0.0900 | 1 | | 3 | 7 | 83.3 | 0.111 | 2.02 | 0.80 | 1.35 | 6 | 0.0800 | 1 | | ? | ? | ? | ? | ? | ? | ? | ? | ? | ? | | 19 | 7 | 79.0 | 0.120 | 1.55 | 1.37 | 3.60 | 19 | 0.0940 | 0 | | 20 | 7 | 81.2 | 0.160 | 2.67 | 1.05 | 4.30 | 12 | 0.1050 | 0 | | ? | ? | ? | ? | ? | ? | ? | ? | ? | ? | | 26 | 8 | 116.4 | 0.200 | 2.70 | 1.60 | 8.70 | 8 | 0.2120 | 1 | | 27 | 8 | 116.4 | 0.170 | 1.91 | 3.30 | 5.80 | 5 | 0.1600 | 1 | | ? | ? | ? | ? | ? | ? | ? | ? | ? | ? | | 43 | 8 | 70.9 | 0.300 | 2.43 | 2.30 | 12.30 | 13 | 0.2030 | 0 | | 44 | 8 | 47.0 | 0.310 | 2.42 | 2.00 | 3.46 | 8 | 0.1630 | 0 | | 45 | 8 | 117.0 | 0.073 | 7.50 | 1.53 | 11.90 | 26 | 0.2170 | 0 | | ? | ? | ? | ? | ? | ? | ? | ? | ? | ? | | 50 | 9 | 22.0 | 0.200 | 1.94 | 0.43 | 2.61 | 10 | 0.4620 | 1 | | 51 | 9 | 22.0 | 0.240 | 2.08 | 1.15 | 4.50 | 22.2 | 0.4150 | 1 | | ? | ? | ? | ? | ? | ? | ? | ? | ? | ? | | 62 | 9 | 14.0 | 0.160 | 2.25 | 4.90 | 9.38 | 61 | 0.3180 | 0 | | 63 | 9 | 9.6 | 0.210 | 3.15 | 3.50 | 8.35 | 31 | 0.3470 | 0 | | 64 | 9 | 11.0 | 0.160 | 2.76 | 4.50 | 4.50 | 22 | 0.2480 | 0 |
|
Training dataset of sand liquefaction
|

| 序号 | 判别指标 | 液化情况 | | I | L/km | D50/mm | Cu | dw/m | ds/m | N63.5/击 | τd/ | | 1 | 7 | 76.8 | 0.166 | 1.65 | 0.50 | 1.70 | 3 | 0.1000 | 1 | | 2 | 7 | 60.8 | 0.360 | 3.30 | 1.59 | 6.65 | 23 | 0.1030 | 0 | | 3 | 7 | 70.0 | 0.145 | 8.50 | 0.85 | 1.80 | 2 | 0.0890 | 1 | | 4 | 7 | 49.0 | 0.140 | 2.31 | 1.00 | 4.80 | 14 | 0.1080 | 0 | | 5 | 7 | 81.2 | 0.140 | 1.60 | 1.40 | 4.35 | 9 | 0.1000 | 1 | | 6 | 8 | 116.0 | 0.265 | 2.81 | 3.30 | 13.80 | 17 | 0.1900 | 0 | | 7 | 8 | 117.4 | 0.134 | 2.23 | 3.20 | 7.20 | 8 | 0.1720 | 1 | | 8 | 9 | 17.0 | 0.185 | 1.90 | 0.61 | 3.80 | 4 | 0.4580 | 1 |
|
Test dataset of sand liquefaction
|
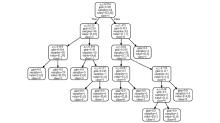
|
Decision tree classification process
|
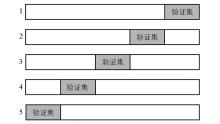
|
Cross-validation sketch
|
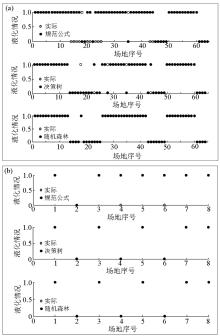
|
Training results(a) and test results(b) of prediction model
|
| [1] |
高大钊, 袁聚云. 土质学与土力学[M]. 北京: 人民交通出版社, 2001.
|
| [1] |
Gao D Z, Yuan J Y. Soil science and soil mechanics[M]. Beijing: China Communications Press, 2001.
|
| [2] |
宫凤强, 李嘉维. 基于PCA-DDA原理的砂土液化预测模型及应用[J]. 岩土力学, 2016,37(s1):448-453.
|
| [2] |
Gong F Q, Li J W. Discrimination model of sandy soil liquefaction based on PCA-DDA principle and its application[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2016,37(s1):448-453.
|
| [3] |
刘章军, 叶燎原, 彭刚. 砂土地震液化的模糊概率评判方法[J]. 岩土力学, 2008,29(4):876-880.
|
| [3] |
Liu Z J, Ye L Y, Peng G. Fuzzy probability comprehensive evaluation method for sand liquefaction during earthquake[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2008,29(4):876-880.
|
| [4] |
谢君斐. 关于修改抗震规范砂土液化判别式的几点意见[J]. 地震工程与工程振动, 1984,4(2):95-109.
|
| [4] |
Xie J F. Some opinions on the modification of sand liquefaction discriminant of seismic code[J]. Earthquake Engineering and Engineering Dynamics, 1984,4(2):95-109.
|
| [5] |
陈国兴, 孔梦云, 李小军, 等. 以标贯试验为依据的砂土液化确定性及概率判别法[J]. 岩土力学, 2015,36(1):9-26.
|
| [5] |
Chen G X, Kong M Y, Li X J, et al. Deterministic and probabilistic triggering correlations for assessment of seismic soil liquefaction at nuclear power plant[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2015,36(1):9-26.
|
| [6] |
刘红军, 薛新华. 砂土地震液化预测的人工神经网络模型[J]. 岩土力学, 2004,25(12):1942-1946.
|
| [6] |
Liu H J, Xue X H. Artificial neural network model for prediction of seismic liquefaction of sand soil[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2004,25(12):1942-1946.
|
| [7] |
刘勇健. 基于聚类—二叉树支持向量机的砂土液化预测模型[J]. 岩土力学, 2008,29(10):2764-2768.
|
| [7] |
Liu Y J. Support vector machine model for predicting sand liquefaction based on clustering binary tree algorithm[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2008,29(10):2764-2768.
|
| [8] |
张菊连, 沈明荣. 基于逐步判别分析的砂土液化预测研究[J]. 岩土力学, 2010,31(s1):298-301.
|
| [8] |
Zhang J L, Shen M R. Sand liquefaction prediction based on stepwise discriminant analysis[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2010,31(s1):298-301.
|
| [9] |
刘年平, 王宏图, 袁志刚, 等. 砂土液化预测的Fisher判别模型及应用[J]. 岩土力学, 2012,33(2):554-557.
|
| [9] |
Liu N P, Wang H T, Yuan Z G, et al. Fisher discriminant analysis model of sand liquefaction and its application[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2012,33(2):554-557.
|
| [10] |
温博文, 董文瀚, 解武杰, 等. 基于改进网格搜索算法的随机森林参数优化[J]. 计算机工程与应用, 2018,54(10):154-157.
|
| [10] |
Wen B W, Dong W H, Xie W J, et al. Parameter optimization method for random forest based on improved grid search algorithm[J]. Computer Engineering and Applications, 2018,54(10):154-157.
|
| [11] |
张亮, 宁芊. CART决策树的两种改进及应用[J]. 计算机工程与设计, 2015,36(5):1209-1214.
|
| [11] |
Zhang L, Ning Q. Two improvements on CART decision tree and its application[J]. Computer Engineering and Design, 2015,36(5):1209-1214.
|
|
|
|
