|
|
|
| Background field removal from airborne transient electromagnetic data |
Wei HUANG1,2,3, Fang BEN1,2,3( ), Jun-Feng LI1,2,3, Chang-Chun YIN4, Zhi-Li XU1,2,3, Jun-Jie LIU1,2,3 ), Jun-Feng LI1,2,3, Chang-Chun YIN4, Zhi-Li XU1,2,3, Jun-Jie LIU1,2,3 |
1. Laboratory of Geophysical Electromagnetic Probing Technologies, Ministry of Natural Resources, Langfang 065000, China
2. Institute of Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, Chinese Academy of Geological Sciences, Langfang 065000, China
3. National Research Center of Geoexploration Technology, Langfang 065000, China
4. College of Geo-exploration Sciences and Technology, Jilin University, Changchun 130026, China |
|
|
|
|
Abstract A comparison with ground transient electromagnetic (EM) method shows that airborne transient EM is more affected by noise, such as sefrics and motion noise. And the influence of background field noise couldn't be neglected. The background contains primary field information, which causes the amplitude of background field to be much larger than the secondary field signal containing geological information. In order to obtain the underground electrical structure clearly, it is necessary to find an efficient method to remove background field. In this paper, the background field problem is studied by linear interpolation. First, according to the responses of the front and back line obtained from the high flight, after cumulative and average calculation, the responses of the same time channel of each measured line in a cycle can be obtained as the background field responses of the corresponding time channel of each line. Using interpolation principle, the background field above each measuring line in the working area is calculated by flight time, so as to remove the background field. Through the real data removal, this method can better remove the background field and then show the anomaly, and can clearly determine the location of the anomaly after removal. Time-domain AEM data preprocessing contains many processing modules. The linear interpolation method proposed in this paper lays a foundation for efficient data preprocessing.
|
|
Received: 19 January 2020
Published: 24 June 2020
|
|
|
|
Corresponding Authors:
Fang BEN
E-mail: benfangzai2008@163.com
|
|
|
|
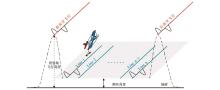
|
The diagram of time-domain AEM actual flight
|
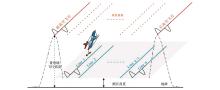
|
The diagram of background field linear interpolation
|
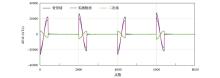
|
The comparison of effect before and after background field removal
|
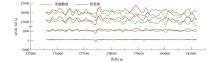
|
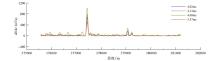
The profile comparison diagram of real data and background field data
|
|
The profile diagram of secondary field
|
| [1] |
殷长春. 航空电磁理论与勘查技术[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2018.
|
| [1] |
Yin C C. Airborne electromagnetic theory and exploration technology [M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2018.
|
| [2] |
殷长春, 张博, 刘云鹤, 等. 航空电磁勘查技术发展现状及展望[J]. 地球物理学报, 2015,58(8):2637-2653.
|
| [2] |
Yin C C, Zhang B, Liu Y H, et al. Review on airborne EM technology and developments[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2015,58(8):2637-2653.
|
| [3] |
裴易峰. 多波发射时间域航空电磁系统数据处理及正反演研究[D]. 长春:吉林大学, 2015.
|
| [3] |
Pei Y F. Research on modeling, data processing and inversion of the time domain airborne Multipulse system[D]. Changchun: Jilin University, 2015.
|
| [4] |
张博. 基于非结构有限元的频率/时间域航空电磁系统仿真研究[D]. 长春:吉林大学, 2017.
|
| [4] |
Zhang B. Research on finite-element method based on unstructured grids for airborne EM modeling[D]. Changchun: Jilin University, 2017.
|
| [5] |
齐彦福. 复杂介质中时间域航空电磁数据仿真技术研究[D]. 长春:吉林大学, 2017.
|
| [5] |
Qi Y F. Time-domain airborne electromagnetic simulation for complex medium[D]. Changchun: Jilin University, 2017.
|
| [6] |
任秀艳. 基于有限体积法时间域航空电磁三维正反演研究[D]. 长春:吉林大学, 2018.
|
| [6] |
Ren X Y. 3D time-domain AEM modeling and inversion with FV method[D]. Changchun: Jilin University, 2018.
|
| [7] |
黄威. 时间域航空电磁系统仿真与关键技术研究[D]. 长春:吉林大学, 2016.
|
| [7] |
Huang W. Time-domain airborne electromagnetic simulation and key technologies[D]. Changchun: Jilin University, 2016.
|
| [8] |
谢宾. 时间域航空电磁数据去噪方法研究[D]. 长春:吉林大学, 2015.
|
| [8] |
Xie B. Study on noise removal of time-domain airborne electromagnetic data[D]. Changchun: Jilin University, 2015.
|
| [9] |
黄威, 贲放, 吴珊, 等. 正交多项式法在航空电磁运动噪声去除中的应用[J]. 物探与化探, 2019,43(4):892-898.
|
| [9] |
Huang W, Ben F, Wu S, et al. Application of orthogonal polynomial fitting method in airborne electromagnetic motion noise removal[J]. Geophysical & Geochemical Exploration, 2019,43(4):892-898.
|
| [10] |
朱凯光, 王凌群, 谢宾, 等. 基于主成分分析的航空电磁数据噪声去除方法[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2013,23(9):2430-2435.
|
| [10] |
Zhu K G, Wang L Q, Xie B, et al. Noise removal for airborne electromagnetic data based on principal component analysis[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2013,23(9):2430-2435.
|
| [11] |
朱凯光, 李玥, 孟洋, 等. 最小噪声分离在航空电磁数据噪声压制中的应用[J]. 吉林大学学报:地球科学版, 2016,46(3):876-883.
|
| [11] |
Zhu K G, Li Y, Meng Y, et al. Application of minimum noise fraction on noise removal for airborne electromagnetic data[J]. Journal of Jilin University:Earth Science Edition, 2016,46(3):876-886.
|
| [12] |
Lane R, Green A, Golding C, et al. An example of 3D conductivity mapping using the TEMPEST airborne electromagnetic system[J]. Exploration Geophysics, 2000,31(2):162-172.

|
| [13] |
Smith R. On removing the primary field from fixed-wing time-domain airborne electromagnetic data: some consequences for quantitative modeling, estimating bird position and detecting perfect conductors[J]. Geophysical Prospecting, 2001,49(4):405-416.

|
| [1] |
LI Zhong-Ping, DAI Guang-Kai, ZHANG Mao-Hui. The impact and effect of DEM grid spacing on the accuracy of gravity remote topographic correction[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2020, 44(6): 1399-1407. |
| [2] |
Wei HUANG, Fang BEN, Shan WU, Si-Yuan SUN, Gui-Xiang LIAO, Yong-Zai XI. The application of orthogonal polynomial fitting method to airborne electromagnetic motion noise removal[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2019, 43(4): 892-898. |
|
|
|
|

