|
|
|
| Distribution properties and time-series comparisons of soil pH-values in Yixing area |
| Yong-Min PAN, Ming HUA, Qi-Lin LIAO, Shu-Gang XU, Yu ZHANG, Hui ZHAI |
| Geological Survey of Jiangsu Province/Key Laboratory of Earth Fissures Geological Disaster, Ministry of Land and Resources, Nanjing 210018,China |
|
|
|
|
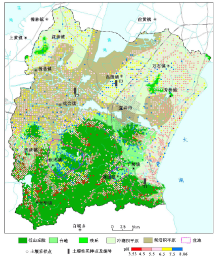
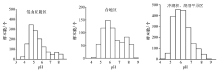
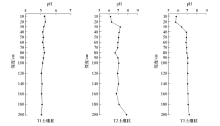
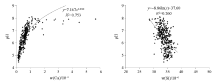
Abstract The geochemistry survey analysis was conducted on the soil samples collected from the Yixing area in 2004, 2009, and 2015 years, and the results show that the pH-value of surface soil varies from 3.53 to 8.86. Specifically, the acidic soils and strongly acidic soil generally distribute in the distribution of hill sandstone strata. The weak alkaline soil generally distributethe in the distribution of limestone strata. In the alluvial lake plain area, most soil is weakly acidic. And it shows the soil parent material and topographic features impact soil PH-values. Comparing with the changes of the surface soil pH-values within the past six years, the result show that there are 49.77% soils with decreased pH-value, the 23.53% soil with increased pH-valua, and 26.70% soils with relative stable PH-value. Due to the impacts of industrialization development on the environment, the acid rain plays an important role in soil acidification. Affected by farming and among others, the pH-value of surface soil in the alluvial lake plain area are lower than those of deep layer soil by around 1.2. The acidification of the surface soil occurs mainly in the tillage layer, the depth is about 30cm, and the bottom soil is basically neutral. From the general point of view, the analytical results of surface soil in the Yixing area show a trend of acidification. Some necessary measures must be done to prevent further deterioration.
|
|
Received: 07 September 2017
Published: 03 August 2018
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|

| 等级 | pH值分级 | pH值变化分级 | | 水平 | 范围 | 范围 | 分级 | | 一 | 强酸性 | <4.5 | ≤-1.0 | 明显酸化 | | 二 | 酸性 | 4.5~5.5 | -1.0~-0.3 | 弱酸化 | | 三 | 微酸性 | 5.5~6.5 | -0.3~0.3 | 基本不变 | | 四 | 中性 | 6.5~7.5 | 0.3~1.0 | 弱碱化 | | 五 | 微碱性 | 7.5~8.5 | ≥1.0 | 明显碱化 |
|
|
|

| 地貌类型 | 样品数 | 最小值 | 最大值 | 平均值 | 标准差 | 变异系数 | | 低山丘陵区 | 1409 | 3.53 | 8.59 | 5.52 | 1.07 | 0.19 | | 台地区 | 705 | 4.09 | 8.54 | 6.31 | 1.03 | 0.16 | | 冲湖积、湖沼平原区 | 2516 | 4.32 | 8.86 | 6.15 | 0.78 | 0.13 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|

| 地层 | 主要岩性 | 样品数 | 最小值 | 最大值 | 平均值 | | 第四系 | 亚黏土为主,局部亚砂土 | 3013 | 3.77 | 8.86 | 6.12 | | 侏罗系 | 安山质火山碎屑岩 | 54 | 4.30 | 6.42 | 5.13 | | 三叠系 | 薄—中厚层灰岩 | 247 | 7.12 | 8.40 | 7.96 | | 二叠系 | 硅质页岩或白云质灰岩 | 115 | 4.93 | 8.44 | 6.58 | | 石炭系 | 厚层灰岩为主 | 17 | 5.34 | 8.22 | 6.83 | | 志留系、泥盆系 | 砂岩为主夹数层砂质泥岩 | 318 | 3.73 | 6.23 | 4.71 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
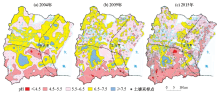
|
|
|
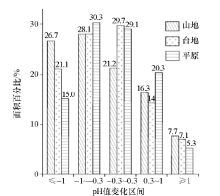
|
|
|

| 地貌类型 | 年份 | 样本数 | 均值 | 下降值 | 下降幅度/% | | 低山丘陵区 | 2004
2009
2015 | 139
220
1030 | 6.62
6.16
5.68 | 0.46
0.48 | 6.95
7.79 | | 台地区 | 2004
2009
2015 | 21
126
587 | 7.14
6.71
6.26 | 0.43
0.45 | 6.02
6.70 | | 平原区 | 2004
2009
2015 | 183
512
1669 | 6.72
6.37
6.13 | 0.35
0.24 | 5.21
3.76 |
|
|
|

| 年份 | 降水pH范围 | 酸雨发生率/% | PH年均值 | | 2010 | 3.53~7.01 | 45.9 | 4.34 | | 2011 | 4.05~6.81 | 45.3 | 4.65 | | 2012 | 3.98~7.02 | 46.3 | 4.88 | | 2014 | 4.02~5.25 | 100 | 4.23 | | 2015 | 4.01~6.70 | 79.8 | 4.66 |
|
|
|
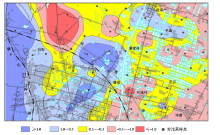
|
|
|
| [1] |
李学垣 . 土壤化学[M]. 北京: 高校出版社, 2001.
|
| [2] |
鲁如坤 . 土壤农业化学分析方法[M]. 北京: 中国农业科技出版社, 2000.
|
| [3] |
李婷, 张世熔, 干文芝 . 成都平原pH的时空分布特征及影响因素[J]. 四川农业大学学报, 2006,24(3):313-318.

|
| [4] |
江宁县土壤普查办公室, 南京市土壤普查办公室, 江苏省土壤普查办公室. 江苏省江宁县土壤志[M]. 南京: 江苏科学技术出版社, 1985.
|
| [5] |
王志刚, 赵永存, 廖启林 , 等. 近20年来江苏省土壤pH值时空变化及其驱动力[J]. 生态学报, 2008,28(2):720-727.
|
| [6] |
王媛华, 段增强, 董金龙 , 等. 可溶性盐对土壤pH测定的影响及消除初探[J]. 土壤学报, 2014,32(2):1-13.
|
| [7] |
熊建成, 周富忠 . 利川市耕地土壤酸化现状与对策[J]. 农业与技术, 2015,35(19):19-21.

|
| [8] |
张甘霖, 朱永官, 傅伯杰 . 城市土壤质量演变及其生态环境效应[J]. 生态学报, 2003,23(3):539-546.

|
| [9] |
卢瑛, 龚子同, 张甘霖 . 南京城市土壤的特性及其分类的初步讲究. 土壤, 2001,33(1):47-51.
|
| [10] |
谢天洋, 周卫军, 罗思颖 , 等. 石门县耕地土壤pH值的时空演变特征[J]. 现代农业科技, 2016,45(9):198-200.

|
| [11] |
李冰, 王昌全, 谭婷 , 等. 成都平原土壤重金属区域分布特征及其污染评价[J]. 核农学报, 2009,23(2):308-315.

|
| [12] |
潘永敏, 廖启林, 华明 , 等. 江苏南部典型地区耕作层土壤及农作物重金属评价[J]. 物探与化探, 2014,38(2):318-323.

|
| [13] |
农忠武 . 江州地区耕地土壤酸碱度现状分析及调节对策[J]. 农业与技术, 2016,36(9):170-171.

|
|
|
|
