|
|
|
| Deep sea methane electrochemical in-situ long-term monitoring technology and its significance in the ocean environmental investigation and gas hydrate exploration |
Chun-Yan SUN1, Dong-Lin WANG1,2( ), Shi-Qiang ZHANG1, Hui-Ce HE1,3, Hao ZHAO1, Fan LING4,5, Wen-Bin YIN4 ), Shi-Qiang ZHANG1, Hui-Ce HE1,3, Hao ZHAO1, Fan LING4,5, Wen-Bin YIN4 |
1. School of Engineering and Technology, China University of Geosciences (Beijing), Beijing 100083, China
2. No.5 Gold Geological Party of PAP, Xi’an 710100, China;
3. Guangzhou Marine Geological Survey, China Geological Survey, Guangzhou 510075,China
4. Hunan Geo-sun High-Technology Co.,Ltd, Changsha 410208, China
5. School of Geosciences and Info-Physics of Central South University,Changsha 410083, China; |
|
|
|
|
Abstract The continuous acquisition of dissolved methane concentration data in the deep sea has important scientific significance and practical application value for dynamic monitoring of marine environment and methane diffusion in gas hydrates development. This paper introduces key technologies of electrochemical in-situ long-term monitoring technology for deep sea methane in detail, which include the technical ideas of "seawater degassing, quantitative injection of gas samples, and high-precision electrochemical detection", the technical method of "sea water circulation controlled by supercharged drainage system, decompressed steady flow, gas-liquid separation, and improvement of high precision detection technology for hydrocarbon components". Based on the long-term monitoring experiment data obtained from bottom water in Jiaozhou Bay during 94 days, the authors studied and evaluated the technical performance, data quality and geological effect of the in-situ sensors. Some conclusions have been reached: (1) In-situ sensor has an index range of 0.01~10 000 nmol/L and sensitivity reaches 0.01 nmol/L. It has good stability and selectivity for the detection of hydrocarbon components; (2) The range of dissolved methane in the monitoring area is 19.01~106.87 nmol/L, the normal methane background is 32.41 nmol/L, and the local anomalous methane background is 80.60 nmol/L. These data show that abnormality is related to sewage discharge and seawater pollution; (3) The results of measured methane data are consistent with those obtained from previous investigation and study of seawater environment in Jiaozhou Bay, which proves that the measured data are objective and scientific; (4) The sea trial monitoring results show that the in-situ sensor is reliable in testing, reasonable in structure design and scientific in design ideas, and it basically has the capability for acquiring seawater methane concentration data in marine scientific investigation. It has practical application value and scientific significance in the dynamic monitoring of methane diffusion and long-term monitoring of deep sea methane concentration during the development of marine gas hydrate in the future.
|
|
Received: 25 June 2018
Published: 20 February 2019
|
|
|
|
|
|
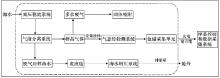
|
The simple working principle of deep-sea dissolved methane in-situ long-term monitoring instrument
|
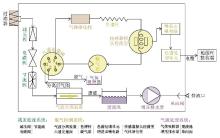
|
The overall structure and main components of deep-sea dissolved methane in-situ long-term monitoring instrument
|
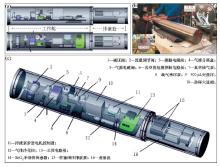
|
Interior installation layout and physical drawings of deep-sea dissolved methane in-situ long-term monitoring instrument
a—side view and top view;b—physical drawings:c—layout of components
|

|
Interior layout plan (a) and physical map (b) of the drainage tank
|
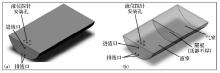
|
Waste pool appearance (a) and interior (b) design
|

| 液位情况 | 液室内探针长度/cm | 液位高度/cm | 液体容积/mL | 内部气压/MPa | | 初始 | | 0 | 0 | 0.101 | | 接触T1 | 4.5 | 1.0 | 80 | 0.105 | | 接触T2 | 4.0 | 1.5 | 146 | 0.109 | | 接触T3 | 2.5 | 3.0 | 400 | 0.129 | | 接触T4 | 1.0 | 4.5 | 714 | 0.168 | | 液室充满 | | 5.5 | 943 | 0.210 |
|
Design of waste liquid pool and liquid probe parameters
|

| 液位情况 | 探针间电平信号 | 系统工作情况 | | T1-T2 | T1-T3 | T1-T4 | | 0~T1 | 高 | 高 | 高 | 不排液 | | 达到T1及T1~T2间 | 高 | 高 | 高 | 不排液 | | 达到T2及T2~T3间 | 低 | 高 | 高 | 启动排液,将液位排至T2以下 | | 达到T3及T3~T4间 | 低 | 低 | 高 | 优先排液,将液位排至T3或T2以下 | | 到达T4 | 低 | 低 | 低 | 强制排液,强制排液至T3或T2以下 |
|
Automatic control design of drainage system
|
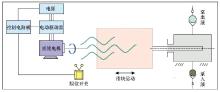
|
Structure design of pressurized drainage pump
|

|
Overall installation of the drainage system
|

| 压力 /MPa | 排量 /(mL·次-1) | 电流 /A | 功率 /W | | 0 | 6.8 | 0.62 | 14.88 | | 7 | 6.1 | 0.71 | 17.04 | | 10 | 5.6 | 0.75 | 18.00 | | 15 | 5.0 | 0.81 | 19.44 | | 20 | 4.5 | 0.84 | 20.16 |
|
The displacement, current and power of drainage pump under different pressure
|

|
The power (left) and the displacement (right) of drainage pump with the change of pressure
|

| 压力/MPa | 温度/℃ | 脱气前顶空CH4浓度/(μL·L-1) | 脱气后顶空CH4浓度/(μL·L-1) | 脱气效率/% | | 5 | 3~4 | 38.70 | 16.88 | 56.4 | | 10 | 3~4 | 49.25 | 18.38 | 62.7 | | 15 | 3~4 | 53.75 | 25.91 | 51.8 | | 20 | 3~4 | 83.63 | 28.67 | 65.7 |
|
Degassing efficiency of the degassing system at 5 mL/min
|

| 柱材质 | 固定相 | 规格(长×直径) | 载气流速 | 老化 | | PTFE | 1.5%阿皮松+
Al2O3颗粒(60~80目) | 1.5 m×φ3 mm | 7~8 mL/min | 马弗炉150℃
高温老化3~5 h |
|
Technical indexes of optimal chromatographic column
|
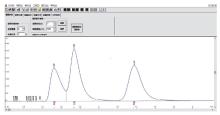
|
Spectral peak curve of separation of methane, ethane and propane
|
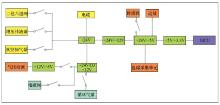
|
Schematic diagram of power supply structure
|
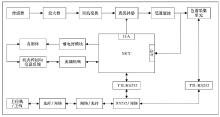
|
Schematic diagram of system integration control
|
|
Work interface of gaseous hydrocarbon detection software
|

| 样品编号 | 甲烷传感器测试浓度/(μL·L-1) | 气相色谱仪测试浓度/(μL·L-1) | 相对误差/% | | 甲烷 | 乙烷 | 丙烷 | 甲烷 | 乙烷 | 丙烷 | 甲烷 | 乙烷 | 丙烷 | | 1 | 0.531 | 0.401 | 0.437 | 0.347 | 0.282 | 0.279 | 21.31 | 34.64 | 44.15 | | 2 | 0.948 | 1.015 | 1.096 | 0.896 | 0.790 | 0.774 | 5.64 | 24.99 | 34.50 | | 3 | 1.839 | 1.634 | 1.672 | 2.105 | 2.079 | 2.029 | 13.49 | 23.97 | 19.29 | | 4 | 3.631 | 3.549 | 3.658 | 4.005 | 3.725 | 3.705 | 9.80 | 4.84 | 1.29 | | 5 | 9.444 | 9.054 | 9.088 | 10.315 | 9.840 | 9.820 | 8.82 | 8.33 | 7.75 | | 6 | 20.891 | 20.480 | 19.887 | 21.360 | 21.275 | 21.290 | 2.22 | 3.81 | 6.81 | | 7 | 40.003 | 40.002 | 39.999 | 39.645 | 39.640 | 39.630 | 0.92 | 0.46 | 0.44 | | 8 | 60.187 | 60.384 | 58.221 | 56.760 | 56.620 | 56.805 | 6.03 | 6.43 | 2.46 | | 9 | 89.300 | 90.705 | 86.755 | 91.820 | 91.380 | 91.240 | 2.78 | 0.73 | 5.04 | | 10 | 134.846 | 134.620 | 125.893 | 143.990 | 143.620 | 平峰 | 6.55 | 6.73 | | | 11 | 150.925 | 150.899 | 142.537 | 163.350 | 平峰 | 平峰 | 7.90 | | | | 12 | 175.900 | 175.100 | 164.300 | 196.050 | 平峰 | 平峰 | 10.83 | | | | 13 | 181.200 | | | 146.000 | | | 21.51 | | | | 14 | 214.200 | | | 174.640 | | | 20.35 | | | | 15 | 308.000 | | | 251.240 | | | 22.71 | | | | 16 | 300.700 | | | 260.600 | | | 14.29 | | | | 17 | 453.200 | | | 371.820 | | | 19.73 | | | | 18 | 463.700 | | | 380.000 | | | 19.84 | | | | 19 | 539.300 | | | 463.100 | | | 15.20 | | | | 20 | 738.300 | | | 585.300 | | | 23.12 | | | | 21 | 1340.000 | | | 1130.300 | | | 16.98 | | | | 22 | 3722.000 | | | 3262.400 | | | 13.16 | | | | 23 | 6584.000 | | | 4932.500 | | | 28.68 | | |
|
Sensors and gas chromatography parallel experimental data comparison
|

样品
编号 | 第1次测定
值/(μL·L-1) | 第2次测定
值/(μL·L-1) | 两次测试结果/(μL·L-1) | 重复性限r
(r=0.2978m0.9145) | 是否
合格 | | 平均值m | 绝对差值 | | 1 | 0.117 | 0.144 | 0.131 | 0.027 | 0.046 | 合格 | | 2 | 0.224 | 0.322 | 0.273 | 0.098 | 0.091 | 合格 | | 3 | 0.429 | 0.445 | 0.437 | 0.016 | 0.140 | 合格 | | 4 | 0.982 | 0.914 | 0.948 | 0.068 | 0.284 | 合格 | | 5 | 1.743 | 1.934 | 1.839 | 0.191 | 0.520 | 合格 | | 6 | 3.763 | 3.499 | 3.631 | 0.264 | 0.968 | 合格 | | 7 | 9.969 | 8.919 | 9.444 | 1.050 | 2.321 | 合格 | | 8 | 39.743 | 40.263 | 40.003 | 0.520 | 8.690 | 合格 | | 9 | 88.590 | 90.010 | 89.300 | 1.420 | 18.112 | 合格 | | 10 | 151.750 | 150.100 | 150.925 | 1.650 | 29.269 | 合格 | | 11 | 174.800 | 177.000 | 175.900 | 2.200 | 33.668 | 合格 | | 12 | 510.000 | 509.600 | 509.800 | 0.400 | 89.090 | 合格 | | 13 | 784.600 | 776.200 | 780.400 | 8.400 | 131.510 | 合格 | | 14 | 1051.000 | 996.700 | 1023.900 | 54.300 | 168.570 | 合格 | | 15 | 1234.000 | 1260.000 | 1247.000 | 26.000 | 201.880 | 合格 | | 16 | 1401.000 | 1410.000 | 1405.500 | 9.000 | 225.220 | 合格 | | 17 | 1594.000 | 1659.000 | 1626.500 | 65.000 | 257.400 | 合格 | | 18 | 1894.000 | 1807.000 | 1850.500 | 87.000 | 289.640 | 合格 | | 19 | 2190.000 | 2007.000 | 2098.500 | 183.000 | 324.950 | 合格 | | 20 | 2180.000 | 2202.000 | 2191.000 | 22.000 | 338.020 | 合格 |
|
Sensor reproducibility test data
|
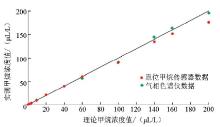
|
The comparison chart of test data from in-situ methane sensor and gas chromatograph
|

|
The situation of sea trial of Qingdao Marine experimental station in Shandong Province
a—shore monitoring platform;b—instrument for launching and release
|
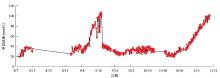
|
The distribution diagram of the dissolved methane concentration effective data in the monitoring point seawater (The straight line is segments which eliminated the fault data)
|

|
The daily mean data distribution of dissolved methane concentration in the monitoring point seawater
|
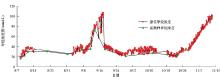
|
A comparison chart of the dissolved methane concentration in seawater by in-situ sensor and laboratory test
|
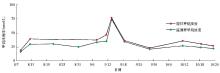
|
Comparison between the daily average value of the monitoring point sensor test and the same time point of the laboratory test sample dissolved seawater methane concentration
|

| 本次海试数据 | 测试时间 | 2017年8月~11月 | | 8/8~8/15 | 9/1~9/11 | 9/18~10/31 | 9/12~9/17 | 11/1~11/9 | | 天数/天 | 8 | 11 | 44 | 6 | 9 | | 均值/(nmol·L-1) | 31.84 | 34.66 | 30.73 | 82.35 | 79.44 | | 数据分布状态 | 中低数值 | 局部异常 | | 实测甲烷数据范围及均值(nmol·L-1) | 19.01~57.73(均值32.41) | 50.62~106.87(均值80.60) | | 监测点甲烷浓度均值/(nmol·L-1) | 30.32(最大值35.11) | 73.83(仅一个数据) | 无 | | 文献数据 | 测试时间 | 8月~11月 | | 2008年1月 | 2014年4月 | 2008年4月 | 2008年7月 | 2006年8月 | 2008年11月 | | 甲烷浓度范围/(nmol·L-1) | 6.30~203.29 | 7.00~21.90 | 6.86~702.49 | 30.73~1175.00 | 11.32~23.81 | 6.85~327.44 | | 数据来源 | 杨晶[34] | 赵慧敏[31] | 杨晶[34] | 杨晶[34] | 李佩佩、张桂玲[35] | 杨晶[34] |
|
Test data of dissolved methane concentration in sea trials and distribution of methane concentration in seawater in Jiaozhou Bay
|
| [1] |
喻西崇, 李清平, 安维杰 .海底沉积物中天然气水合物生成和分解规律研究进展[J].中国海上油气, 2006, 18(1):61-67.

|
| [1] |
Yu X C, Li Q P, An W J . Some advances in studying formation and dissociation of gas hydrate in submarine sediments[J]. China Offshore and Gas , 2006,18(1):61-67.
|
| [2] |
于晓果, 金翔龙 . 天然气水合物分解与全球变暖[J]. 第四纪研究, 2001,21(6):568.

|
| [2] |
Yu X G, Jin X L . Gas hydrate decomposition and global warming[J]. Quaternary Sciences, 2001,21(6):568.
|
| [3] |
Sloan E D . Clathrate hydrates of natural gases(2ed.)[M]. New York:Marcel Dekker Inc, 1998.
|
| [4] |
金庆焕 . 天然气水合物资源概论[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2006.
|
| [4] |
Jin Q H. Overview of gas hydrate resources[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2006.
|
| [5] |
孙春岩, 赵浩, 贺会策 , 等 .海洋底水原位探测技术与中国南海天然气水合物勘探[J].地学前缘, 2017, 24(6):225-241.

|
| [5] |
Sun C Y, Zhao H, He H C , et al. In-situ detection of ocean floor seawater and gas hydrate exploration of the South China Sea[J]. Earth Science Frontiers , 2017,24(6) : 225-241.
|
| [6] |
Garcia M L, Masson M . Environmental and geologic application of solid-state methane sensors [J]. Environmental Geology, 2004, 46(1059):1063-.

|
| [7] |
Isern A R . National science foundation’s ocean observatory initiative [J].Sealing Technology, 2005,46(6) : 55-60.
|
| [8] |
杨涛, 蒋少涌, 葛璐 , 等. 南海北部琼东南盆地HQ-1PC沉积物孔隙水的地球化学特征及其对天然气水合物的指示意义[J]. 中国科学:地球科学, 2013, 43(3): 329-338.

|
| [8] |
Yang T, Jiang S Y, Ge L , et al .Geochemistry of pore waters from HQ-1PC of the Qiongdongnan Basin, northern South China Sea, and its implications for gas hydrate exploration[J]. Science China: Earth Sciences , 2013,43(3):329-338.
|
| [9] |
Kastner M, Claypool G, Robertson G . Geochemical constraints on the origin of the pore fluids and gas hydrate distribution at Atwater Valley and Keathley Canyon,northern Gulf of Mexico[J].Marine and Petroleum Geology 2008,25(9):860-872.

|
| [10] |
陈勇, 袁东星, 李权龙 , 等 .常温吹扫捕集—气相色谱法测定海水中氧化亚氮[J].分析化学, 2007, 35(897):900-.

|
| [10] |
Chen Y, Yuan D X, Li Q L , et al. Determination of nitrous oxide in seawater by room temperature purge and trap-gas chromatography[J]. Chinese Journal of Analytical Chemistry, 2007,35(6):897-900.
|
| [11] |
黄永样, Suess E, 吴能友, 等. 南海北部陆坡甲烷和天然气水合物地质:中德合作SO-177航次成果专报[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2008.
|
| [11] |
Huang Y Y, Suess E, Wu N Y, et al. Methane and gas hydrate geology of the northern South China Sea:Sino-german cooperative SO-177 cruise report[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 2008.
|
| [12] |
Boulart C, Connelly D P, Mowlem M C . Sensors and technologies for in-situ dissolved methane measurements and their evaluation using Technology Readiness Levels[J]. Trac Trends in Analytical Chemistry,2010,29(2):186-195 .

|
| [13] |
尹希杰, 周怀阳, 杨群慧 , 等 南海北部甲烷渗漏活动存在的证据:近底层海水甲烷高浓度异常[J].海洋学报:中文版, 2008, 30(6):69-75.

|
| [13] |
Yin X J, Zhou H Y, Yang, Q H , et al. The evidence for the existence of methane seepages in the northern South China Sea: Abnormal high methane concentration in bottom waters[J]. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 2008 , 30(6):69-75.
|
| [14] |
周怀阳, 吴自军, 彭晓彤 , 等 .大西洋洋中脊Logatchev热液场水柱中甲烷羽状流的探测[J].科学通报, 2007, 52(9):1058-1063.

|
| [14] |
Zhou H Y, Wu Z J, Peng X T , et al. Detection of methane plumes in the hydrothermal field water column of logatchev in the mid-atlantic ridge[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2007 , 52(9):1058-1063.
|
| [15] |
邸鹏飞, 冯东, 高立宝 , 等 .海底冷泉流体渗漏的原位观测技术及冷泉活动特征[J].地球物理学进展, 2008, 23(5):1592-1602.

|
| [15] |
Di P F, Feng D, Gao L B , et al. In-situ measurement of fluid flow and signatures of seep activity at marine seep sites[J]. Progress in Geophysics, 2008,23(5):1592-1602.
|
| [16] |
邸鹏飞, 陈庆华, 陈多福 . 海底冷泉渗漏气体流量原位在线测量技术研究[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2012, 31(5):83-87.

|
| [16] |
Di P F, Chen Q H, Chen D F . In situ on-line measuring device of gas seeping flux at marine seep sites and experimental study[J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2012,31(5):83-87.
|
| [17] |
王庆光, 徐瑞松, 王洁 , 等 .南海北部油气化探研究——以甲烷浓度为例[J].海洋科学, 2010, 34(6):9-15.

|
| [17] |
Wang Q G, Xu R S, Wang J , et al. Oil and gas geochemical exploration in the northern South China Sea:A case study of methane concentration[J]. Marine Sciences, 2010,34(6):9-15.
|
| [18] |
于新生, 李丽娜, 胡亚丽 , 等 .海洋中溶解甲烷的原位检测技术研究进展[J].地球科学进展, 2011, 26(10):1030-1037.
|
| [18] |
Yu X S, Li L N, Hu Y L , et al. The development of in-situ sensors for dissolved methane measurement in the Sea[J]. Advances in Earth Science, 2011,26(10) : 1 030-1037.
|
| [19] |
Kroger S, LAW R J . Sensing the sea[J]. Trends in biotechnology,2005,23(5): 250-256.

|
| [20] |
Varney M S. Chemical sensors in oceanography[M]. Boca Raton: CRC Press, 2000.
|
| [21] |
申正伟, 孙春岩, 贺会策 , 等. 深海原位溶解甲烷传感器(METS) 的原理及应用研究[J].海洋技术学报, 2015, 34(5):19-25.

|
| [21] |
Shen Z W, Sun C Y, He H C , et al. The principle and applied research of in-situ METS for dissolved methane measurement in deep sea[J]. Journal of Ocean Technology, 2015,34(5):19-25.
|
| [22] |
王维熙, 孙春岩, 杨慧 , 等 .海洋油气勘探中高灵敏度气态烃现场探测系统的研制[J].地球科学, 2004, 29(2):163-168.

|
| [22] |
Wang W X, Sun C Y, Yang H , et al. Investigation to on-site detection system for gaseous hydrocarbon with high sensitivity be used to explore gas and oil in sea[J]. Earth Science:Journal of China University of Geosciences, 2004,29(2):163-168.
|
| [23] |
魏小芳, 罗一菁, 刘可禹 , 等 .油气藏埋存二氧化碳生物转化甲烷的机理和应用研究进展[J].地球科学进展, 2011, 26(5):499-506.

|
| [23] |
Wei X F, Luo Y J, Liu K Y , et al. Research progress on the mechanism and potential application of CH4 bioconversion form CO2 in oil and gas reservoirs[J]. Advances in Earth Science, 2011,26(5):499-506.
|
| [24] |
臧家业, 王相芹 .海湾地区海水中的溶存甲烷浓度、分布特征及成因[J].黄渤海海洋, 1997, 15(1):20-29.

|
| [24] |
Zang J Y, Wang X Q . The dissolved methane in seawater of estuaries,distribution features and formation[J]. Journal of Oceanography of Huanghai and Bohai Seas, 1997,15(1):20-29.
|
| [25] |
孙春岩, 张志冰, 庞云天 , 等. 一种海水中甲烷浓度原位探测系统[P].中国专利:201110196474. 4, 2013.
|
| [25] |
Sun C Y, Zhang Z B, Pang Y T , et al. In-situ detecting system of methane (CH4) concentration in seawater[P].China Patent: 201110196474. 4, 2013.
|
| [26] |
竺玮煌 . 天然气水合物海水中甲烷原位富集和高精度探测系统的研制[D].北京:中国地质大学( 北京), 2011.
|
| [26] |
Zhu W H . The research on CH4 in sea water for sample in-situ collecting and extra accurate detecting system of marine gas hydrates[D].Beijing: China University of Geosciences( Beijing), 2011.
|
| [27] |
张志冰 . 海水中甲烷浓度原位地球化学探测系统的研发与应用[D].北京:中国地质大学( 北京), 2013.
|
| [27] |
Zhang Z B . Development and application on in-situ geochemical detection technology of methane concentration in seawater[D].Beijing: China University of Geosciences( Beijing), 2013.
|
| [28] |
李东梁 . 海洋探测仪器承压舱的设计[J]. 机械研究与应用, 2013, 26(5):126-128.

|
| [28] |
Li D L . Design of the exploration instrument cabin used in ocean[J]. Mechanical Research and Application, 2013,26(5):126-128.
|
| [29] |
中华人民共和国国家质量监督检验检疫总局. JJG 700-2016 气相色谱仪检定规程[S].北京: 中国标准出版社, 2016.
|
| [29] |
AQSIQ. JJG 700-2016 Verification regulation of gas chromatogaphs[S]. Beijing: China Standard Press , 2016.
|
| [30] |
中华人民共和国国家质量监督检验检疫总局. GB/T 29173-2012 油气地球化学勘探试样测定方法[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2013.
|
| [30] |
AQSIQ. GB/T 29173-2012 Determination method for samples of geochemical exploration for oil and gas[S]. Beijing : China Standard Press, 2013.
|
| [31] |
赵慧敏, 丁海兵, 吕丽娜 , 等 .胶州湾海水甲烷氧化速率的水平与垂直变化初步研究[J].中国海洋大学学报:自然科学版, 2016, 46 (6):90-99.

|
| [31] |
Zhao H M, Ding H B, Luy L N , et al. The preliminary study of horizontal and vertical variations of methane oxidation rates in the Jiaozhou Bay[J]. Periodical of Ocean University of China, 2016,46(6):90-99.
|
| [32] |
曹兴朋, 张桂玲, 马啸 , 等 .春季东、黄海溶解甲烷的分布和海气交换通量[J].环境科学, 2013, 34(7):2565-2573.

|
| [32] |
Cao X P, Zhang G L, Ma X , et al. Distribution and air-sea fluxes of methane in the Yellow Sea and the East China Sea in the spring[J]. Environmental Science, 2013,34(7):2565-2573.
|
| [33] |
张桂玲 . 中国近海部分海域溶解甲烷和氧化亚氮的生物地球化学研究[D]. 青岛:中国海洋大学, 2004.
|
| [33] |
Zhang G L . Studies on biogeochemistry of dissolved methane and nitrous oxide in the coastal waters of China[D]. Qingdao: Ocean University of China, 2004.
|
| [34] |
杨晶 . 胶州湾水体及沉积物中甲烷和氧化亚氮的生物地球化学研究[D]. 青岛:中国海洋大学, 2009.
|
| [34] |
Yang J . Biogeochemistry of methane and nitrous oxide in the water and sediments of Jiaozhou Bay[D]. Qingdao: Ocean University of China, 2009.
|
| [35] |
李佩佩, 张桂玲, 赵静 , 等 .胶州湾及周边海域大气和海水中N2O和CH4的分布及海气交换通量[J].中国海洋大学学报:自然科学版, 2009, 39(4):805-814 .
|
| [35] |
Li P P, Zhang G L, Zhao J , et al. The distributions and atmospheric fluxes of nitrous oxide and methane in Jiaozhou Bay and its adjacent coastal area[J]. Periodical of Ocean University of China, 2009,39(4):805-814.
|
|
|
|

